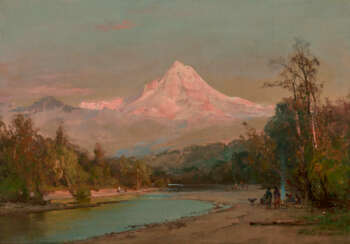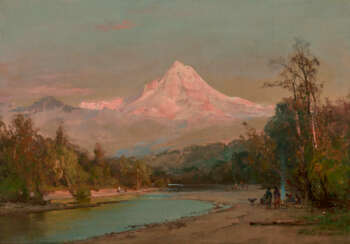19th Century American Art

Albert Bierstadt, a German-American painter, became renowned for his expansive and romanticized landscapes of the American West. Born in Solingen, Germany, in 1830, Bierstadt moved to New Bedford, Massachusetts, at the age of two with his family. Largely self-taught, he initially worked as a drawing teacher before traveling to Europe to hone his skills. Bierstadt's European studies, particularly in Düsseldorf, greatly influenced his artistic style, equipping him with the techniques that he would later apply to his majestic depictions of the American wilderness.
Bierstadt's first major expedition to the West in 1859 marked the beginning of his lifelong fascination with the region. His works from this period, such as "The Rocky Mountains, Lander's Peak" (1863), captured the public imagination and established him as a leading figure in the Hudson River School. These paintings were celebrated for their detailed and idealized portrayal of the rugged landscapes and played a role in shaping the perception of the American West during a time of rapid territorial expansion and exploration.
Despite his success, Bierstadt's style fell out of favor towards the end of his career as tastes shifted towards realism and Impressionism. His later works, including "The Last of the Buffalo" (1888), were criticized for their perceived theatricality and excessive romanticism. Bierstadt's popularity waned, and he faced financial difficulties, but his legacy experienced a resurgence in the mid-20th century as interest in his technique and contributions to American art history grew.
For collectors and enthusiasts of American landscape painting, Bierstadt’s works offer a vivid, albeit embellished, glimpse into the 19th-century frontier spirit. His paintings are housed in major institutions like the Metropolitan Museum of Art and the National Gallery of Art, serving as testaments to his skill and vision.
To stay updated on exhibitions and sales related to Albert Bierstadt's works, consider signing up for alerts tailored to his artistic contributions. This subscription will keep you informed about new discoveries and auction events specifically linked to Bierstadt's enduring legacy.

Benjamin Champney was a painter known for his role in White Mountain art of the 19th century. He began his training as a lithographer under celebrated marine artist Fitz Henry Lane at Pendleton's Lithography shop in Boston. Most art historians consider him the founder of the "North Conway Colony" of painters who came to North Conway, New Hampshire and the surrounding area during the second half of the 19th century. His paintings were often used to make chromolithographs that were subsequently sold to tourists who could not afford Champney's originals. He exhibited regularly at the Boston Athenæum and was a founder of the Boston Art Club.
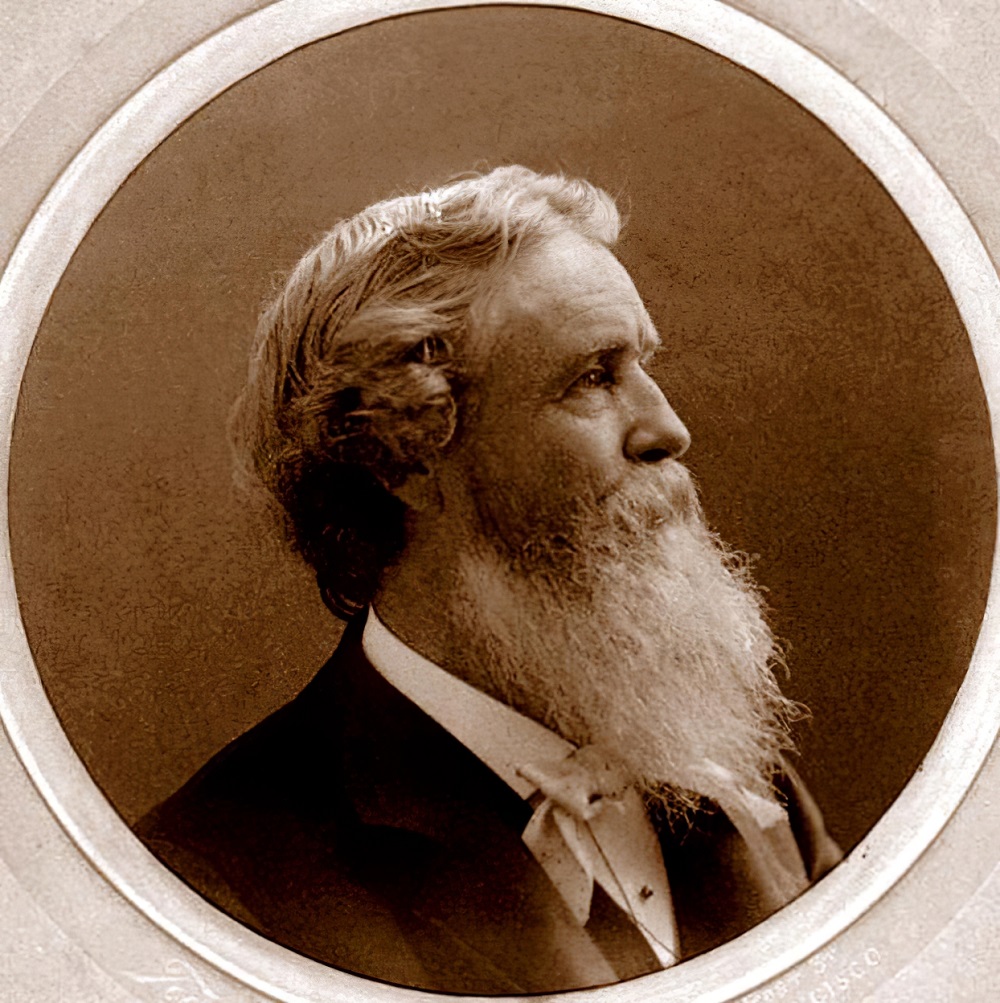

Thomas Hill was an English-born American artist of the 19th century. He produced many fine paintings of the California landscape, in particular of the Yosemite Valley, as well as the White Mountains of New Hampshire.

Albert Bierstadt, a German-American painter, became renowned for his expansive and romanticized landscapes of the American West. Born in Solingen, Germany, in 1830, Bierstadt moved to New Bedford, Massachusetts, at the age of two with his family. Largely self-taught, he initially worked as a drawing teacher before traveling to Europe to hone his skills. Bierstadt's European studies, particularly in Düsseldorf, greatly influenced his artistic style, equipping him with the techniques that he would later apply to his majestic depictions of the American wilderness.
Bierstadt's first major expedition to the West in 1859 marked the beginning of his lifelong fascination with the region. His works from this period, such as "The Rocky Mountains, Lander's Peak" (1863), captured the public imagination and established him as a leading figure in the Hudson River School. These paintings were celebrated for their detailed and idealized portrayal of the rugged landscapes and played a role in shaping the perception of the American West during a time of rapid territorial expansion and exploration.
Despite his success, Bierstadt's style fell out of favor towards the end of his career as tastes shifted towards realism and Impressionism. His later works, including "The Last of the Buffalo" (1888), were criticized for their perceived theatricality and excessive romanticism. Bierstadt's popularity waned, and he faced financial difficulties, but his legacy experienced a resurgence in the mid-20th century as interest in his technique and contributions to American art history grew.
For collectors and enthusiasts of American landscape painting, Bierstadt’s works offer a vivid, albeit embellished, glimpse into the 19th-century frontier spirit. His paintings are housed in major institutions like the Metropolitan Museum of Art and the National Gallery of Art, serving as testaments to his skill and vision.
To stay updated on exhibitions and sales related to Albert Bierstadt's works, consider signing up for alerts tailored to his artistic contributions. This subscription will keep you informed about new discoveries and auction events specifically linked to Bierstadt's enduring legacy.
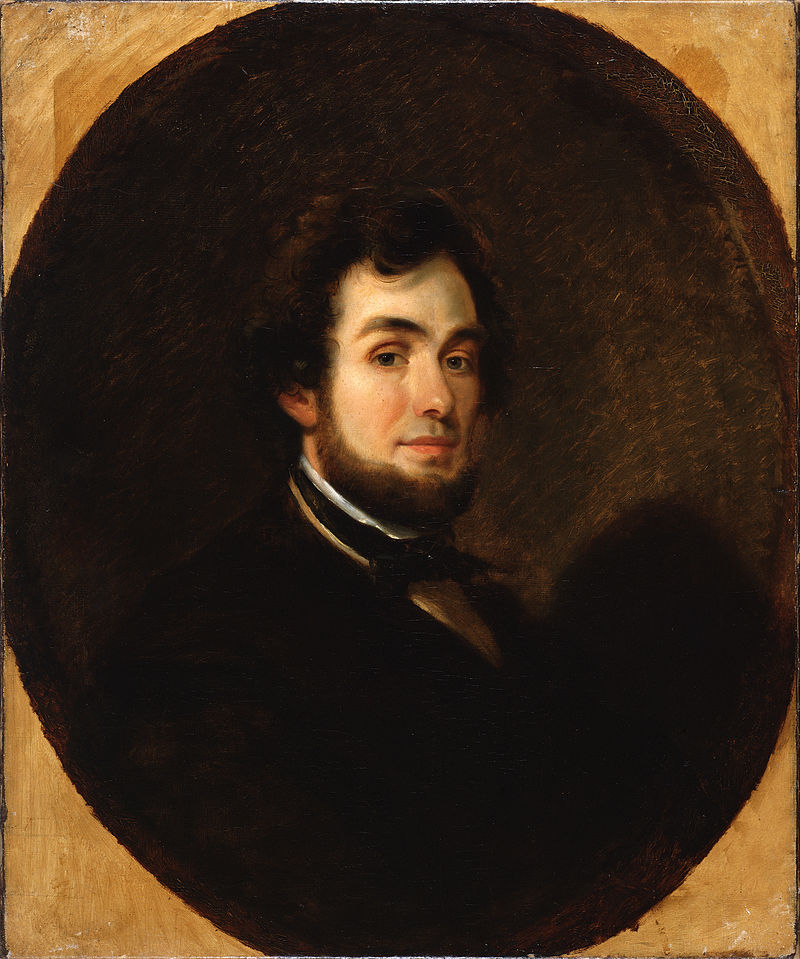

Alfred Jacob Miller was an American artist best known for his paintings of trappers and Native Americans in the fur trade of the western United States. He also painted numerous portraits and genre paintings in and around Baltimore during the mid-nineteenth century.
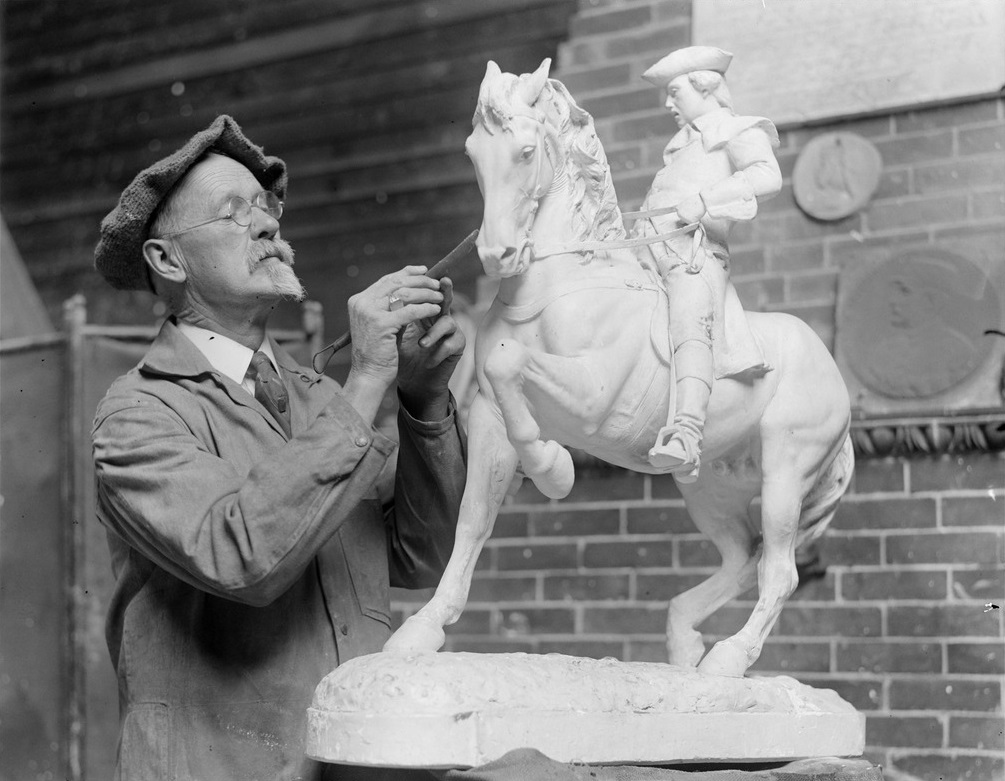

Cyrus Edwin Dallin was an American sculptor. He is known for his sculptures of Native American figures, as well as for his equestrian and civic monuments.
Dallin grew up in Utah and showed an early talent for sculpture. He studied art in Boston and later in Paris, where he became influenced by the naturalism of French sculptors like Auguste Rodin. Dallin returned to the United States in 1897 and began to create a series of sculptures depicting Native American figures.
In addition to his work as a sculptor, Dallin also taught art and was an active member of the art community in Boston. He designed several civic monuments, including the Paul Revere Monument in Boston's North End and the Soldiers' and Sailors' Monument in Springfield, Massachusetts.
Dallin was a member of the National Academy of Design, the American Academy of Arts and Letters, and the National Sculpture Society. His work is in the collections of many major museums, including the Metropolitan Museum of Art, the National Gallery of Art, and the Boston Museum of Fine Arts.
Today, Dallin is widely regarded as one of the most important sculptors of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and his sculptures of Native American figures are recognized as powerful and sympathetic depictions of a culture that had long been misrepresented in American art.
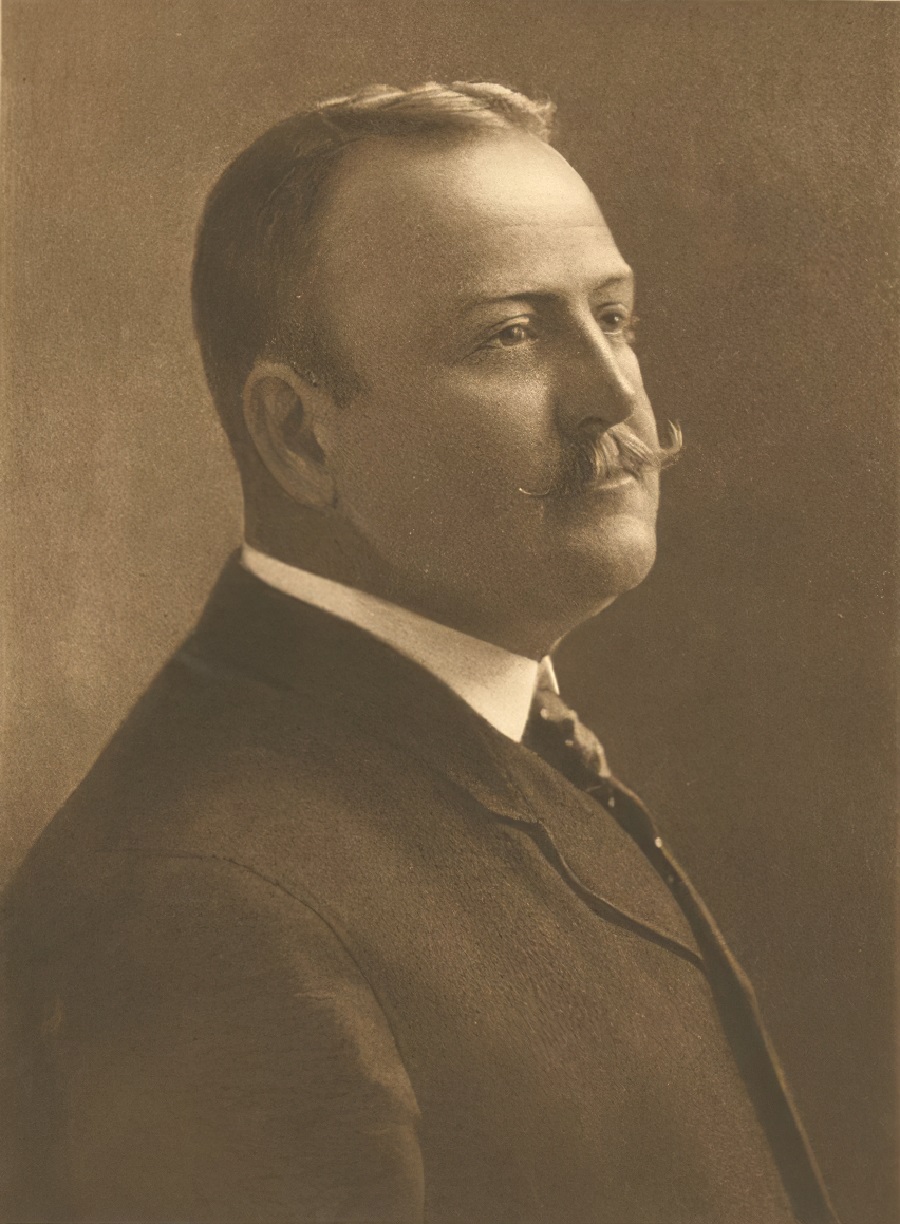

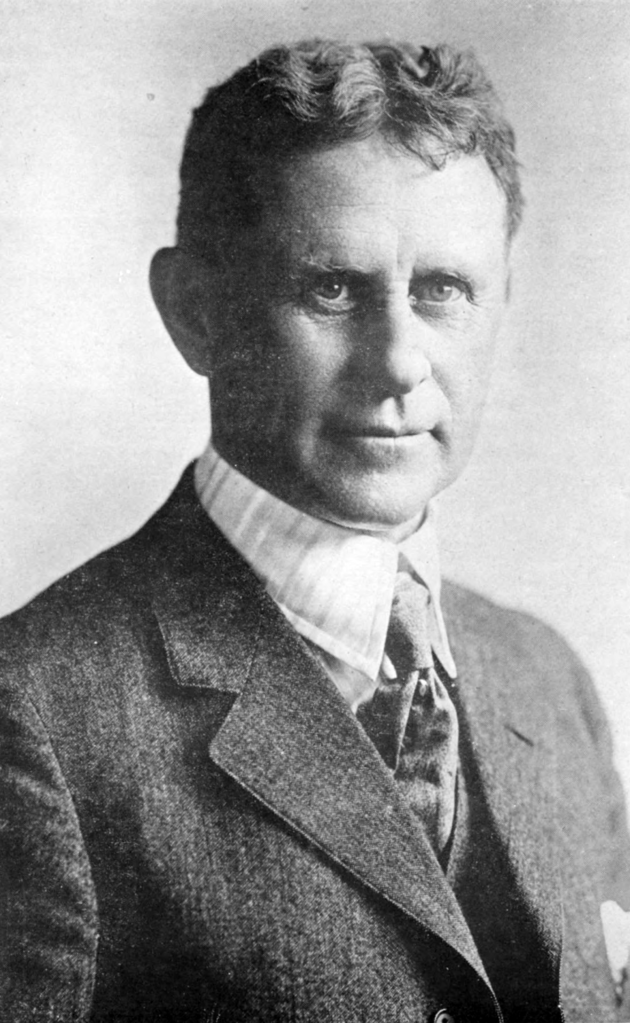
Frederic Sackrider Remington, an American artist born in 1861 in Canton, New York, is celebrated for his vivid portrayals of the American West. Specializing in painting, sculpture, and illustration, Remington captured the essence of Western life through dynamic scenes of cowboys, Native Americans, and the U.S. Cavalry, evoking a nostalgic era that was quickly vanishing by the late 19th century.
Remington's early experiences in the West, which included ventures into sheepherding and prospecting, profoundly influenced his artwork. Despite initial business failures and personal setbacks, his first-hand encounters with the rugged landscapes and frontier characters provided authentic material for his art. By the mid-1880s, Remington’s work began to gain recognition, and he quickly established himself as a significant figure in Western art, contributing illustrations to popular magazines like Harper’s Weekly.
In his later years, Remington's style evolved, displaying a notable shift towards impressionism and atmospheric mood in his "Nocturnes" series. These paintings are characterized by a dramatic use of light and shadow to convey the mystery and tension of nighttime in the West. Despite his own critical self-view, these works were highly regarded and marked a significant contribution to American art history. Remington’s art is featured in major collections, including the Metropolitan Museum of Art and the Frederic Remington Art Museum in Ogdensburg, New York, preserving his legacy as an icon of American culture.
For those interested in exploring more about Frederic Remington’s life and works, updates on exhibitions and sales can be subscribed to, keeping enthusiasts connected to new insights and offerings related to this influential artist.

Frederic Sackrider Remington, an American artist born in 1861 in Canton, New York, is celebrated for his vivid portrayals of the American West. Specializing in painting, sculpture, and illustration, Remington captured the essence of Western life through dynamic scenes of cowboys, Native Americans, and the U.S. Cavalry, evoking a nostalgic era that was quickly vanishing by the late 19th century.
Remington's early experiences in the West, which included ventures into sheepherding and prospecting, profoundly influenced his artwork. Despite initial business failures and personal setbacks, his first-hand encounters with the rugged landscapes and frontier characters provided authentic material for his art. By the mid-1880s, Remington’s work began to gain recognition, and he quickly established himself as a significant figure in Western art, contributing illustrations to popular magazines like Harper’s Weekly.
In his later years, Remington's style evolved, displaying a notable shift towards impressionism and atmospheric mood in his "Nocturnes" series. These paintings are characterized by a dramatic use of light and shadow to convey the mystery and tension of nighttime in the West. Despite his own critical self-view, these works were highly regarded and marked a significant contribution to American art history. Remington’s art is featured in major collections, including the Metropolitan Museum of Art and the Frederic Remington Art Museum in Ogdensburg, New York, preserving his legacy as an icon of American culture.
For those interested in exploring more about Frederic Remington’s life and works, updates on exhibitions and sales can be subscribed to, keeping enthusiasts connected to new insights and offerings related to this influential artist.
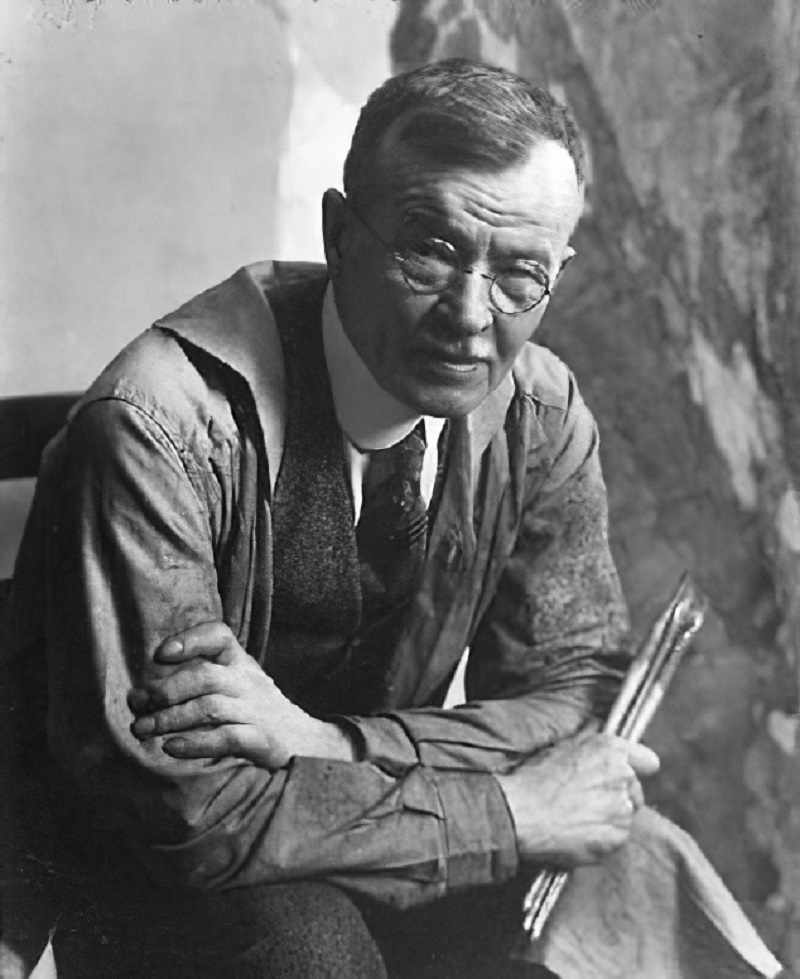

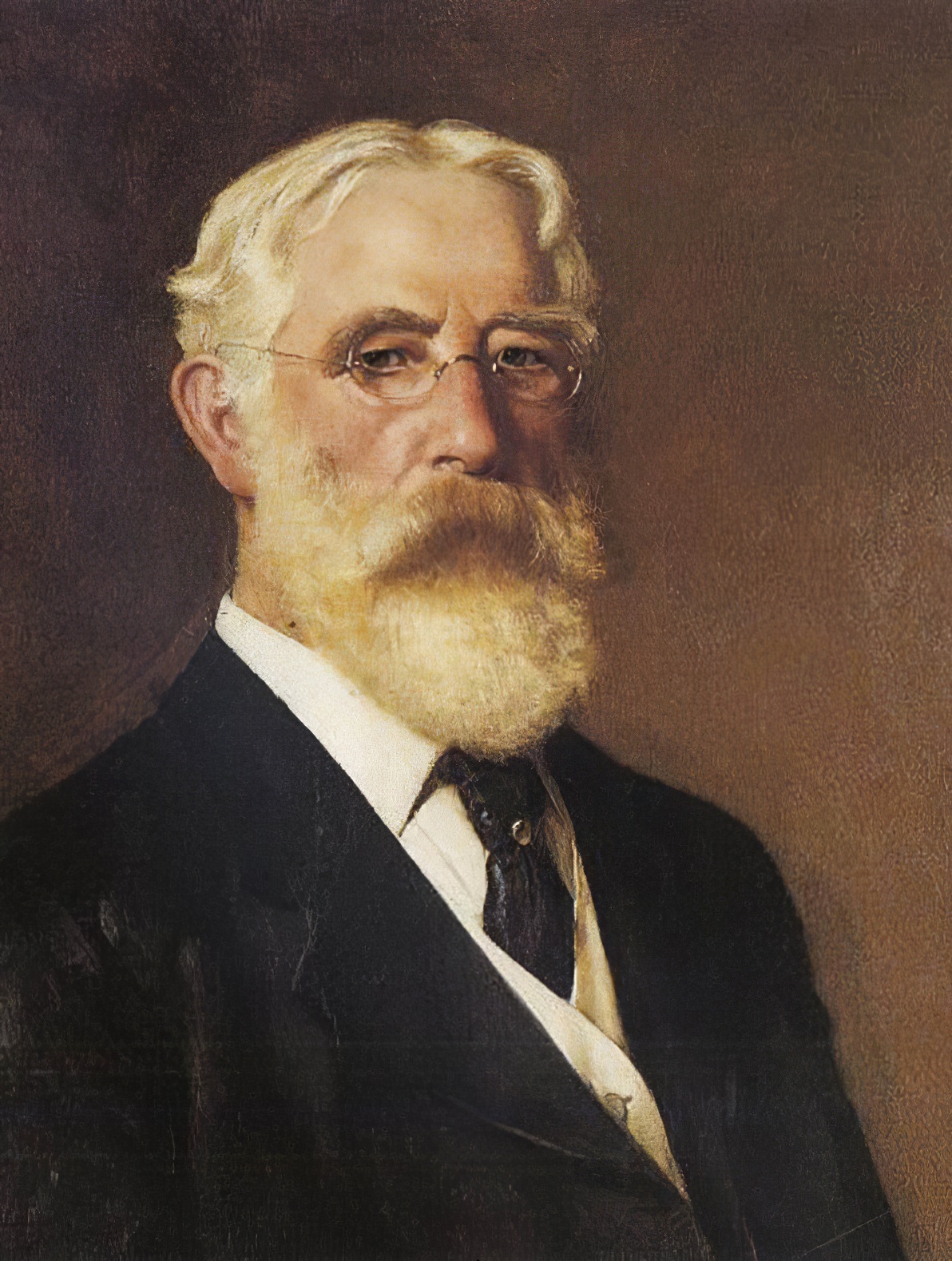
Carl Clemens Moritz Rungius was a leading American wildlife artist. He was born in Germany though he immigrated to the United States and he spent his career painting in the western United States and Canada. Active primarily in the first half of the 20th century, he earned a reputation as the most important big game painter and the first career wildlife artist in North America.
Rungius was an avid sportsman, and spent more time in the wilderness than other artists. By direct observation in nature, he was able to gain an exceptional insight into the animals and their environment. Rungius painted both landscapes and wildlife, often with both into a single picture. He situated animals in their natural environment, a practice that was new to painting in early twentieth century North America. His paintings are highly romanticized, and represent an Eden-like world without any signs of a human impact.
Among other places, his works are featured at the American National Museum of Wildlife Art (which has the largest public collection of Rungius work), the Dutch Rijksmuseum Twenthe, and Calgary's Glenbow Museum. His work was also part of the painting event in the art competition at the 1928 Summer Olympics.
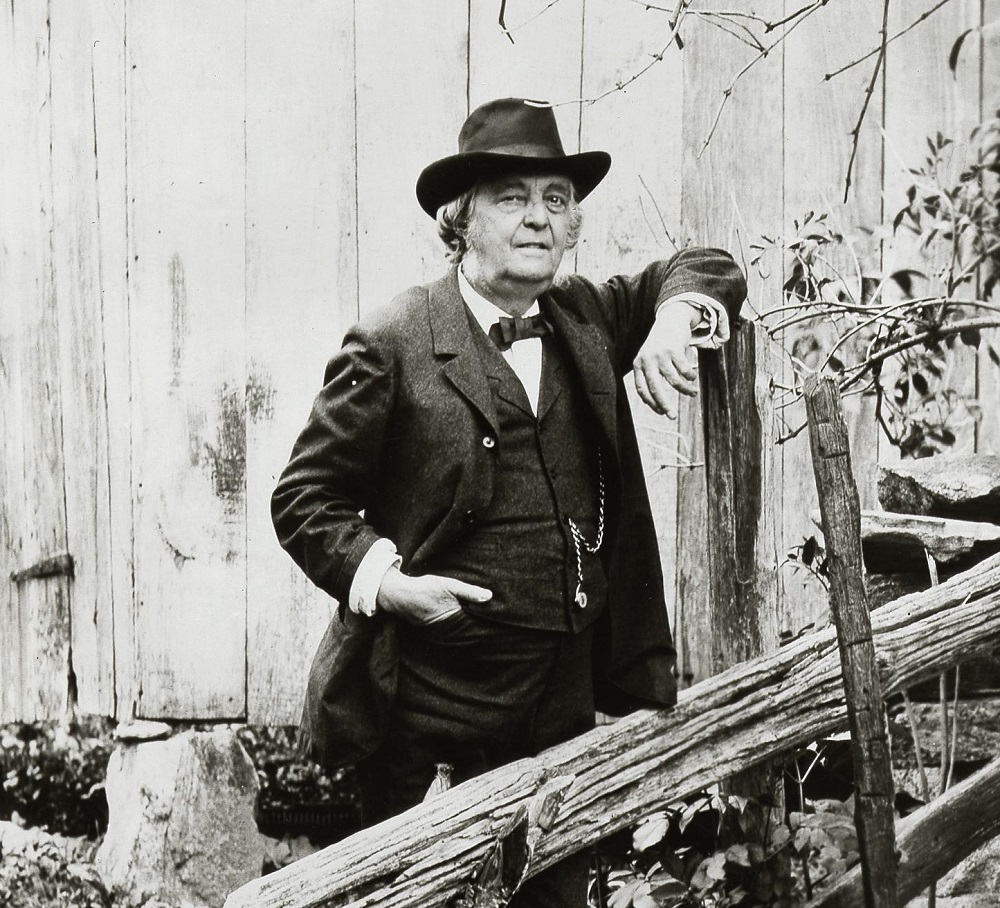

Arthur Fitzwilliam Tait was a British-American artist who is known mostly for his paintings of wildlife. During most of his career, he was associated with the New York City art scene.

Arthur Fitzwilliam Tait was a British-American artist who is known mostly for his paintings of wildlife. During most of his career, he was associated with the New York City art scene.
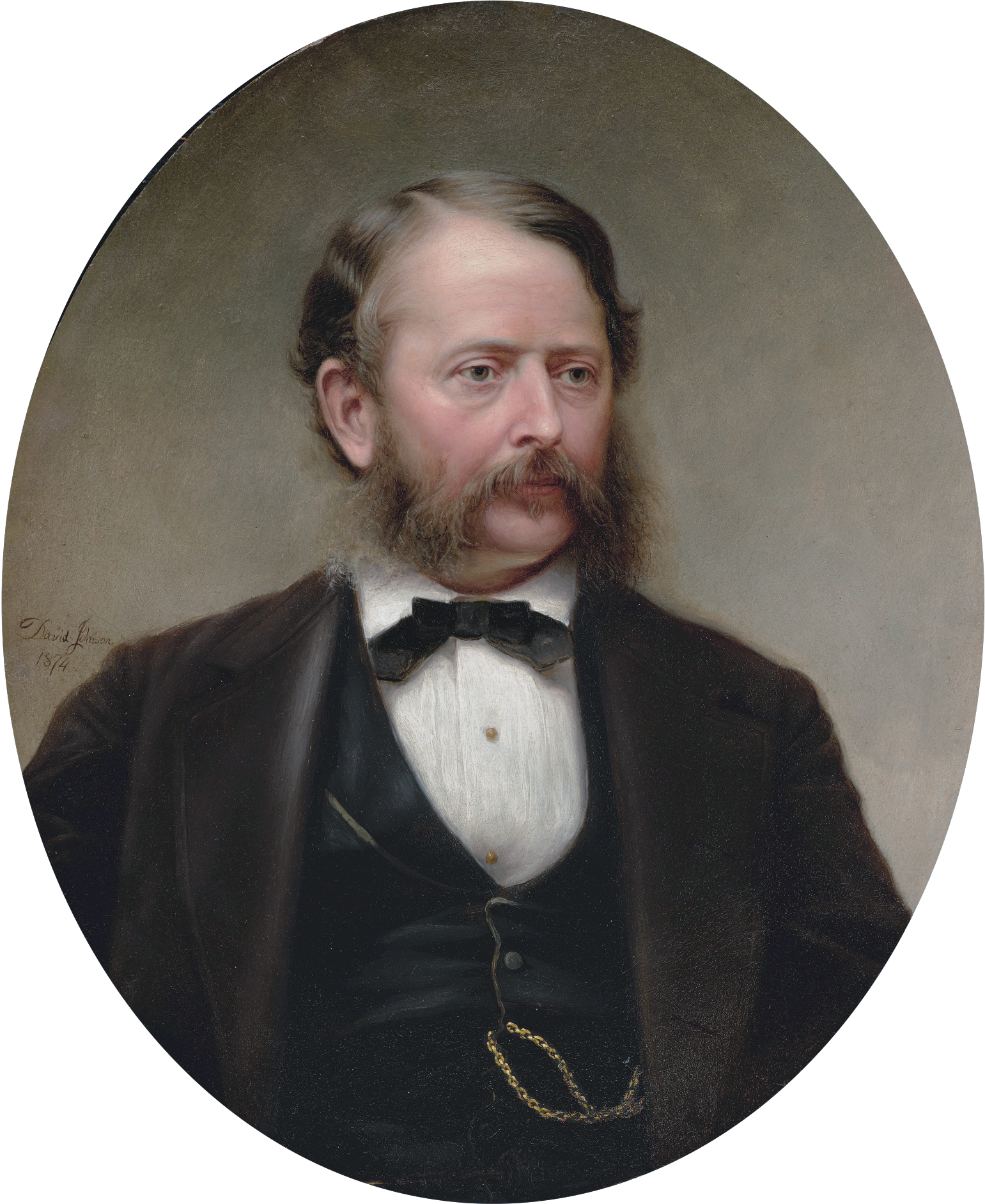

John Frederick Kensett was an American landscape painter and engraver born in Cheshire, Connecticut. He was a member of the second generation of the Hudson River School of artists. Kensett's signature works are landscape paintings of New England and New York State, whose clear light and serene surfaces celebrate transcendental qualities of nature, and are associated with Luminism. Kensett's early work owed much to the influence of Thomas Cole, but was from the outset distinguished by a preference for cooler colors and an interest in less dramatic topography, favoring restraint in both palette and composition. The work of Kensett's maturity features tranquil scenery depicted with a spare geometry, culminating in series of paintings in which coastal promontories are balanced against glass-smooth water. He was a founder of the Metropolitan Museum of Art.
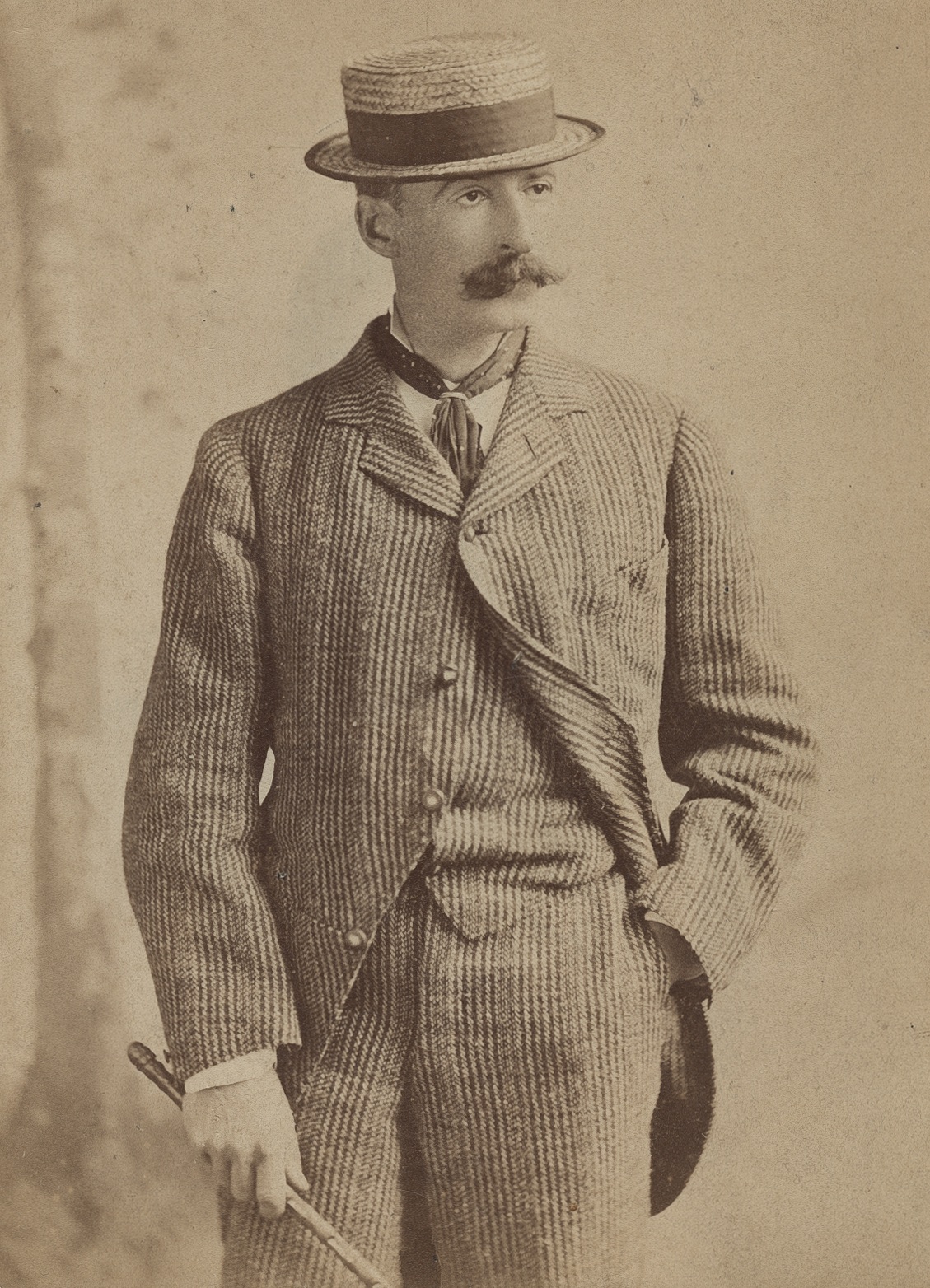

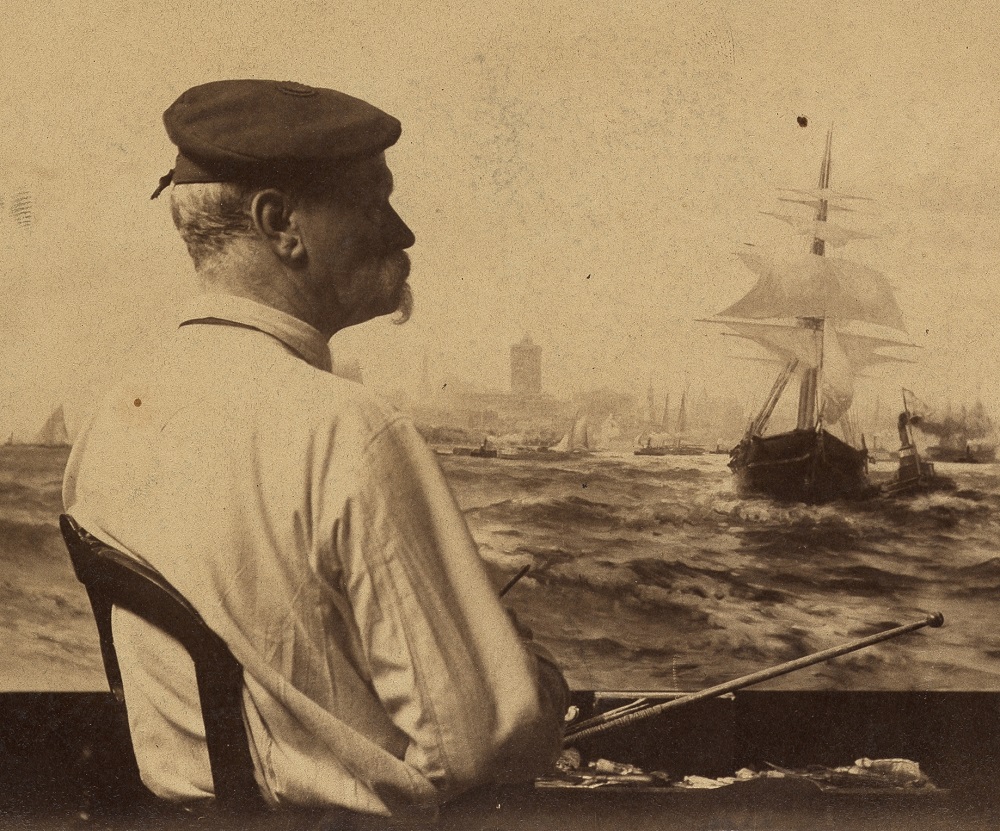
Winslow Homer was an American landscape painter and printmaker, renowned for his mastery of marine subjects and considered a preeminent figure in 19th-century American art. Born in Boston, Massachusetts in 1836, Homer was largely self-taught, starting his career as a commercial illustrator before venturing into oil painting and watercolors.
Homer's art evolved significantly over his lifetime. During the American Civil War, he worked as a correspondent, creating sketches that conveyed both the immediacy and the human cost of the war. This experience deeply influenced his later work, particularly his powerful oil paintings depicting war and its aftermath. After the war, Homer's focus shifted towards scenes of nature and rural America, reflecting a national nostalgia for simpler times. His works from this period, such as "The Cotton Pickers" and "Snap the Whip," showcase his ability to capture everyday life with poignant realism and emotional depth.
Later in his career, Homer became renowned for his watercolors and seascapes, such as "Breezing Up (A Fair Wind)" and "The Gulf Stream," which are celebrated for their dynamic composition and vivid portrayal of human interaction with nature. His late seascapes, which often depicted the rugged coastlines of Maine, are particularly noted for their dramatic intensity and hint at modernist abstraction, capturing the formidable power and timeless beauty of the sea.
Homer's works are held in high regard and continue to be featured in major museums and galleries, providing inspiration and insight into the American experience of the 19th century.
For those interested in the works of Winslow Homer and the impact of his art, you can sign up for updates related to new product sales and auction events featuring his work. This will keep you informed on opportunities to engage more deeply with Homer's enduring legacy.
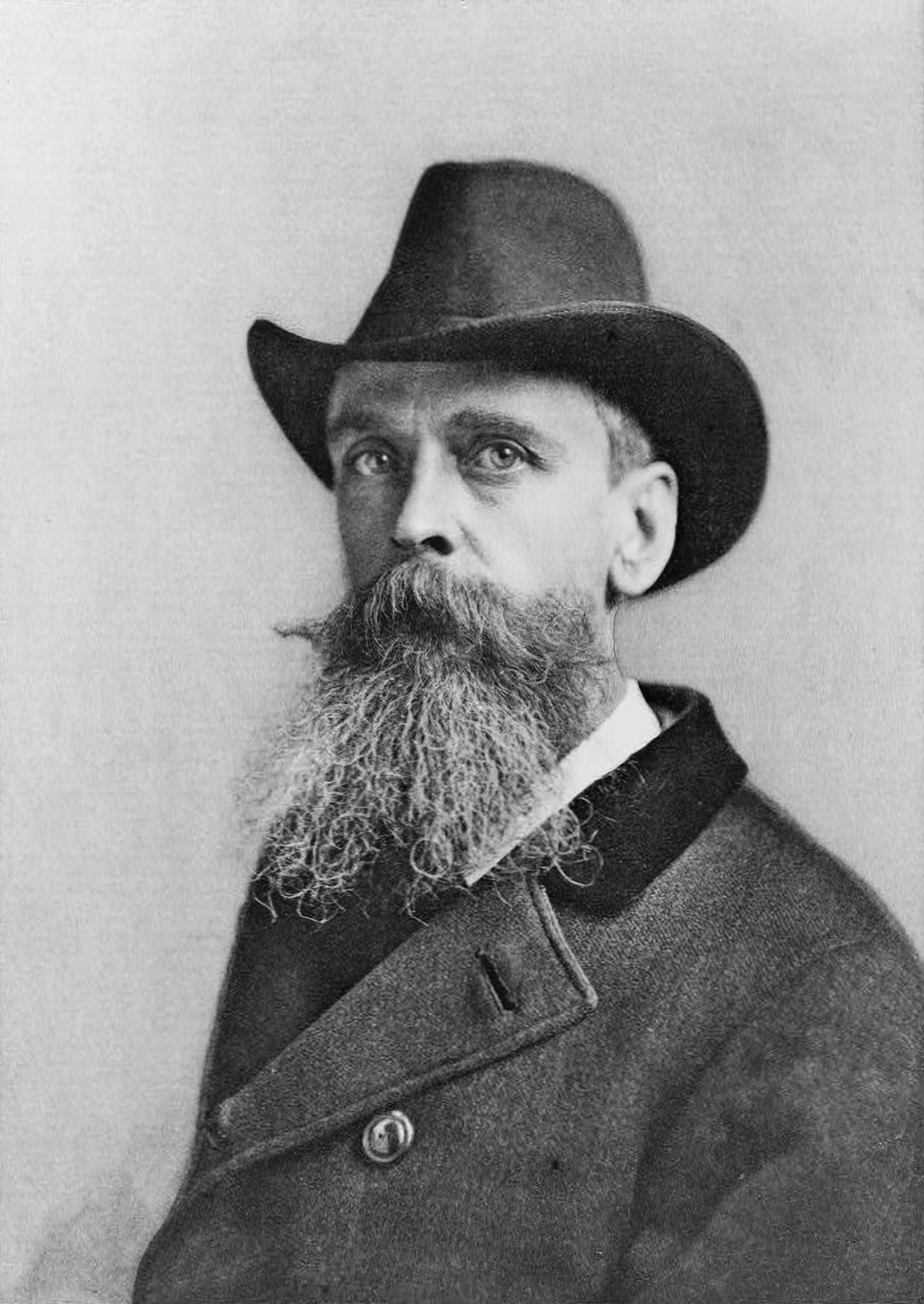

Thomas Moran was an American painter and printmaker of the Hudson River School in New York whose work often featured the Rocky Mountains. Moran and his family, wife Mary Nimmo Moran and daughter Ruth took residence in New York where he obtained work as an artist. He was a younger brother of the noted marine artist Edward Moran, with whom he shared a studio. A talented illustrator and exquisite colorist, Thomas Moran was hired as an illustrator at Scribner's Monthly. During the late 1860s, he was appointed the chief illustrator for the magazine, a position that helped him launch his career as one of the premier painters of the American landscape, in particular, the American West.
Moran along with Albert Bierstadt, Thomas Hill, and William Keith are sometimes referred to as belonging to the Rocky Mountain School of landscape painters because of all of the Western landscapes made by this group.

Thomas Moran was an American painter and printmaker of the Hudson River School in New York whose work often featured the Rocky Mountains. Moran and his family, wife Mary Nimmo Moran and daughter Ruth took residence in New York where he obtained work as an artist. He was a younger brother of the noted marine artist Edward Moran, with whom he shared a studio. A talented illustrator and exquisite colorist, Thomas Moran was hired as an illustrator at Scribner's Monthly. During the late 1860s, he was appointed the chief illustrator for the magazine, a position that helped him launch his career as one of the premier painters of the American landscape, in particular, the American West.
Moran along with Albert Bierstadt, Thomas Hill, and William Keith are sometimes referred to as belonging to the Rocky Mountain School of landscape painters because of all of the Western landscapes made by this group.

Alfred Thompson Bricher was a painter associated with White Mountain art and the Hudson River School.
In the 1870s, he primarily did maritime themed paintings, with attention to watercolor paintings of landscape, marine, and coastwise scenery. He often spent summers in Grand Manan, where he produced such notable works as Morning at Grand Manan (1878). In 1879, Bricher was elected into the National Academy of Design as an Associate member.
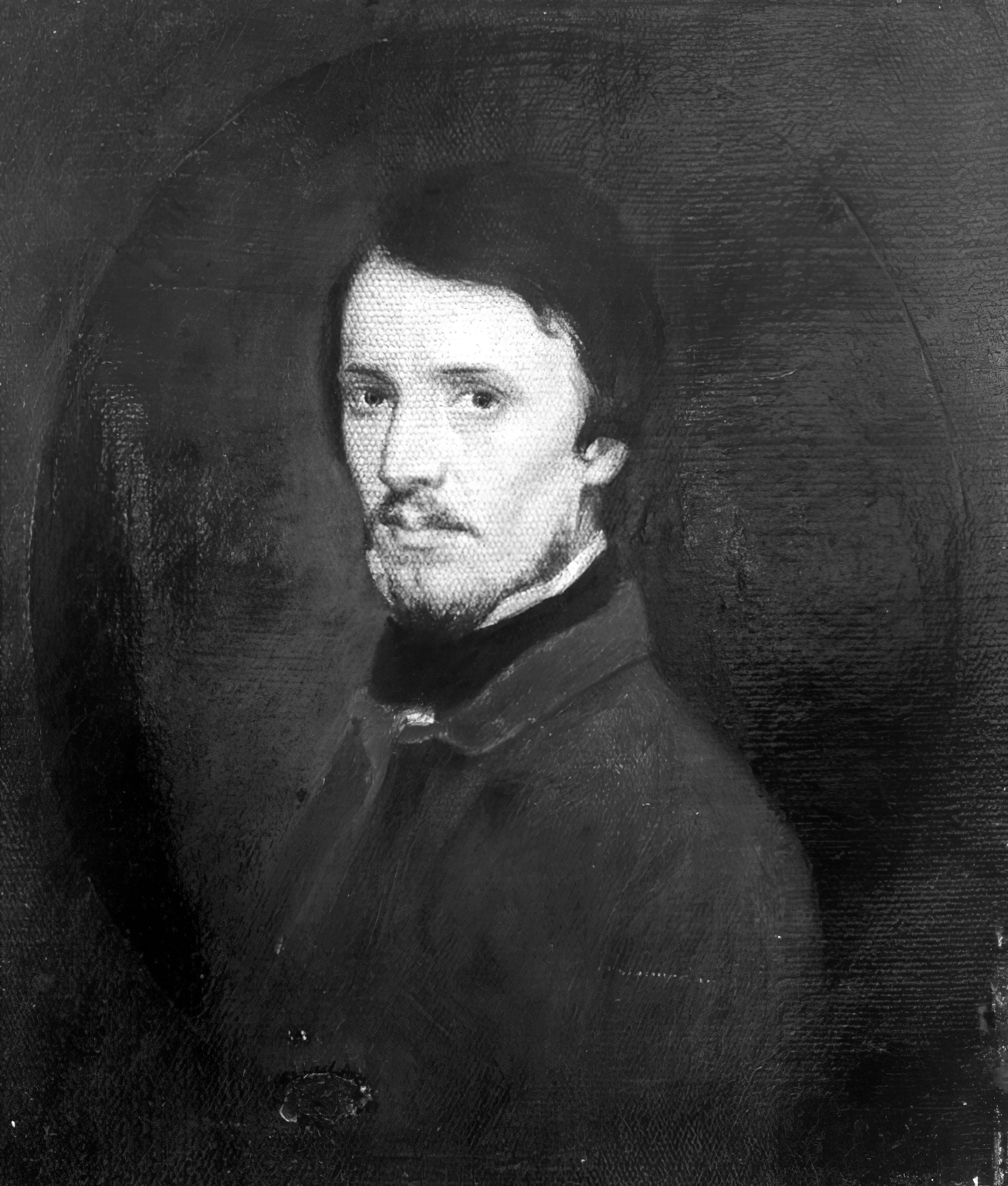
Sanford Robinson Gifford was an American landscape painter and a leading member of the second generation of Hudson River School artists. A highly-regarded practitioner of Luminism, his work was noted for its emphasis on light and soft atmospheric effects.
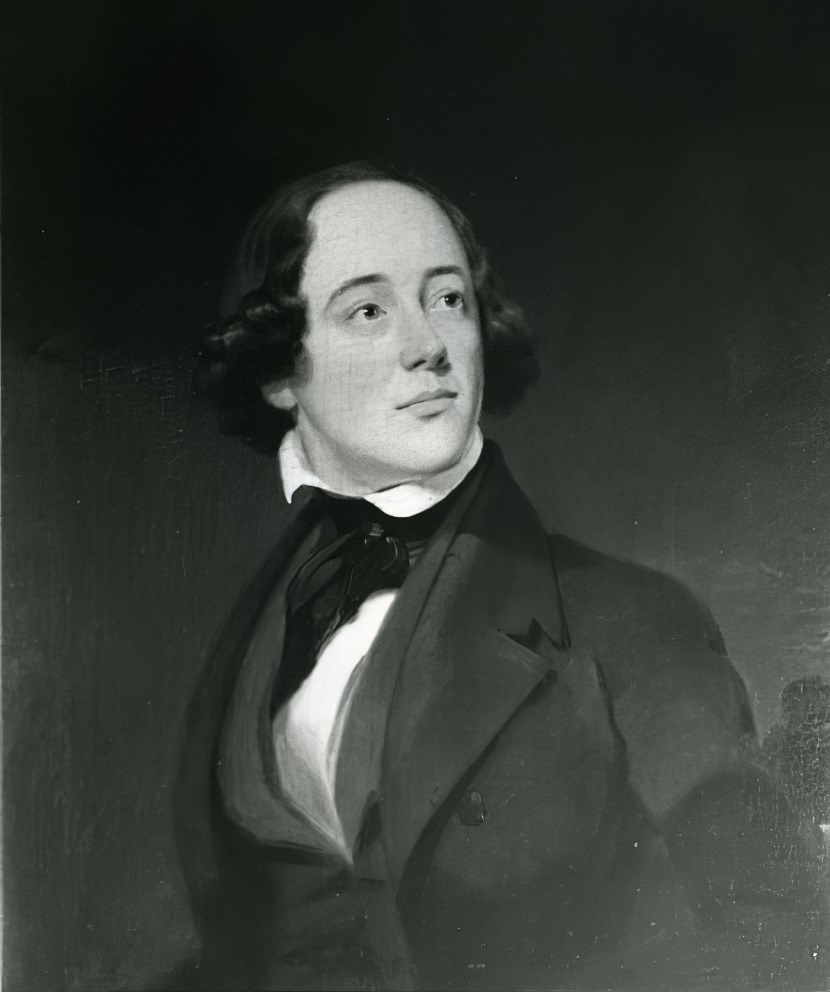

Martin Johnson Heade was an American painter known for his salt marsh landscapes, seascapes, and depictions of tropical birds (such as hummingbirds), as well as lotus blossoms and other still lifes. His painting style and subject matter, while derived from the romanticism of the time, are regarded by art historians as a significant departure from those of his peers.

Martin Johnson Heade was an American painter known for his salt marsh landscapes, seascapes, and depictions of tropical birds (such as hummingbirds), as well as lotus blossoms and other still lifes. His painting style and subject matter, while derived from the romanticism of the time, are regarded by art historians as a significant departure from those of his peers.
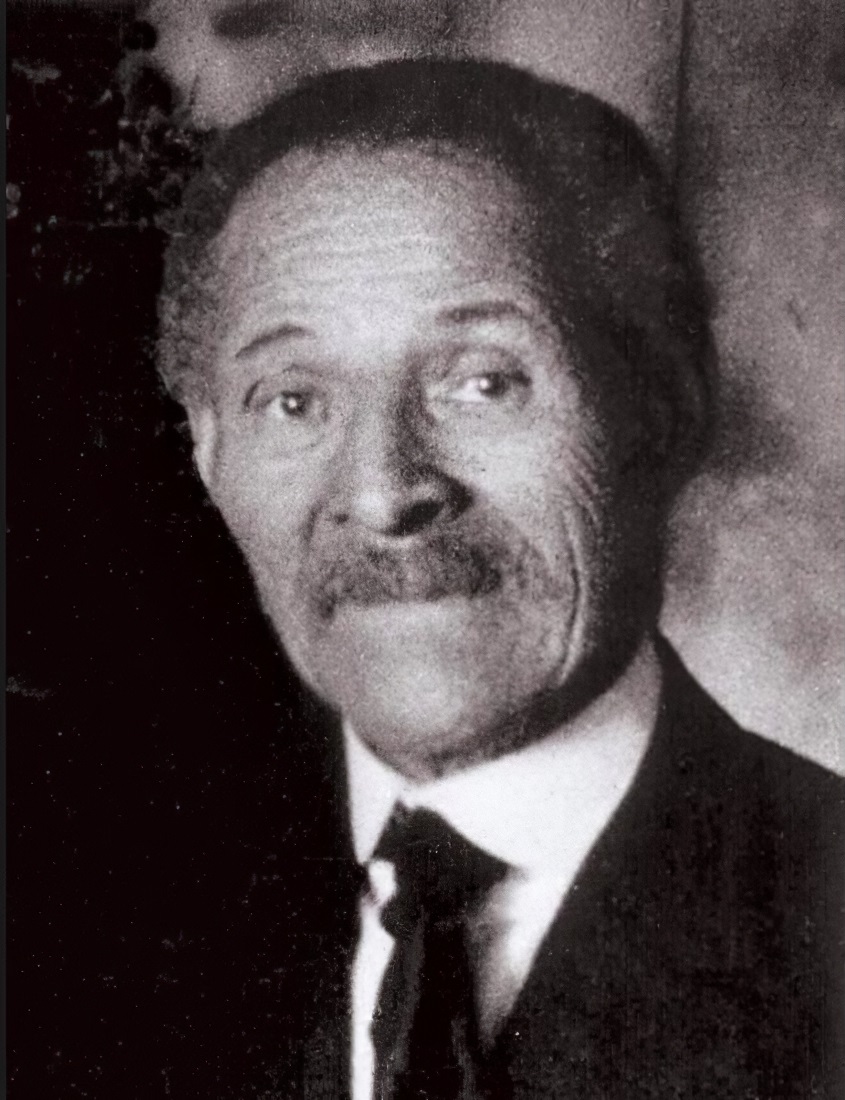

Charles Ethan Porter was an American painter who specialized in still life painting. A student at the National Academy of Design in New York City, he was one of the first African Americans to exhibit there. He was the only African-American artist at the turn of the century who painted in still life.
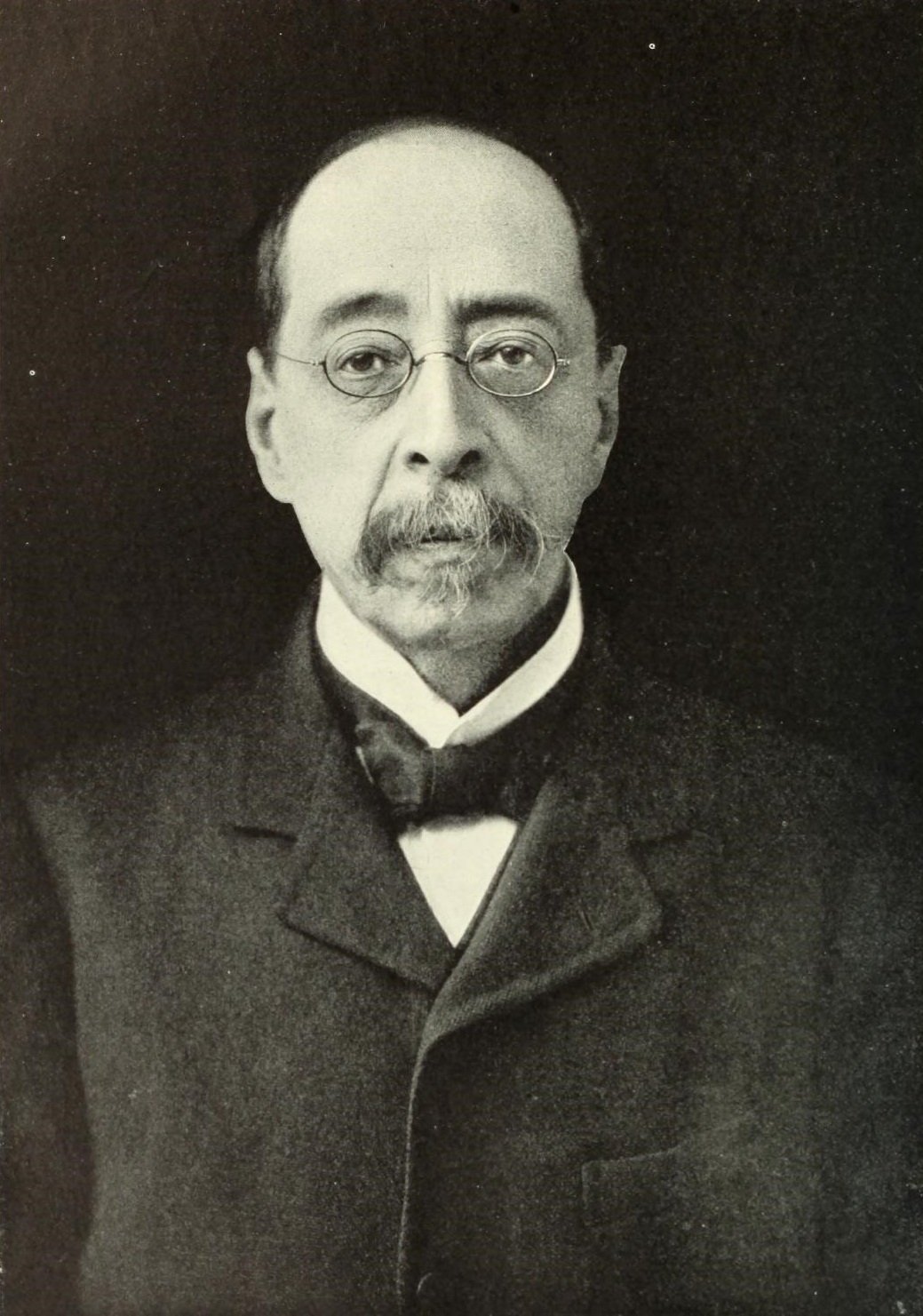

John La Farge was an American artist whose career spanned illustration, murals, interior design, painting, and popular books on his Asian travels and other art-related topics.
La Farge is best known for his production of stained glass, mainly for churches on the American east coast, beginning with a large commission for Henry Hobson Richardson's Trinity Church in Boston in 1878, and continuing for thirty years. La Farge designed stained glass as an artist, as a specialist in color, and as a technical innovator, holding a patent granted in 1880 for superimposing panes of glass. That patent would be key in his dispute with contemporary and rival Louis Comfort Tiffany.
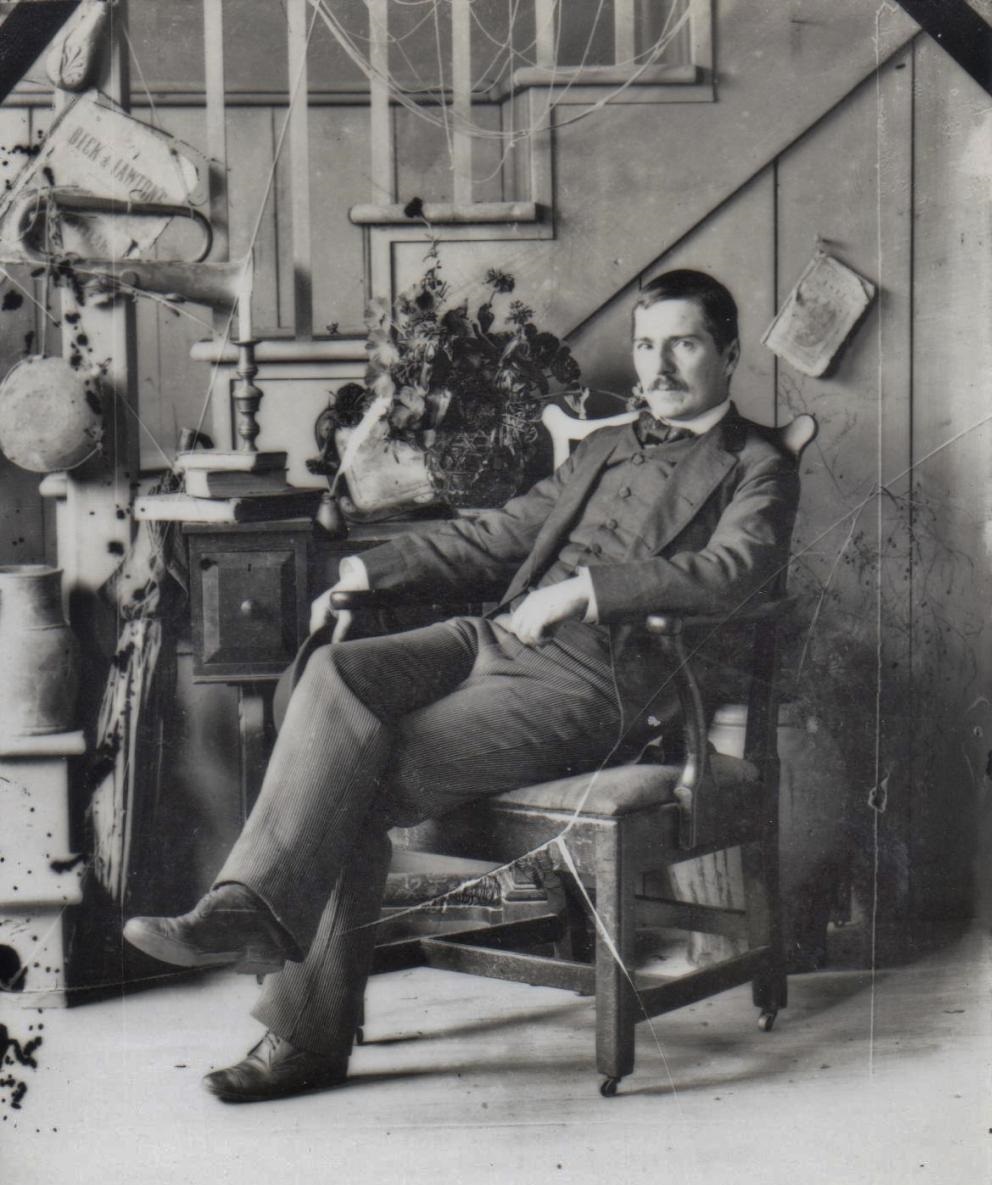

John Frederick Peto was an American trompe-l'œil ("fool the eye") painter who was long forgotten until his paintings were rediscovered along with those of fellow trompe-l'œil artist William Harnett.

John Frederick Peto was an American trompe-l'œil ("fool the eye") painter who was long forgotten until his paintings were rediscovered along with those of fellow trompe-l'œil artist William Harnett.
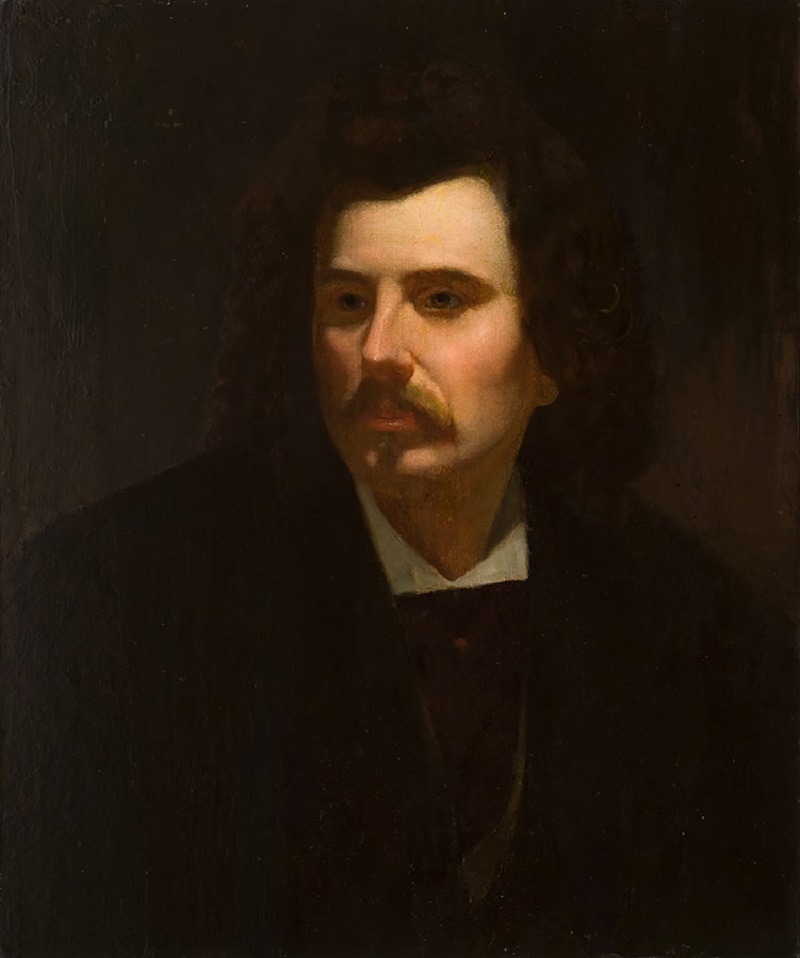

William Holbrook Beard was an American artistic painter who is known best for his satirical paintings of beasts performing human-like activities.
Beard was a prolific artist. His humorous treatment of bears, cats, dogs, horses and monkeys, generally with some human occupation and expression, usually satirical, gave him a great vogue at one time, and his pictures were much reproduced.
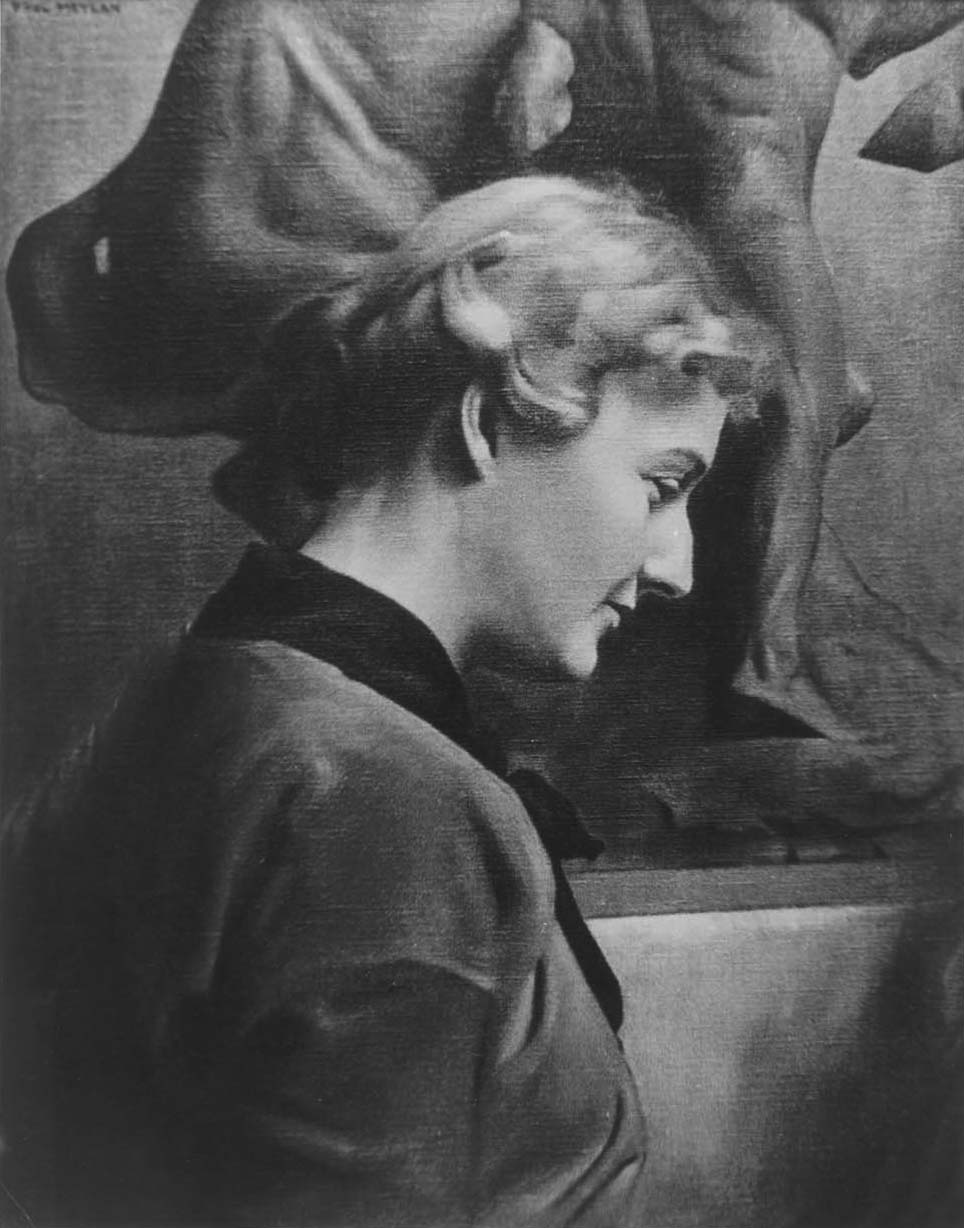

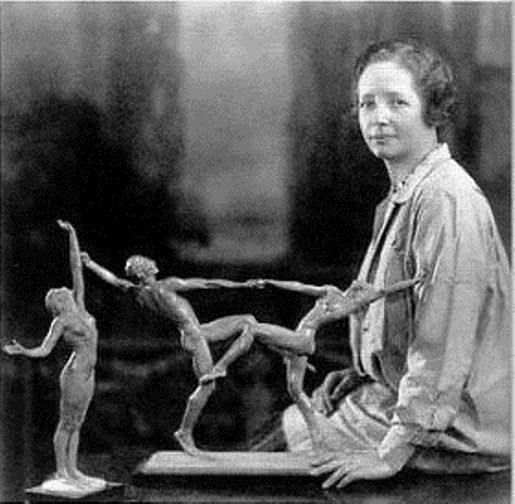
Anna Vaughn Hyatt Huntington was an American sculptor who was among New York City's most prominent sculptors in the early 20th century. At a time when very few women were successful artists, she had a thriving career. Hyatt Huntington exhibited often, traveled widely, received critical acclaim at home and abroad, and won multiple awards and commissions.
During the first two decades of the 20th century, Hyatt Huntington became famous for her animal sculptures, which combine vivid emotional depth with skillful realism. In 1915, she created the first public monument by a woman to be erected in New York City. Her Joan of Arc, located on Riverside Drive at 93rd Street, is the city's first monument dedicated to a historical woman.