Medicine & science — Printed and Manuscript Americana & Science

Leonhart Fuchs was a German humanist scientist, botanist, and physician.
Fuchs received a humanistic education under Catholic guidance, but later became a Protestant. He studied medicine and became a professor in Tübingen. He was most interested in the medicinal properties of plants. Well acquainted with the Greek and Latin classics and an excellent observer, he gave precise descriptions, and his beautiful engravings of plants established the tradition of depicting plants with precise illustrations and in alphabetical order.
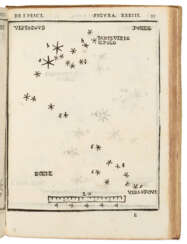
In 1542 Fuchs published his most important work, De Historia Stirpium Commentarii Insignes (Famous Commentaries on the History of Plants). The book was a great success, especially because of the magnificent woodcuts and the 487 plants, which were described for the first time in such a systematic form. De Historia Stirpium survived several editions and was translated into Dutch and German.
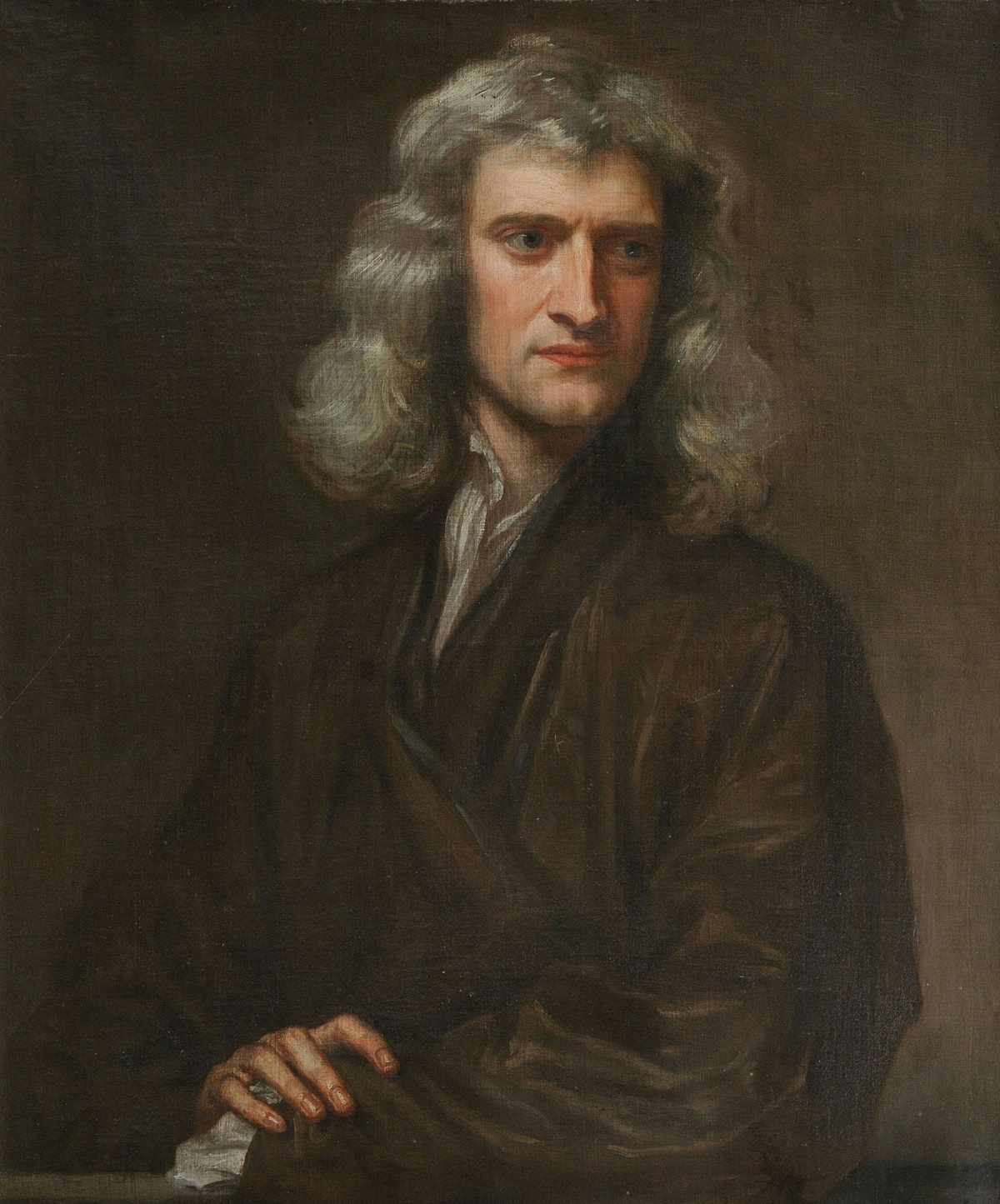

Isaac Newton was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus.
In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for tides, the trajectories of comets, the precession of the equinoxes and other phenomena, eradicating doubt about the Solar System's heliocentricity. He demonstrated that the motion of objects on Earth and celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton's inference that the Earth is an oblate spheroid was later confirmed by the geodetic measurements of Maupertuis, La Condamine, and others, convincing most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over earlier systems.
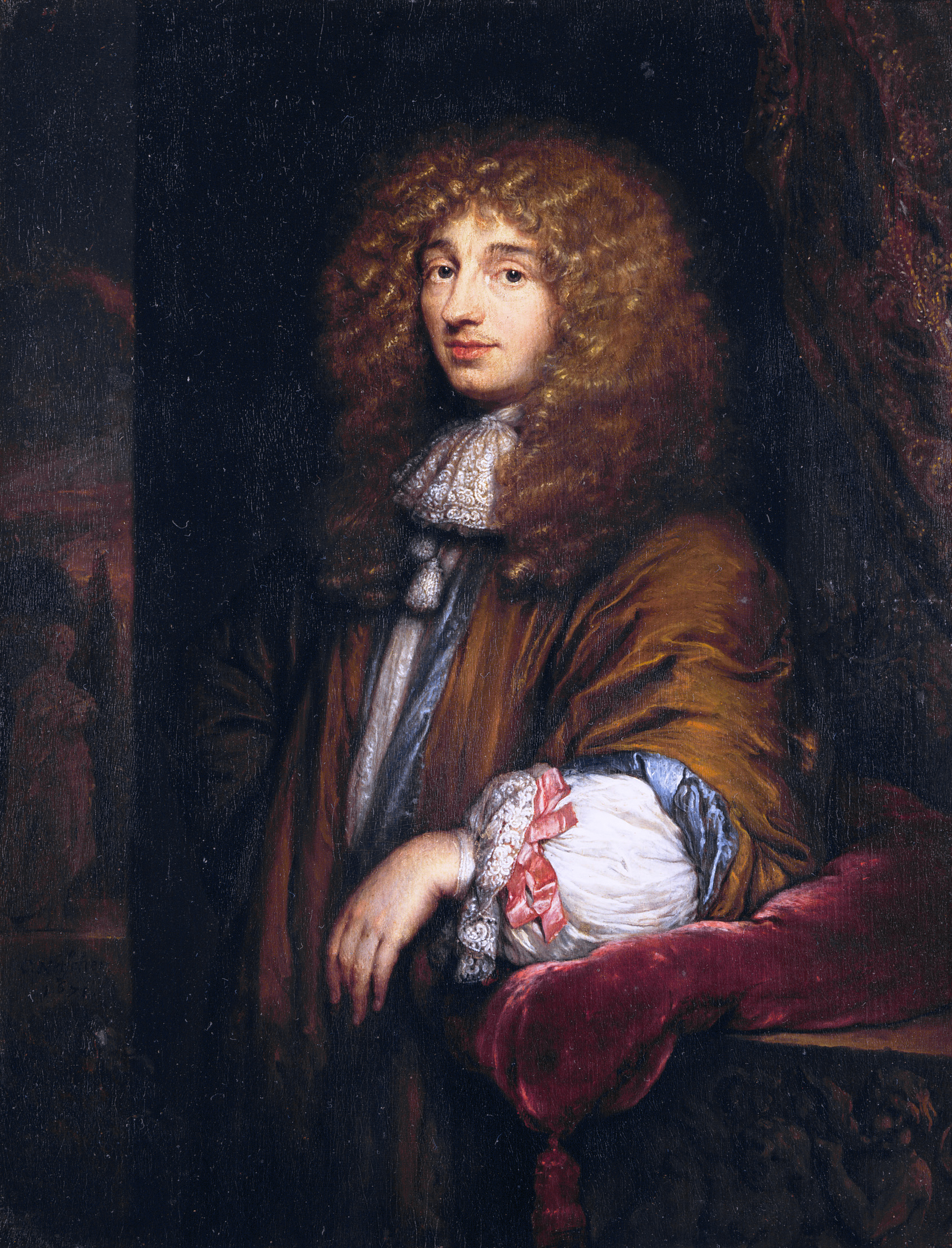

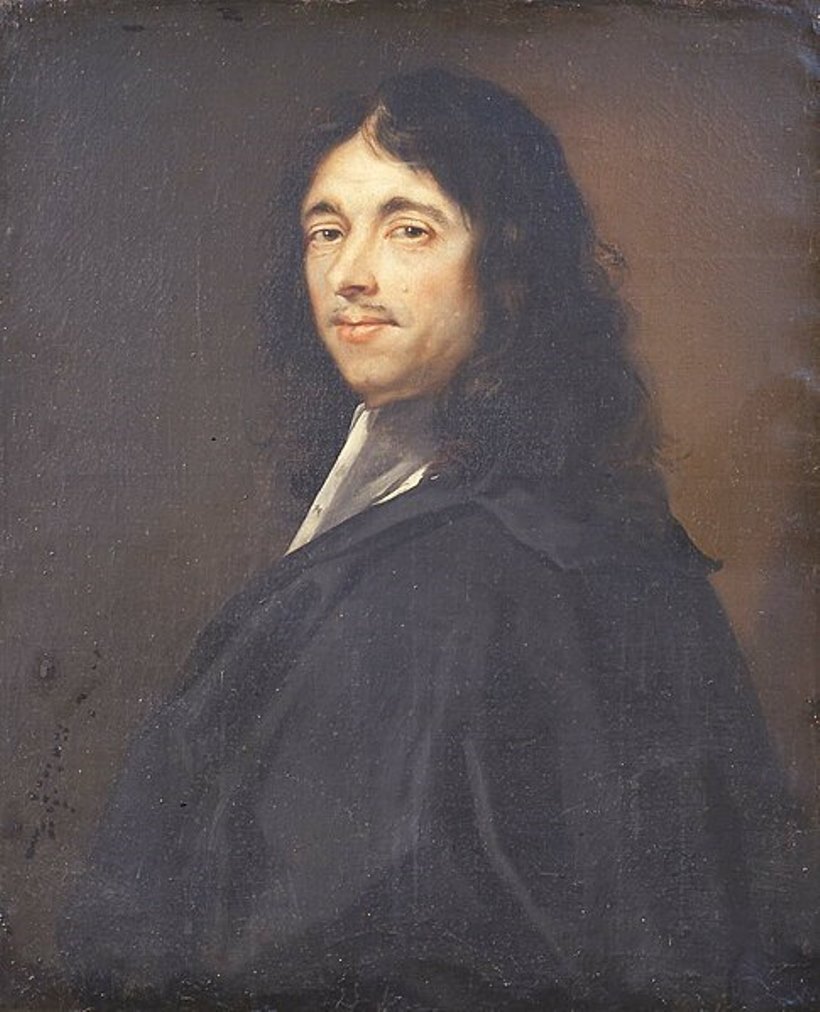
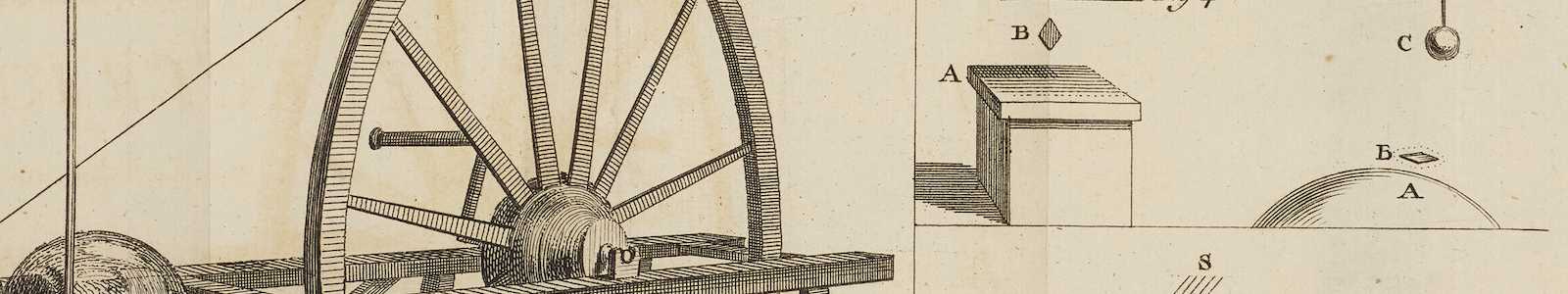
Christiaan Huygens van Zeelhem was a Dutch mechanic, physicist, mathematician, inventor and astronomer who formulated the wave theory of light.
An admirer of Descartes, Huygens preferred to conduct new experiments himself to observe and formulate laws. In physics, he contributed to the development of the crucial Huygens-Fresnel principle, which applies to wave propagation. He also extensively investigated free fall. He experimentally proved the law of conservation of momentum. He derived the law of centrifugal force for uniform circular motion.
He also invented the pendulum clock, discovered centrifugal force and the true shape of Saturn's rings as well as its moon Titan. Huygens is considered the first theoretical physicist to use formulas in physics and one of the founders of theoretical mechanics and probability theory.
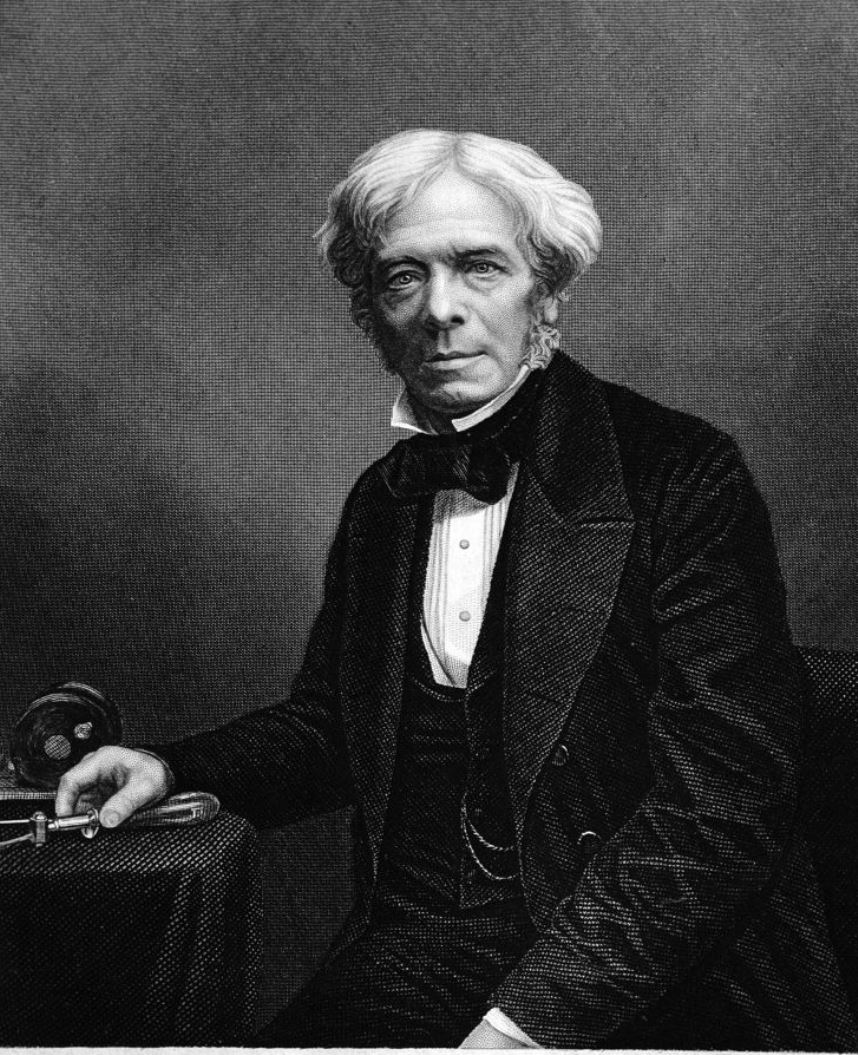

Michael Faraday was a British physicist and chemist, explorer and experimenter.
Faraday, because of his family's poverty, was unable to receive a formal education, but at the bookbinding shop in London where he worked, he read many books, including encyclopedias and textbooks on chemistry and physics. He persevered in self-education, attending hearings at the City Philosophical Society and later lectures by Sir Humphry Davy at the Royal Institution, who as a result took the able student on as an apprentice. In 1825 he replaced the seriously ill Davy in the management of the laboratory of the Royal Institution.
In 1833 Faraday was appointed to a research chair of chemistry created especially for him, where, among other achievements, the scientist liquefied various gases, including chlorine and carbon dioxide. His study of heating and lighting oils led to the discovery of benzene and other hydrocarbons, and he experimented extensively with various steel alloys and optical glasses. Faraday was an excellent experimentalist who presented his ideas in simple language. He is best known for his contributions to the understanding of electricity and electrochemistry. The concepts behind electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and electrolysis were some of his most important discoveries. His electromagnetic research formed the basis of the electromagnetic equations that James Clerk Maxwell developed in the 1850s and 1860s.
Between 1831 and 1855, Faraday read a series of 30 papers before the Royal Society, which were published in his three-volume Experimental Investigations in Electricity. His bibliography numbers some 500 printed articles. By 1844 he had been elected a member of some 70 scientific societies, including the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences.
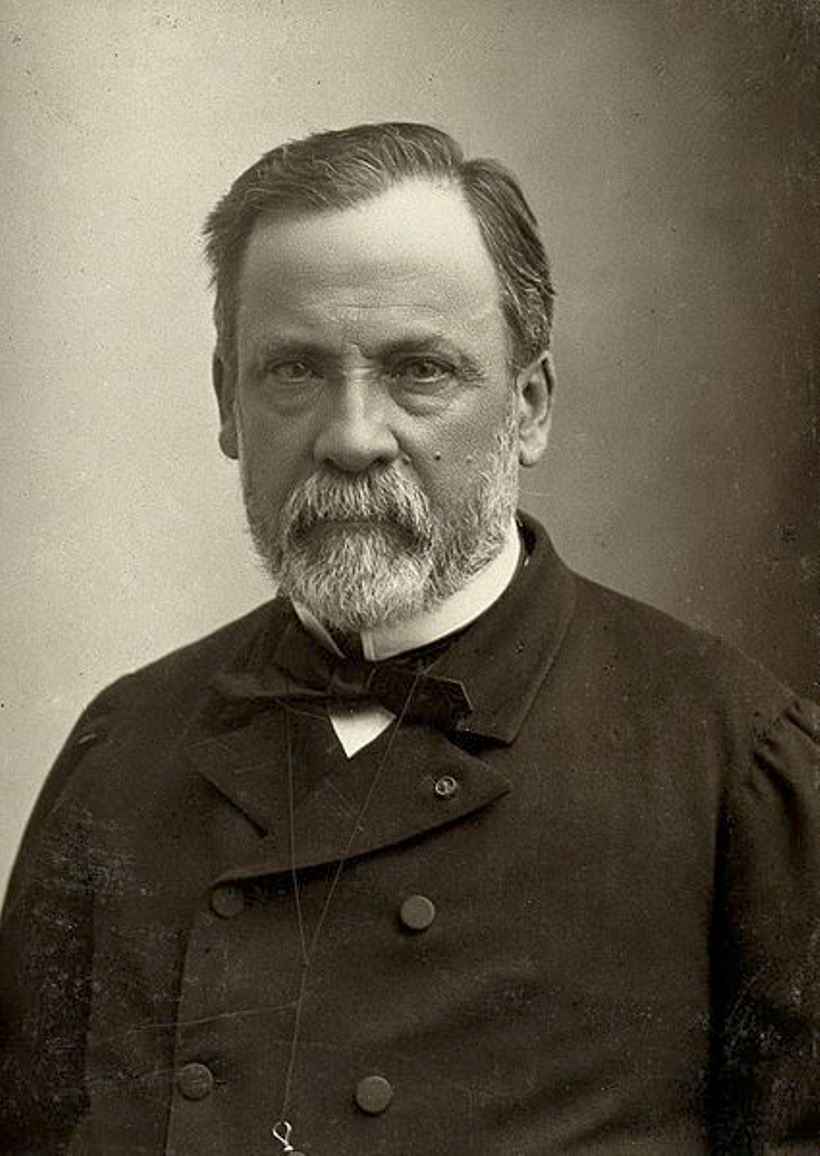

Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and the founder of microbiology and vaccination.
Pasteur received a bachelor of arts and sciences from the Royal College of Besançon and a doctorate from the École Normale in Paris, then spent several years as a researcher and teacher at the Lycée de Dijon. In 1848 he became professor of chemistry at the University of Strasbourg, and in the following year began to study the nature of wine fermentation, which began his revolutionary journey of most important scientific discoveries.
He invented a way to kill bacteria by boiling and then cooling the liquid, a process known today as pasteurization. Pasteur discovered the first vaccine in 1879 when he was exposed to a disease called chicken cholera. By accidentally exposing chickens to a weakened form of the culture, he demonstrated that they became resistant to the actual virus. Pasteur subsequently expanded his theory of germs and developed causes and vaccines against anthrax, cholera, tuberculosis, and smallpox, and the success of Pasteur's rabies vaccine in 1885 brought him worldwide fame.
Louis Pasteur's contribution to science, technology and medicine cannot be overemphasized. He pioneered the study of molecular asymmetry; discovered that microorganisms cause fermentation and disease; invented the process of pasteurization; saved the brewing, wine and silk industries in France; developed vaccines against the dreaded diseases anthrax and rabies, which saved millions of lives.
In 1873, Pasteur was elected an associate member of the Academy of Medicine, in 1882 - a member of the French Academy, and in 1888 in Paris was opened the Pasteur Institute. He was also awarded France's highest honor, the Legion of Honor.

Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".

Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".

Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".

Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".

Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".

Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".

Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".

Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".

Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".

Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".