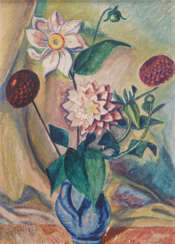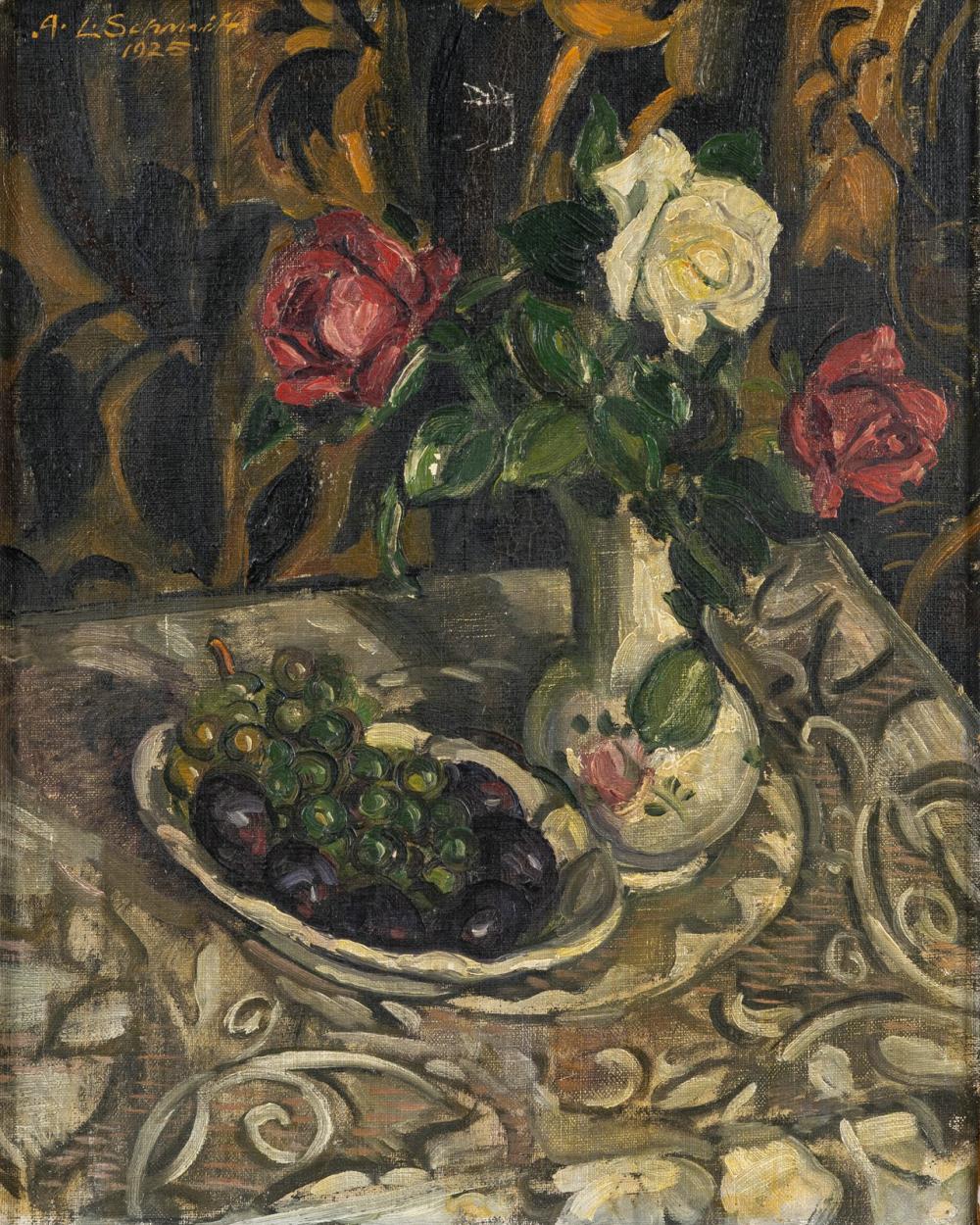Modern Art — 815-2 | Moderne & Zeitgenössische Kunst, Design

Carl Emil Uphoff (German: Carl Emil Uphoff) was a German painter and writer who worked in the artists' colony of Worpswede. He first studied at the Folkwang-Kreis under Christian Rolfs and then on study trips to Belgium, Holland and France. In Paris he was promoted by Henri Matisse.
Karl Emil Uphoff was a member of the NSDAP and the Nazi community Kraft durch Freude.

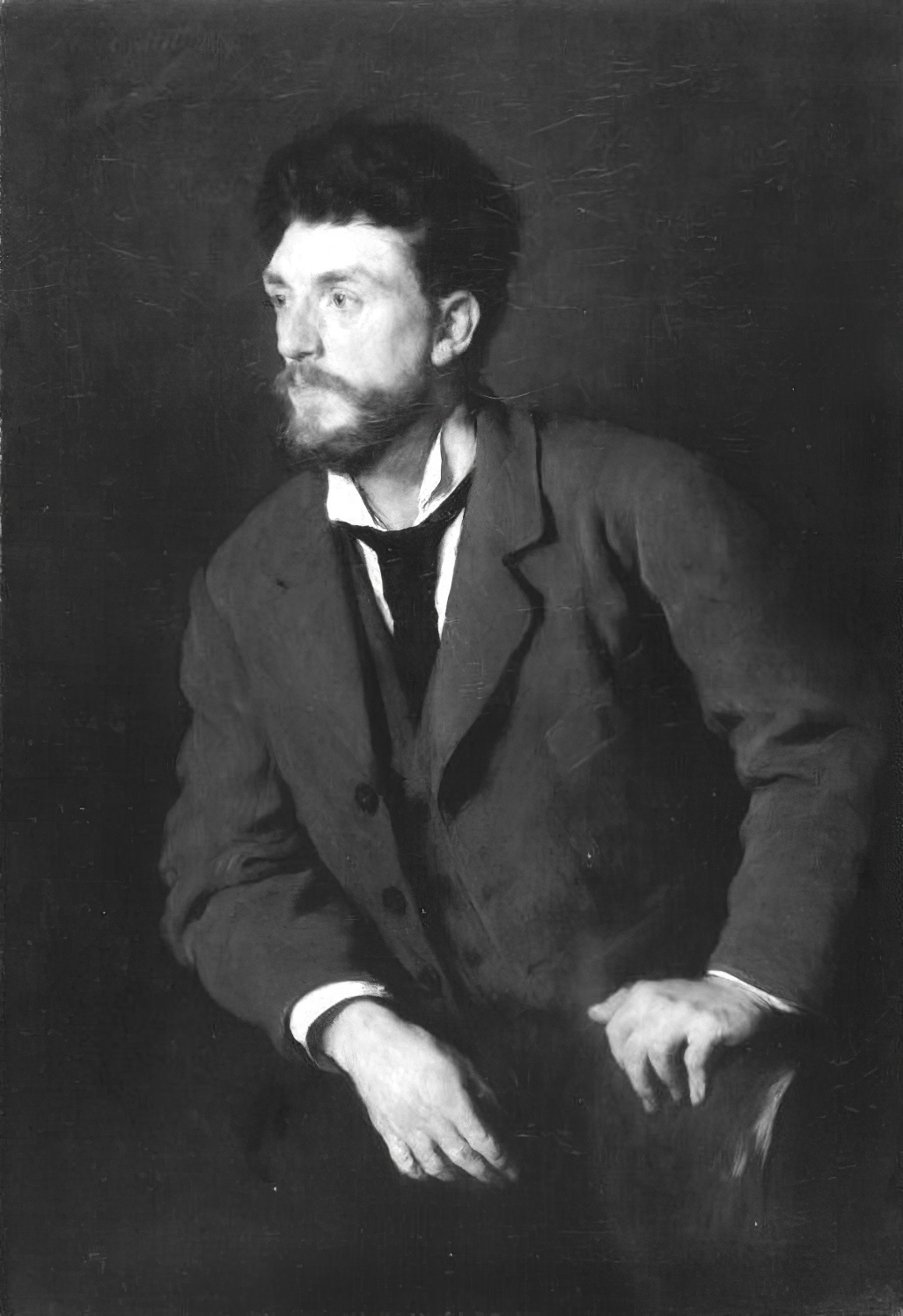
Lovis Corinth was a German artist and writer whose mature work as a painter and printmaker realized a synthesis of impressionism and expressionism.
Corinth studied in Paris and Munich, joined the Berlin Secession group, later succeeding Max Liebermann as the group's president. His early work was naturalistic in approach. Corinth was initially antagonistic towards the expressionist movement, but after a stroke in 1911 his style loosened and took on many expressionistic qualities. His use of color became more vibrant, and he created portraits and landscapes of extraordinary vitality and power. Corinth's subject matter also included nudes and biblical scenes.

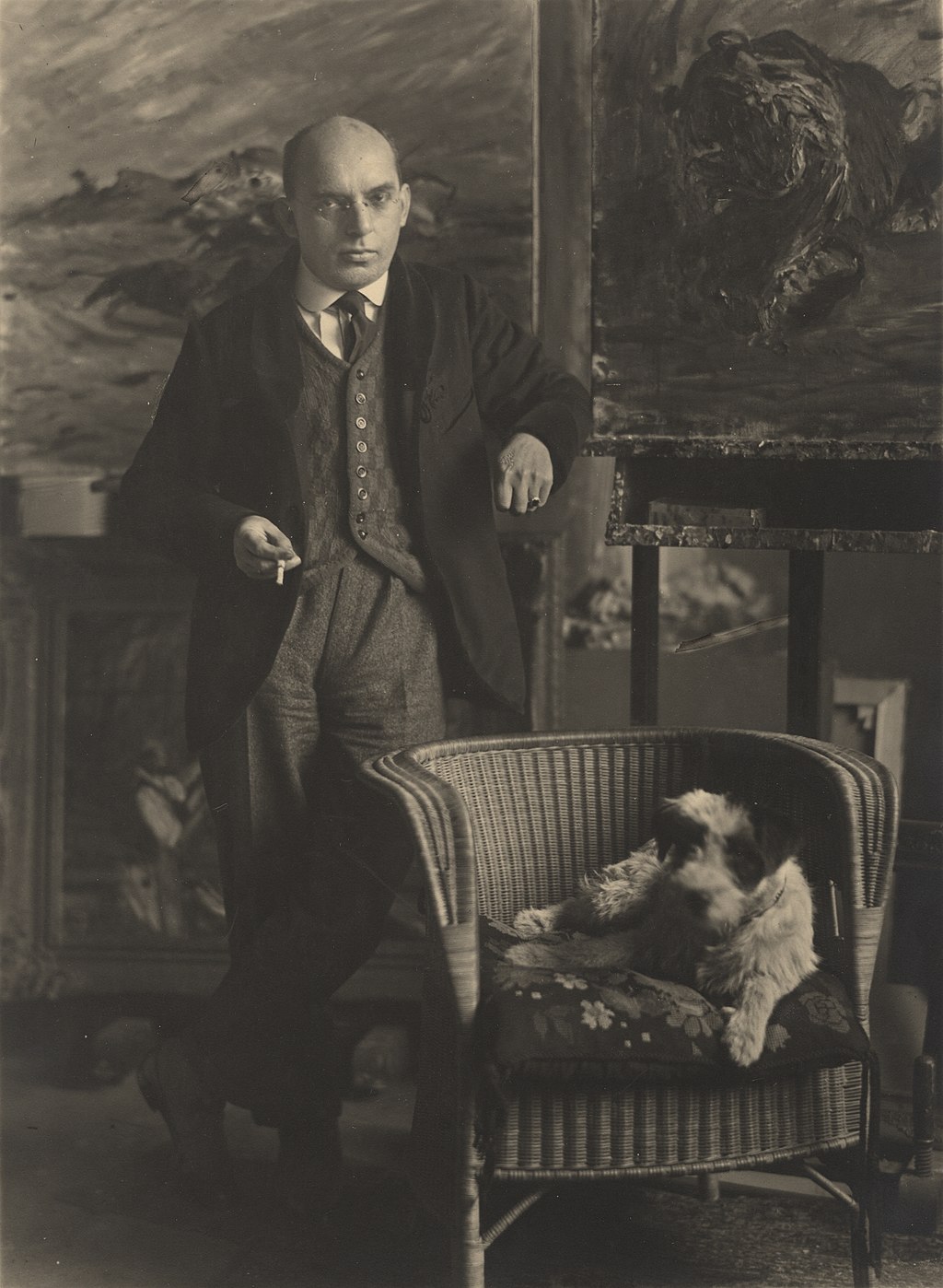
Bernhard Pankok, full name Bernhard Wilhelm Maria Pankok, was a German painter and graphic artist, designer, applied artist and architect of the Art Nouveau period.
After acquiring skills as a painter and restorer, Bernhard Pankok studied painting at the Düsseldorf Academy of Fine Arts, then in Berlin. In 1892, he began working in Munich in his own painting studio, doing illustrations for the magazines Pan and Jugend, among others. Pancock was one of the founders of the Munich Association of Art Craft Workshops.
In 1897, Pankok began designing furniture and exhibited his work at numerous exhibitions, including the landmark 1900 "Universal and International Exposition" in Paris. In the same year the art historian Konrad Lange commissioned Bernhard Pancock to design the Haus Lange for him; he worked extensively as an architect in general and designed other buildings in Stuttgart. Pankok was prolific and versatile: he designed sets for opera stages and salons for ocean liners and even the passenger cabins of zeppelins, worked as an architect, furniture designer, interior decorator, painter and graphic artist.
In 1907, he co-founded the Deutsche Werkbund. In 1901 he was invited to teach at the Royal Training and Experimental Workshop in Stuttgart; in 1913 he became its head and in that capacity merged it with the School of Arts and Crafts.
.jpg)
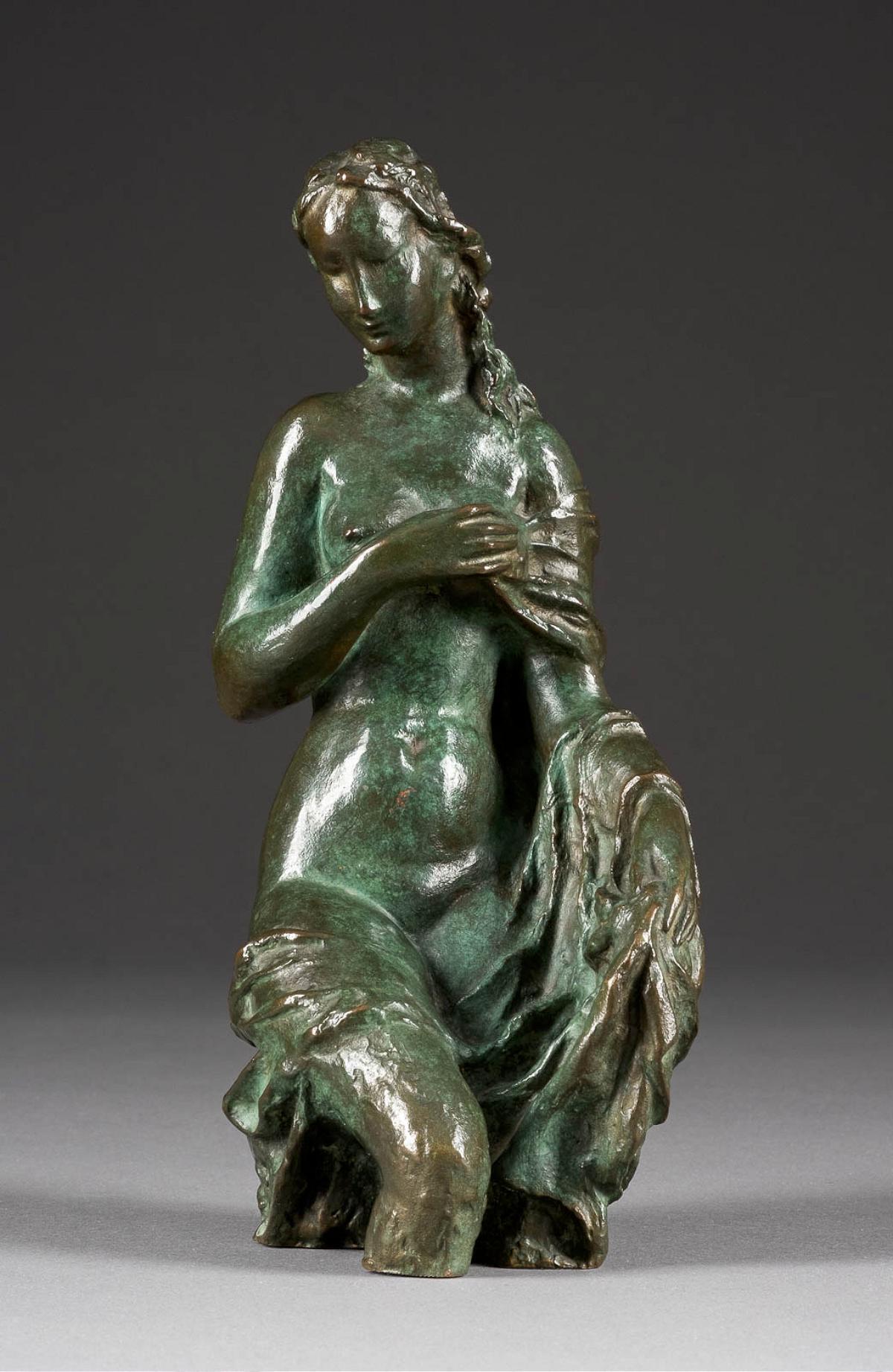
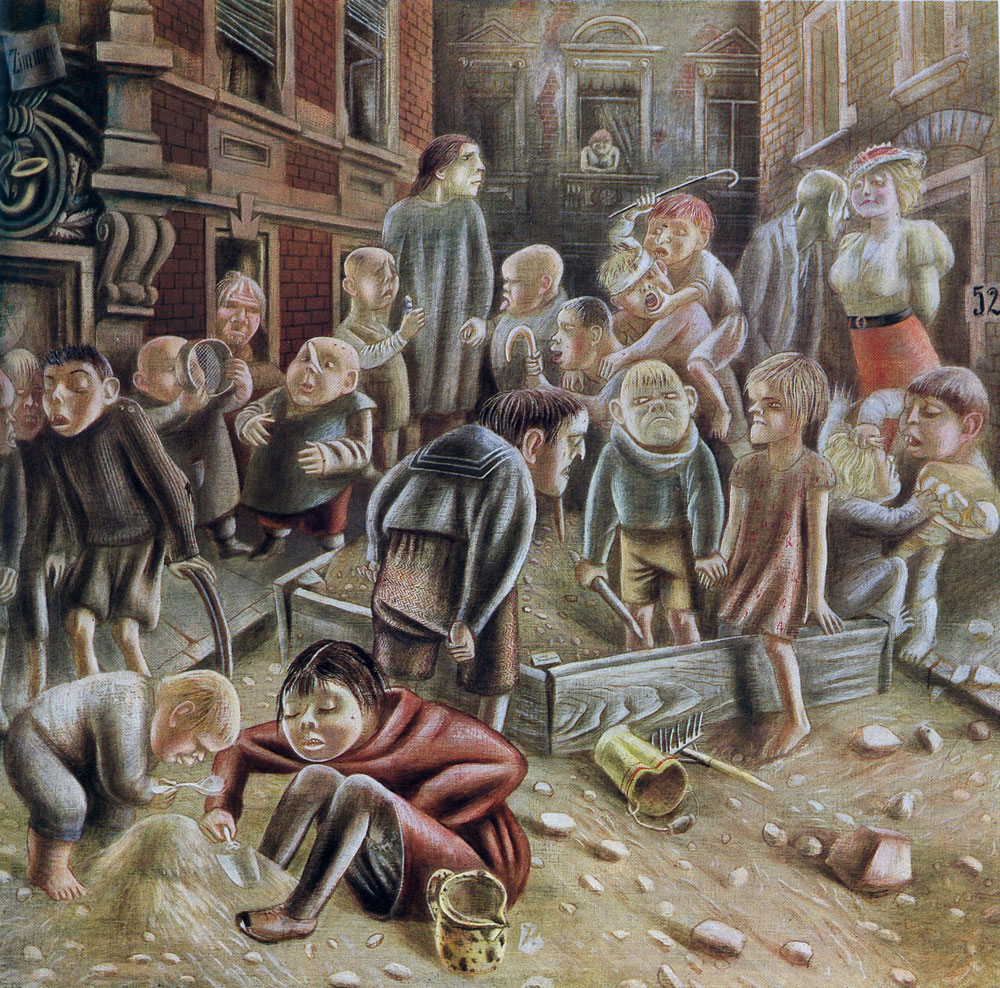
Ernst Heinrich Barlach was a German expressionist sculptor, medallist, printmaker and writer. Although he was a supporter of the war in the years leading to World War I, his participation in the war made him change his position, and he is mostly known for his sculptures protesting against the war. This created many conflicts during the rise of the Nazi Party, when most of his works were confiscated as degenerate art. Stylistically, his literary and artistic work would fall between the categories of twentieth-century Realism and Expressionism.
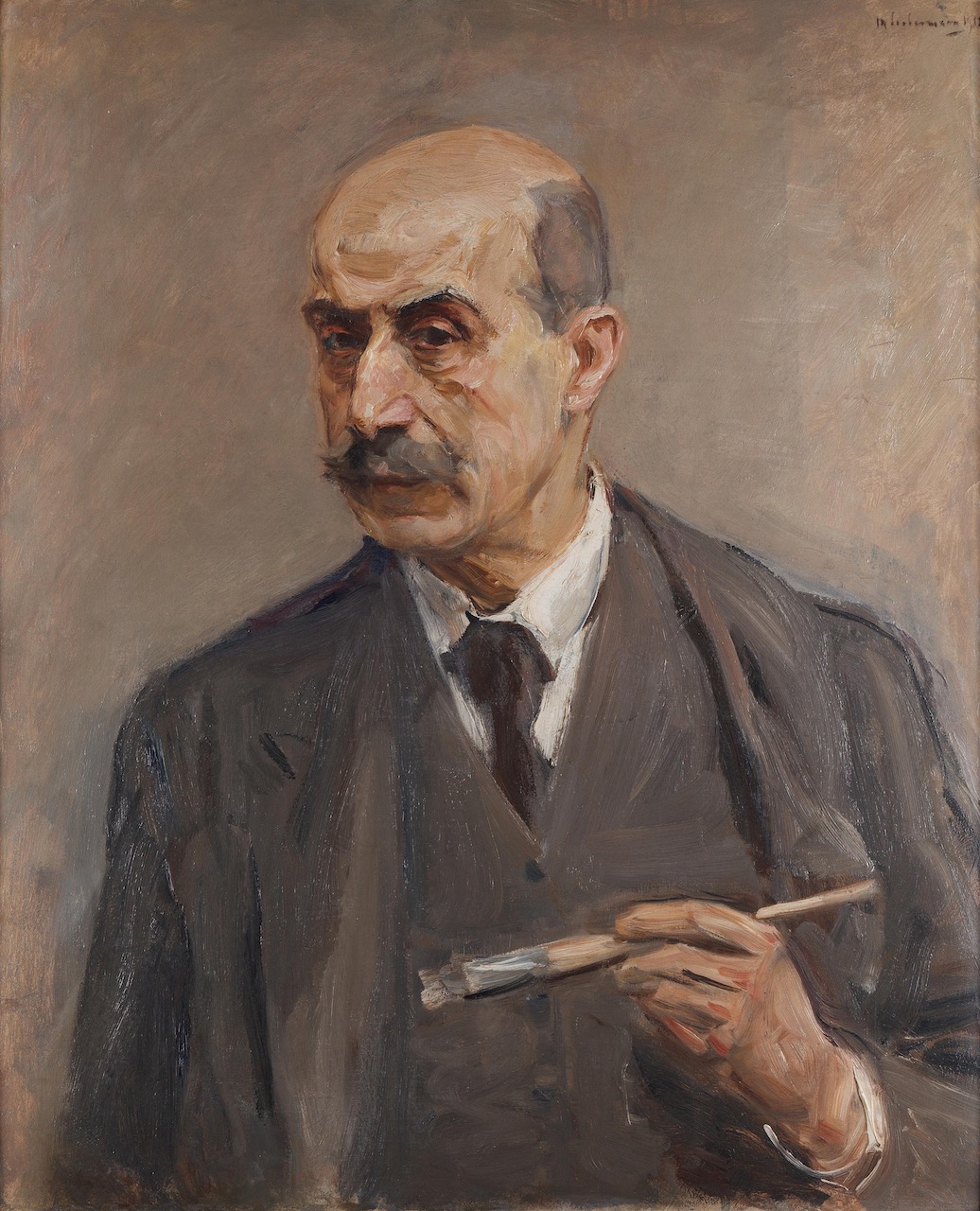

Max Liebermann was a German painter and printmaker, and one of the leading proponents of Impressionism in Germany and continental Europe. In addition to his activity as an artist, he also assembled an important collection of French Impressionist works.
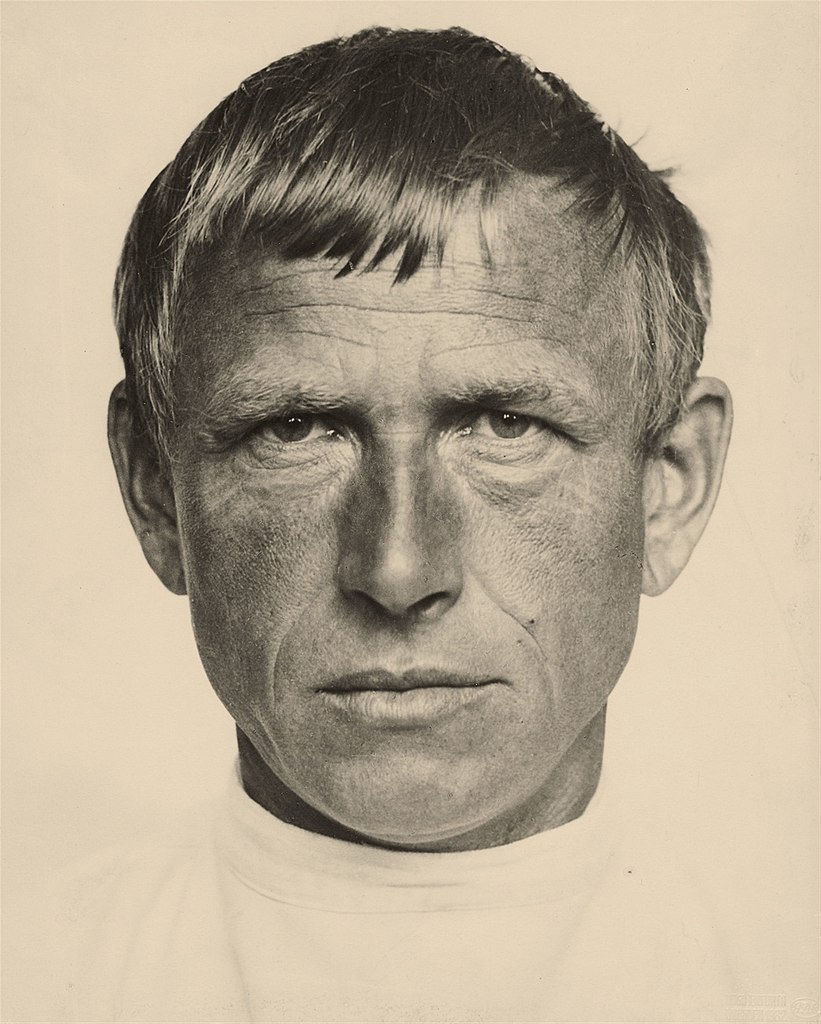
Wilhelm Heinrich Otto Dix was a German artist whose work stands as a stark, unyielding reflection of the societal tumult and trauma of the early 20th century. Born in 1891 in Untermhaus, Germany, Dix's early life was steeped in the arts, his ambition to become an artist nurtured by both familial influence and formal education in Dresden. His experiences as a soldier in World War I deeply influenced his artistic direction, leading him to vividly depict the horrors of war and the decay of the Weimar Republic with a brutal realism that became his signature style.
Dix's association with the Dada movement and the New Objectivity (Neue Sachlichkeit) further honed his critical, often cynical portrayal of post-war society. His works, such as "The Trench" and "War Cripples," expose the visceral aftermath of conflict, while his engagement with the Dadaists imbued his art with a disruptive, confrontational energy against societal norms and the art establishment.
Perhaps most notable is Dix's ability to capture the psychological depth and societal critiques through his portraits and landscapes, which ranged from the grotesque to the surreal. Paintings like "Portrait of the Journalist Sylvia von Harden" and the triptychs "Metropolis" and "War" are emblematic of his keen observation and stark depiction of the era's social and political unrest.
Despite facing significant adversity, including being labeled a degenerate artist by the Nazi regime and facing professional and personal setbacks, Dix's legacy as a painter and printmaker endures. His works are not only historical documents but also profound reflections on humanity, war, and society, resonating with collectors and art experts alike.
For enthusiasts of culture, art, and history, Dix's oeuvre offers an unflinching look into the human condition under the strain of societal and political upheaval. His contributions to painting and printmaking continue to be celebrated in museums and galleries worldwide, underscoring the enduring relevance of his work.
For those interested in exploring the profound depth and historical significance of Otto Dix's work, signing up for updates on new product sales and auction events related to his art can provide invaluable insights. This subscription is a gateway to staying informed about opportunities to engage with the tangible pieces of Dix's enduring legacy.
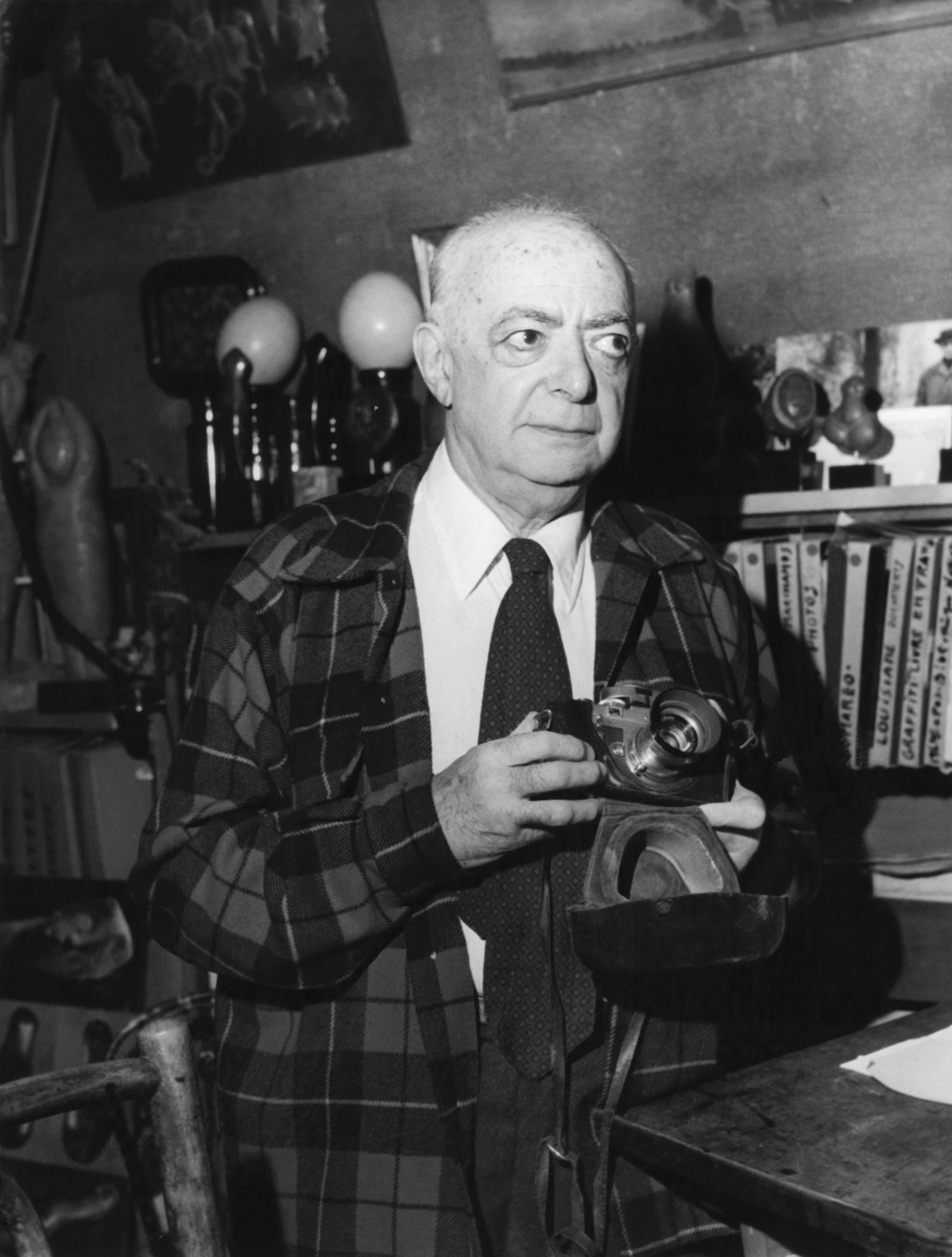

Brassaï, whose real name was Gyula Halász, was a Hungarian-French artist and photographer best known for his work documenting the streets of Paris during the 1920s and 1930s. He was one of the key figures of the Surrealist movement and his work continues to influence photographers and artists to this day.
Brassaï moved to Paris in the 1920s to pursue a career in art. He initially worked as a journalist and began taking photographs to accompany his articles. However, it was his nocturnal photographs of the city that would bring him international fame.
Brassaï's photographs of the streets of Paris at night captured the city's seedier side, including its prostitutes, bars, and cabarets. His work is known for its use of dramatic lighting and strong contrast, which helped to create a moody, evocative atmosphere.
In addition to his photography, Brassaï was also a talented painter and sculptor. He was a close friend of many of the leading artists and writers of the time, including Pablo Picasso, Salvador Dalí, and Henry Miller.
Brassaï's work has been exhibited in major museums and galleries around the world, and his photographs have been published in numerous books and magazines. He was one of the most influential photographers of the 20th century, and his legacy continues to inspire artists and photographers today.