крик

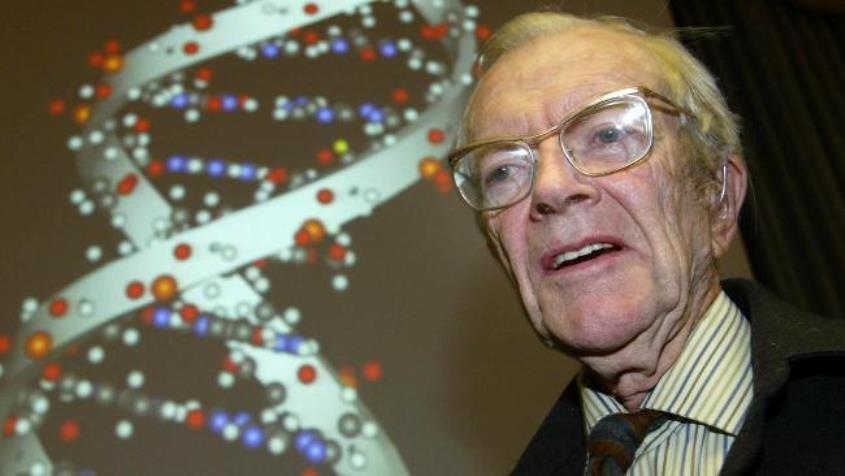
Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.



Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.
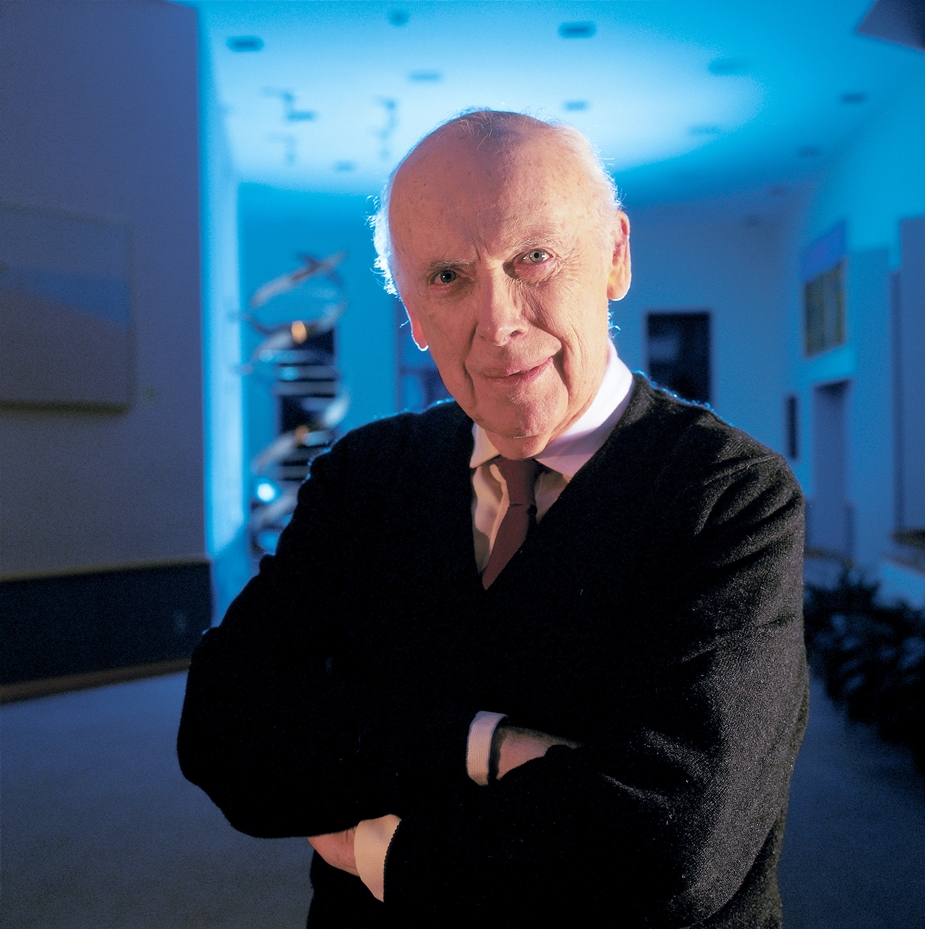


James Dewey Watson was an American geneticist and biophysicist who won the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
At the age of 15, Watson enrolled at the University of Chicago, then attended Indiana University, earning advanced degrees. After working at the University of Copenhagen, where he first decided to investigate DNA, he conducted research at the Cavendish Laboratory (1951-53). There, Watson learned the techniques of X-ray diffraction and worked with Francis Crick on the problem of DNA structure.
Their joint discovery was a key factor in allowing Watson and Crick to formulate the molecular model of DNA, a double helix, similar to a spiral staircase. It played a crucial role in discovering the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, the substance underlying heredity. For this achievement, he was awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, along with Francis Crick and Maurice Wilkins.
James Watson subsequently taught at Harvard University (1955-76), where he served as professor of biology. He conducted research on the role of nucleic acids in protein synthesis. In 1965, he published The Molecular Biology of the Gene, which became one of the modern biology textbooks. From 1988 to 1992, Watson directed the Human Genome Project at the National Institutes of Health. James Dewey Watson is an honorary member of numerous universities and academies around the world, he has received dozens of honors and awards, and he has written numerous books.

Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


James Dewey Watson was an American geneticist and biophysicist who won the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
At the age of 15, Watson enrolled at the University of Chicago, then attended Indiana University, earning advanced degrees. After working at the University of Copenhagen, where he first decided to investigate DNA, he conducted research at the Cavendish Laboratory (1951-53). There, Watson learned the techniques of X-ray diffraction and worked with Francis Crick on the problem of DNA structure.
Their joint discovery was a key factor in allowing Watson and Crick to formulate the molecular model of DNA, a double helix, similar to a spiral staircase. It played a crucial role in discovering the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, the substance underlying heredity. For this achievement, he was awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, along with Francis Crick and Maurice Wilkins.
James Watson subsequently taught at Harvard University (1955-76), where he served as professor of biology. He conducted research on the role of nucleic acids in protein synthesis. In 1965, he published The Molecular Biology of the Gene, which became one of the modern biology textbooks. From 1988 to 1992, Watson directed the Human Genome Project at the National Institutes of Health. James Dewey Watson is an honorary member of numerous universities and academies around the world, he has received dozens of honors and awards, and he has written numerous books.

Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


James Dewey Watson was an American geneticist and biophysicist who won the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
At the age of 15, Watson enrolled at the University of Chicago, then attended Indiana University, earning advanced degrees. After working at the University of Copenhagen, where he first decided to investigate DNA, he conducted research at the Cavendish Laboratory (1951-53). There, Watson learned the techniques of X-ray diffraction and worked with Francis Crick on the problem of DNA structure.
Their joint discovery was a key factor in allowing Watson and Crick to formulate the molecular model of DNA, a double helix, similar to a spiral staircase. It played a crucial role in discovering the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, the substance underlying heredity. For this achievement, he was awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, along with Francis Crick and Maurice Wilkins.
James Watson subsequently taught at Harvard University (1955-76), where he served as professor of biology. He conducted research on the role of nucleic acids in protein synthesis. In 1965, he published The Molecular Biology of the Gene, which became one of the modern biology textbooks. From 1988 to 1992, Watson directed the Human Genome Project at the National Institutes of Health. James Dewey Watson is an honorary member of numerous universities and academies around the world, he has received dozens of honors and awards, and he has written numerous books.

Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


James Dewey Watson was an American geneticist and biophysicist who won the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
At the age of 15, Watson enrolled at the University of Chicago, then attended Indiana University, earning advanced degrees. After working at the University of Copenhagen, where he first decided to investigate DNA, he conducted research at the Cavendish Laboratory (1951-53). There, Watson learned the techniques of X-ray diffraction and worked with Francis Crick on the problem of DNA structure.
Their joint discovery was a key factor in allowing Watson and Crick to formulate the molecular model of DNA, a double helix, similar to a spiral staircase. It played a crucial role in discovering the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, the substance underlying heredity. For this achievement, he was awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, along with Francis Crick and Maurice Wilkins.
James Watson subsequently taught at Harvard University (1955-76), where he served as professor of biology. He conducted research on the role of nucleic acids in protein synthesis. In 1965, he published The Molecular Biology of the Gene, which became one of the modern biology textbooks. From 1988 to 1992, Watson directed the Human Genome Project at the National Institutes of Health. James Dewey Watson is an honorary member of numerous universities and academies around the world, he has received dozens of honors and awards, and he has written numerous books.

Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


James Dewey Watson was an American geneticist and biophysicist who won the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
At the age of 15, Watson enrolled at the University of Chicago, then attended Indiana University, earning advanced degrees. After working at the University of Copenhagen, where he first decided to investigate DNA, he conducted research at the Cavendish Laboratory (1951-53). There, Watson learned the techniques of X-ray diffraction and worked with Francis Crick on the problem of DNA structure.
Their joint discovery was a key factor in allowing Watson and Crick to formulate the molecular model of DNA, a double helix, similar to a spiral staircase. It played a crucial role in discovering the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, the substance underlying heredity. For this achievement, he was awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, along with Francis Crick and Maurice Wilkins.
James Watson subsequently taught at Harvard University (1955-76), where he served as professor of biology. He conducted research on the role of nucleic acids in protein synthesis. In 1965, he published The Molecular Biology of the Gene, which became one of the modern biology textbooks. From 1988 to 1992, Watson directed the Human Genome Project at the National Institutes of Health. James Dewey Watson is an honorary member of numerous universities and academies around the world, he has received dozens of honors and awards, and he has written numerous books.

Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.

Norbert Kricke is a German sculptor.
He studied at the Higher School of Art in Berlin and from 1947 began creating abstract sculptures using wire, steel, glass and concrete. Kricke is also known as an innovator of the use of running water in art.
Norbert Kricke was one of the most important artists in the group L'Art Informel and was actively engaged with members of the ZERO and Nouveau Réalisme movements.

Norbert Kricke is a German sculptor.
He studied at the Higher School of Art in Berlin and from 1947 began creating abstract sculptures using wire, steel, glass and concrete. Kricke is also known as an innovator of the use of running water in art.
Norbert Kricke was one of the most important artists in the group L'Art Informel and was actively engaged with members of the ZERO and Nouveau Réalisme movements.

Norbert Kricke is a German sculptor.
He studied at the Higher School of Art in Berlin and from 1947 began creating abstract sculptures using wire, steel, glass and concrete. Kricke is also known as an innovator of the use of running water in art.
Norbert Kricke was one of the most important artists in the group L'Art Informel and was actively engaged with members of the ZERO and Nouveau Réalisme movements.

Norbert Kricke is a German sculptor.
He studied at the Higher School of Art in Berlin and from 1947 began creating abstract sculptures using wire, steel, glass and concrete. Kricke is also known as an innovator of the use of running water in art.
Norbert Kricke was one of the most important artists in the group L'Art Informel and was actively engaged with members of the ZERO and Nouveau Réalisme movements.

Norbert Kricke is a German sculptor.
He studied at the Higher School of Art in Berlin and from 1947 began creating abstract sculptures using wire, steel, glass and concrete. Kricke is also known as an innovator of the use of running water in art.
Norbert Kricke was one of the most important artists in the group L'Art Informel and was actively engaged with members of the ZERO and Nouveau Réalisme movements.

Norbert Kricke is a German sculptor.
He studied at the Higher School of Art in Berlin and from 1947 began creating abstract sculptures using wire, steel, glass and concrete. Kricke is also known as an innovator of the use of running water in art.
Norbert Kricke was one of the most important artists in the group L'Art Informel and was actively engaged with members of the ZERO and Nouveau Réalisme movements.

Norbert Kricke is a German sculptor.
He studied at the Higher School of Art in Berlin and from 1947 began creating abstract sculptures using wire, steel, glass and concrete. Kricke is also known as an innovator of the use of running water in art.
Norbert Kricke was one of the most important artists in the group L'Art Informel and was actively engaged with members of the ZERO and Nouveau Réalisme movements.

Norbert Kricke is a German sculptor.
He studied at the Higher School of Art in Berlin and from 1947 began creating abstract sculptures using wire, steel, glass and concrete. Kricke is also known as an innovator of the use of running water in art.
Norbert Kricke was one of the most important artists in the group L'Art Informel and was actively engaged with members of the ZERO and Nouveau Réalisme movements.