armes japonaise
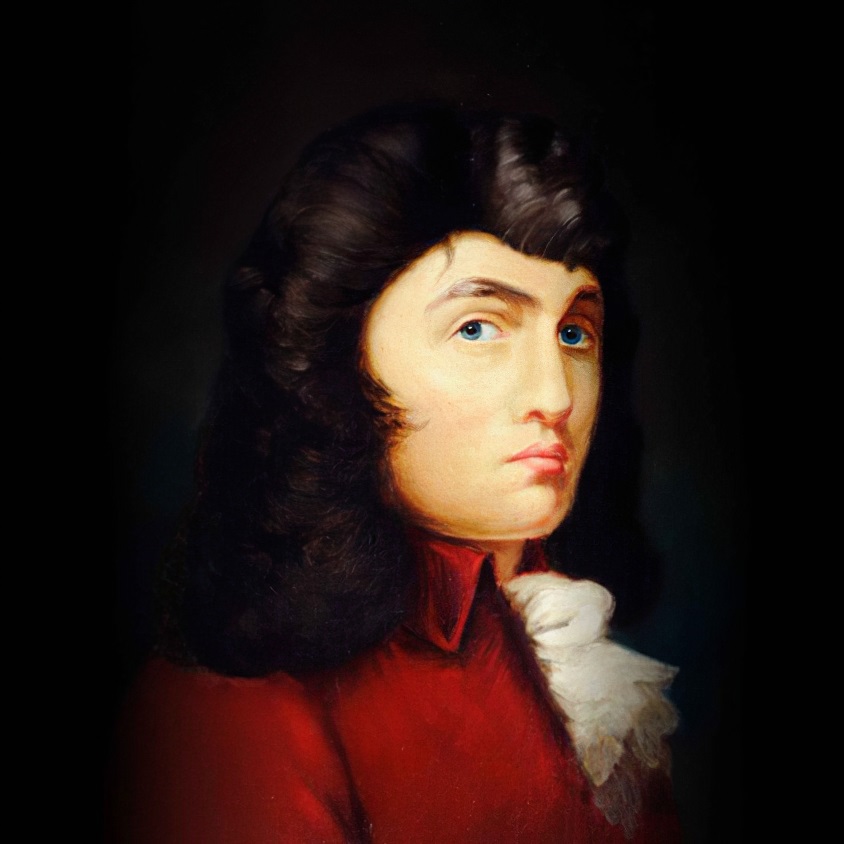

Thomas Chippendale was a cabinet-maker in London, designing furniture in the mid-Georgian, English Rococo, and Neoclassical styles. In 1754 he published a book of his designs in a trade catalogue titled The Gentleman and Cabinet Maker's Director — the most important collection of furniture designs published in England to that point which created a mass market for furniture—upon which success he became renowned. According to the Victoria and Albert Museum, «so influential were his designs, in Britain and throughout Europe and America, that "Chippendale" became a shorthand description for any furniture similar to his Director designs».
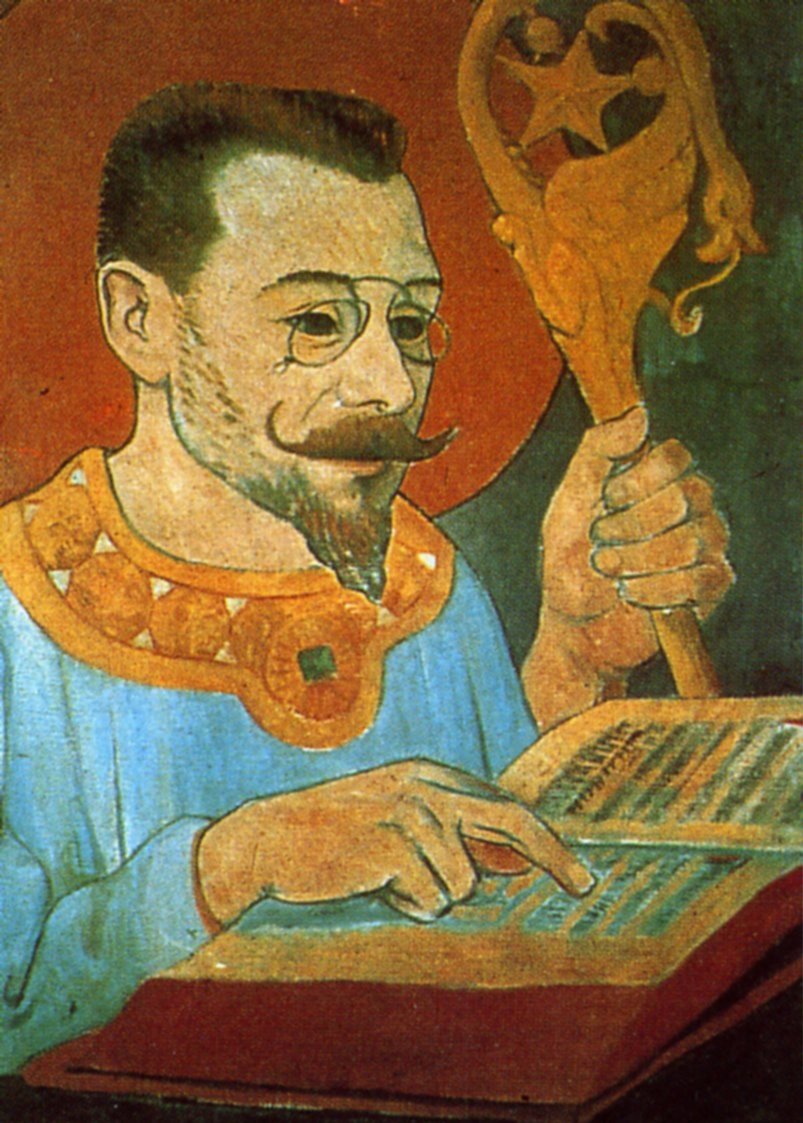



Paul-Élie Ranson, a French painter and writer, emerged as a prominent figure in the late 19th century art scene. Born in Limoges, he was raised by his grandparents and father after his mother's demise during childbirth. Ranson's early artistic inclinations were nurtured with drawing lessons from his grandfather. His educational journey in the arts began at the École des Beaux-Arts Appliqués à l'Industrie and later continued at the Académie Julian in Paris.
Ranson was a pivotal member of "Les Nabis," a group instrumental in transitioning from Impressionism to modern art. Along with notable contemporaries like Paul Sérusier, Pierre Bonnard, and Maurice Denis, he helped establish an art movement that blended elements of Symbolism, Art Nouveau, and Japanese prints. Ranson's role extended beyond painting; he was actively involved in the Symbolist performances at the Théâtre d'Art and directed a notable performance of "Ubu Roi" by Alfred Jarry.
Ranson's artistic oeuvre is marked by a fascination with Theosophy, magic, and occultism, themes that increasingly influenced his work. His paintings often delved into mythology, witchcraft, and anti-clerical subjects. Some of his notable works include "Christ and Buddha" (1880), "Witches Around the Fire" (1891), and "The Blue Room" (circa 1900). These works exemplify his unique blend of thematic and stylistic elements, setting him apart from his contemporaries.
Tragically, Ranson's life was cut short by typhoid fever in 1909. However, his legacy continued through the Académie Ranson, founded by his friends in Les Nabis. This institution, managed initially by Ranson and later by his wife Marie, remained active until 1955, perpetuating his influence on future generations of artists.
For art collectors and experts, Ranson's work offers a unique window into the transitionary period of late 19th-century art, showcasing the interplay of traditional and emerging styles. His contributions to the Symbolist and Nabi movements are particularly noteworthy.
To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Paul-Élie Ranson, sign up for our updates. This subscription service is tailored to keep art aficionados informed about the latest developments and opportunities related to Ranson's art.