calcul






Carlo Scarpa was an Italian architect, influenced by the materials, landscape and the history of Venetian culture, and by Japan. Scarpa translated his interests in history, regionalism, invention, and the techniques of the artist and craftsman into ingenious glass and furniture design.


Carlo Scarpa was an Italian architect, influenced by the materials, landscape and the history of Venetian culture, and by Japan. Scarpa translated his interests in history, regionalism, invention, and the techniques of the artist and craftsman into ingenious glass and furniture design.
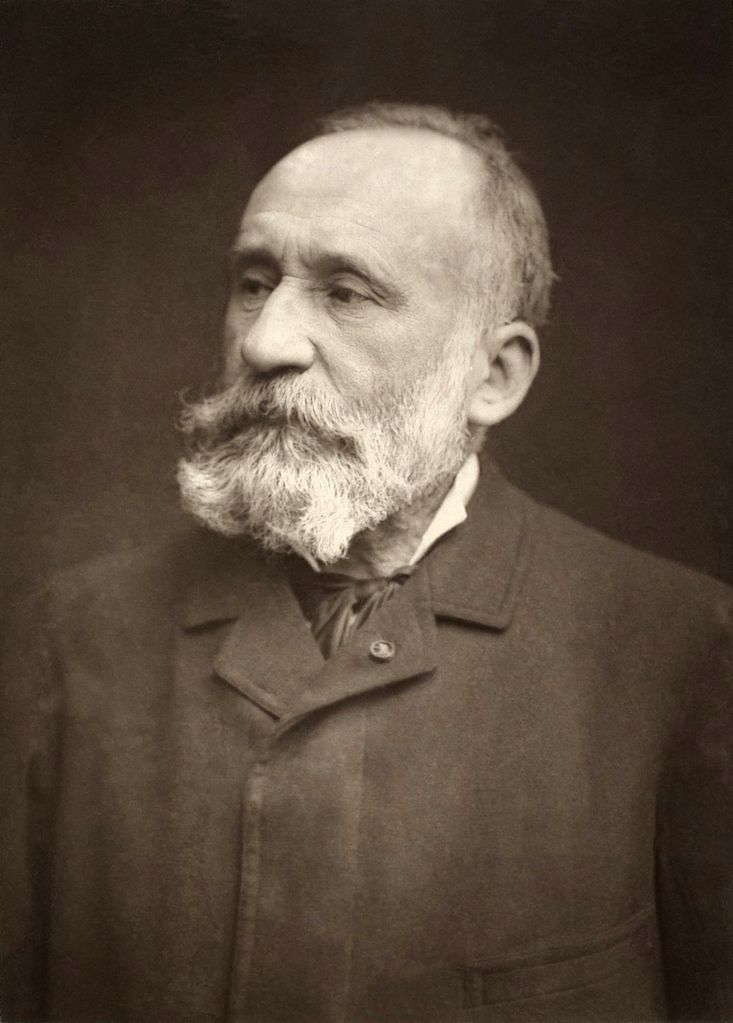



Pierre Cécile Puvis de Chavannes, a prominent French painter, was known as "the painter for France." His influential mural paintings showcased a classicizing style, often referencing visions of Hellenistic Greece.
Puvis received numerous commissions for public and private institutions across France, with significant works in Amiens, Marseille, Lyon, Poitiers, and Paris. His success as a 'painter for France' stemmed from his ability to appeal to various ideologies of the time. In addition to murals, Puvis created easel paintings, some of which can be found in galleries worldwide. Despite his significance, he was not fully appreciated during his lifetime, and his work remains a subject of ongoing art criticism.
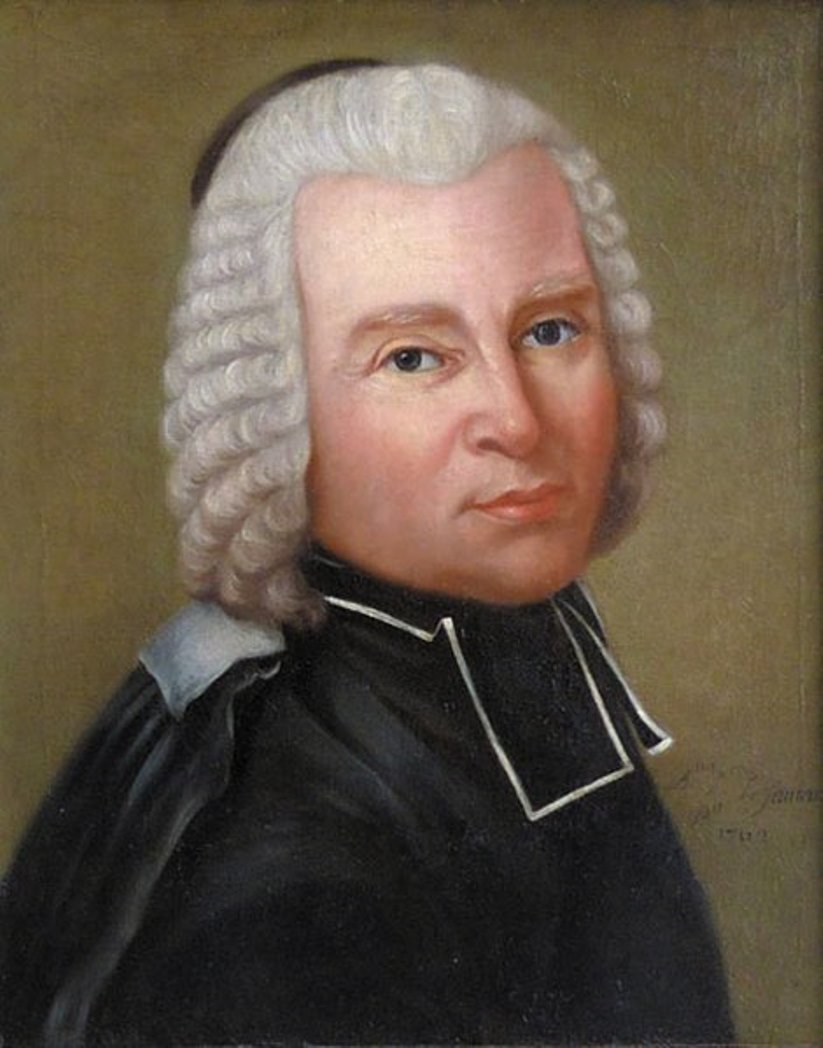


Nicolas-Louis De la Caille was a French astronomer, abbot and educator.
He studied philosophy and theology, became an abbot, but the craving for science overpowered everything, and he studied astronomy on his own. In 1736, la Caille received a place at the Paris Observatory, in 1739 was appointed professor of mathematics at Mazarini-College in Paris and built his own observatory, where he conducted astronomical observations. In 1741 Lacaille was admitted to the Académie des Sciences.
La Caille was an outstanding astronomer: he observed more than 10,000 stars in the Southern Hemisphere and named 14 of the 88 constellations. In 1752, he made an astronomical expedition to the Cape of Good Hope, where he built an observatory and conducted a huge series of observations, including the discovery and cataloging of 42 nebulae. These studies led to la Caille being called "the father of southern astronomy," and his observations from South Africa of the Moon, Venus, and Mars, combined with similar observations already made in the Northern Hemisphere, led to the calculation of more accurate values for the distances to these bodies.
On his return to Paris two years later, in 1754, he resumed his post and taught at the school of Mazarin, continuing his work at the observatory of the College of Mazarini. Among his pupils was the great chemist Antoine Lavoisier. La Caille was a foreign honorary member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences and a member of the Royal Society of London. His Coelum Australe Stelliferum ("Star Catalog of the Southern Sky") was published in 1763.
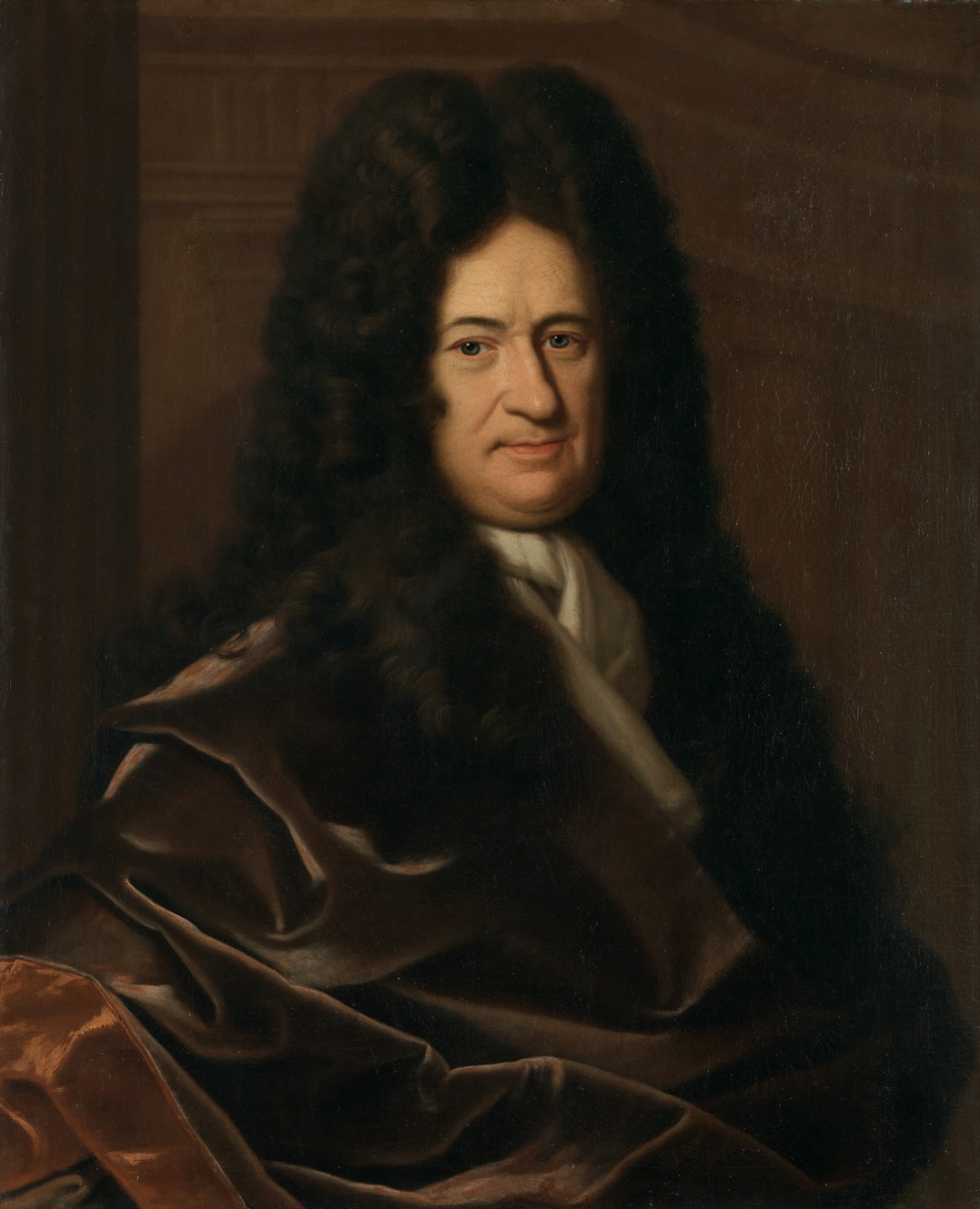


Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was a German philosopher and a prominent polymath in many fields of science.
Leibniz was a universal genius; he showed his talents in logic, mathematics, mechanics, physics, law, history, diplomacy, and linguistics, and in each of the disciplines he has serious scientific achievements. As a philosopher, he was a leading exponent of 17th-century rationalism and idealism.
Leibniz was a tireless worker and the greatest scholar of his time. In the fate of Leibniz, among other things, there is one interesting page: in 1697, he accidentally met the Russian Tsar Peter I during his trip to Europe. Their further meetings led to the realization of several grandiose projects in Russia, one of which was the establishment of the Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg.
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was also the founder and first president of the Berlin Academy of Sciences and a member of the Royal Society of London.
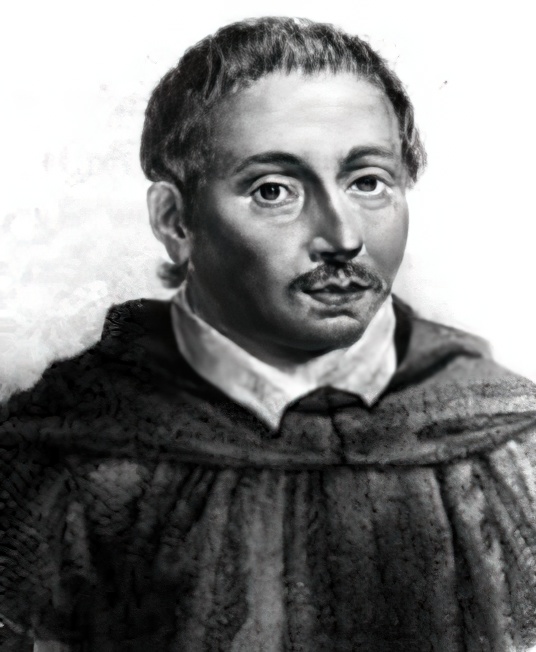


Bonaventura Francesco Cavalieri (Latin: Bonaventura Cavalerius) was an Italian mathematician and a Jesuate. He is known for his work on the problems of optics and motion, work on indivisibles, the precursors of infinitesimal calculus, and the introduction of logarithms to Italy. Cavalieri's principle in geometry partially anticipated integral calculus.


Vincenzo Renieri, born Giovanni Paolo, was an Italian priest, astronomer and mathematician.
Renieri was a member of the Olivetan Order and traveled throughout Italy. In 1633 in Siena, he met the already blind Galileo, who, appreciating his knowledge, instructed him to update his astronomical tables of the motion of the satellites of Jupiter, adding new ones. Rainieri later met the astronomer and scientist Vincenzo Viviani (1622-1703), with whom he worked for many years, continuing Galileo's observations of Jupiter's moons.
Renieri was also professor of mathematics at the University of Pisa and taught Greek there. In 1639 he published his work Tabulae Mediceae secundorum Mobilium Universales in Florence. One of the lunar craters is named after Renieri.


Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".
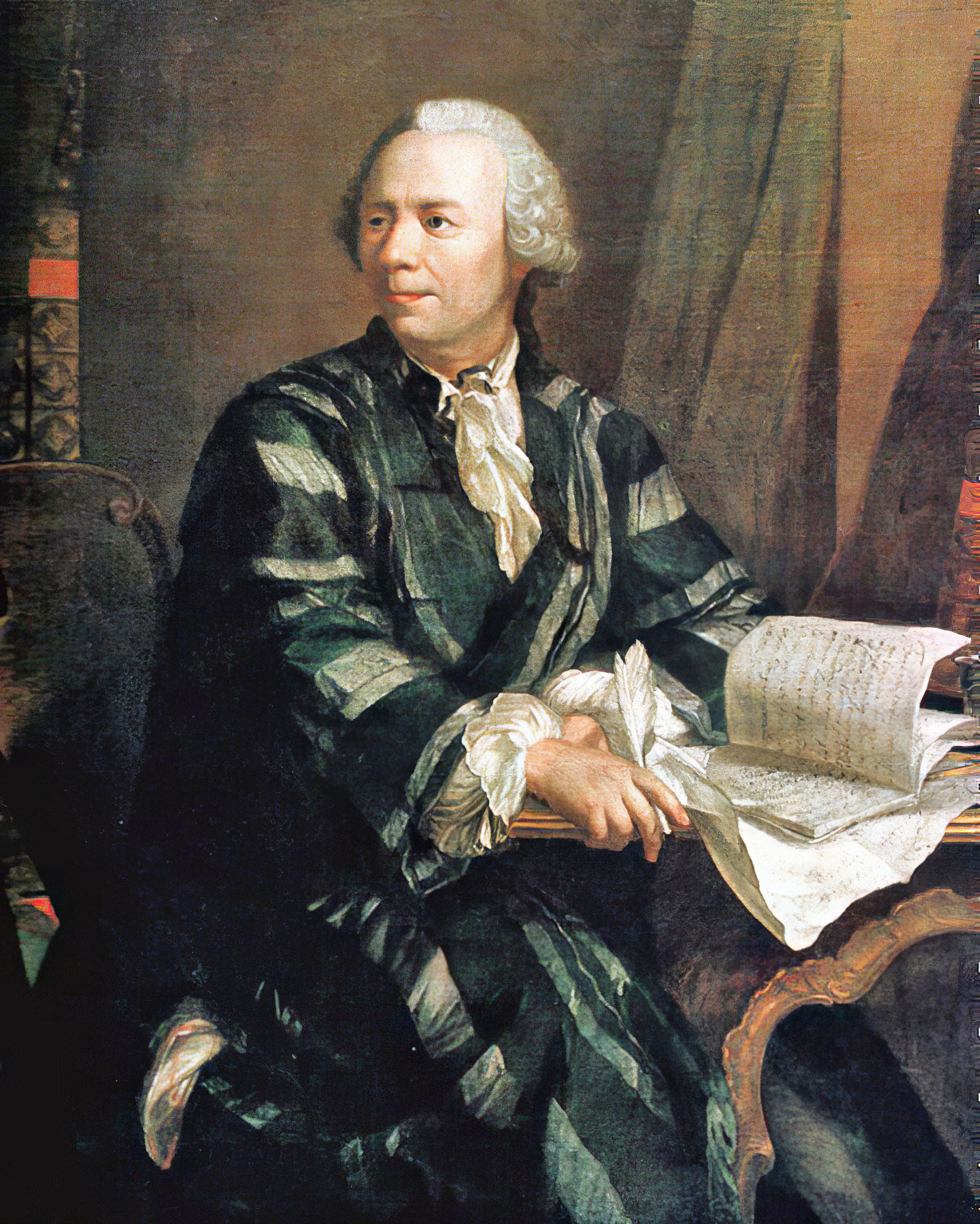


Leonhard Euler was the greatest mathematician of the 18th century and history in general.
Euler brilliantly graduated from the University of Basel and entered the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, then began to work at the Berlin Academy, and later to lead it. In 1766, the scientist received an invitation from the Russian Empress Catherine II and again came to St. Petersburg to continue his scientific work.
Here he published about 470 works in a wide variety of fields. One of them is a large-scale work "Mechanics" - an in-depth study of this science, including celestial mechanics. Euler by that time was practically blind, but continued to be actively engaged in science, in the records he was helped by his son Johann Albrecht and stenographers. Leonhard Euler made many fundamental discoveries that brought great benefit to mankind.
His massive contribution to the development of mathematics, mechanics, physics and astronomy cannot be overestimated, and his knowledge in the most diverse branches of science is admirable. During his lifetime, he published more than 850 works that contain in-depth studies of botany, chemistry, medicine, ancient languages, and music. Euler held membership in many academies of science around the world.


Leonhard Euler was the greatest mathematician of the 18th century and history in general.
Euler brilliantly graduated from the University of Basel and entered the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, then began to work at the Berlin Academy, and later to lead it. In 1766, the scientist received an invitation from the Russian Empress Catherine II and again came to St. Petersburg to continue his scientific work.
Here he published about 470 works in a wide variety of fields. One of them is a large-scale work "Mechanics" - an in-depth study of this science, including celestial mechanics. Euler by that time was practically blind, but continued to be actively engaged in science, in the records he was helped by his son Johann Albrecht and stenographers. Leonhard Euler made many fundamental discoveries that brought great benefit to mankind.
His massive contribution to the development of mathematics, mechanics, physics and astronomy cannot be overestimated, and his knowledge in the most diverse branches of science is admirable. During his lifetime, he published more than 850 works that contain in-depth studies of botany, chemistry, medicine, ancient languages, and music. Euler held membership in many academies of science around the world.


Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".