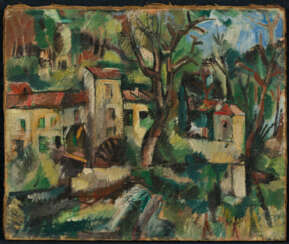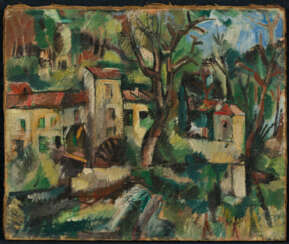cats<br />

Peter Brüning was an internationally renowned German modernist painter and sculptor. His works of the 1950s can be classified as Informel.


Vik Muniz is a Brazilian artist and photographer. Initially a sculptor, Muniz grew interested with the photographic representations of his work, eventually focusing completely on photography. Primarily working with unconventional materials such as tomato sauce, diamonds, magazine clippings, chocolate syrup, dust, dirt, etc., Muniz creates works of art, referencing old master's paintings and celebrity portraits, among other things, and then photographs them. His work has been met with both commercial success and critical acclaim, and has been exhibited worldwide. He is currently represented by Galeria Nara Roesler based in New York and Brazil.


Gerhard Richter is a German visual artist. Richter has produced abstract as well as photorealistic paintings, and also photographs and glass pieces. He is widely regarded as one of the most important contemporary German artists and several of his works have set record prices at auction.
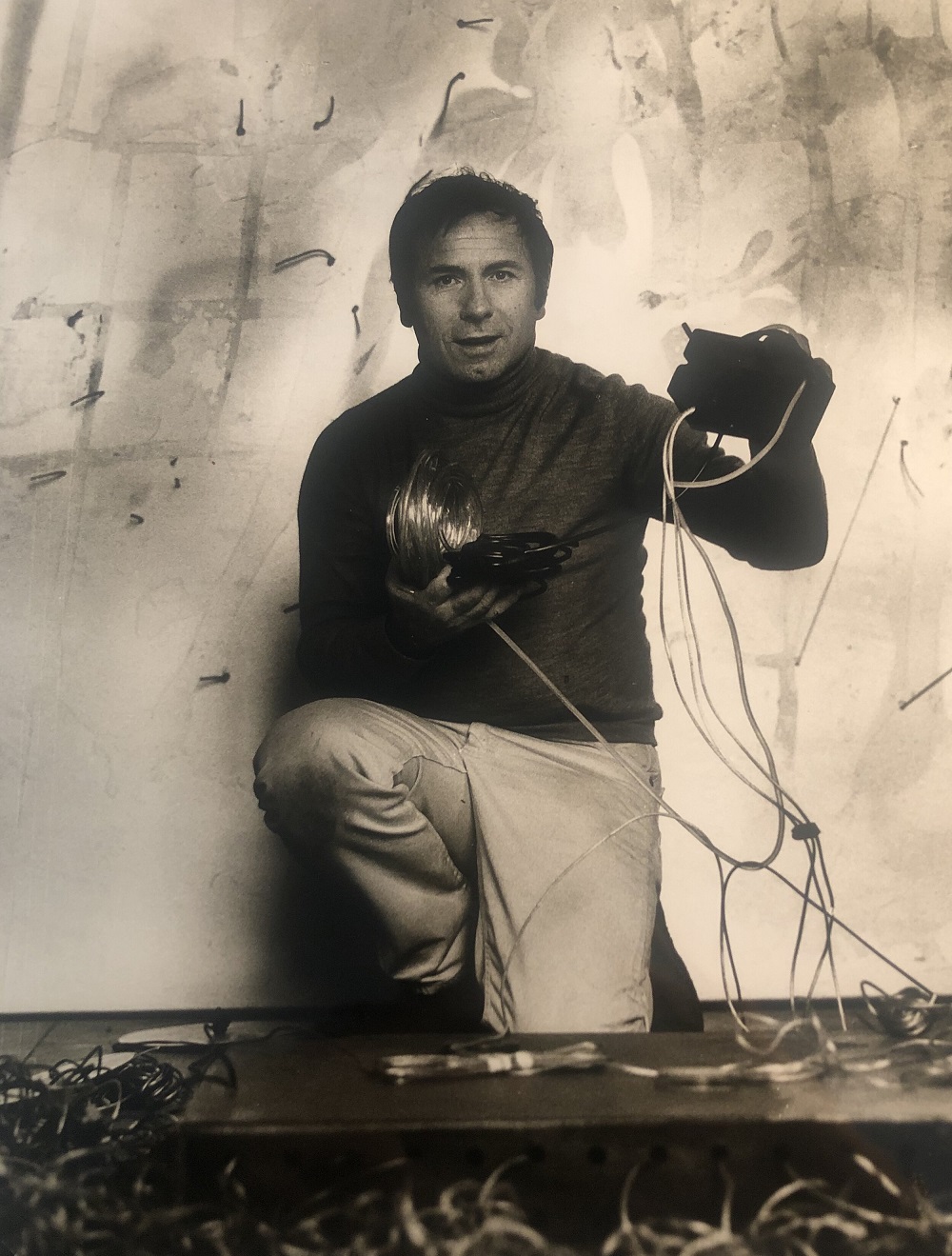


Gerhard Hoehme was a German expressionist painter.

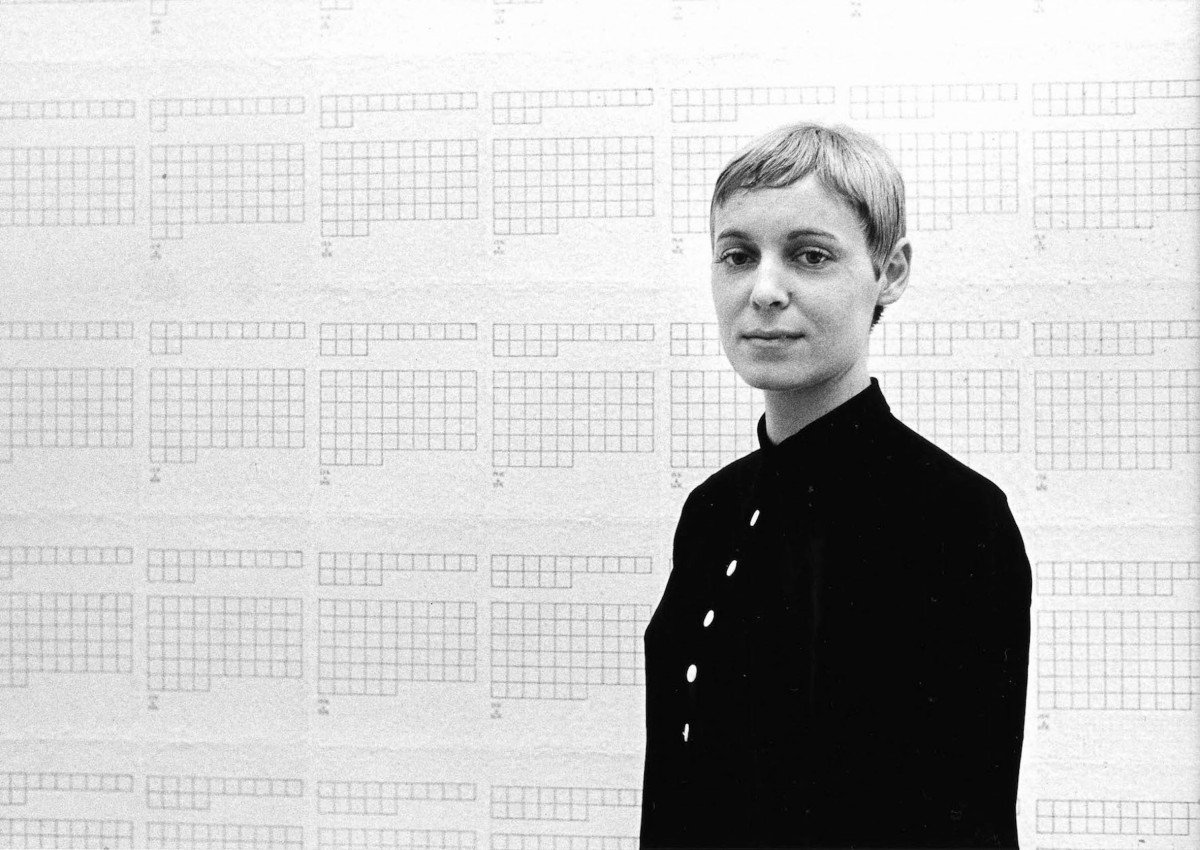
Hanne Darboven was a German conceptual artist known for her large-scale installations, drawings, and writings that explore the intersections of mathematics, language, and time.
Darboven studied at the Hochschule für Bildende Künste in Hamburg. In the 1960s, she became associated with the Conceptual Art movement, creating works that often involved systems of numerical and textual notation.
In the 1970s, Darboven began to produce her signature installations, which combined writing, drawing, and found objects to create immersive environments that explored complex systems of meaning and structure. One of her most famous works is "Kulturgeschichte 1880-1983", a monumental installation consisting of 1,590 framed sheets of paper, each containing a series of numbers, letters, and symbols that chart the course of modern history.
Throughout her career, Darboven continued to explore the relationship between language, numbers, and time, often drawing inspiration from her own life and experiences. She exhibited her work widely in Europe and the United States, and was the subject of numerous retrospectives and solo exhibitions.
Her legacy as a pioneering conceptual artist continues to be recognized and celebrated by the art world today.
.
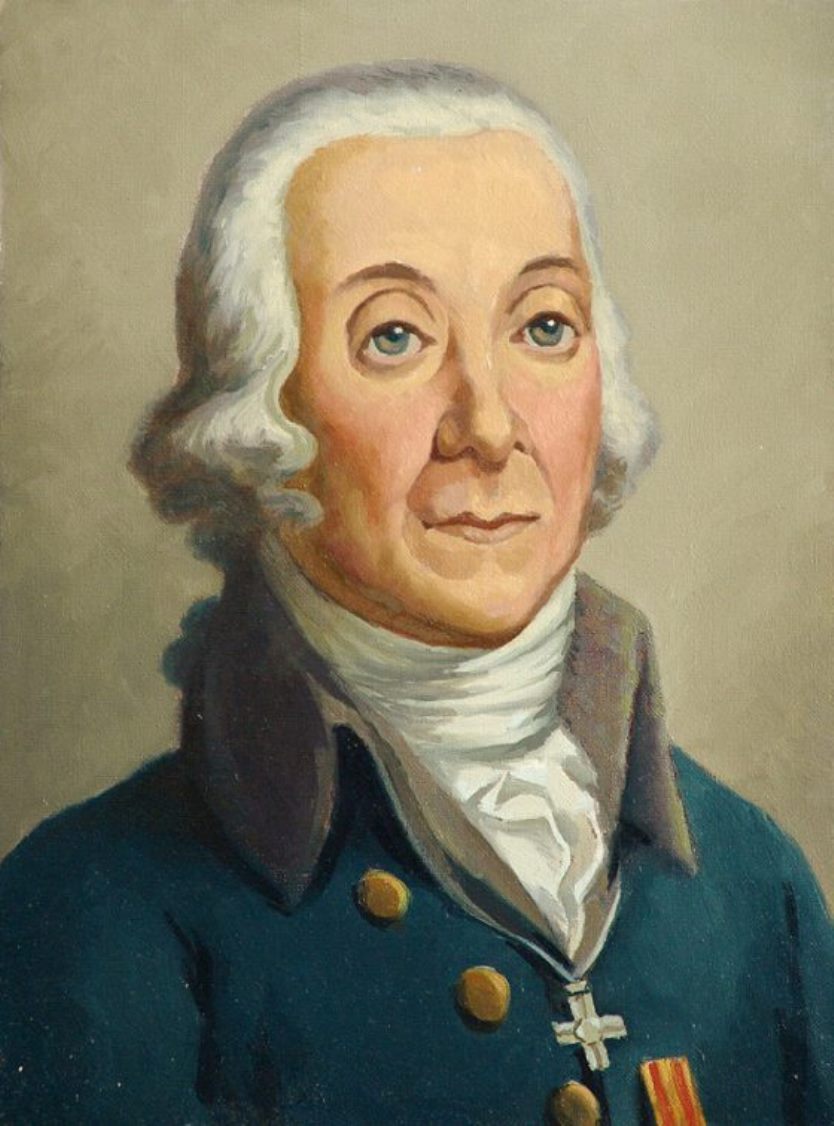


Peter Simon Pállas was a German and Russian scientist-encyclopedist, naturalist and traveler, who gave almost all his life to the service of Russia.
The breadth of his scientific interests made him a true encyclopedist, but he was particularly interested in natural sciences. By the age of 25, Pallas had already acquired European fame as a major scientist-naturalist. At the same time he received an invitation from the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, where he was offered a professorship. In 1767, Pallas arrived in St. Petersburg with his wife and soon led several important expeditions to Siberia and southern Russia. In his numerous ethnographic descriptions, the scientist was the first to report in detail on the Kalmyks, Tatars, Mordvins, Chuvashs, Nagaians, Tungus (Evenks), Votyaks (Udmurts), and Cheremis (Mari). In addition, he brought with him large natural-scientific collections. Later he traveled with scientific expeditions to Kamchatka, the Kuril Islands, Crimea and other previously unexplored lands.
In 1785 Catherine II attracted Pallas to the collection and comparative analysis of the languages of the peoples inhabiting America, Asia, Europe and Russia, and he compiled and published a comparative dictionary in two parts (1787-1789), in which more than 200 languages and dialects of the peoples of Asia and Europe were presented. In the last years of his life, among other things, Pallas was engaged in the preparation of a fundamental three-volume work on the fauna of Russia, Zoographia rosso-asiatica ("Russian-Asiatic Zoology"), in which more than 900 species of vertebrates, including 151 species of mammals, of which about 50 new species were introduced. This work was so extensive, and the descriptions of the animals were so thorough and detailed, that until the early 20th century the book remained the main source of knowledge about the fauna of Russia. In 1810. Peter Pallas went to Berlin to prepare illustrations for this work, but a year later the famous scientist died and was buried in Berlin.
A volcano in the Kuril Islands, a reef off New Guinea, and many animals and plants are named after Pallas.


Peter Simon Pállas was a German and Russian scientist-encyclopedist, naturalist and traveler, who gave almost all his life to the service of Russia.
The breadth of his scientific interests made him a true encyclopedist, but he was particularly interested in natural sciences. By the age of 25, Pallas had already acquired European fame as a major scientist-naturalist. At the same time he received an invitation from the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, where he was offered a professorship. In 1767, Pallas arrived in St. Petersburg with his wife and soon led several important expeditions to Siberia and southern Russia. In his numerous ethnographic descriptions, the scientist was the first to report in detail on the Kalmyks, Tatars, Mordvins, Chuvashs, Nagaians, Tungus (Evenks), Votyaks (Udmurts), and Cheremis (Mari). In addition, he brought with him large natural-scientific collections. Later he traveled with scientific expeditions to Kamchatka, the Kuril Islands, Crimea and other previously unexplored lands.
In 1785 Catherine II attracted Pallas to the collection and comparative analysis of the languages of the peoples inhabiting America, Asia, Europe and Russia, and he compiled and published a comparative dictionary in two parts (1787-1789), in which more than 200 languages and dialects of the peoples of Asia and Europe were presented. In the last years of his life, among other things, Pallas was engaged in the preparation of a fundamental three-volume work on the fauna of Russia, Zoographia rosso-asiatica ("Russian-Asiatic Zoology"), in which more than 900 species of vertebrates, including 151 species of mammals, of which about 50 new species were introduced. This work was so extensive, and the descriptions of the animals were so thorough and detailed, that until the early 20th century the book remained the main source of knowledge about the fauna of Russia. In 1810. Peter Pallas went to Berlin to prepare illustrations for this work, but a year later the famous scientist died and was buried in Berlin.
A volcano in the Kuril Islands, a reef off New Guinea, and many animals and plants are named after Pallas.

Peter Simon Pállas was a German and Russian scientist-encyclopedist, naturalist and traveler, who gave almost all his life to the service of Russia.
The breadth of his scientific interests made him a true encyclopedist, but he was particularly interested in natural sciences. By the age of 25, Pallas had already acquired European fame as a major scientist-naturalist. At the same time he received an invitation from the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, where he was offered a professorship. In 1767, Pallas arrived in St. Petersburg with his wife and soon led several important expeditions to Siberia and southern Russia. In his numerous ethnographic descriptions, the scientist was the first to report in detail on the Kalmyks, Tatars, Mordvins, Chuvashs, Nagaians, Tungus (Evenks), Votyaks (Udmurts), and Cheremis (Mari). In addition, he brought with him large natural-scientific collections. Later he traveled with scientific expeditions to Kamchatka, the Kuril Islands, Crimea and other previously unexplored lands.
In 1785 Catherine II attracted Pallas to the collection and comparative analysis of the languages of the peoples inhabiting America, Asia, Europe and Russia, and he compiled and published a comparative dictionary in two parts (1787-1789), in which more than 200 languages and dialects of the peoples of Asia and Europe were presented. In the last years of his life, among other things, Pallas was engaged in the preparation of a fundamental three-volume work on the fauna of Russia, Zoographia rosso-asiatica ("Russian-Asiatic Zoology"), in which more than 900 species of vertebrates, including 151 species of mammals, of which about 50 new species were introduced. This work was so extensive, and the descriptions of the animals were so thorough and detailed, that until the early 20th century the book remained the main source of knowledge about the fauna of Russia. In 1810. Peter Pallas went to Berlin to prepare illustrations for this work, but a year later the famous scientist died and was buried in Berlin.
A volcano in the Kuril Islands, a reef off New Guinea, and many animals and plants are named after Pallas.
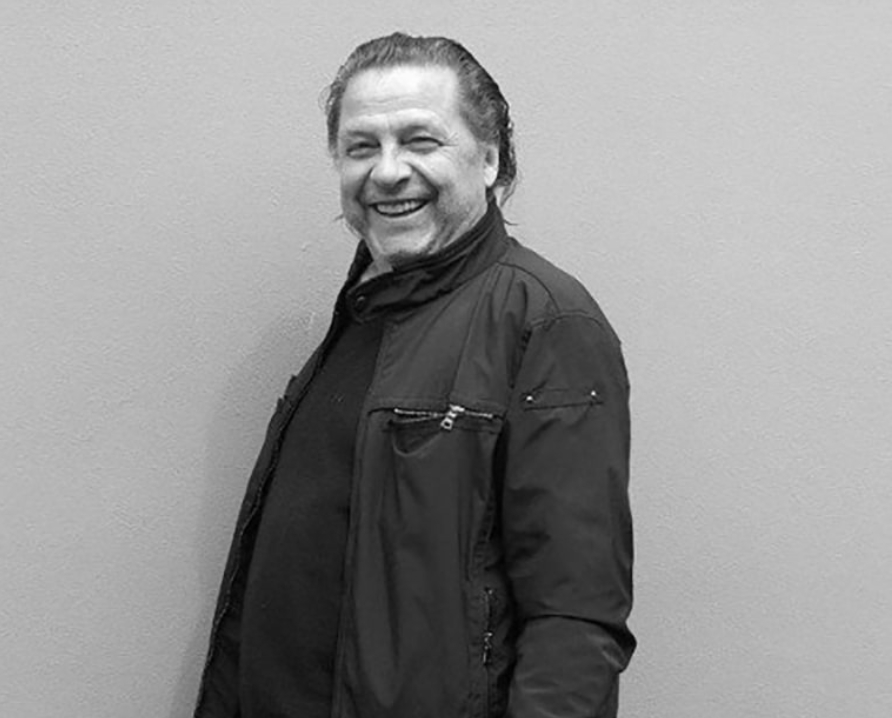


Georg Herold is a German artist. He works in sculpture, installation, painting, photography, and video art. He lives and works in Cologne, Germany.
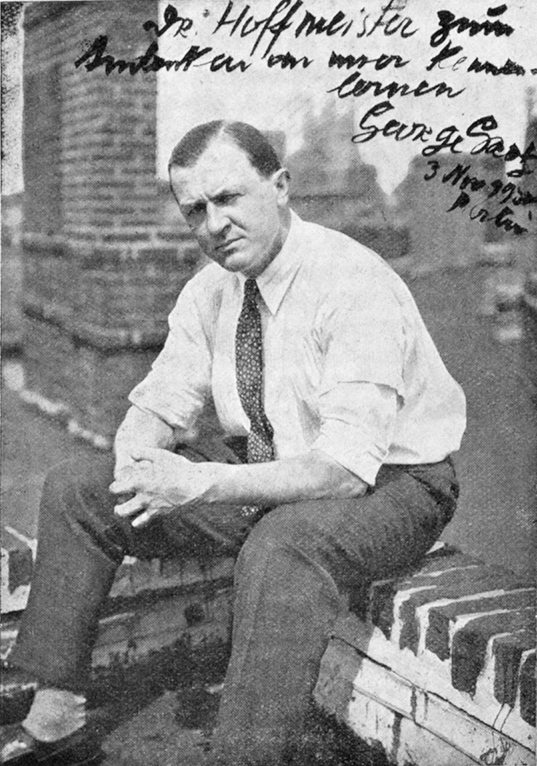


George Grosz was a twentieth-century German painter, graphic artist, and cartoonist. In his work one can find features of various styles of avant-garde art, including Dadaism, Expressionism, and Futurism.
George Grosz drew in every style in a sharp-grotesque and satirical spirit, ridiculing the vices of society. The erotic theme, which occupied a prominent place in Gross's work, was executed in the same spirit.
Grosz devoted more than 20 years to teaching at the Art Students League of New York, and was elected an honorary member of the American and Berlin Academies for his outstanding services to the arts.
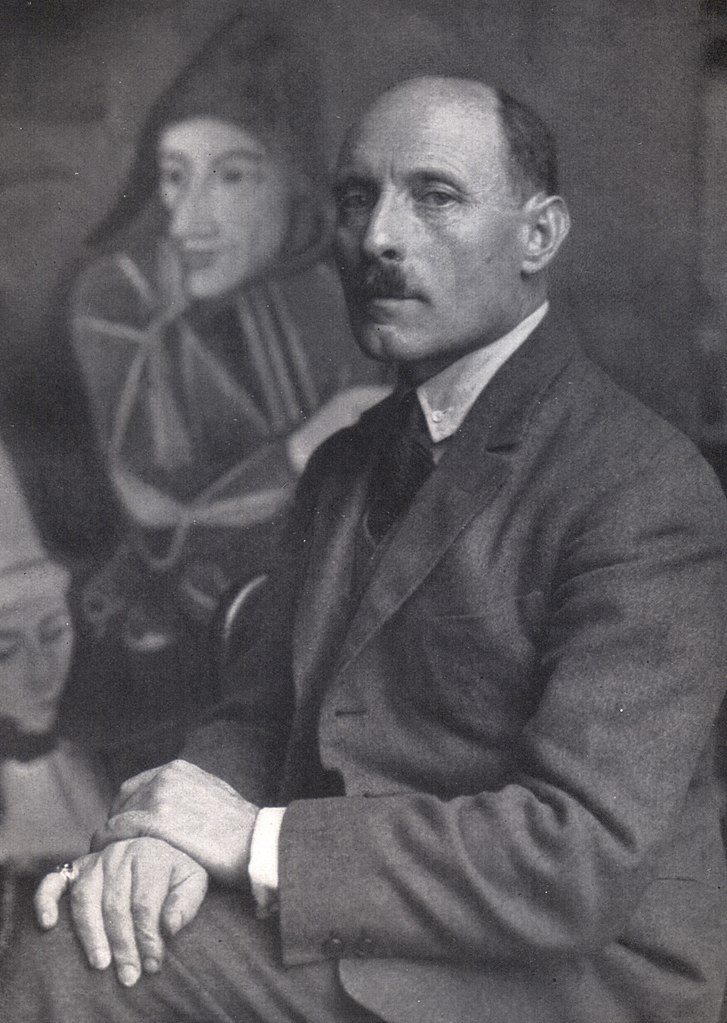


Karl Hofer was a German expressionist painter. He was director of the Berlin Academy of Fine Arts.
One of the most prominent painters of expressionism, he never was a member of one of the expressionist painting groups, like "Die Brücke", but was influenced by their painters. His work was among those considered degenerate art by the Nazis, but after World War II he regained recognition as one of the leading German painters.

.jpg)
Max Ernst was a pivotal figure in the 20th-century art world, whose work transcended the boundaries of nationality and genre to leave an indelible mark on culture, art, sculpture, and painting. Born in Germany on April 2, 1891, and later becoming a naturalized American and French citizen, Ernst's career was a testament to his relentless innovation and creativity. Known primarily as an artist and painter, Ernst was a founding member of the Dada movement in Cologne before becoming a major proponent of Surrealism in Paris. His early encounters with the works of Pablo Picasso, Vincent van Gogh, and Paul Gauguin at the Sonderbund exhibition in 1912 deeply influenced his artistic direction, infusing it with elements of Cubism and Expressionism. Despite his lack of formal artistic training, Ernst's experimentation with techniques such as collage and frottage showcased his unique ability to blend the absurd with the sublime, making him a central figure in the artistic avant-garde of his time.
Ernst's work is notable for its exploration of the unconscious, using dreamlike imagery and symbolic figures to critique societal norms and delve into the chaos of the human psyche. His experiences in World War I profoundly impacted his worldview, leading to a deep skepticism of Western culture and an enduring search for meaning through art. This is evident in works such as "Europe After the Rain II," which reflects the devastation of war and "The Fireside Angel," inspired by the political turmoil of the Spanish Civil War, showcasing his ability to address contemporary issues through a surreal lens.
Ernst's contributions to art are preserved in major museums and galleries worldwide, including the Tate in the United Kingdom and the Museum of Modern Art in New York. His sculptures, paintings, and collages continue to be celebrated for their innovative techniques and imaginative scope, marking him as a revolutionary figure in modern art. Among his most significant works are "Ubu Imperator," "The Elephant Celebes," and "The Virgin Spanking the Christ Child before Three Witnesses," each reflecting his mastery over a diversity of mediums and themes.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Max Ernst remains a symbol of artistic freedom and exploration. His ability to navigate through various artistic movements while maintaining a distinct, innovative voice is a testament to his enduring legacy in the art world. To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Max Ernst, signing up for updates is a valuable opportunity for those deeply invested in the nuances of modern and surreal art.
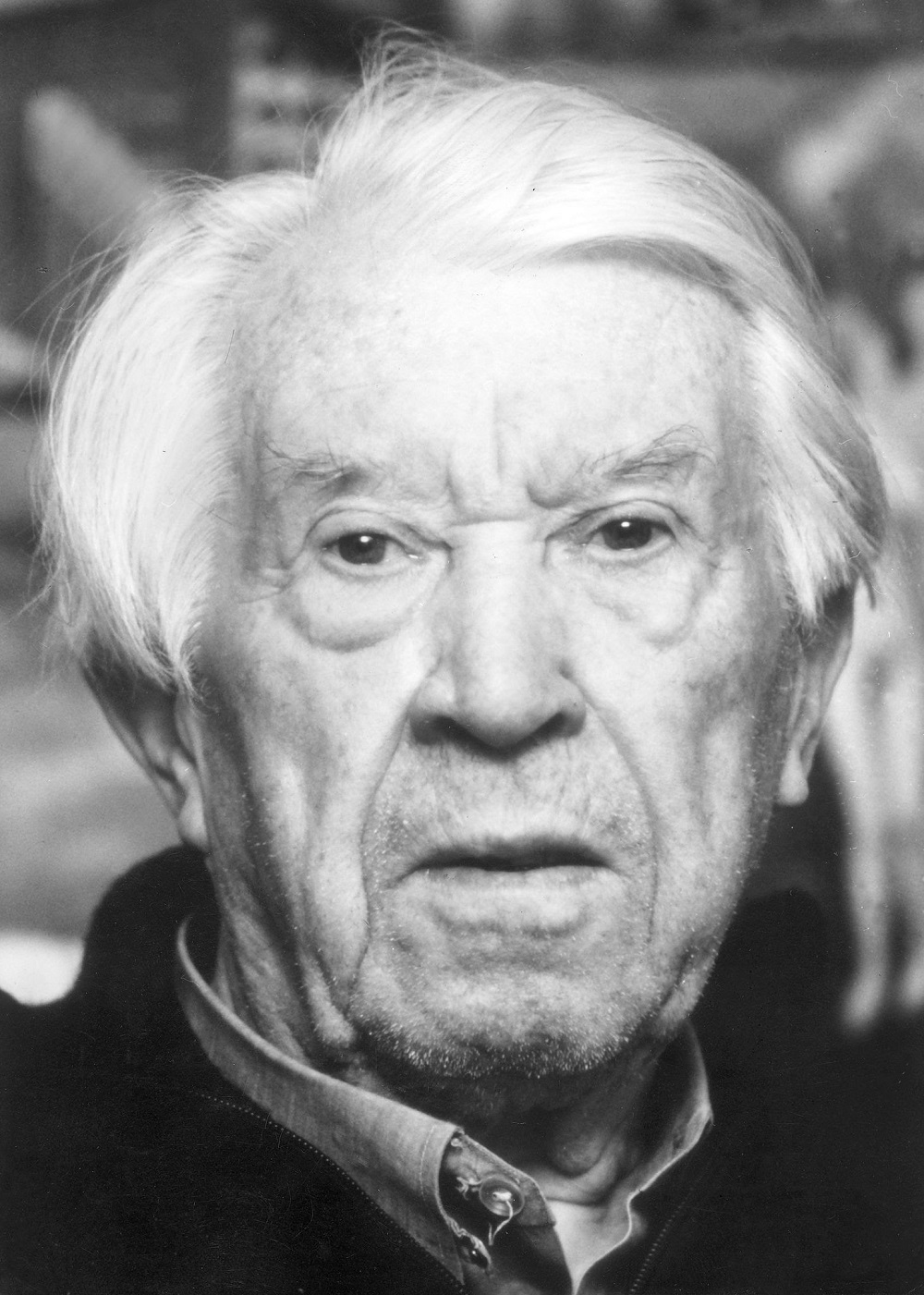


Franz Radziwill was a German artist of the twentieth century. He is known as a landscape painter, graphic artist and printmaker associated with the artistic movement of "new materiality".
Franz Radziwill created paintings that are characterized by careful elaboration and the use of glaze techniques borrowed from the Old Masters. He used elements of industrial buildings and modern technology, including ships and airplanes, in his landscapes. The results of his work can be categorized as magical realism.
In 1933 Radziwill became professor of painting at the Düsseldorf Academy of Art, but in 1935 the Nazis stripped him of this position, declaring his work degenerate art.
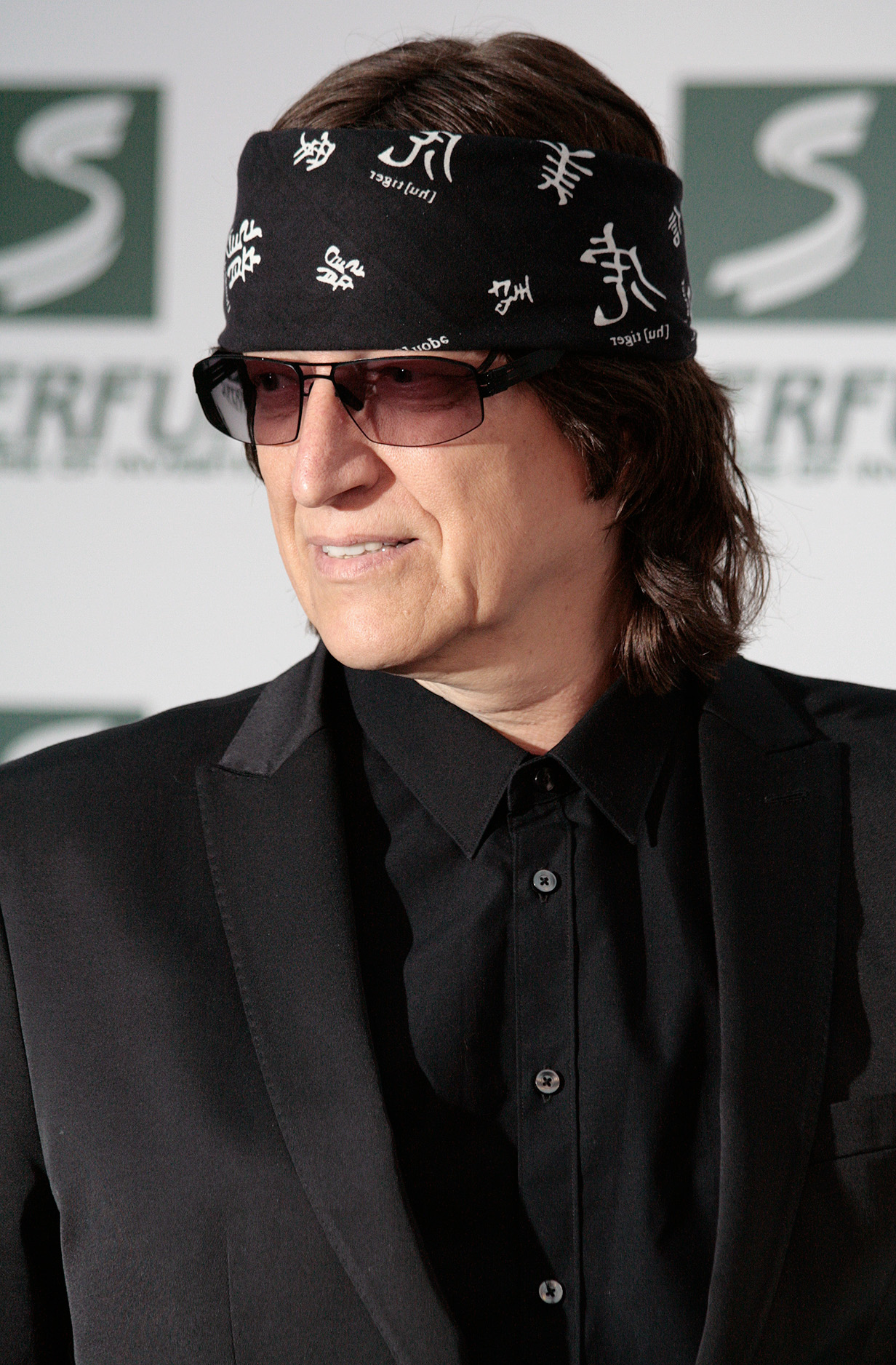


Gottfried Helnwein is an Austrian-Irish visual artist. He has worked as a painter, draftsman, photographer, muralist, sculptor, installation and performance artist, using a wide variety of techniques and media.
His work is concerned primarily with psychological and sociological anxiety, historical issues and political topics. His subject matter is the human condition. The metaphor for his art is dominated by the image of the child, particularly the wounded child, scarred physically and emotionally from within. His works often reference taboo and controversial issues from recent history, especially the Nazi rule and the horror of the Holocaust. As a result, his work is often considered provocative and controversial.
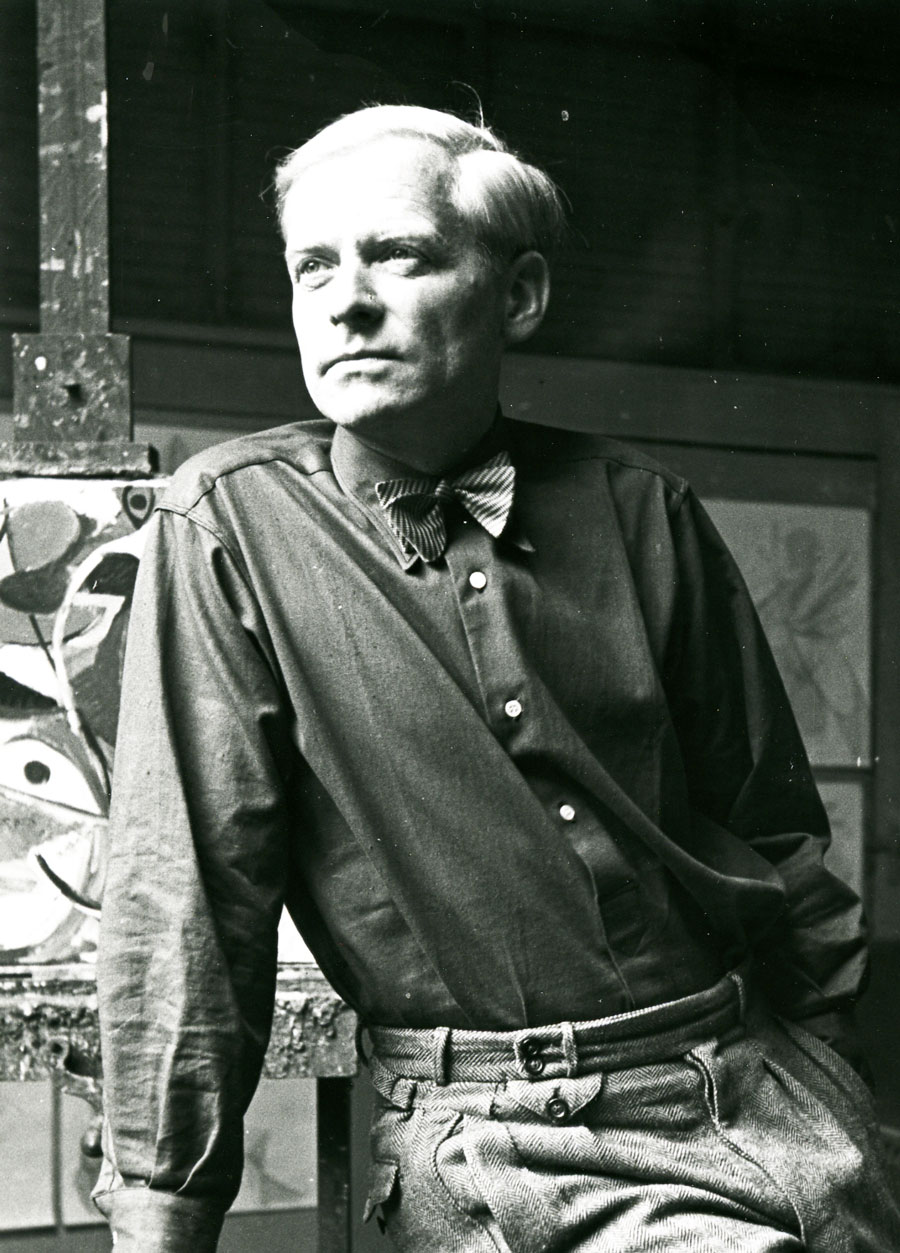


Ernst Wilhelm Nay was a German painter and graphic designer of classical modernism. He is considered one of the most important painters of German post-war art.
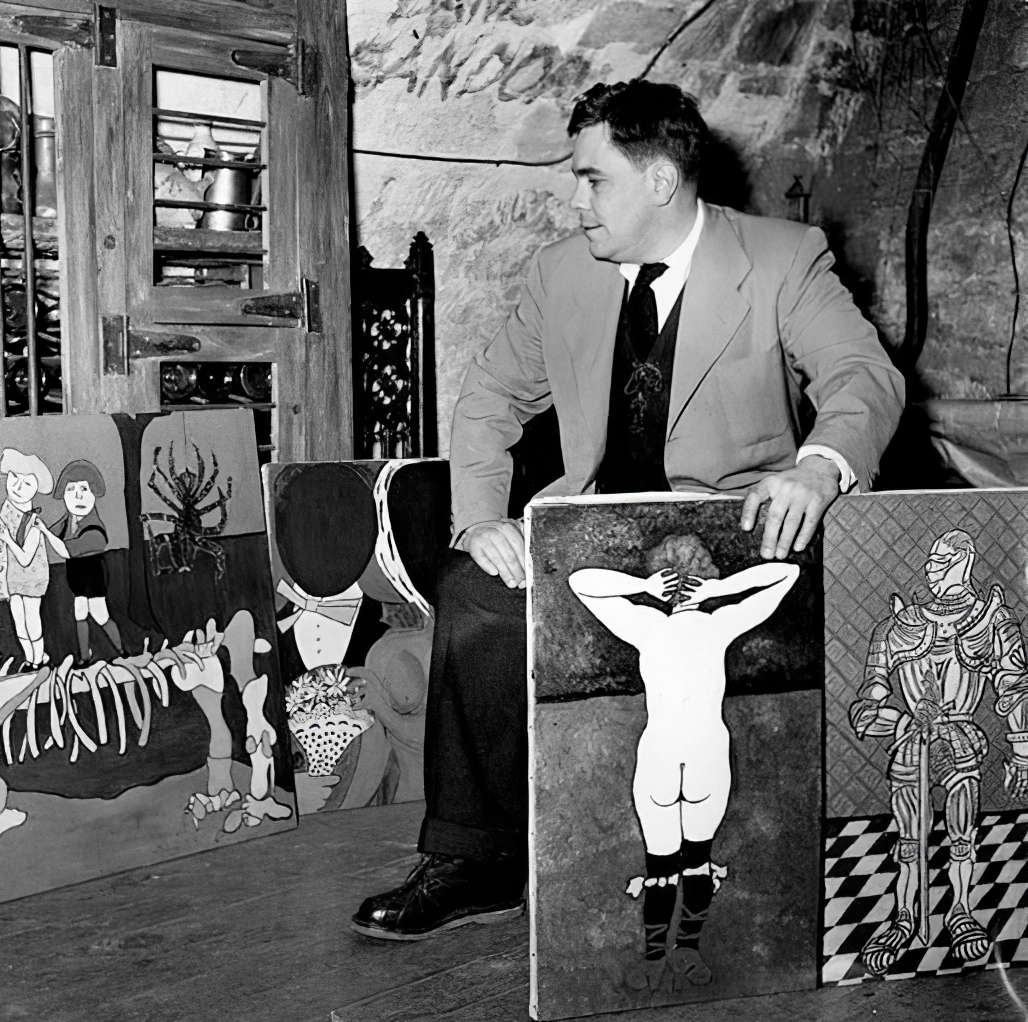


William Nelson Copley was an American painter, writer, gallerist, collector, patron, publisher and art entrepreneur. His works as an artist have been classified as late Surrealist and precursory to Pop Art.


Lovis Corinth was a German artist and writer whose mature work as a painter and printmaker realized a synthesis of impressionism and expressionism.
Corinth studied in Paris and Munich, joined the Berlin Secession group, later succeeding Max Liebermann as the group's president. His early work was naturalistic in approach. Corinth was initially antagonistic towards the expressionist movement, but after a stroke in 1911 his style loosened and took on many expressionistic qualities. His use of color became more vibrant, and he created portraits and landscapes of extraordinary vitality and power. Corinth's subject matter also included nudes and biblical scenes.


William Nelson Copley was an American painter, writer, gallerist, collector, patron, publisher and art entrepreneur. His works as an artist have been classified as late Surrealist and precursory to Pop Art.
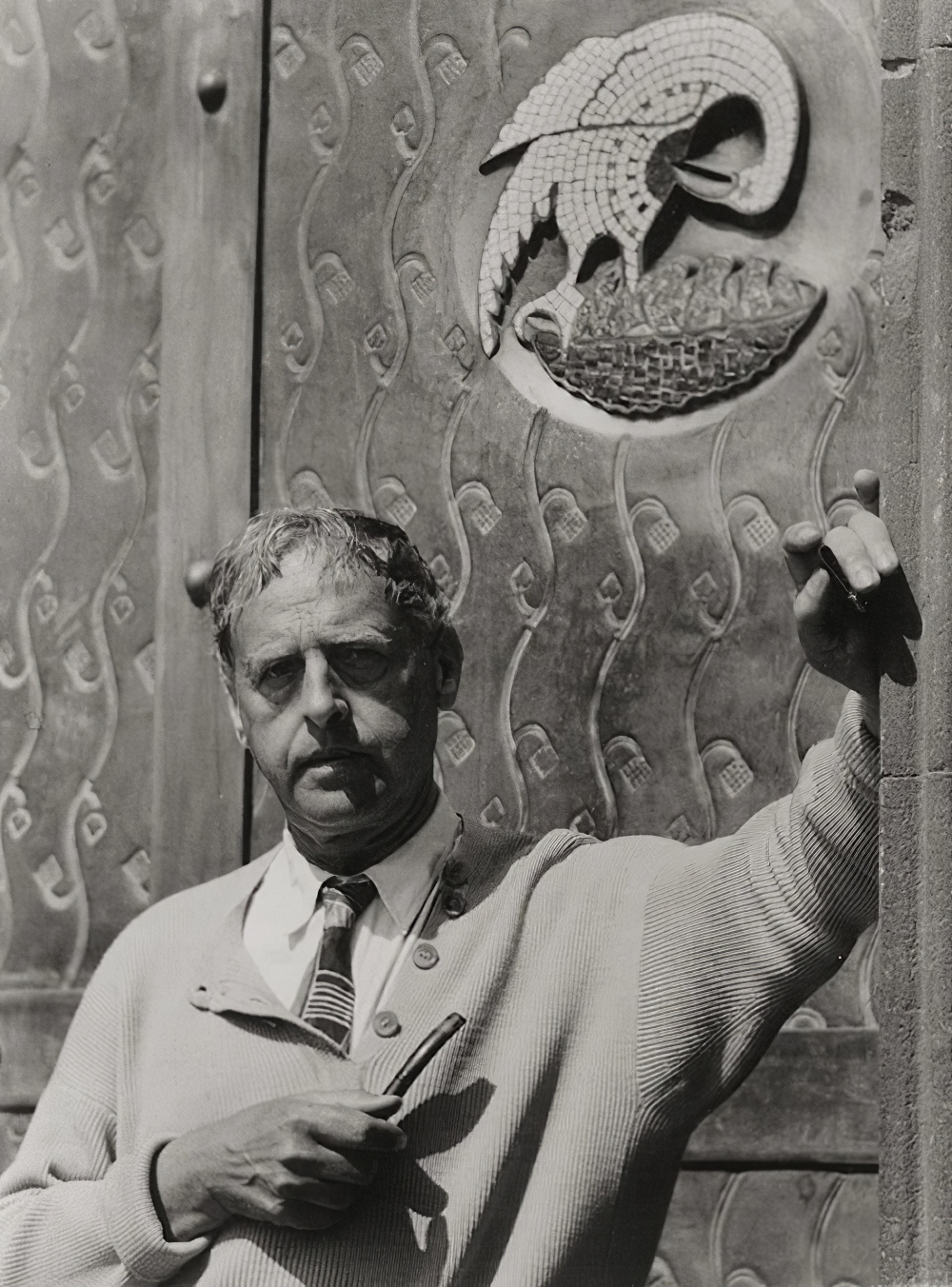


Ewald Wilhelm Hubert Mataré was a German painter and sculptor, who dealt with, among other things, the figures of men and animals in a stylized form.
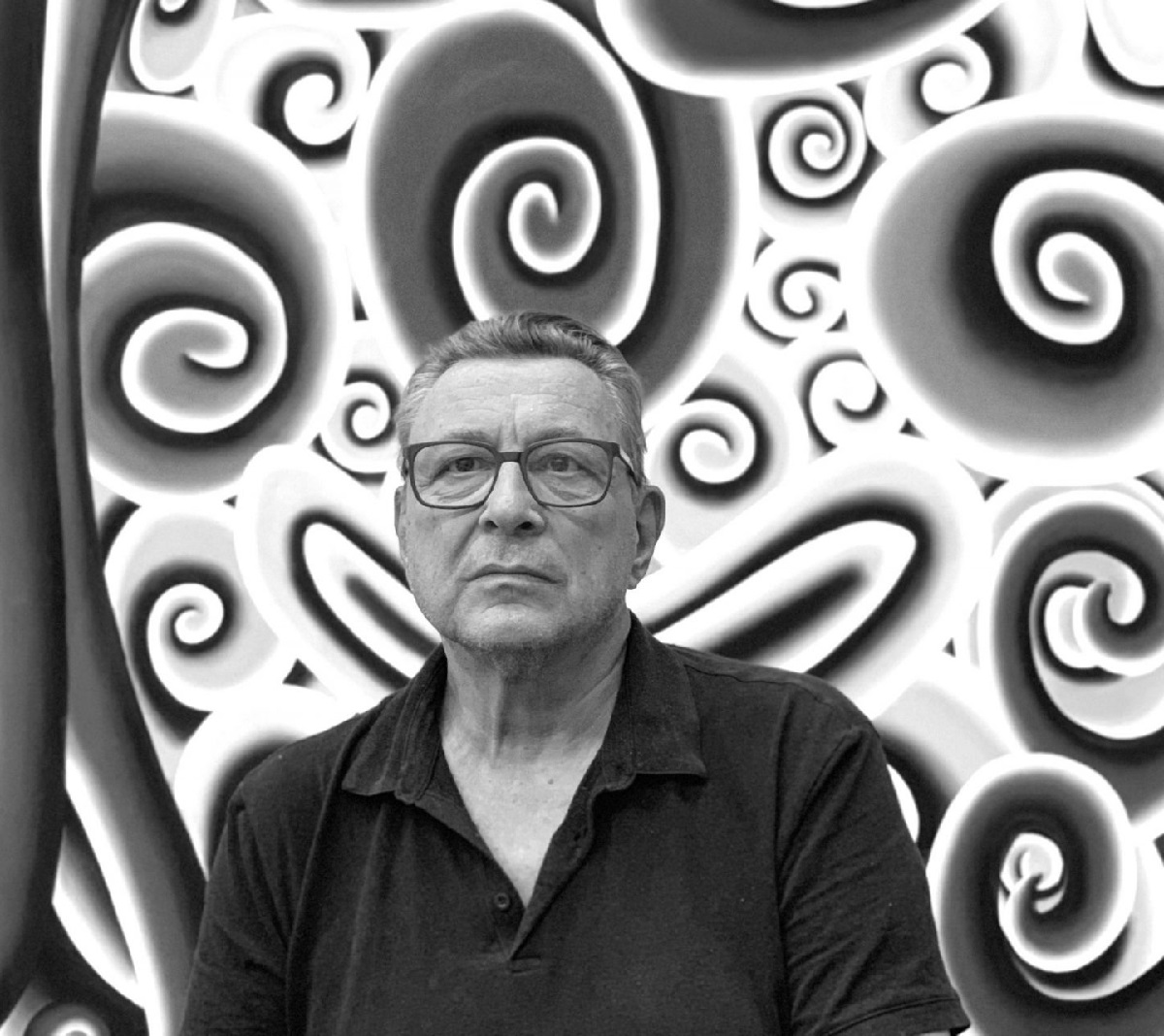


Andreas Schulze is a German painter.
Andreas Schulze first began showing alongside neo-expressionist artists in the 1980s, although his work was considerably less gestural than that of his contemporaries. The artist instead opted for more rounded forms, which he used to create a playful, humorous style of figuration. Typical subjects included the contents interior spaces — such as pillows, lamps, and furniture — which he merged with more ominous abstraction.


Franz Radziwill was a German artist of the twentieth century. He is known as a landscape painter, graphic artist and printmaker associated with the artistic movement of "new materiality".
Franz Radziwill created paintings that are characterized by careful elaboration and the use of glaze techniques borrowed from the Old Masters. He used elements of industrial buildings and modern technology, including ships and airplanes, in his landscapes. The results of his work can be categorized as magical realism.
In 1933 Radziwill became professor of painting at the Düsseldorf Academy of Art, but in 1935 the Nazis stripped him of this position, declaring his work degenerate art.

.jpg)
Max Ernst was a pivotal figure in the 20th-century art world, whose work transcended the boundaries of nationality and genre to leave an indelible mark on culture, art, sculpture, and painting. Born in Germany on April 2, 1891, and later becoming a naturalized American and French citizen, Ernst's career was a testament to his relentless innovation and creativity. Known primarily as an artist and painter, Ernst was a founding member of the Dada movement in Cologne before becoming a major proponent of Surrealism in Paris. His early encounters with the works of Pablo Picasso, Vincent van Gogh, and Paul Gauguin at the Sonderbund exhibition in 1912 deeply influenced his artistic direction, infusing it with elements of Cubism and Expressionism. Despite his lack of formal artistic training, Ernst's experimentation with techniques such as collage and frottage showcased his unique ability to blend the absurd with the sublime, making him a central figure in the artistic avant-garde of his time.
Ernst's work is notable for its exploration of the unconscious, using dreamlike imagery and symbolic figures to critique societal norms and delve into the chaos of the human psyche. His experiences in World War I profoundly impacted his worldview, leading to a deep skepticism of Western culture and an enduring search for meaning through art. This is evident in works such as "Europe After the Rain II," which reflects the devastation of war and "The Fireside Angel," inspired by the political turmoil of the Spanish Civil War, showcasing his ability to address contemporary issues through a surreal lens.
Ernst's contributions to art are preserved in major museums and galleries worldwide, including the Tate in the United Kingdom and the Museum of Modern Art in New York. His sculptures, paintings, and collages continue to be celebrated for their innovative techniques and imaginative scope, marking him as a revolutionary figure in modern art. Among his most significant works are "Ubu Imperator," "The Elephant Celebes," and "The Virgin Spanking the Christ Child before Three Witnesses," each reflecting his mastery over a diversity of mediums and themes.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Max Ernst remains a symbol of artistic freedom and exploration. His ability to navigate through various artistic movements while maintaining a distinct, innovative voice is a testament to his enduring legacy in the art world. To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Max Ernst, signing up for updates is a valuable opportunity for those deeply invested in the nuances of modern and surreal art.
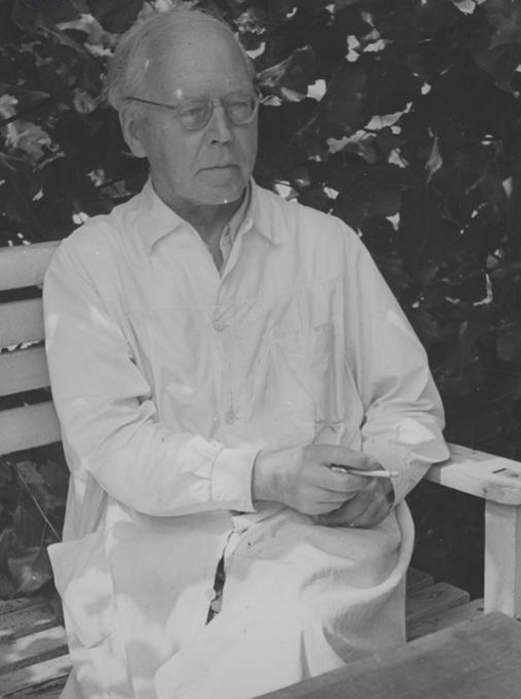


Georg Kolbe was a German sculptor of the first half of the twentieth century. He is known as a master of Classicism and Symbolism. Throughout most of his professional career he was an artist in demand by various German authorities.
Georg Kolbe, despite the strong influence of the Expressionists, managed to develop his own unique style. He left a notable mark not only in sculpture, his artistic legacy includes a large number of drawings and hundreds of engravings.
His biography is closely connected with Berlin, where he lived for more than 40 years. Kolbe is named for the prize awarded by the Artists' Union of Berlin. The artist's former studio now houses a museum with permanent solo exhibitions of works by renowned sculptors of modern art.
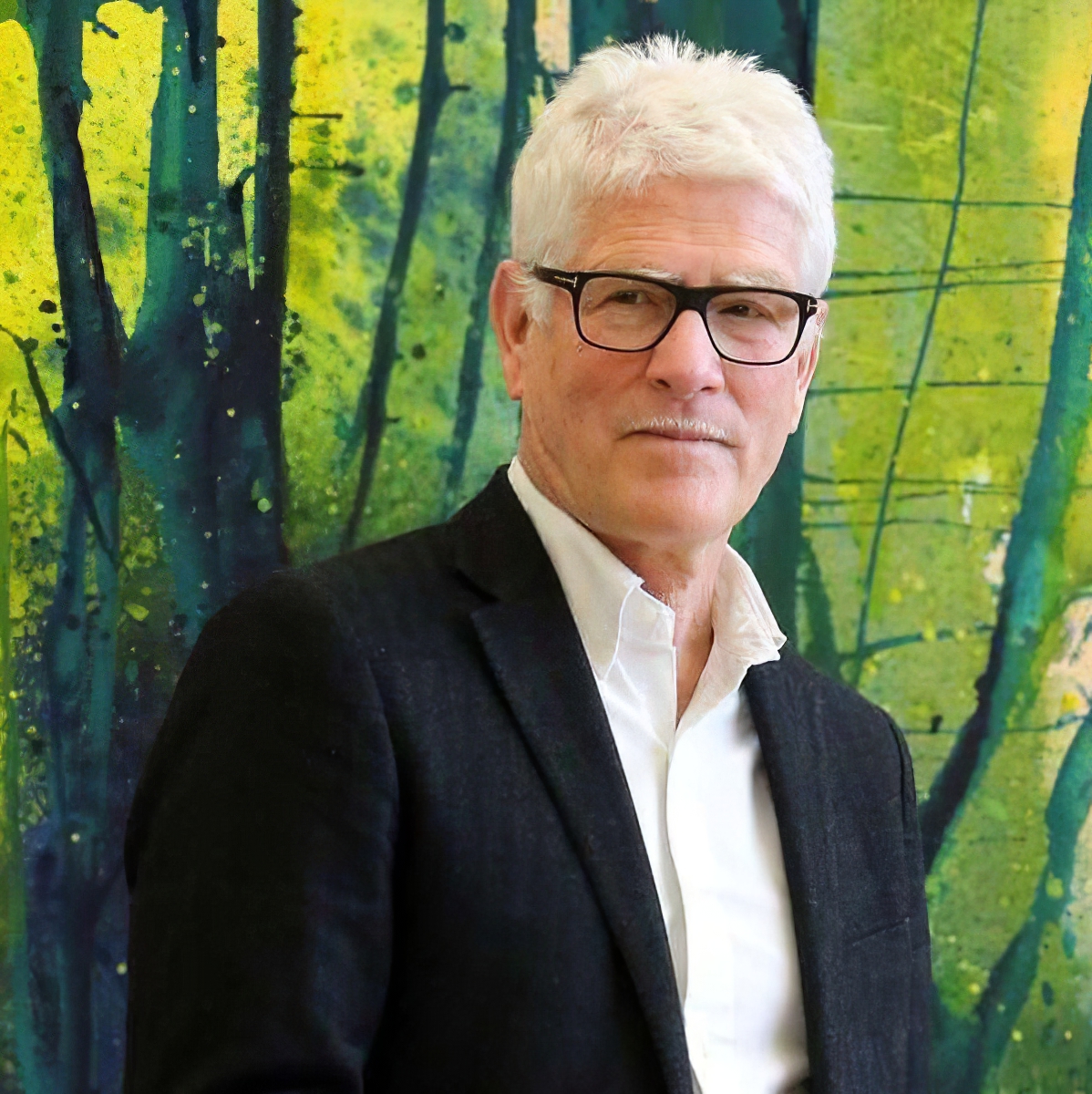


Bernd Zimmer is a Neue Wilden contemporary German artist.
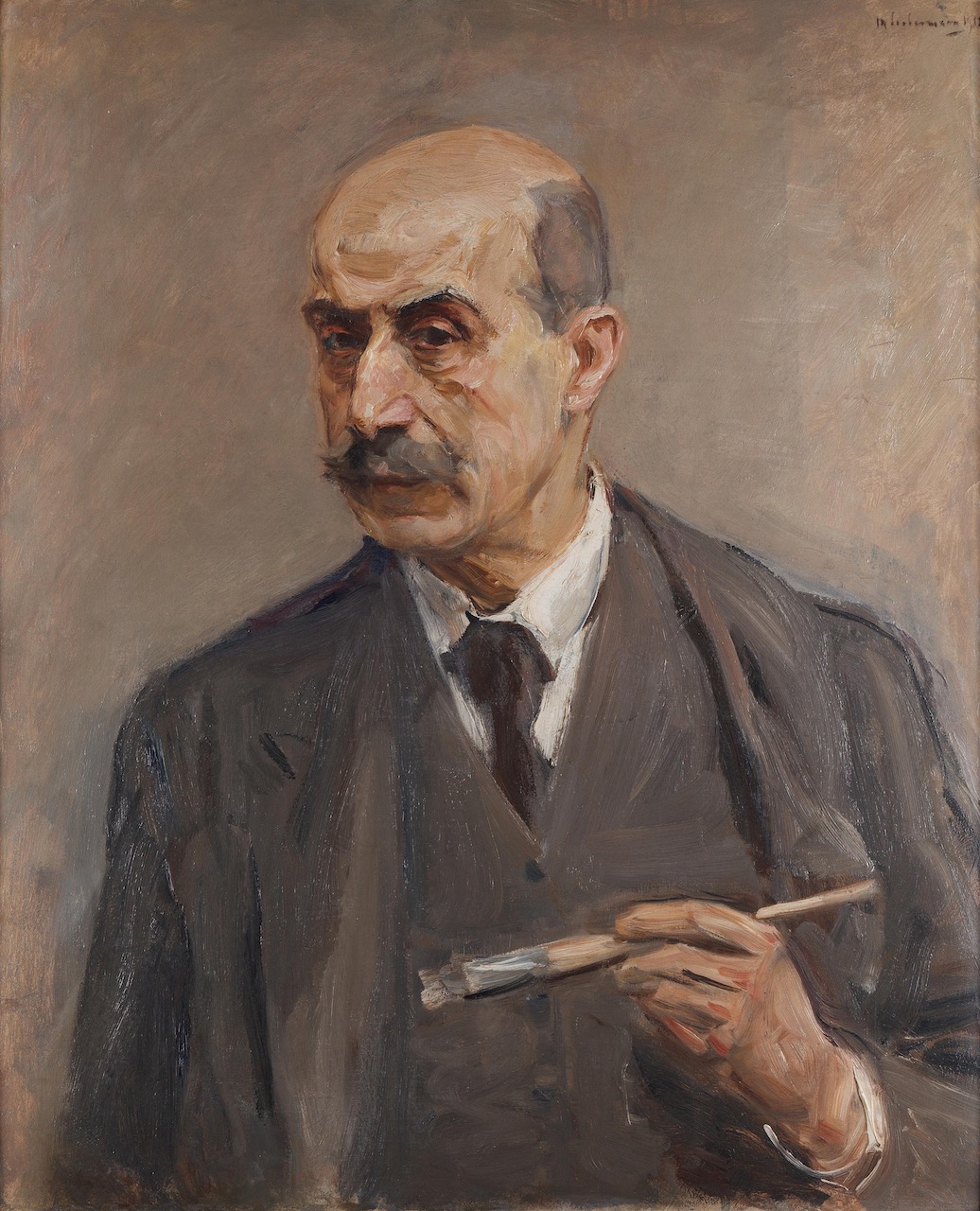


Max Liebermann was a German painter and printmaker, and one of the leading proponents of Impressionism in Germany and continental Europe. In addition to his activity as an artist, he also assembled an important collection of French Impressionist works.
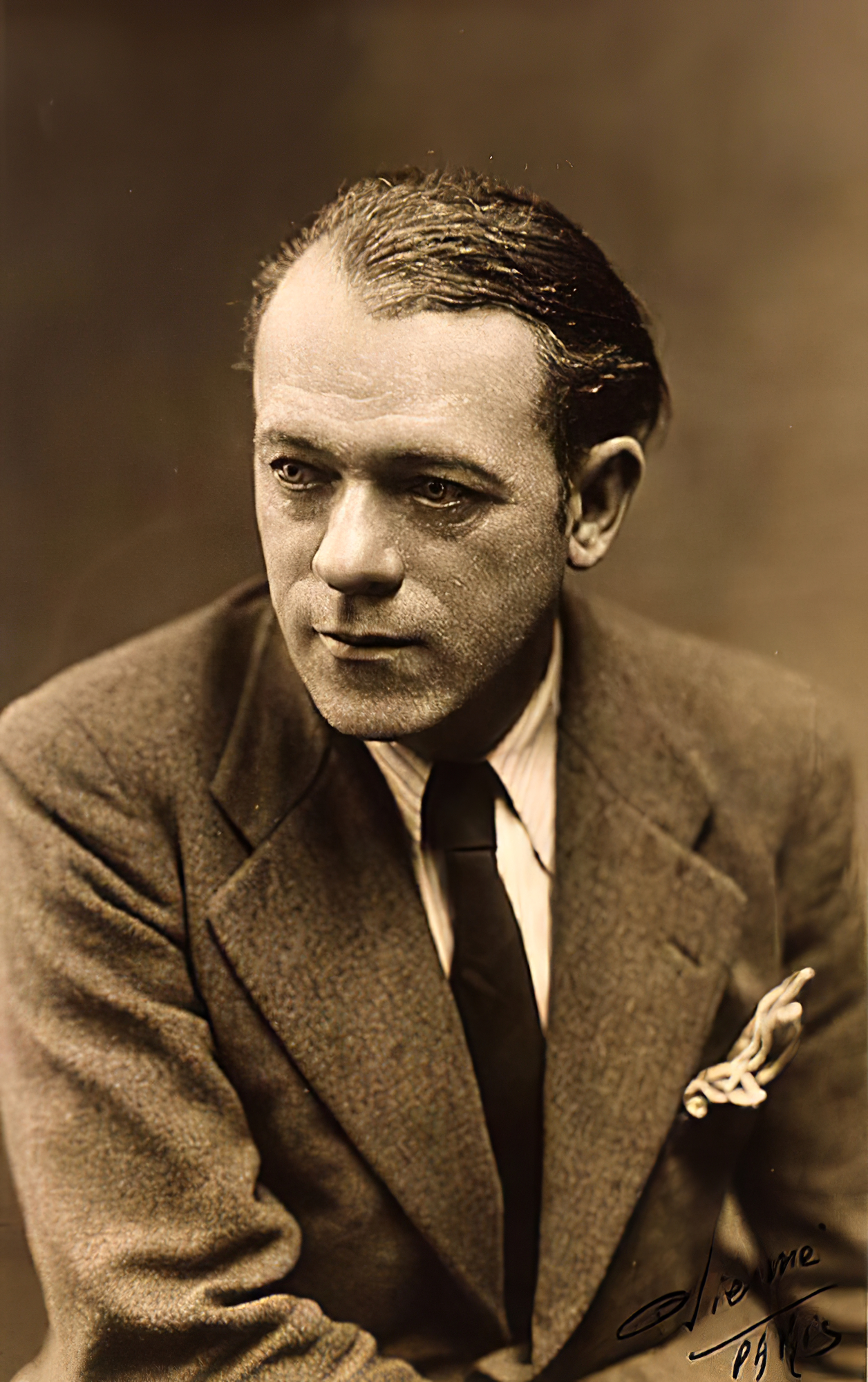


Jean Dufy was a French painter of the late 19th century and the first half of the 20th century. He is known as a painter and designer who worked in various styles, including Cubism and Fauvism. Contemporaries appreciated Dufy's talent as a colorist who constantly experimented with colors, finding inspiration, in particular, in jazz music.
Jean Dufy preferred to depict life in Paris in his oil and watercolor paintings. One of his favorite subjects was the spectacle, especially the circus. Dufy was also in demand as a designer. For 30 years he designed porcelain and in 1925 at the International Exhibition of Decorative Arts, Dufy was awarded the gold medal for his design of the porcelain service Chateaux of France. Jean Dufy also helped his brother Raoul Dufy create a 600 square meter fresco for the Electricity Pavilion at the 1937 World Fair in Paris.
Jean Dufy's work was exhibited in prestigious museums and galleries throughout his career. Today his paintings are in the public collections of the Museum of Modern Art in New York, the Pompidou Center in Paris, the Albertina Gallery in Vienna and other world art centers.