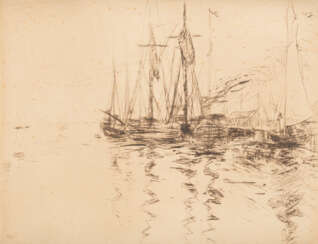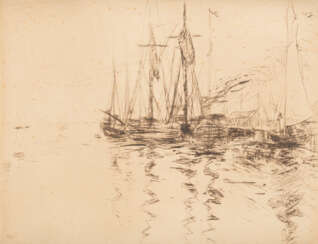kaltnadelradierung in:
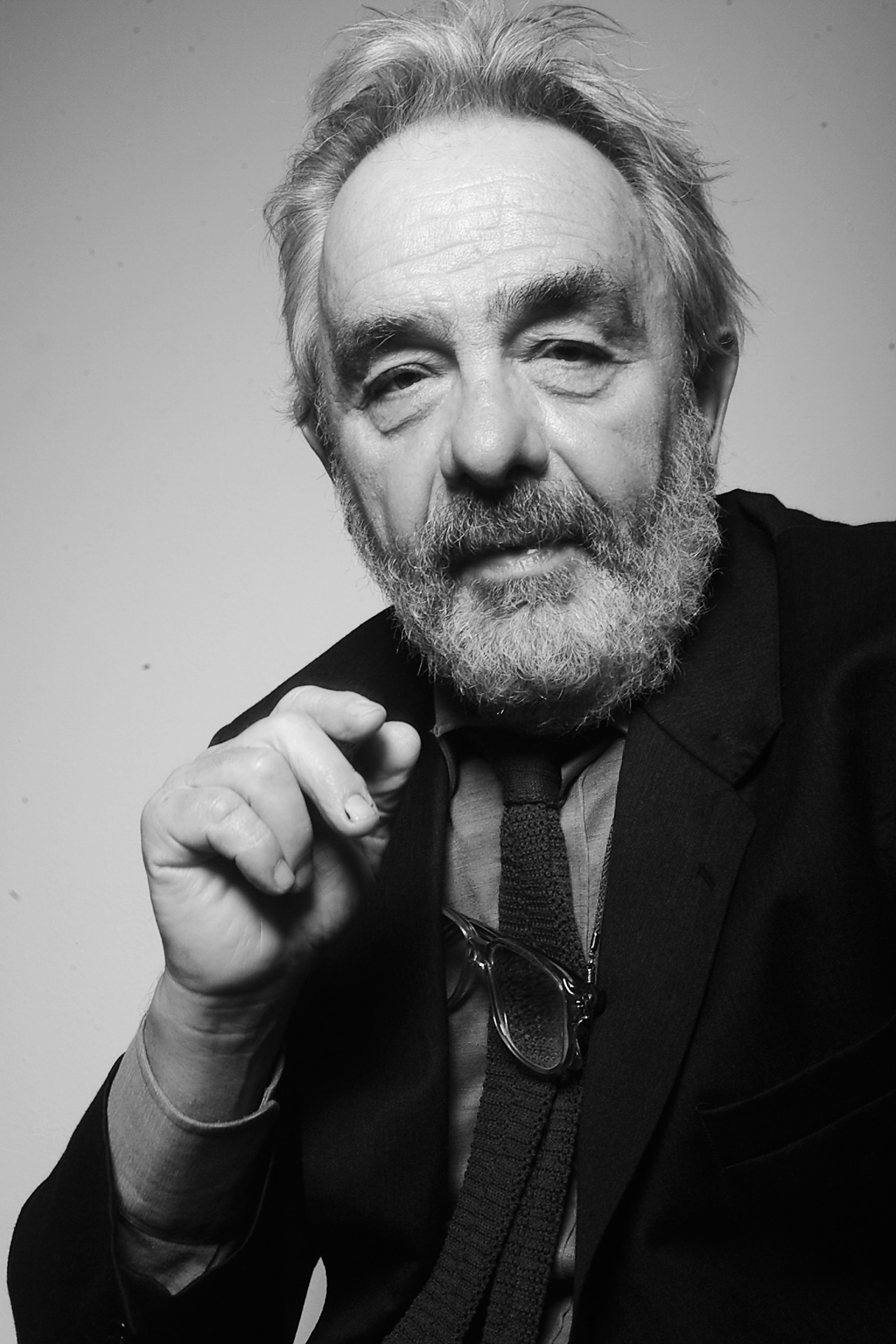

Arnulf Rainer is an Austrian artist who painted in the genre of informal abstract art.
From his early works the artist was inspired by the ideas of Surrealism. He also created works of art where he applied paint over photographs and works of other artists.
In the 1950s, Rainer painted a series of blindfold paintings in the technique of Surrealist automatism. In 1978 he received the Austrian Grand National Prize. Rainer has exhibited in New York, London, Vienna, Paris, Berlin and Munich. His works are in the collections of the Albertina, the Pompidou Center, the Stedelijk Museum, the Metropolitan Museum of Art and the Museum of Modern Art.


Arnulf Rainer is an Austrian artist who painted in the genre of informal abstract art.
From his early works the artist was inspired by the ideas of Surrealism. He also created works of art where he applied paint over photographs and works of other artists.
In the 1950s, Rainer painted a series of blindfold paintings in the technique of Surrealist automatism. In 1978 he received the Austrian Grand National Prize. Rainer has exhibited in New York, London, Vienna, Paris, Berlin and Munich. His works are in the collections of the Albertina, the Pompidou Center, the Stedelijk Museum, the Metropolitan Museum of Art and the Museum of Modern Art.



Käthe Kollwitz (born as Schmidt) was a German artist who worked with painting, printmaking (including etching, lithography and woodcuts) and sculpture. Her most famous art cycles, including The Weavers and The Peasant War, depict the effects of poverty, hunger and war on the working class. Despite the realism of her early works, her art is now more closely associated with Expressionism. Kollwitz was the first woman not only to be elected to the Prussian Academy of Arts but also to receive honorary professor status.
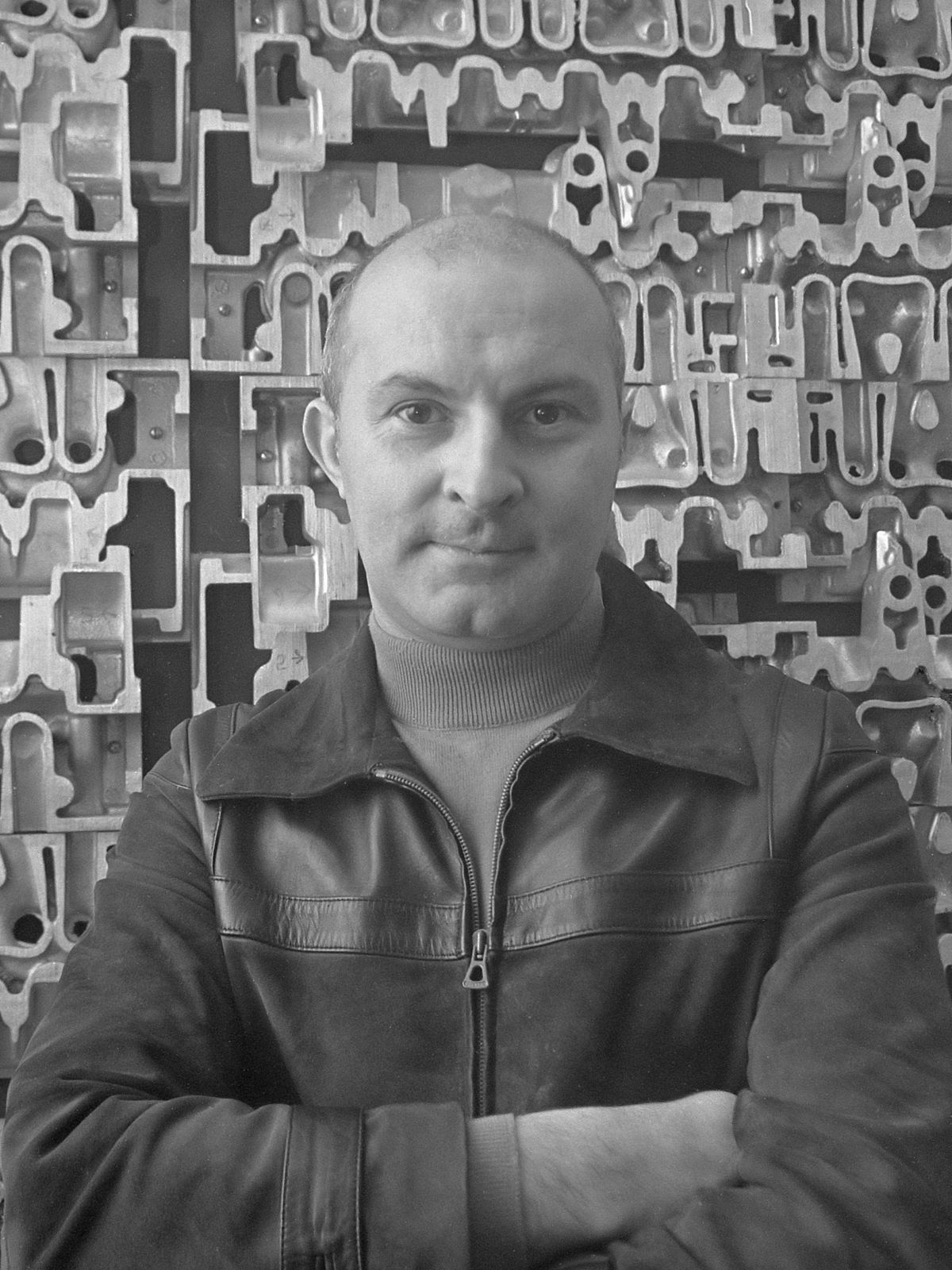


Armand Pierre Fernandez, widely known by his mononym Arman, was a French-born American artist celebrated for his innovative contributions to the Nouveau Réalisme movement and his radical use of everyday objects in art. Born in Nice, France, on November 17, 1928, Arman's early exposure to art came from his father, an antiques dealer and amateur artist, which deeply influenced his later artistic endeavors.
Arman moved beyond traditional painting techniques early in his career, instead creating his signature "Accumulations" and "Poubelles" (trash) sculptures. These works involved assembling and compacting everyday items like watches, clocks, and even automobiles, embedding these objects in layers of concrete or encasing them in Plexiglas. One of his most notable large-scale works is "Long Term Parking," a 60-foot high sculpture made of concrete-encased cars, situated in Jouy-en-Josas, France.
His work is an essential bridge between European and American trends in Pop art and has been widely exhibited in major institutions like the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York, the Tate Gallery in London, and the Centre Pompidou in Paris. Arman's innovative techniques and philosophical approach to materials challenged conventional categorizations of art and inspired future generations of artists.
For collectors and enthusiasts interested in staying updated on exhibitions and sales related to Arman's work, signing up for updates can provide essential insights and opportunities related to this influential artist. Join our community to ensure you don't miss out on new discoveries and auction events associated with Arman's legacy.

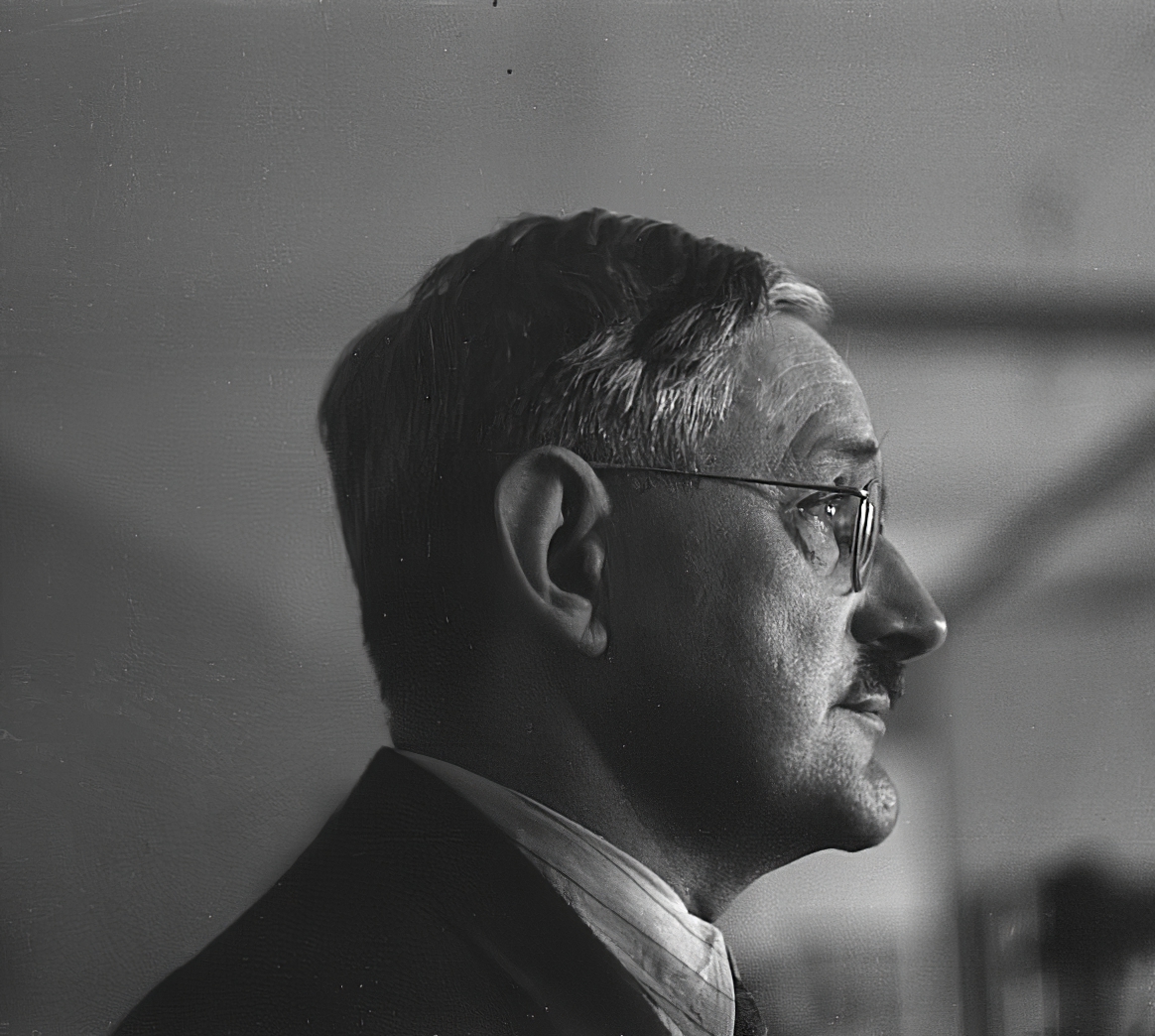
Conrad Felixmüller was a twentieth-century German artist, born Conrad Felix Müller. He is known as a painter, graphic artist, illustrator and printmaker, a representative of the New Materiality movement, who worked in the Expressionist style.
Felixmüller created about 2,500 paintings and graphic drawings, the main motif of which was the human being. The artist considered himself a socially critical expressionist, and his works reflected scenes from everyday life. In the 1930s, many of his works were confiscated by the Nazis as examples of degenerate art and destroyed. As a result of the bombing of Berlin in 1944, Felixmüller lost much of his work.
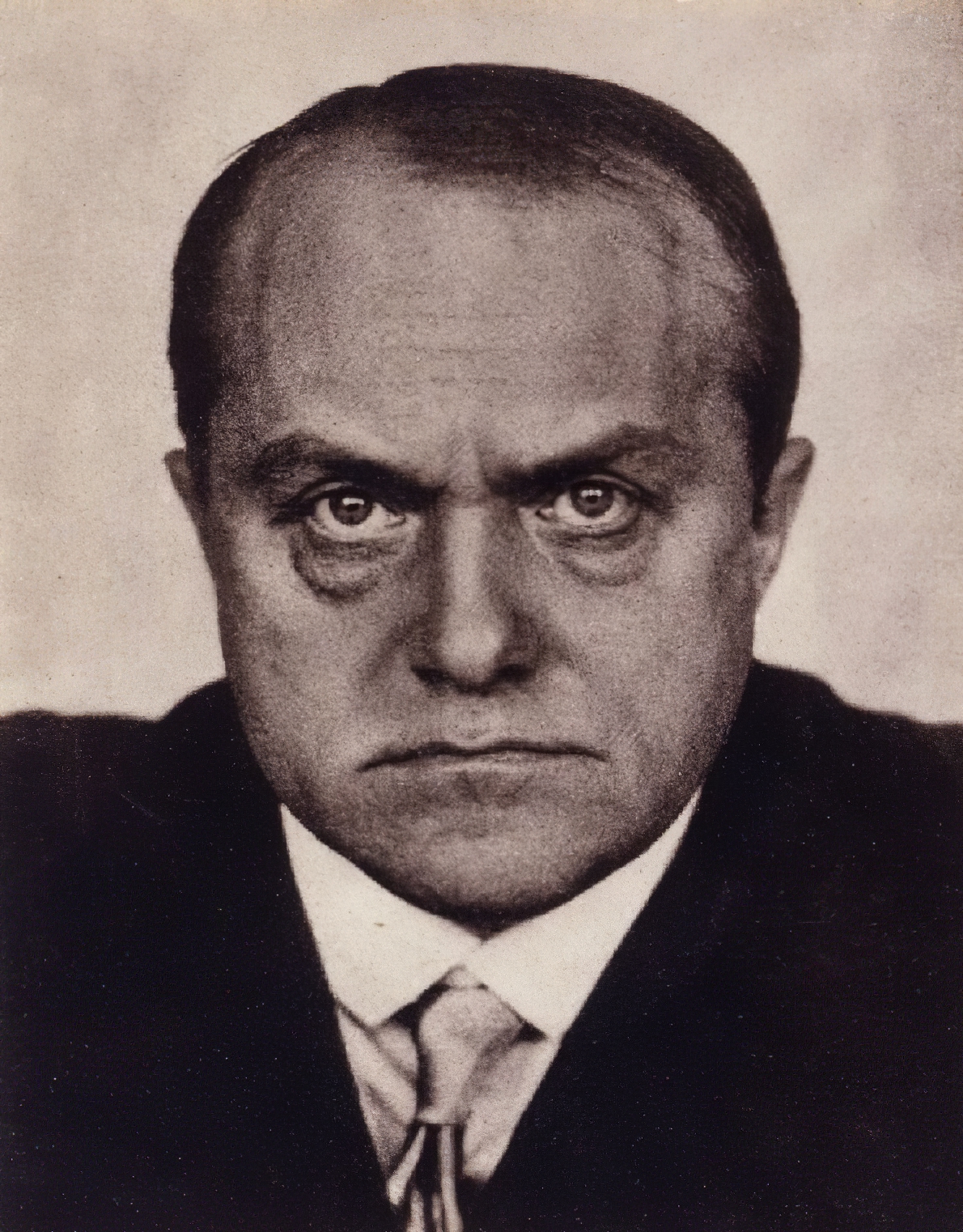


Max Beckmann, a German painter, printmaker, sculptor, and writer, stood out in the early 20th century for his profound contributions to modern art. Beckmann's career spanned a tumultuous period in history, deeply influencing his thematic and stylistic choices. Unlike many of his contemporaries who embraced non-representational painting, Max Beckmann persisted with and evolved the tradition of figurative painting, drawing inspiration from a wide array of artists spanning from Cézanne and Van Gogh to medieval masters like Bosch and Bruegel.
Max Beckmann's experiences, particularly those related to the World Wars, significantly shaped his work. Following Adolf Hitler's rise to power and the subsequent condemnation of modern art as "degenerate," Beckmann fled Germany, spending a decade in self-imposed exile in Amsterdam before eventually relocating to the United States. His art from this period, especially his large triptychs, is considered some of his most potent, offering a stark reflection on humanity and the chaos of the times.
One of Max Beckmann's most personally allegorical works, "Beginning" (1949), encapsulates his knack for blending real and imagined elements from his life to comment on the broader human condition. This piece, alongside others, underscores Beckmann's enduring fascination with the existential struggles modern society faces, teetering between desire and societal roles.
Max Beckmann's legacy is cemented not just by his unique approach to modernism but also by his influence on subsequent generations of artists, particularly in the United States, where he spent his final years teaching and working. Despite a path that often diverged from the mainstream narratives of art history, Beckmann's work continues to resonate, housed in prestigious institutions like The Museum of Modern Art and The Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Max Beckmann's oeuvre offers a compelling exploration of 20th-century art and history. To stay informed about new discoveries, sales, and auction events related to Max Beckmann, consider signing up for updates. This subscription ensures access to the latest opportunities to engage with the work of one of modernism's most individual voices.