modern first editions
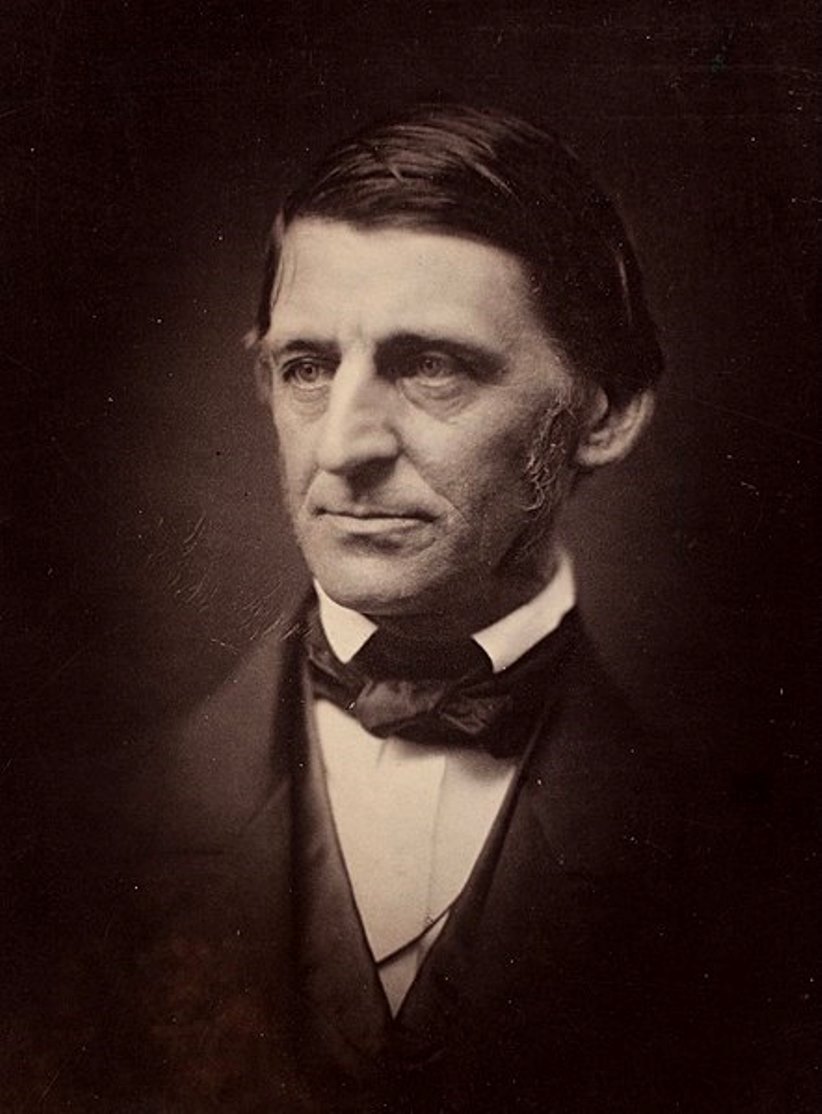

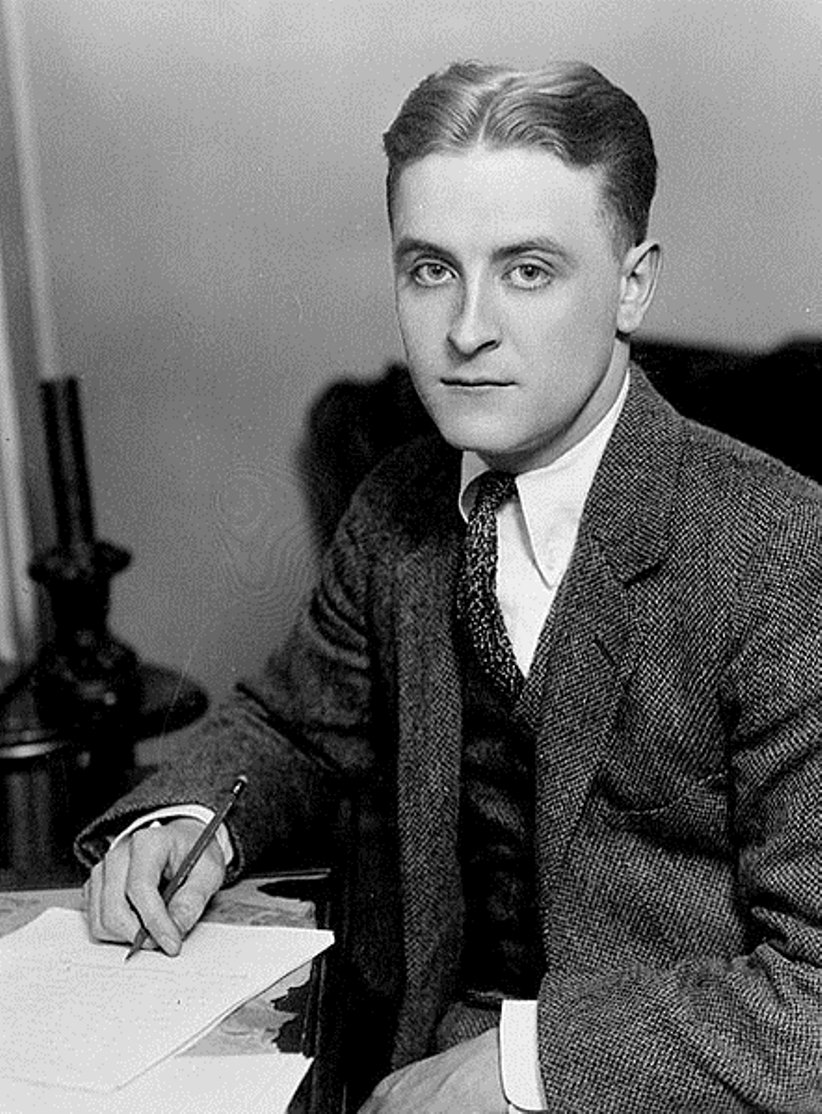
Ralph Waldo Emerson was an American philosopher, lecturer and poet, one of the most prominent thinkers and writers in the United States, and the originator of transcendentalism.
Ralph studied at Boston State Latin School and then at Harvard College (later Harvard University), began to preach, but soon doubted his chosen path and resigned his ministry. Emerson went to Europe, where new acquaintances and knowledge led him to new thoughts, and, returning to the United States in 1833, he began writing his famous book "Nature", where he first formulated a philosophy called transcendentalism. Soon other thinkers rallied around him, forming a group of like-minded thinkers.
In the essay "Nature," published in 1836, and in the following works, "The American Scholar" and "An Address in the School of Theology," Emerson consistently developed his ideas. Emerson's doctrine of the self-sufficiency and self-reliance of the individual stems from his view that a person need only look into his own heart to receive the spiritual guidance that has hitherto been the prerogative of the official churches. One must then have the courage to be oneself and trust the inner power within oneself, living one's life according to the commandments one has intuitively derived. These thoughts are not new, but Emerson put them in imaginative and accessible language.
Emerson's speeches led to his being ostracized at Harvard for many years. However, the informal Transcendental Club, founded in 1836, was joined and supported by his young students. The world fame of the brilliant thinker Emerson brought his "Essays" in two volumes, published in 1841 and 1844. As the main representative of transcendentalism, Emerson gave direction to the religious, philosophical and ethical movement, which above all emphasized belief in the spiritual potential of each person.
A later work of confession, The Conduct of Life (1860), demonstrates the author's developed humanism and full awareness of human limitations. The voluminous collection of poems cemented Emerson's reputation as a major American poet.
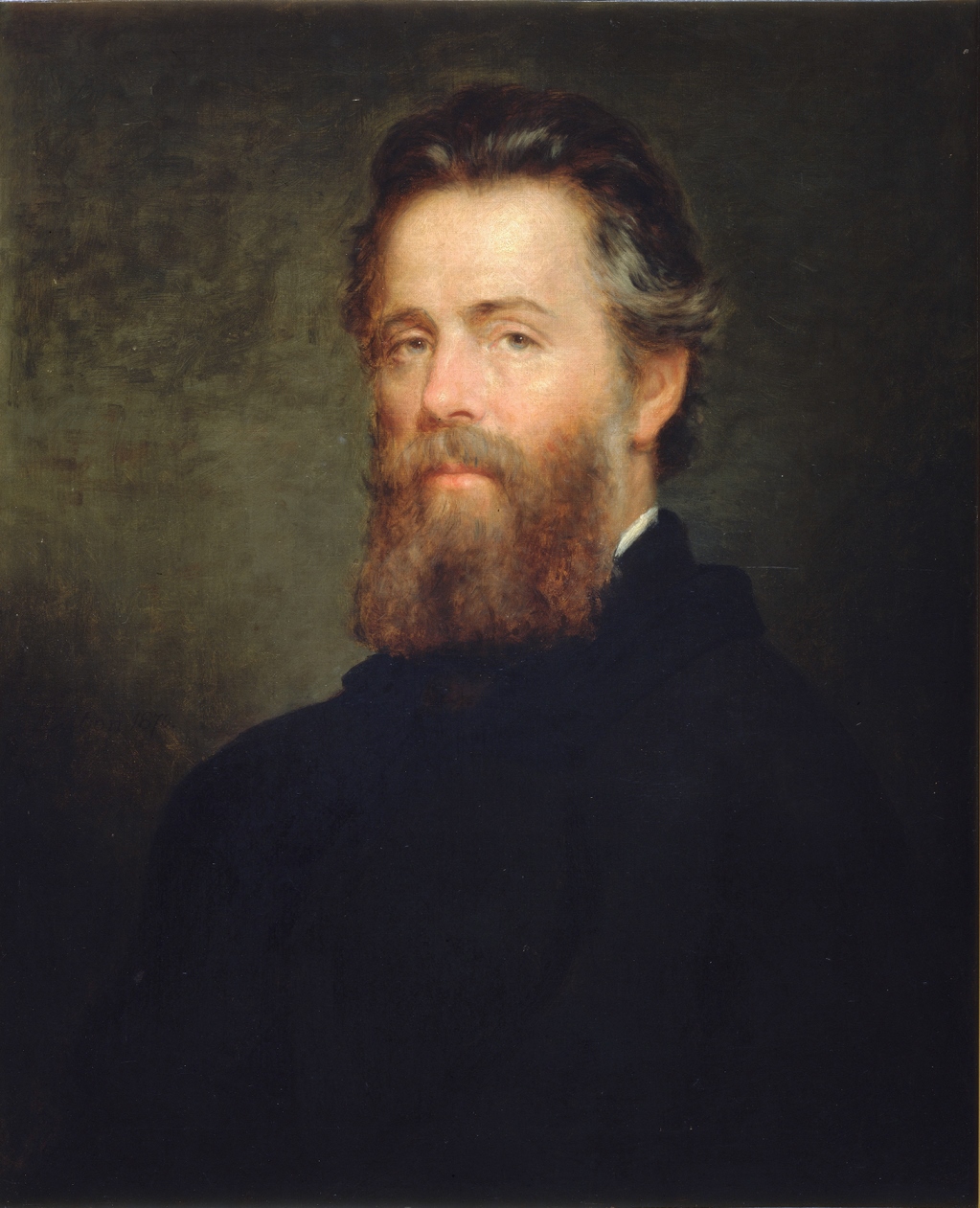




Herman Melville was an American writer, poet, and sailor.
Melville's hardship-filled youth ended on a whaling ship. He returned from his adventures in the South Seas in October 1844, and wrote "Taipi" the following spring. The book was based on the events surrounding Melville's desertion from the whaling ship Acushnet in 1842 and subsequent adventures in the Marquesas Islands.
Melville wrote several other novels and short stories and many poems, but during his lifetime his works were little appreciated by his contemporaries. Only in the 1920s began to rethink Melville, and he was recognized as a classic of world literature. World fame Melville already in the 20th century brought irrational novel "Moby Dick".
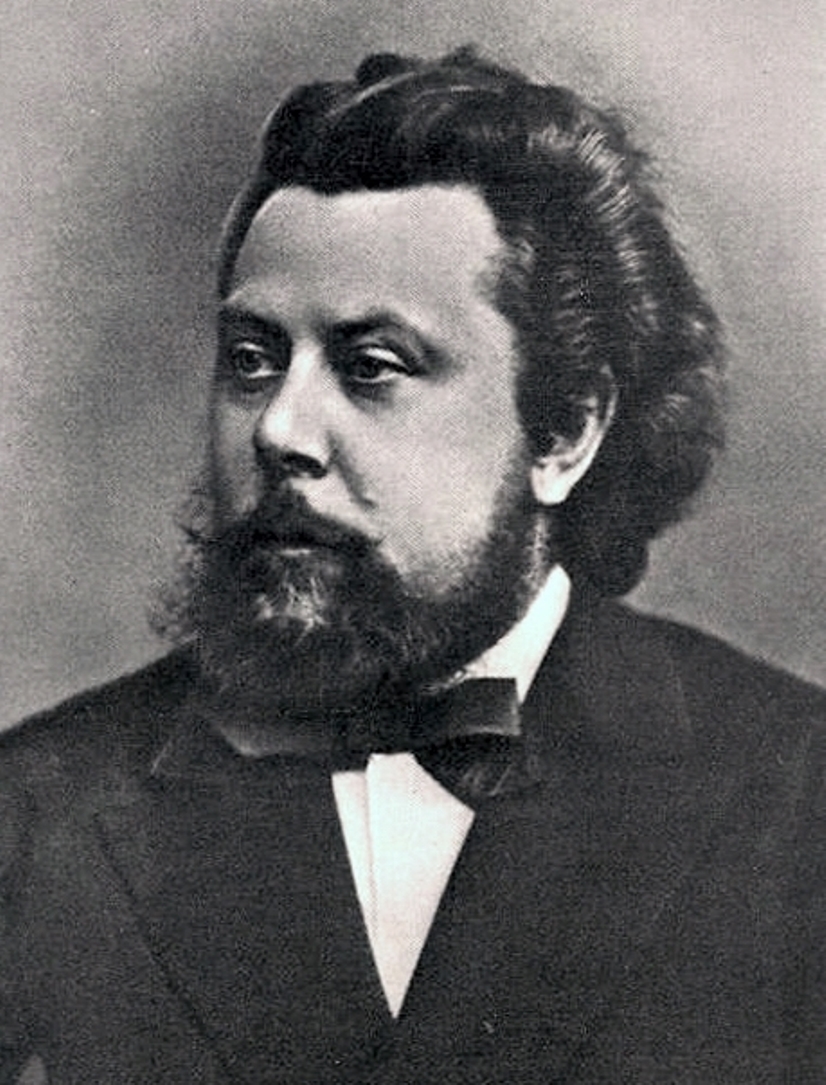






Modest Petrovich Musorgskii (russian: Модест Петрович Мусоргский) was a Russian composer and pianist.
Born into an old Russian noble family, Modest was trained on the piano from an early age, then served as an officer in the Life Guards of the Preobrazhensky Regiment. In 1856-57 Mussorgsky became acquainted with the composer Alexander Borodin, and later with Alexander Dargomyzhsky, Cesar Cui, Mili Balakirev and the music critic Vladimir Stasov. Together they formed a friendly community that became known as the Mighty Handful.
In 1858, Musorgskii left military service and took up only music. Later, however, for the sake of earning money, he was forced to enter the civil service and work in various official positions. In music he tried for a long time to find his own style, experimented a lot, took on different genres. He composed piano and orchestral works, many satirical romances, vocal pictures and songs with vivid characters. Musorgskii's symphonic work Intermezzo (1861) and fantasy Night on Bald Mountain, the cycle of pieces Pictures at an Exhibition, written for piano in 1874 as musical illustrations to Victor Hartmann's watercolors, and the vocal cycle Children's, which included seven pieces, are widely known and often performed.
Musorgskii gradually became popular in Russia and abroad. The pinnacle of Musorgskii's work in the 1860s was his opera Boris Godunov, based on Alexander Pushkin's drama, staged at the Mariinsky Theater in St. Petersburg in 1874. In 1872 he almost completed his last opera, Khovanshchina; Sorochinskaya Yarmarka and several other operas remained unfinished.
After Musorgskii's death, his friend the composer Rimsky-Korsakov decided to put all his works in order and publish them. He made many changes to the melodic and harmonic order of the compositions completed by the author, including Boris Godunov.
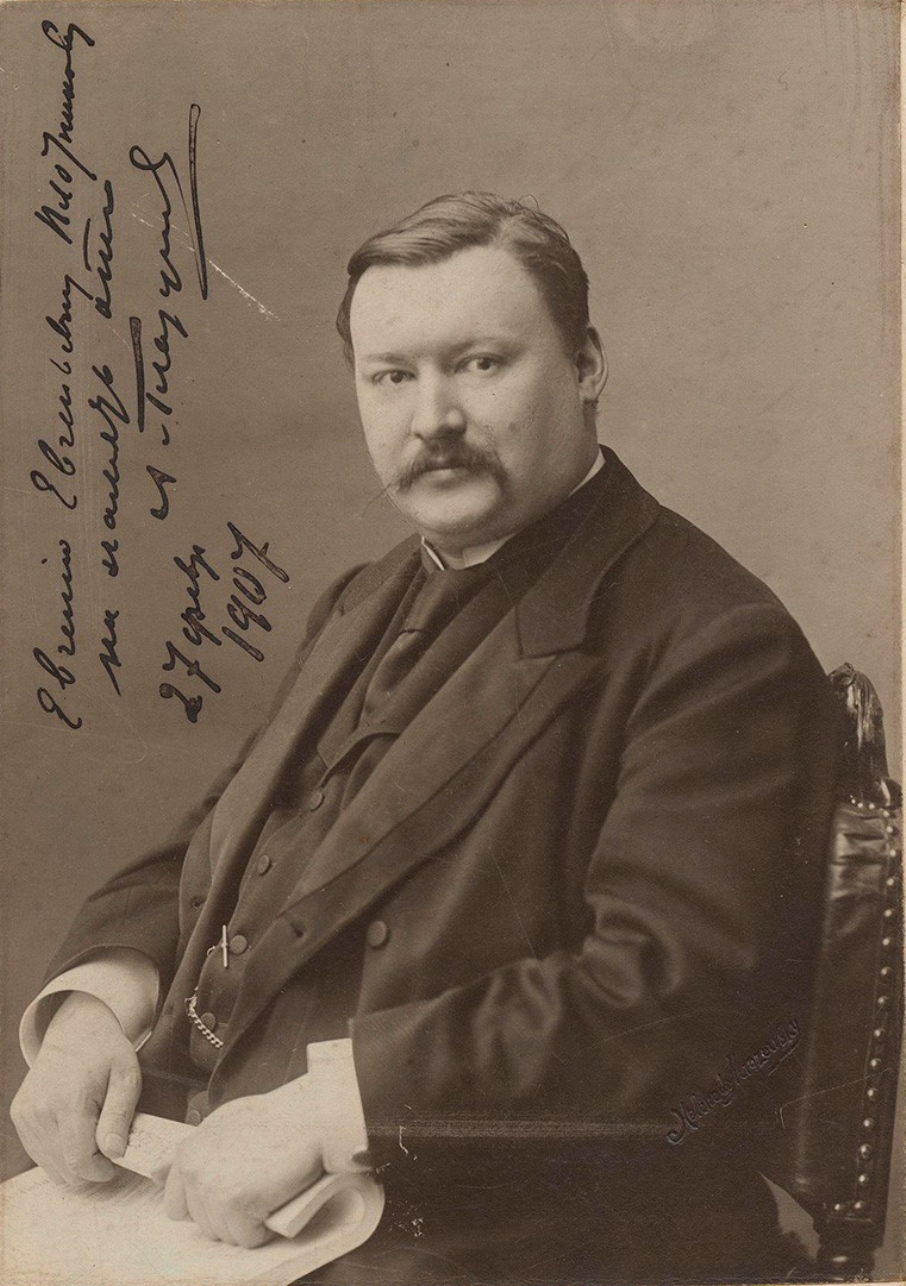

Aleksandr Konstantinovich Glazunov (russian: Александр Константинович Глазунов) was a Russian late Romantic composer, conductor and teacher.
Glazunov belonged to a well-known dynasty of book publishers in St. Petersburg and showed musical ability early on. He studied music with Balakirev and Rimsky-Korsakov, wrote his first symphony at the age of sixteen, and was noticed by the patron of the arts Mitrofan Belyaev, who became his admirer and benefactor. Thanks to him, the young Glazunov traveled all over Europe and was introduced in Weimar to Franz Liszt, who promoted the performance of his First Symphony at the congress of the General German Musical Union.
After the death of composer Borodin, Glazunov helped Rimsky-Korsakov finish his opera Prince Igor, and in the late 1890s he was already collaborating with the Imperial Theaters and writing three ballets. In 1899 Glazunov was appointed professor at the St. Petersburg Conservatory, and from the end of 1905 he became its director, retaining this post even after the October Revolution of 1917. Glazunov's personality is characterized by the fact that he spent his director's salary on helping poor students. And in general, during the hungry years of post-revolutionary devastation, he supported students, even if he did not share their musical beliefs - among them the greats Sergei Prokofiev and Dmitri Shostakovich.
In 1922, Aleksandr Glazunov was named People's Artist of the young Soviet republic. In 1928 he traveled to Vienna to take part in the jury of the Schubert Centenary Composition Competition and never returned to the USSR. However, even while living in Europe, he retained his Soviet citizenship. Officially, Glazunov's stay in Paris was explained by his serious state of health and the need for medical treatment. Already in 1972 Glazunov's ashes were transported to the USSR and reburied in the Alexander Nevsky Lavra.
In addition to ballets, Aleksandr Glazunov wrote eight symphonies (the ninth remained unfinished), seven string quartets and a great deal of orchestral music. He wrote mainly for piano and organ, and at the end of his life he composed works for saxophone - a solo concerto and a quartet for saxophones. Glazunov's most popular works today are his ballets The Seasons (1898) and Raymonda (1897), his Fourth, Fifth and Sixth Symphonies, the Polonaise from Les Sylphides, and his two concert waltzes.

Nikolai Andreevich Rimskii-Korsakov (russian: Николай Андреевич Римский-Корсаков) was a Russian composer, teacher and conductor, music critic, and member of the Mighty Handful.
Originally from an old noble family, Rimskii-Korsakov studied piano from the age of six and by the age of nine was already trying to compose music. After graduating from the St. Petersburg Naval School, in 1862-1865 he was on a round-the-world voyage, during which he was made an officer. He participated in an expedition to the shores of North America, visited Great Britain, Spain, Norway. In 1873-1884 he worked as an inspector of military bands of the fleet.
During his studies at the school and during the expedition Nikolai Rimskii-Korsakov continued to study music. His acquaintance in 1861 with the composer Miliy Balakirev and his circle "The Mighty Handful", which included composers Caesar Cui, Modest Mussorgsky and Alexander Borodin, became the impetus for his work. Rimskii-Korsakov 's aesthetic views and worldview were formed under the influence of the "Mighty Handful" and its ideologist V. Stasov.
Nikolai Rimskii-Korsakov was very prolific, and almost all of his works are based on folk and classical Russian literature and melodies. He composed 15 operas, including The Pskovite Girl (1872), May Night (1879), The Snow Maiden (1881), Sadko (1896), The Tsar's Bride (1898), The Tale of Tsar Saltan (1900), Kashchey the Immortal (1902), The Tale of the Invisible City of Kitezh..." (1904), The Golden Cockerel (1907). Fragments from some operas have become the most performed in the world, among them "The Song of the Indian Guest" from "Sadko" and "The Flight of the Bumblebee" from "Saltan".
The composer's works also include three symphonies (the first of which he completed while sailing around the world), symphonic works, instrumental concertos, cantatas, chamber instrumental, vocal and sacred music. In 1886-1890 Rimskii-Korsakov conducted the "Russian Symphonic Concertos" in St. Petersburg, and in 1898 - in Moscow, at the same time he was also engaged in teaching. In 1871 he became a professor at the St. Petersburg Conservatory, where he taught classes in practical composition, instrumentation and orchestration.
As a teacher, Rimskii-Korsakov trained over 200 composers and musicians, including Alexander Glazunov, Mikhail Gnesin, Alexander Grechaninov, Anatoly Lyadov, Sergei Prokofiev, and Igor Stravinsky. He also published several textbooks on harmony and orchestration. Rimskii-Korsakov's work had a great influence on the development of Russian classical and foreign music.
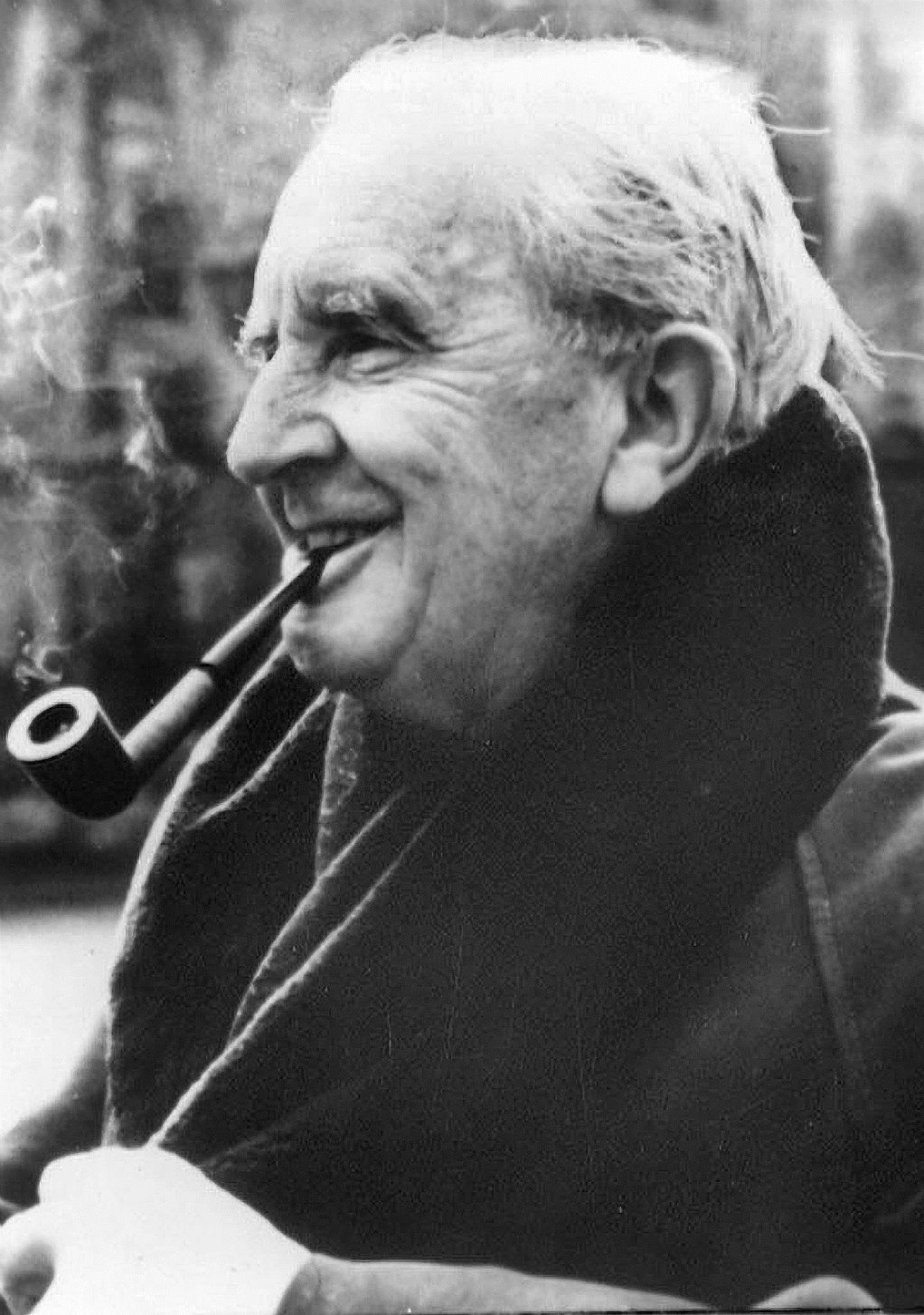


John Ronald Reuel Tolkien was a British writer and poet, translator, philologist, and linguist.
Tolkien wrote many works in the genre of magical fiction. He became world famous for his fantasy books The Hobbit (1937) and The Lord of the Rings (1954-55).
"The Hobbit" was published in 1937 with drawings by the author and proved so popular that the publisher asked him to write a sequel. The result, 17 years later, was Tolkien's masterpiece, "The Lord of the Rings," which was voted the best book of the 20th century. By the beginning of the 21st century, more than 50 million copies had been sold in 30 languages. The film version of "The Lord of the Rings" by New Zealand director Peter Jackson, released in three parts in 2001-2003, broke world viewing records.
Tolkien has been called the "father" of modern high fantasy literature.
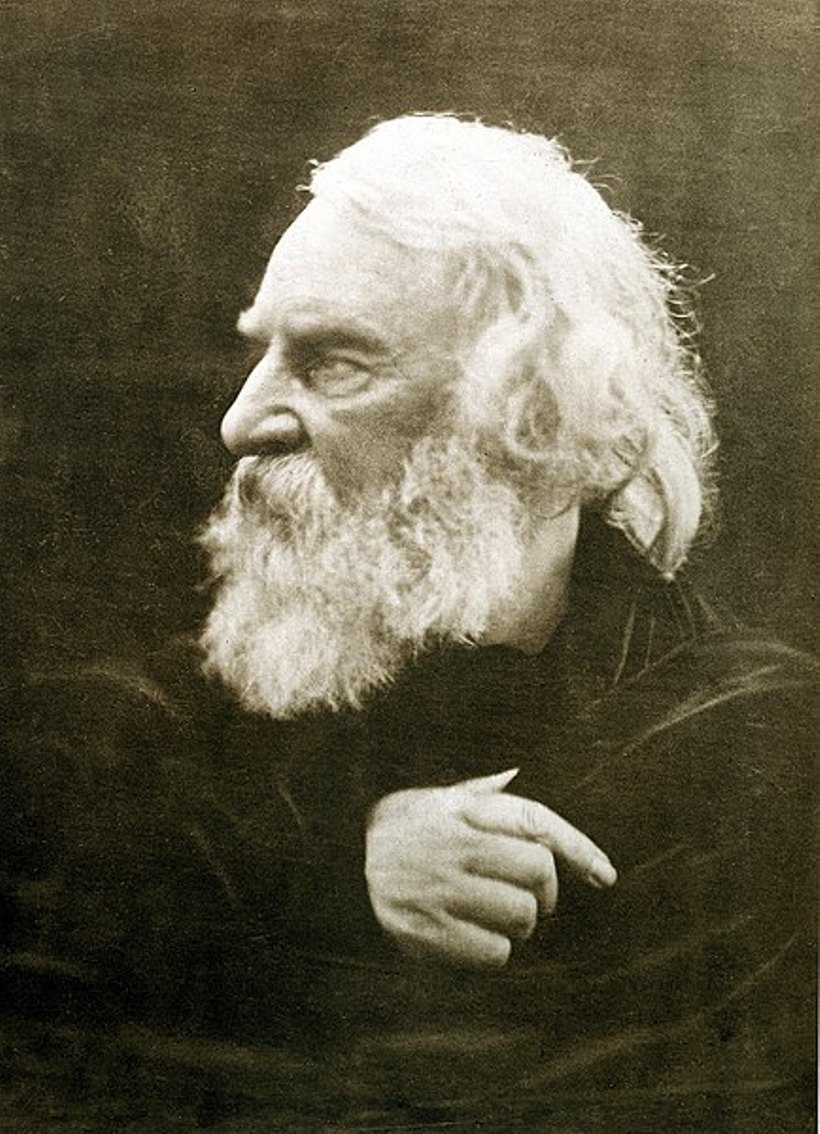


Henry Wadsworth Longfellow was the most popular American poet of the nineteenth century.
Longfellow is one of the most revered poets in the United States. His poems "Paul Revere's Ride", "Evangeline", "The Tale of Acadia" (1847) and "Psalm of Life" were included in elementary and high school curricula and have long been remembered by generations of readers who studied them as children. Longfellow revitalized American literary life by linking American poetry to European traditions outside of England.