saint helena



Napoleon I Bonaparte was a French statesman and military leader, Emperor of France (1804-1815).
Napoleon was born in the family of an ignorant Corsican nobleman, graduated from the Brienne military school, then the Paris military school. In 1785 he began military service in the rank of junior lieutenant of artillery in the Royal Army. From the first days of the Great French Revolution of 1789-1799 Bonaparte joined the political struggle on the island of Corsica, in 1792 in Valence joined the Jacobin Club and actively participated in all the turbulent political and military events.
In November 1799 Napoleon was at the head of a coup d'état: the government of the Directory was deposed, and the French Republic was headed by three consuls, the first of whom was Napoleon. In June 1804 Bonaparte was proclaimed Emperor Napoleon I of France, and in December a lavish coronation ceremony took place. After Italy recognized him as its king, in March 1805 he was also crowned in Milan.
With his rise to power, France entered a period of almost continuous warfare. Napoleon greatly expanded the territory of the empire, made most of the states of Western and Central Europe dependent on France. His brothers became kings: Joseph in Naples, Louis in Holland, and Jerome in Westphalia. In 1812, Napoleon made a campaign against Russia and even reached Moscow, but the Russian troops under the leadership of commander M.I. Kutuzov with the active support of all the people completely defeated the "invincible army". This military campaign was the beginning of the collapse of Napoleon's empire. The entry of the anti-French coalition troops into Paris in March 1814 forced Napoleon I to abdicate (April 6, 1814).
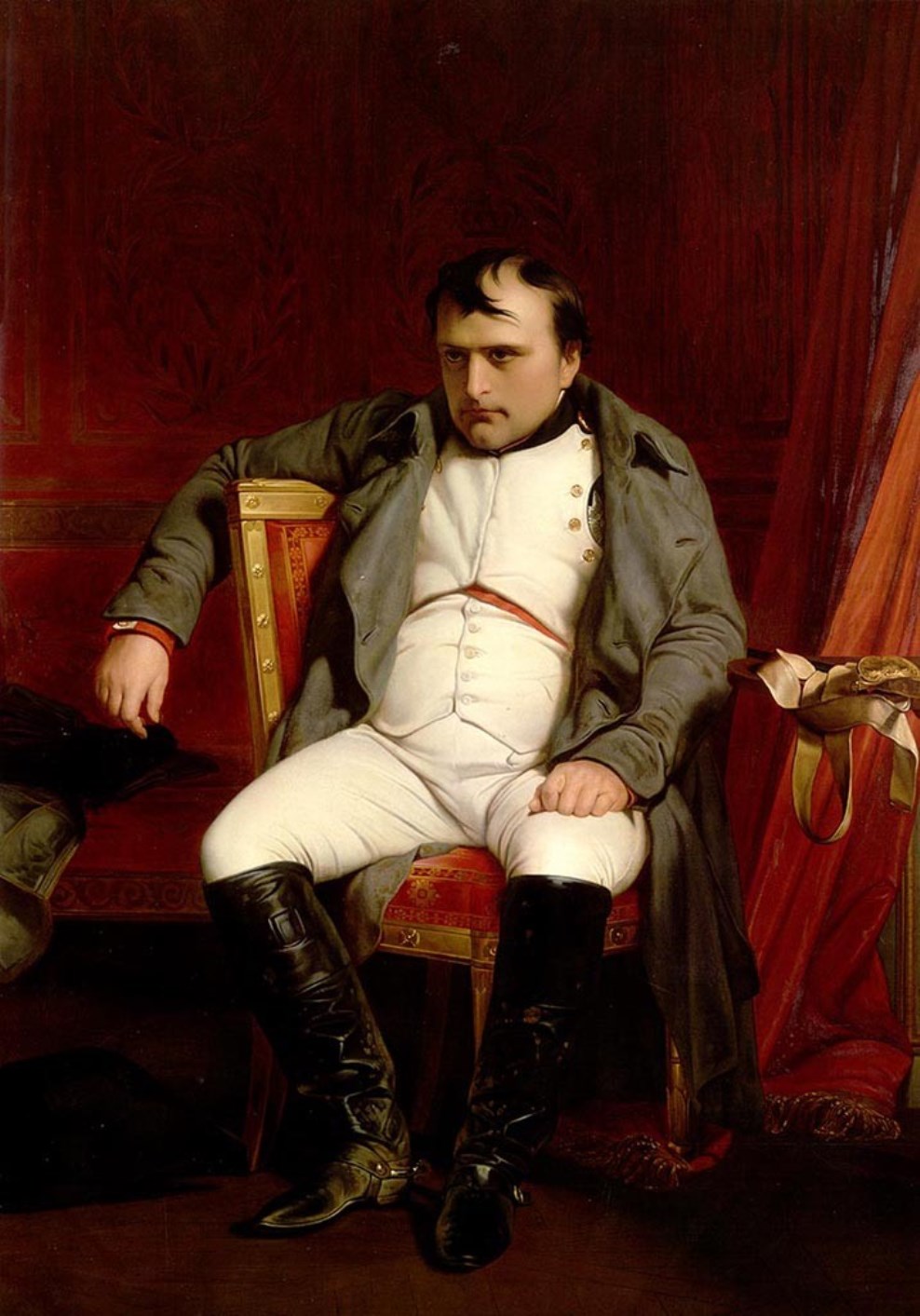
Napoleon retained the title of Emperor and was given possession of the island of Elba in the Mediterranean Sea. However, in March 1815, the deposed emperor at the head of a small detachment suddenly landed in the south of France and three weeks later, without a single shot entered Paris. But the emperor failed to live up to the hopes of the people of France, plus his defeat at the Battle of Waterloo all led to his second abdication. As a result, Napoleon Bonaparte was exiled to the island of St. Helena in the Atlantic Ocean, where he died on May 5, 1821.
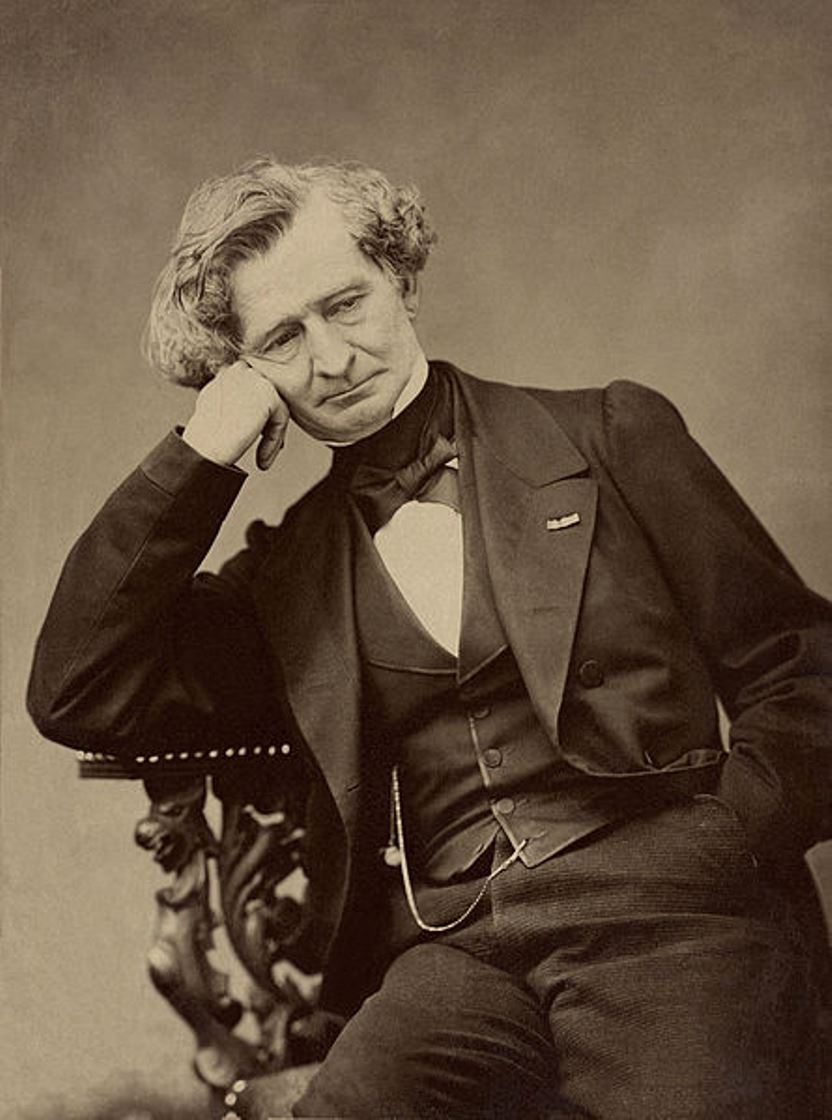


Hector Berlioz, full name Louis-Hector Berlioz, was a French composer, conductor, and music critic of the Romantic era.
Berlioz received his primary education from his father, an enlightened physician, who gave him his first lessons in music and Latin. By the age of 12, he was already composing music for local chamber ensembles and learning to play the guitar and flute with virtuosity. In 1821 his father sent him to Paris to study medicine, and he received his first scientific degree. But in parallel, he often visited the Paris Opera, where he studied the entire repertoire on the score.
Against the will of his parents, Berlioz took a compulsory course of study at the Conservatory of Paris and in 1830 received the Prix de Rome. In Italy he met the Russian composer Mikhail Glinka and became lifelong friends with Mendelssohn. From 1832 Berlioz worked for 30 years as a music critic for periodicals. He was acquainted with many of the leading writers and musicians of his time, including Victor Hugo, Alexandre Dumas, Niccolò Paganini, and George Sand.
Berlioz adored the works of Weber and Beethoven, as well as Gluck, and tirelessly introduced audiences to their works. As a result of his many trips as a conductor to Germany, Belgium, England, Russia, and Austria-Hungary, he taught the leading orchestras of Europe a new style.
Berlioz during these years wrote, among other things, the "Symphonie Fantastique" (1830) that made him famous, and the symphony "Harold in Italy" (1834). After a concert in 1838, where he conducted their performance, the famous violin virtuoso Paganini declared Hector Berlioz a continuator of Beethoven's musical traditions and presented him with 20,000 francs. A grateful Berlioz wrote a choral symphony, Romeo and Juliet, dedicated to Paganini.
In 1844, Berlioz created "Treatise on Modern Instrumentation and Orchestration", which is not just a technical manual, it served as an introduction to the aesthetics of expression in music for generations to come. Among Berlioz's dramatic works, The Damnation of Faust (1846) and The Nativity (1854) are world-famous.