sparrow
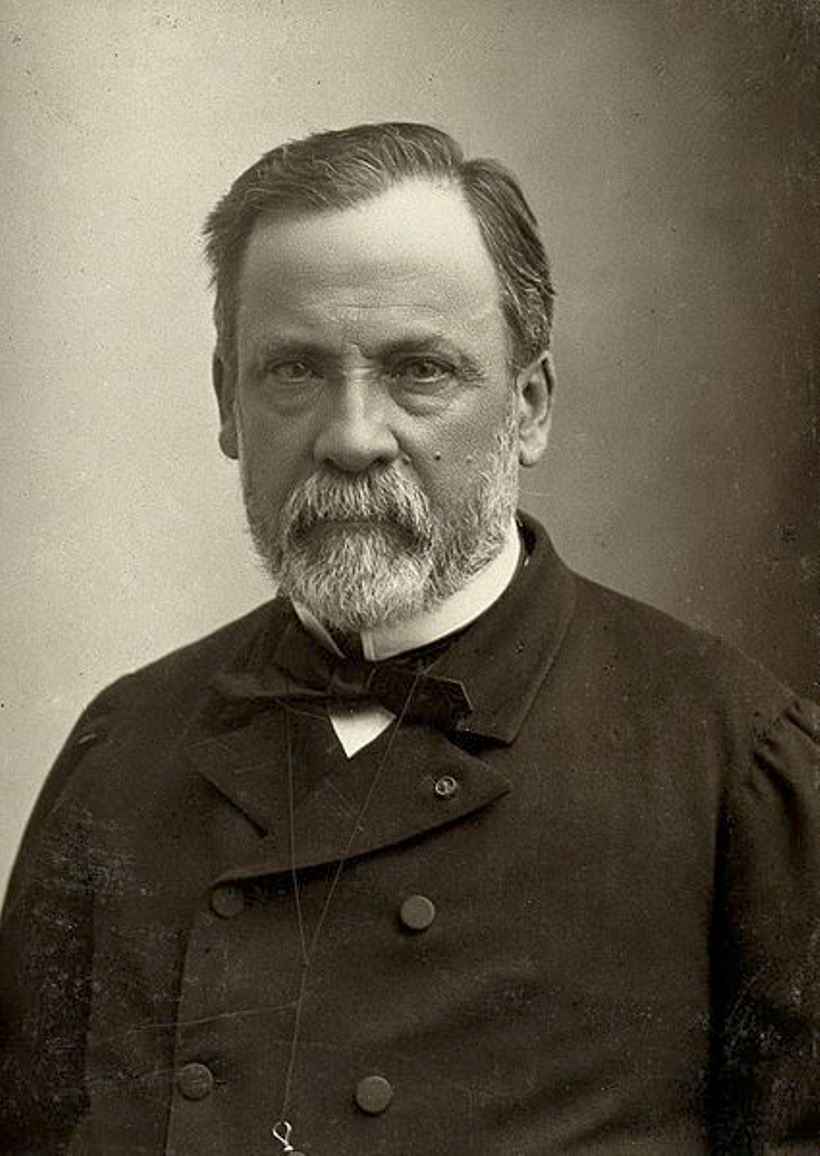




Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and the founder of microbiology and vaccination.
Pasteur received a bachelor of arts and sciences from the Royal College of Besançon and a doctorate from the École Normale in Paris, then spent several years as a researcher and teacher at the Lycée de Dijon. In 1848 he became professor of chemistry at the University of Strasbourg, and in the following year began to study the nature of wine fermentation, which began his revolutionary journey of most important scientific discoveries.
He invented a way to kill bacteria by boiling and then cooling the liquid, a process known today as pasteurization. Pasteur discovered the first vaccine in 1879 when he was exposed to a disease called chicken cholera. By accidentally exposing chickens to a weakened form of the culture, he demonstrated that they became resistant to the actual virus. Pasteur subsequently expanded his theory of germs and developed causes and vaccines against anthrax, cholera, tuberculosis, and smallpox, and the success of Pasteur's rabies vaccine in 1885 brought him worldwide fame.
Louis Pasteur's contribution to science, technology and medicine cannot be overemphasized. He pioneered the study of molecular asymmetry; discovered that microorganisms cause fermentation and disease; invented the process of pasteurization; saved the brewing, wine and silk industries in France; developed vaccines against the dreaded diseases anthrax and rabies, which saved millions of lives.
In 1873, Pasteur was elected an associate member of the Academy of Medicine, in 1882 - a member of the French Academy, and in 1888 in Paris was opened the Pasteur Institute. He was also awarded France's highest honor, the Legion of Honor.
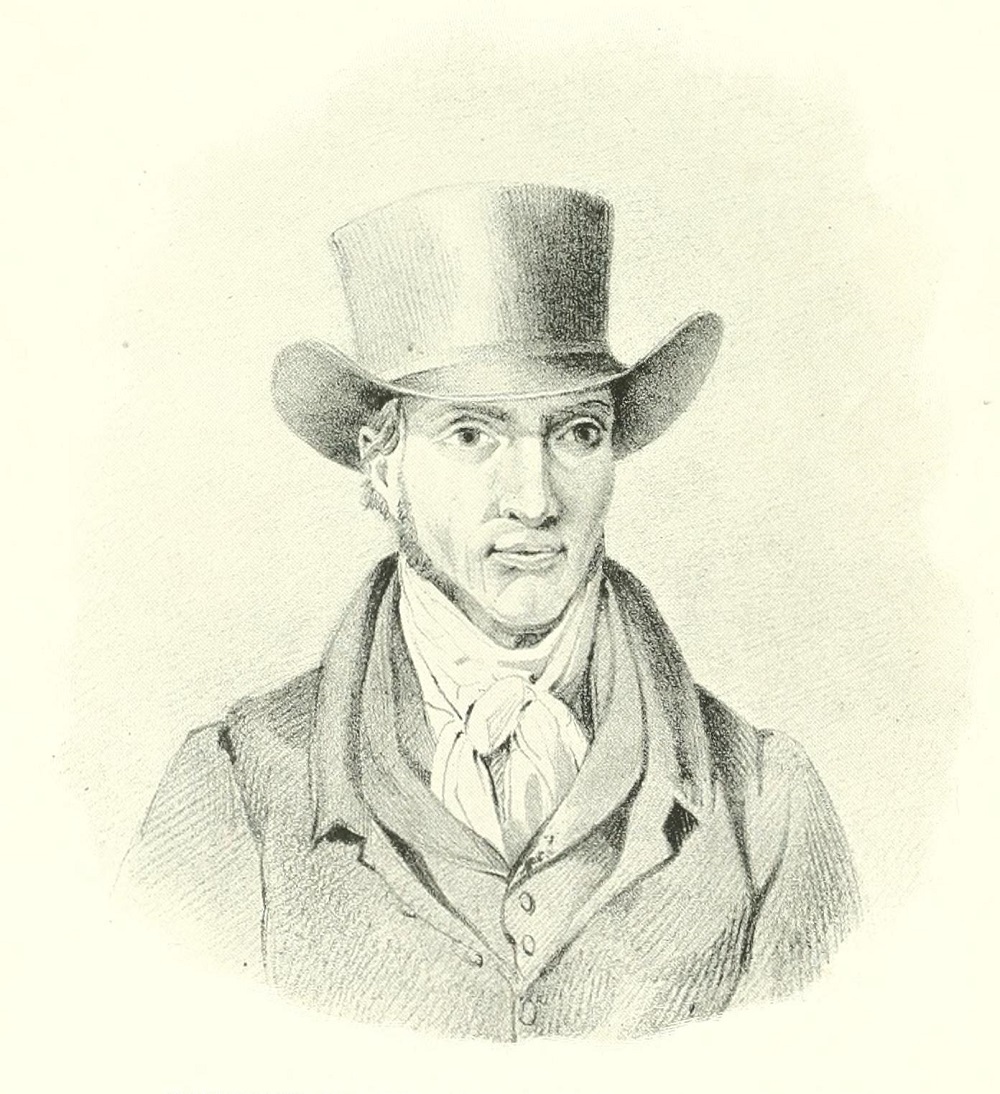


Henry Thomas Alcken was an English painter and engraver chiefly known as a caricaturist and illustrator of sporting subjects and coaching scenes. His most prolific period of painting and drawing occurred between 1816 and 1831.
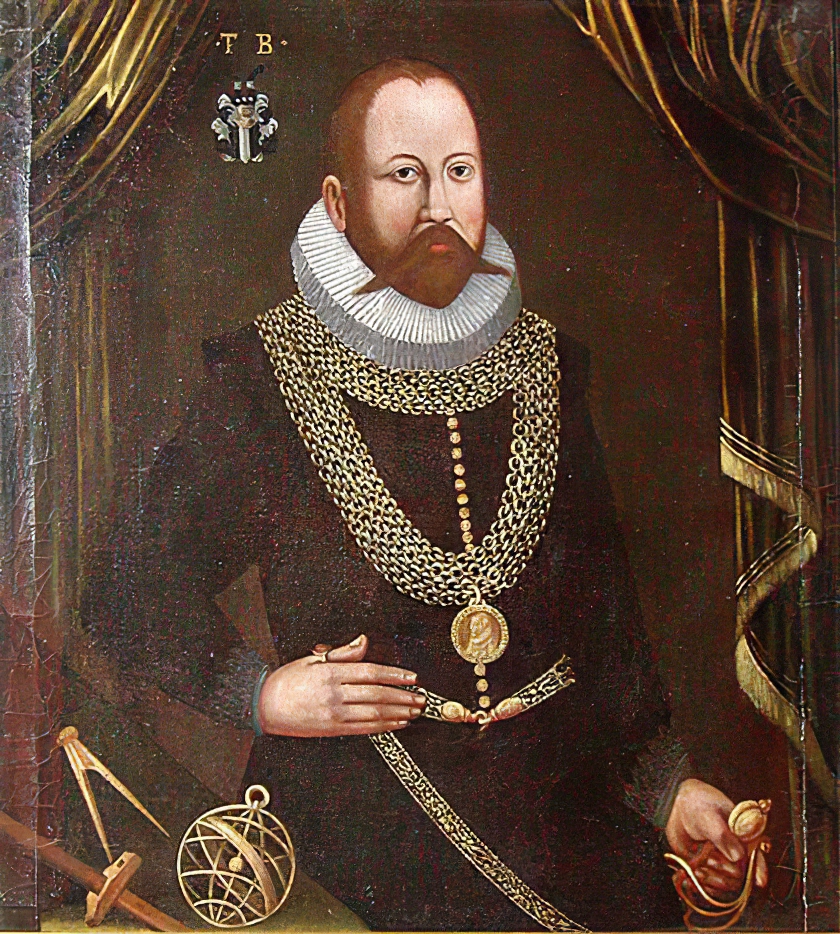


Tycho Brahe, born Tyge Ottesen Brahe, more commonly called Tycho, was a prominent Danish astronomer, astrologer, and alchemist of the Renaissance.
As a young man he traveled extensively throughout Europe, studying in Wittenberg, Rostock, Basel, and Augsburg and acquiring mathematical and astronomical instruments. In 1572 Tycho unexpectedly even for himself discovered a new star in Cassiopeia, and the publication of this turned the young Dane into an astronomer of European reputation. For further astronomical research he established an observatory and gathered around him modern progressive scientists.
Besides practicing astronomy, Tycho was an artist, scientist, and craftsman, and everything he undertook or surrounded himself with had to be innovative and beautiful. He even founded a printing house to produce and bind his manuscripts in his own way, and he perfected sanitary ware for convenience. His development of astronomical instruments and his work in measuring and fixing the positions of the stars laid a solid foundation for future discoveries.
Tycho's observations - the most accurate possible before the invention of the telescope - included a comprehensive study of the solar system and the precise positions of more than 777 fixed stars. What Tycho accomplished using only his simple instruments and intellect remains a remarkable achievement of the Renaissance.