strützel &
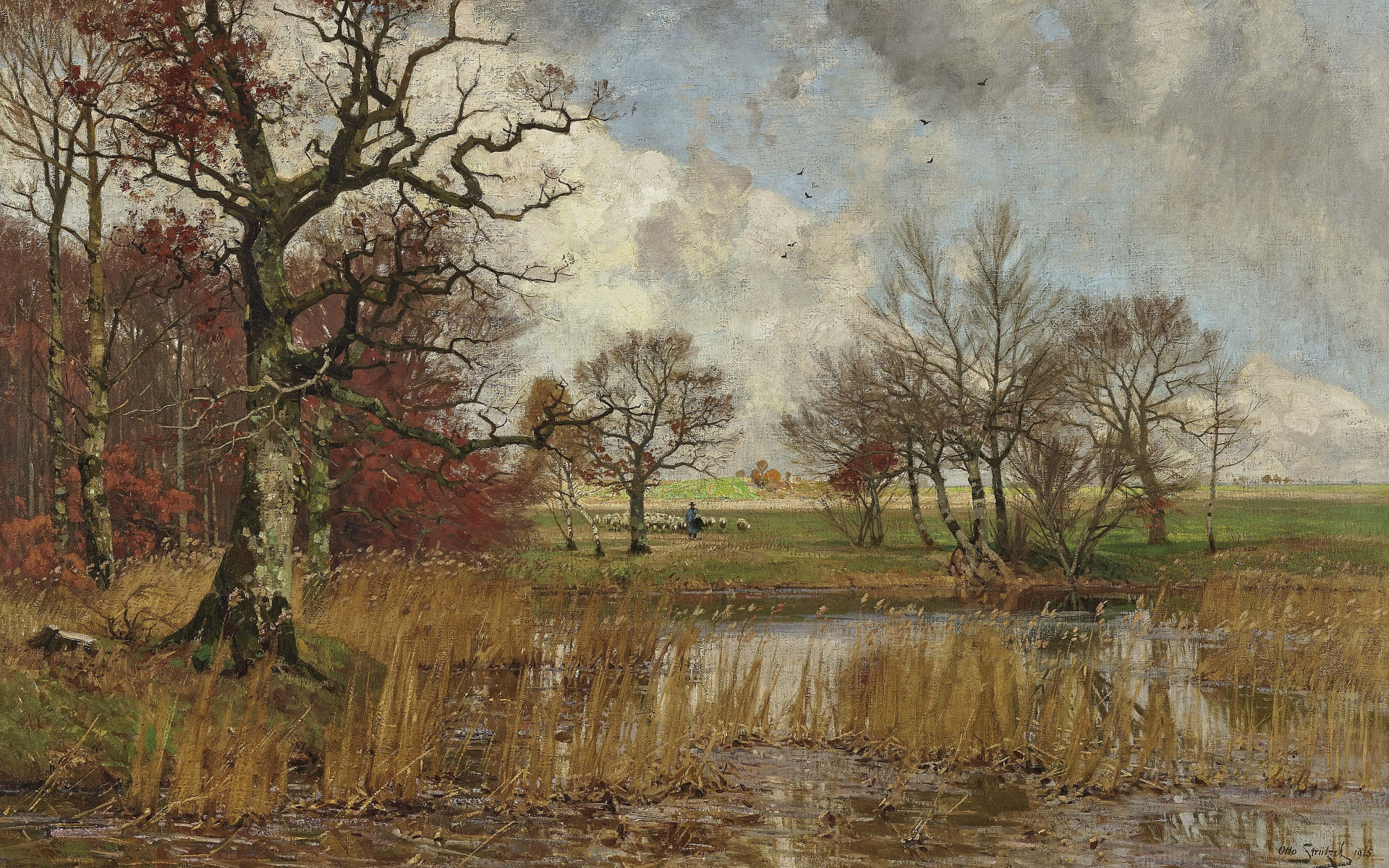

Leopold Otto Strützel was a German artist of the last third of the nineteenth and first third of the twentieth centuries. He is known as a landscape and animal painter, graphic artist and illustrator.
Strützel often depicted horses, bulls, peasants in the fields and shepherds with their flocks in his landscapes around Dachau, on the banks of the Isar River in Munich and elsewhere. He also created templates for greeting cards. Some of his works were lost in a fire in 1931. In total, he created about 773 works.


Leopold Otto Strützel was a German artist of the last third of the nineteenth and first third of the twentieth centuries. He is known as a landscape and animal painter, graphic artist and illustrator.
Strützel often depicted horses, bulls, peasants in the fields and shepherds with their flocks in his landscapes around Dachau, on the banks of the Isar River in Munich and elsewhere. He also created templates for greeting cards. Some of his works were lost in a fire in 1931. In total, he created about 773 works.


Leopold Otto Strützel was a German artist of the last third of the nineteenth and first third of the twentieth centuries. He is known as a landscape and animal painter, graphic artist and illustrator.
Strützel often depicted horses, bulls, peasants in the fields and shepherds with their flocks in his landscapes around Dachau, on the banks of the Isar River in Munich and elsewhere. He also created templates for greeting cards. Some of his works were lost in a fire in 1931. In total, he created about 773 works.
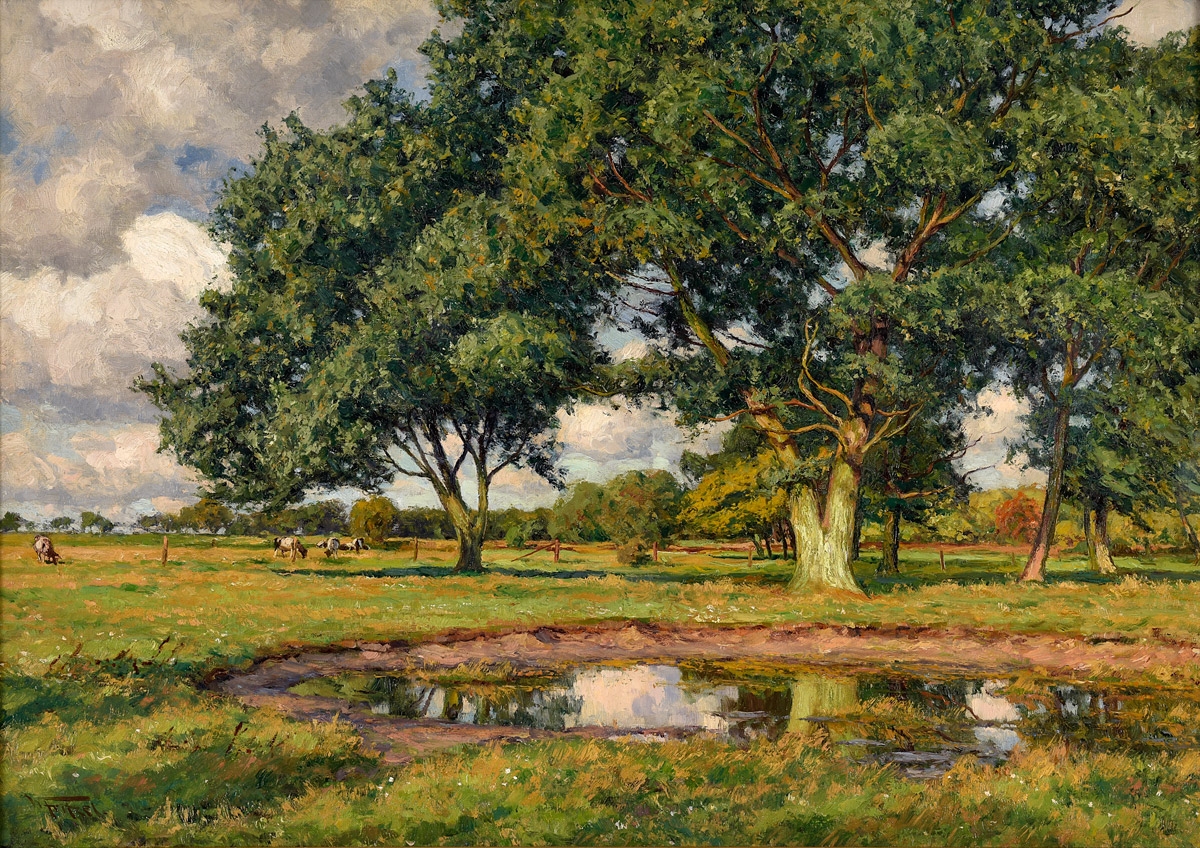


Wilhelm Fritzel was a German impressionist painter and master of rural landscape painting.


Wilhelm Fritzel was a German impressionist painter and master of rural landscape painting.
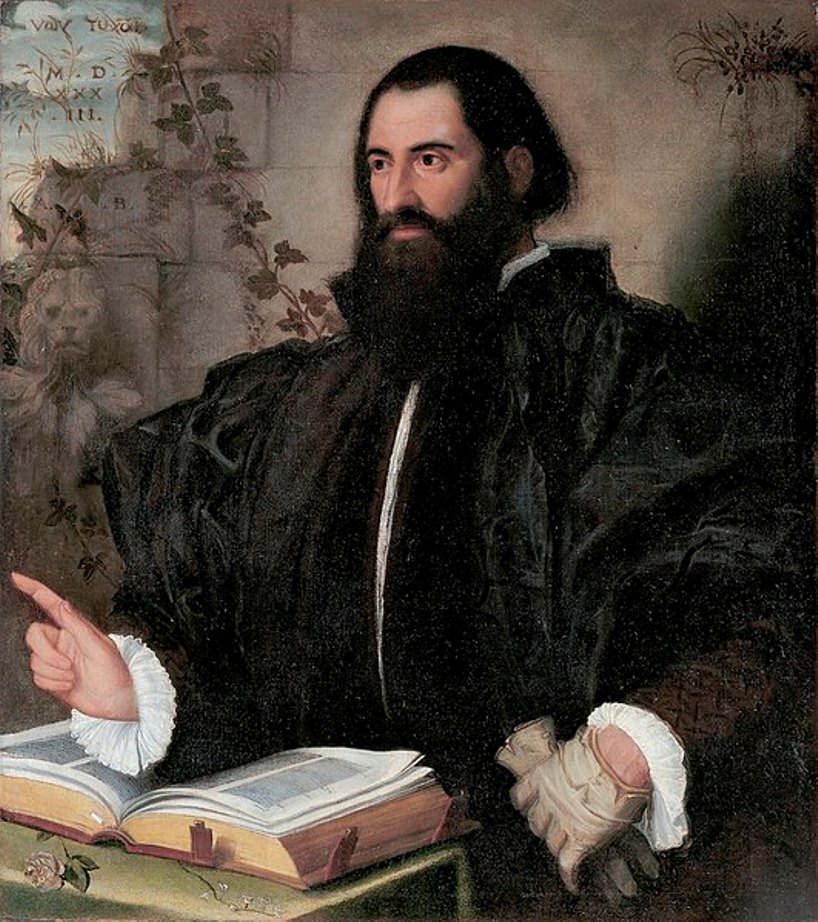


Pietro Andrea Gregorio Mattioli was a 16th-century Italian physician, botanist and pharmacist.
Mattioli studied medicine in Padua and obtained a medical practice first in his hometown. Later, in the 1555-1560s, he served as personal physician to the imperial court of Ferdinand II, Archduke of Austria, and Emperor Maximilian II. This high position allowed him to test the effects of poisonous plants on prisoners for scientific purposes.
Mattioli published several scientific works in which he included many of his own observations on the flora of the Alps, including previously unexplored plants. These works, based on the study of books by predecessor scientists, gave impetus to the development of botany throughout Italy at the time. Mattioli kept up a lively correspondence with other researchers, describing specimens of rare plants received from them. The genus of flowering plants Matthiola is named after Mattioli.
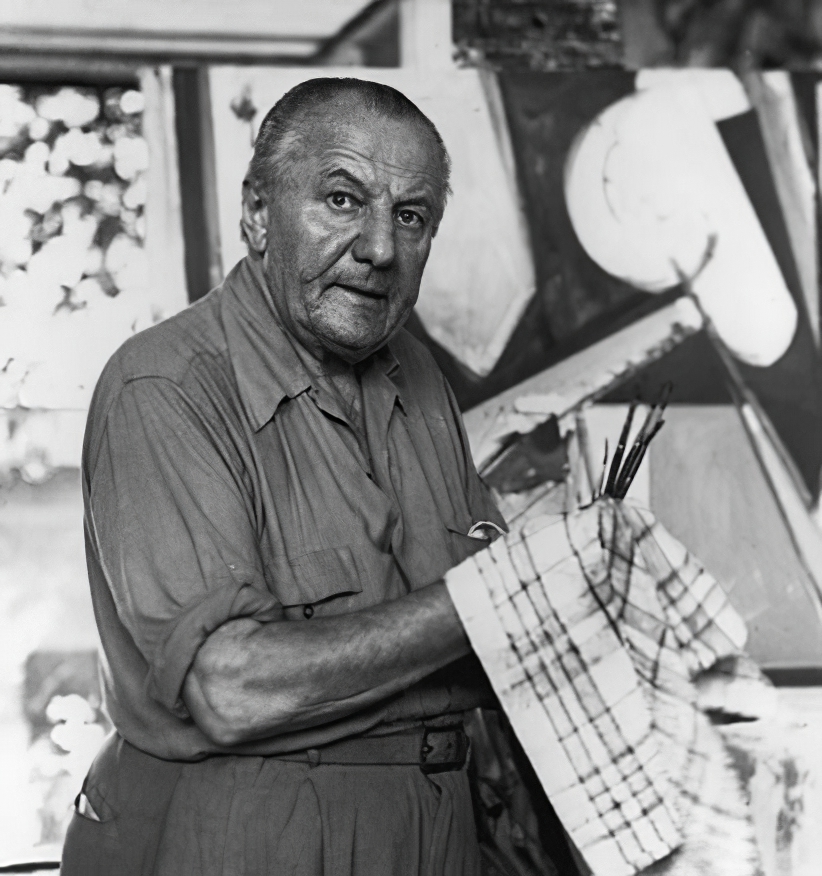


Hans Hofmann, a German-American painter, stands as a towering figure in the 20th-century art world, celebrated for his vibrant contributions to abstract expressionism. Born in Germany in 1880, Hofmann's journey in art took him across continents, from Europe to the United States, where his innovative teaching methods and bold, color-filled canvases left an indelible mark on generations of artists. His unique approach to painting, characterized by a dynamic interplay of color and form, helped bridge the gap between the European modernist traditions and the emerging American abstract art scene.
Hofmann's work is distinguished by its intense color palettes and the technique he termed "push and pull," which refers to the careful balance of color and shape to create depth and movement within the canvas. This technique not only showcased his mastery over the medium but also influenced the development of abstract expressionism, making Hofmann a pivotal figure among his contemporaries. His paintings, such as "The Gate" (1959-60), exemplify this approach and are celebrated in prestigious museums worldwide, including the Museum of Modern Art in New York and the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art.
Beyond his personal contributions as an artist, Hofmann was an esteemed educator, guiding the next generation of artists through his schools in New York and Provincetown. His teaching philosophy emphasized the importance of understanding the fundamental elements of art—color, form, and space—and their interrelation, which he believed was key to achieving harmony and expression in painting.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Hans Hofmann's works represent not just significant artistic achievements but also valuable pieces of cultural history. His paintings and teachings continue to inspire and influence the art world, making his pieces highly sought after in galleries and auctions.
We invite you to sign up for updates on new product sales and auction events related to Hans Hofmann. This subscription is your gateway to owning a piece of art history, ensuring you're informed of the latest opportunities to add to your collection. Join us in celebrating the legacy of a master whose work transcends time and continues to dazzle the art world.


Leonhart Fuchs was a German humanist scientist, botanist, and physician.
Fuchs received a humanistic education under Catholic guidance, but later became a Protestant. He studied medicine and became a professor in Tübingen. He was most interested in the medicinal properties of plants. Well acquainted with the Greek and Latin classics and an excellent observer, he gave precise descriptions, and his beautiful engravings of plants established the tradition of depicting plants with precise illustrations and in alphabetical order.
In 1542 Fuchs published his most important work, De Historia Stirpium Commentarii Insignes (Famous Commentaries on the History of Plants). The book was a great success, especially because of the magnificent woodcuts and the 487 plants, which were described for the first time in such a systematic form. De Historia Stirpium survived several editions and was translated into Dutch and German.

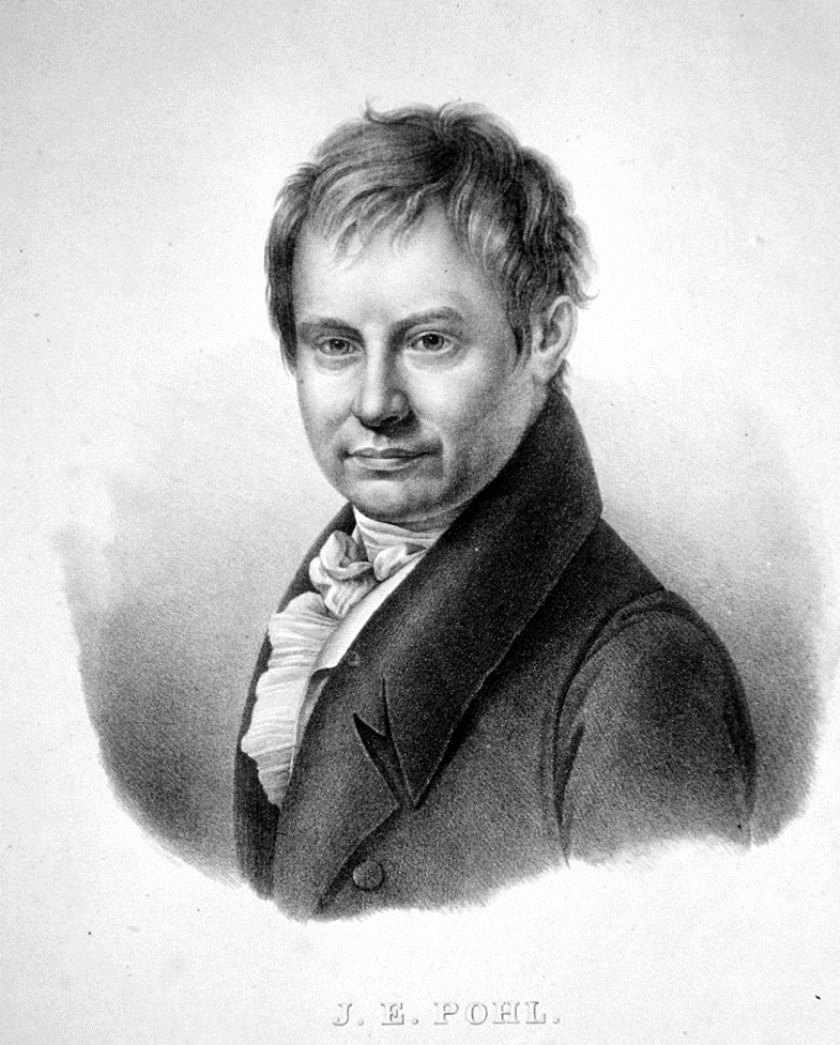
Johann Baptist Emanuel Pohl was an Austrian and Czech scientist, botanist, naturalist, and traveler.
Pohl studied in Prague, earned a doctorate in medicine and practiced science, becoming one of the most prominent botanists in Bohemia. Consequently, he was invited on an expedition to Brazil. Johann Pohl arrived in Brazil in 1817 with the Italian botanist Giuseppe Raddi as part of a large scientific expedition sent by Francis I of Austria, and spent four years traveling through the states of Minas Gerais, Goias, Bahia, and Rio de Janeiro, including some 30 rivers in the country. He collected thousands of plant specimens, as well as studying minerals and zoology, exploring gold and diamond mines, caves, and villages of local people.
After his return to Europe, Pohl served as curator of the Vienna Museum of Natural History and the Museum of Brazil in Vienna until his death. His extensive collections, including some 4,000 plant specimens, were housed here along with the expedition's other scientific collections.
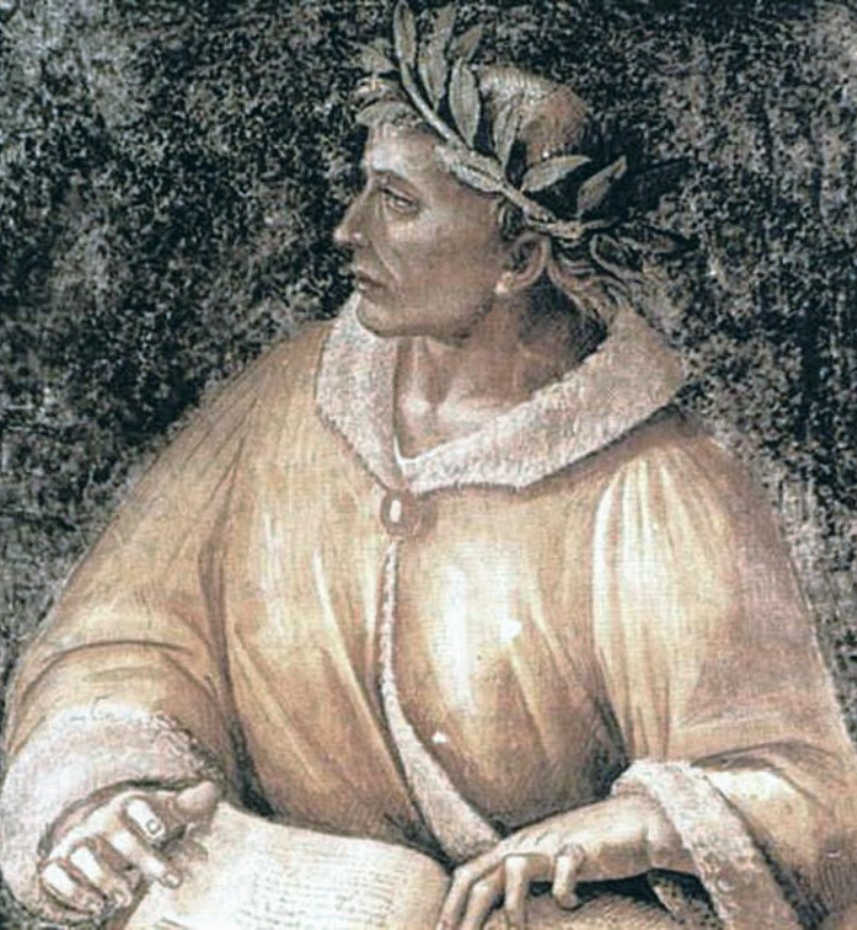


Publius Ovidius Naso, known as Ovidius (Ovid), was an ancient Roman poet who lived during the reign of Emperor Augustus.
Most of the information about the life and work of Ovid, scholars have drawn from his own works, as well as from the works of Seneca the Elder and Marcus Fabius Quintilianus. Ovid was from a fairly high class of "horsemen", studied rhetoric at the maestros of oratory of the ancient Roman Empire, and then went traveling, visiting Athens, Asia Minor and Sicily. As a young man, Ovid held minor public offices, was a member of the college of civil affairs, and served in an office that performed spiritual and secular duties at the state level.
However, Ovid was much more attracted to poetry, and he resigned and about 29-25 BC joined the circle of those chosen under the patronage of Marcus Valerius Messala Corvinus. After publishing Amores, a collection of love-erotic lyrics, around 15-16 BC, Ovid became one of Rome's most popular poets. He became famous for his works in the genre of elegy, as well as for his epic poem Metamorphoses (8 AD), which became one of the most important sources in the study of classical mythology.
For reasons unknown to us, in 8 A.D. Ovid was disgraced and exiled for the rest of his life to Tomes on the Black Sea, where he wrote his "Mournful Elegies" and a poem cycle entitled "Letters from Pontus". A contemporary of Virgil and Horace, Ovid was one of the three canonical representatives of Latin literature.
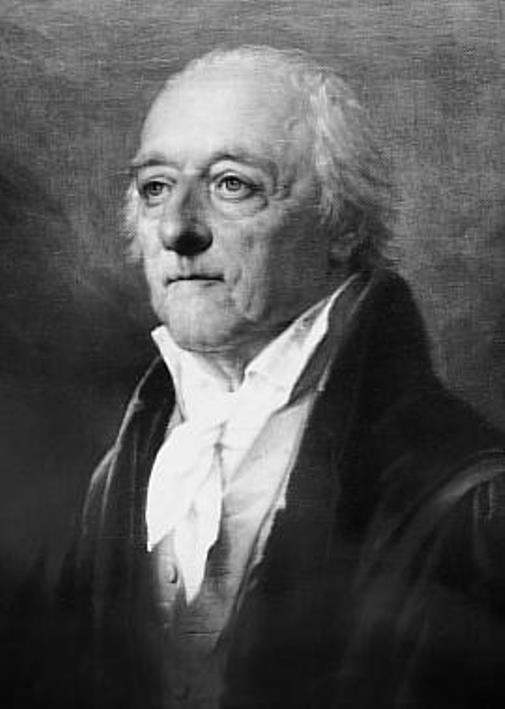


Nikolaus von Jacquin, full name Nikolaus Joseph Freiherr von Jacquin, also Baron Nikolaus von Jacquin, was an Austrian and Dutch scientist, professor of chemistry and botany, and director of the Vienna Botanical Garden.
Jacquin is considered a pioneer of scientific botany in Austria. He wrote fundamental works in botany, was the first to describe many plants, fungi, and animals, introduced experimental methods in chemistry, and successfully campaigned for the introduction of Linnaeus' system of plants in Austria. On behalf of Emperor Franz I, von Jacquin was in charge of the imperial gardens (including Schoenbrunn) and also led a scientific expedition to Central America from 1754 to 1759, from which he returned with an extensive collection of plants.
In 1768, Nikolaus von Jacquin was appointed professor of botany and chemistry at the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Vienna and director of the newly founded botanical garden, which he reorganized according to scientific principles. Nikolaus von Jacquin was a member of the Royal Society of London, a foreign honorary member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, and a correspondent of the Paris Academy of Sciences.