volcano




William Hamilton was an English artist and illustrator.




Athanasius Kircher was a German scholar, inventor, professor of mathematics and oriental studies, and a friar of the Jesuit order.
Kircher knew Greek and Hebrew, did scientific and humanities research in Germany, and was ordained in Mainz in 1628. During the Thirty Years' War he was forced to flee to Rome, where he remained for most of his life, serving as a kind of intellectual and information center for cultural and scientific information drawn not only from European sources but also from an extensive network of Jesuit missionaries. He was particularly interested in ancient Egypt and attempted to decipher hieroglyphics and other riddles. Kircher also compiled A Description of the Chinese Empire (1667), which was long one of the most influential books that shaped the European view of China.
A renowned polymath, Kircher conducted scholarly research in a variety of disciplines, including geography, astronomy, mathematics, languages, medicine, and music. He wrote some 44 books, and more than 2,000 of his manuscripts and letters have survived. He also assembled one of the first natural history collections.
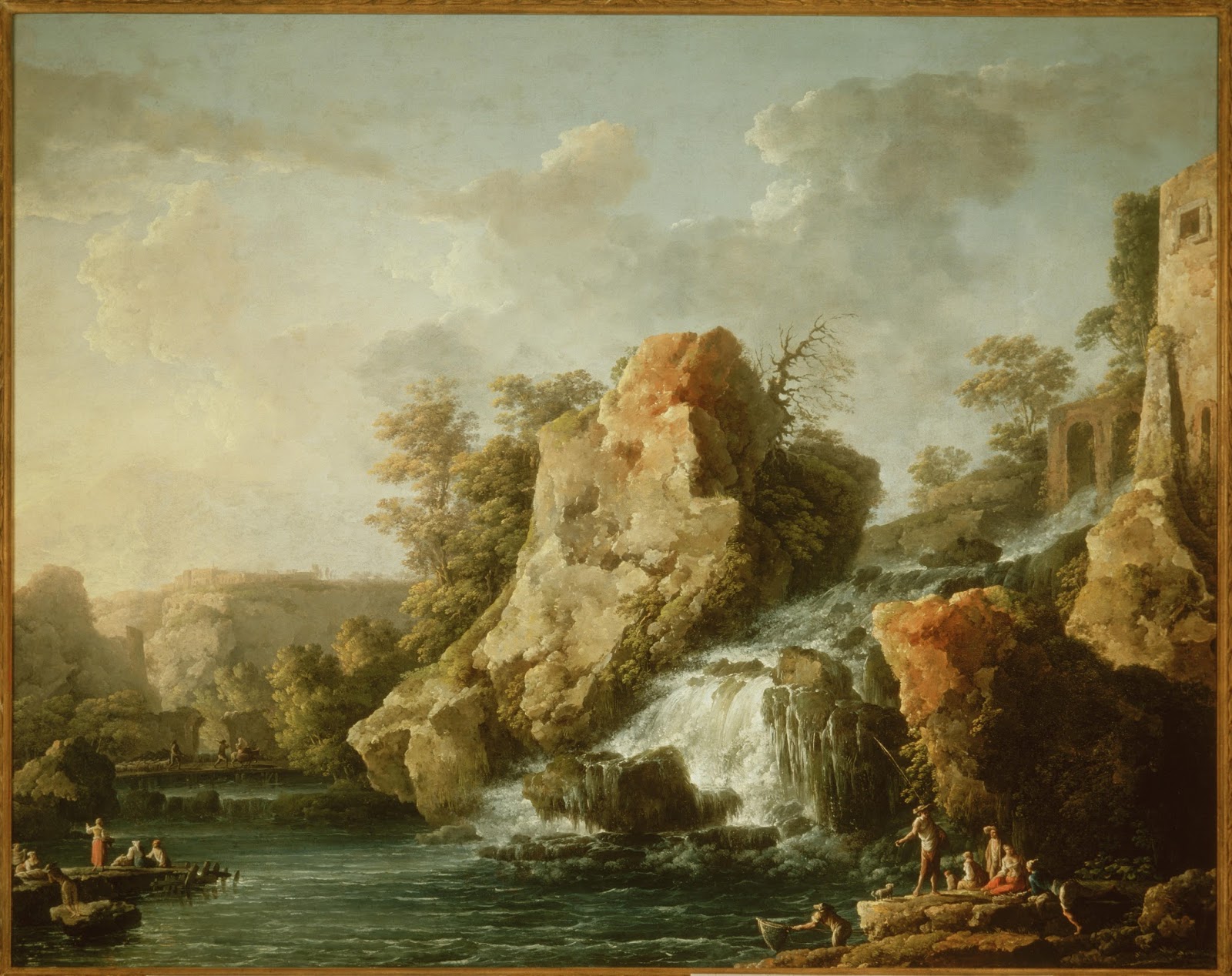




Carlo Bonavia was an Italian painter known for idyllic landscape paintings, engravings and drawings.
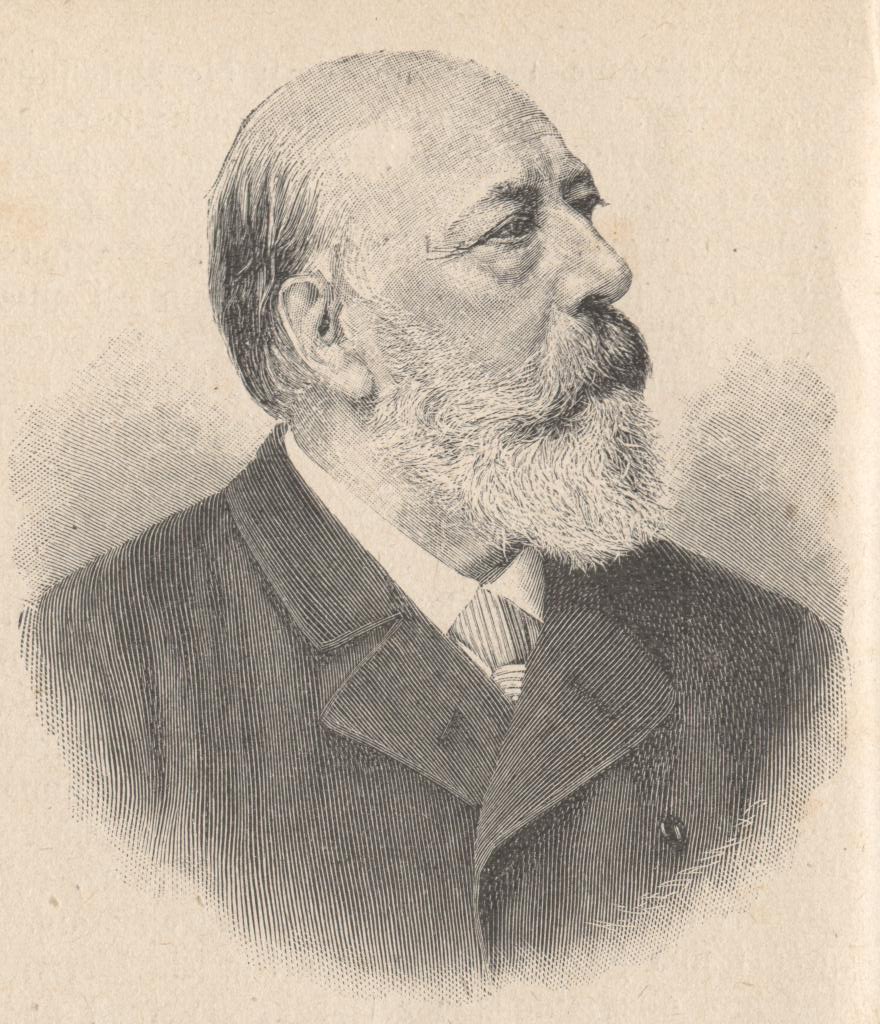


Andreas Achenbach was a German landscape and seascape painter in the Romantic style. He is considered to be one of the founders of the Düsseldorf School.[citation needed] His brother, Oswald, was also a well known landscape painter. Together, based on their initials, they were known as the "Alpha and Omega" of landscape painters.
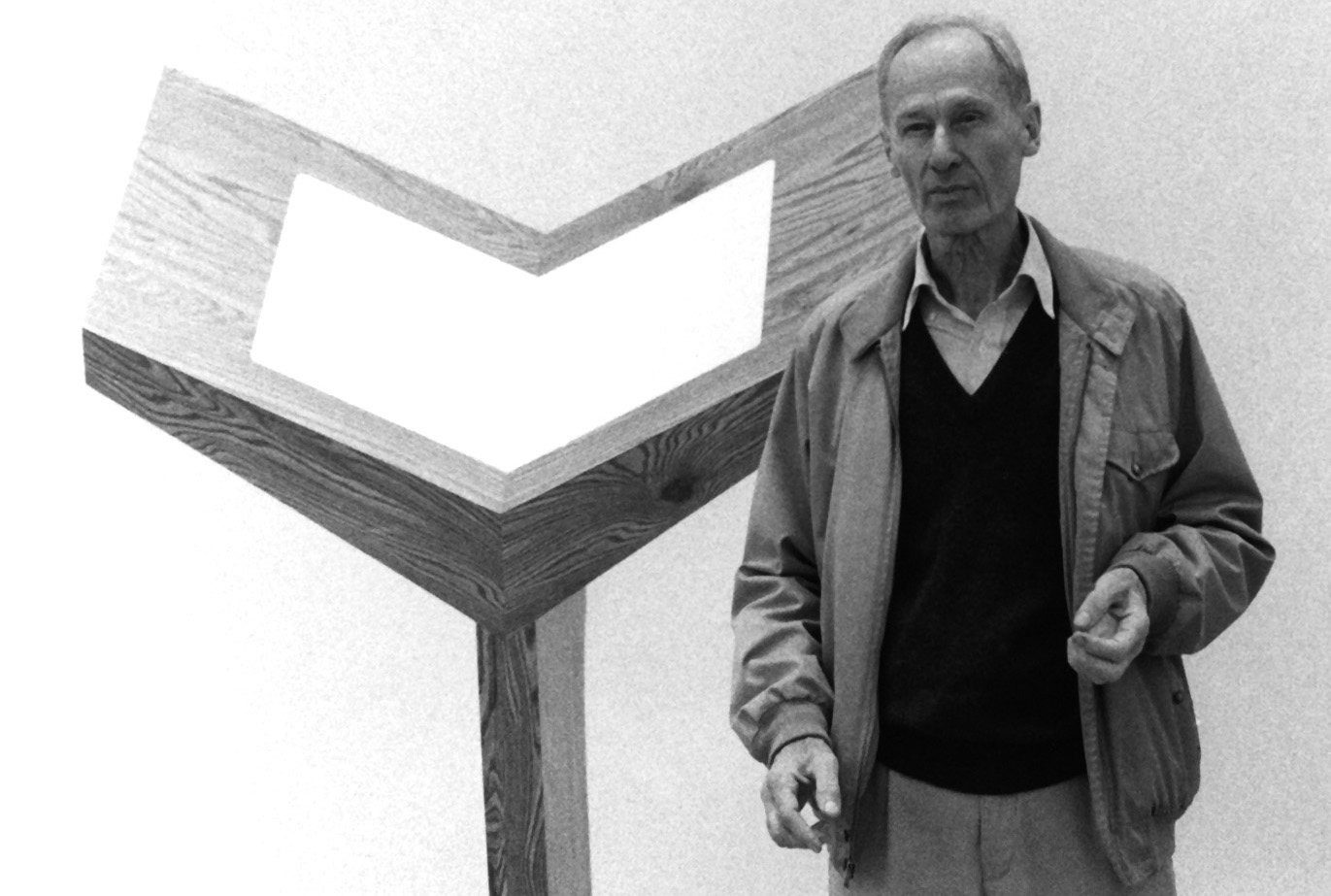


Richard Ernst Artschwager was an American painter, illustrator and sculptor. His work has associations with Pop Art, Conceptual art and Minimalism.
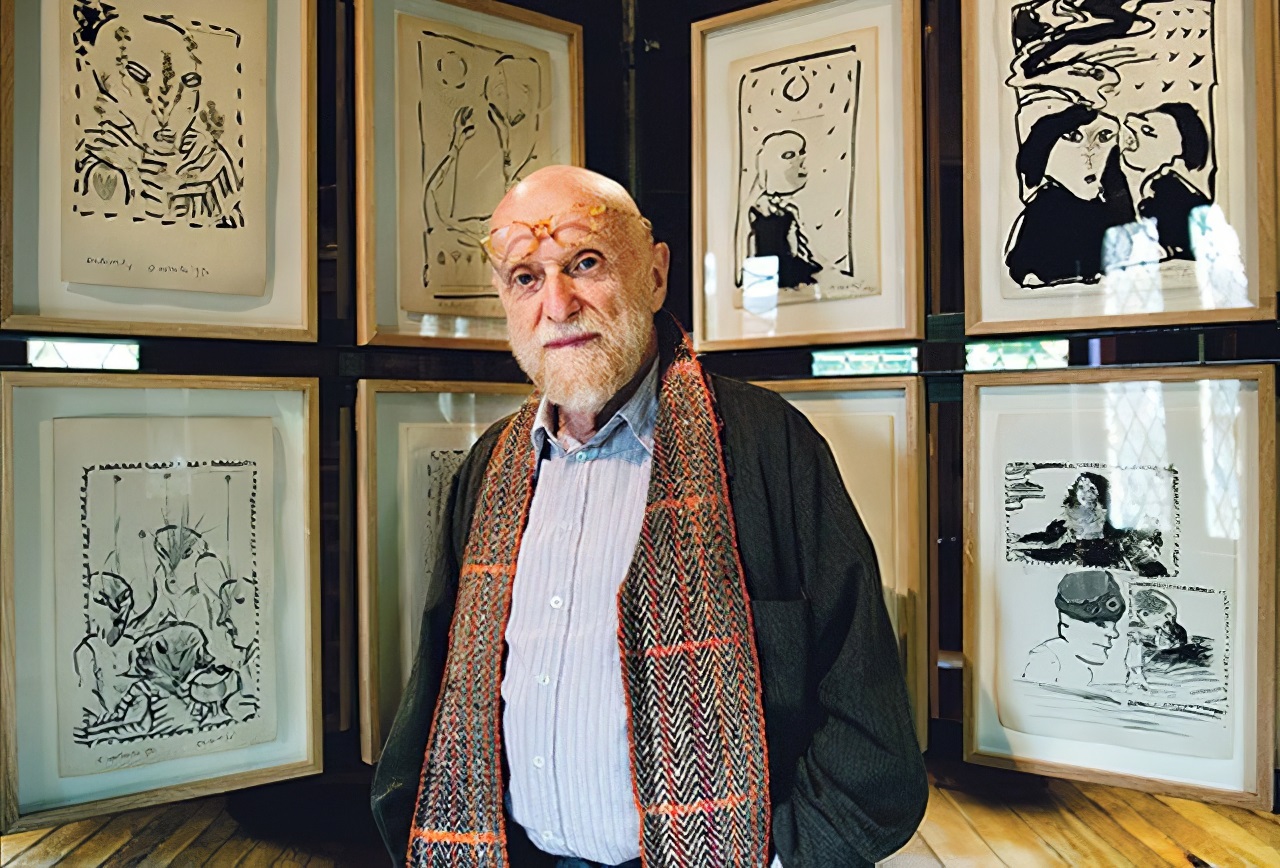


Pierre Alechinsky is a Belgian artist. He has lived and worked in France since 1951. His work is related to tachisme, abstract expressionism, and lyrical abstraction.
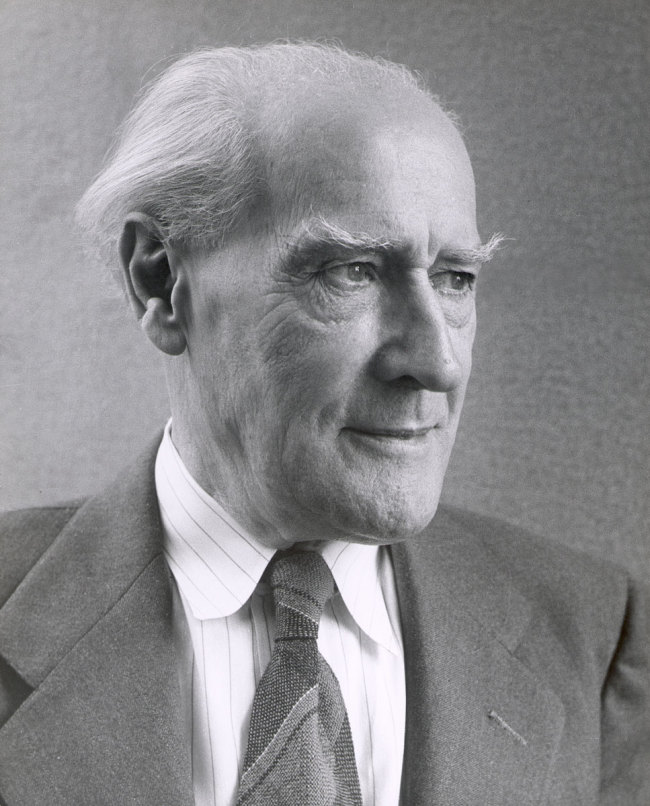


Lyonel Charles Adrian Feininger was an American-German artist renowned for his unique integration of Expressionism, Cubism, and Bauhaus principles. His body of work, which spans several critical decades in modernism's development, is celebrated for its distinctive blend of architectural and nautical motifs, articulated through planar shifts and jagged lines of Cubism, with a vibrant Orphist color palette.
Lyonel Feininger's journey as an artist began in earnest when he was 36, becoming a pivotal figure in various German expressionist groups and a founding member of the Bauhaus, where he led the printmaking workshop. His art, which also includes significant contributions to caricature and photography, explores the intricate relationship between humanity and industrialization, evident in his depictions of architectural and mechanized forms.
His work was subject to Nazi criticism, being labeled as "degenerate," which led to his return to the United States, where he continued to evolve his artistic style. Posthumously, Lyonel Feininger's art has been the focus of several retrospectives, and his pieces, like "Jesuits III," continue to fetch high figures at auctions, underscoring his lasting impact on the art world.
Notably, Lyonel Feininger's "Cathedral" woodcut, representing the Bauhaus's utopian vision, remains one of his most iconic works, symbolizing the integration of art and craftsmanship with its avant-garde yet traditional approach. His legacy is further carried by his sons, Andreas and T. Lux Feininger, who also made their marks in the arts.
For collectors and art and antiques experts, Feininger's work represents a fascinating intersection of various art movements and a testament to the enduring nature of expressive and innovative artistry. To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Lyonel Feininger, consider signing up for updates, ensuring you're informed about the latest opportunities to engage with his enduring legacy.






























![William Hamilton | Campi phlegraei. Paris, [1799-1802], a deluxe copy with plates in two states](/assets/image/picture_3552953/71e1c/swqxwjtgq1ugvnwqi2apzgfoiilhqdrokd3a-bot1khfha9pyeckuouug-95a3ll1699088974jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![William Hamilton | Campi phlegraei. Paris, [1799-1802], a deluxe copy with plates in two states](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3552953/71e1c/swqxwjtgq1ugvnwqi2apzgfoiilhqdrokd3a-bot1khfha9pyeckuouug-95a3ll1699088974jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)

















































