поль жув (1878 - 1973)
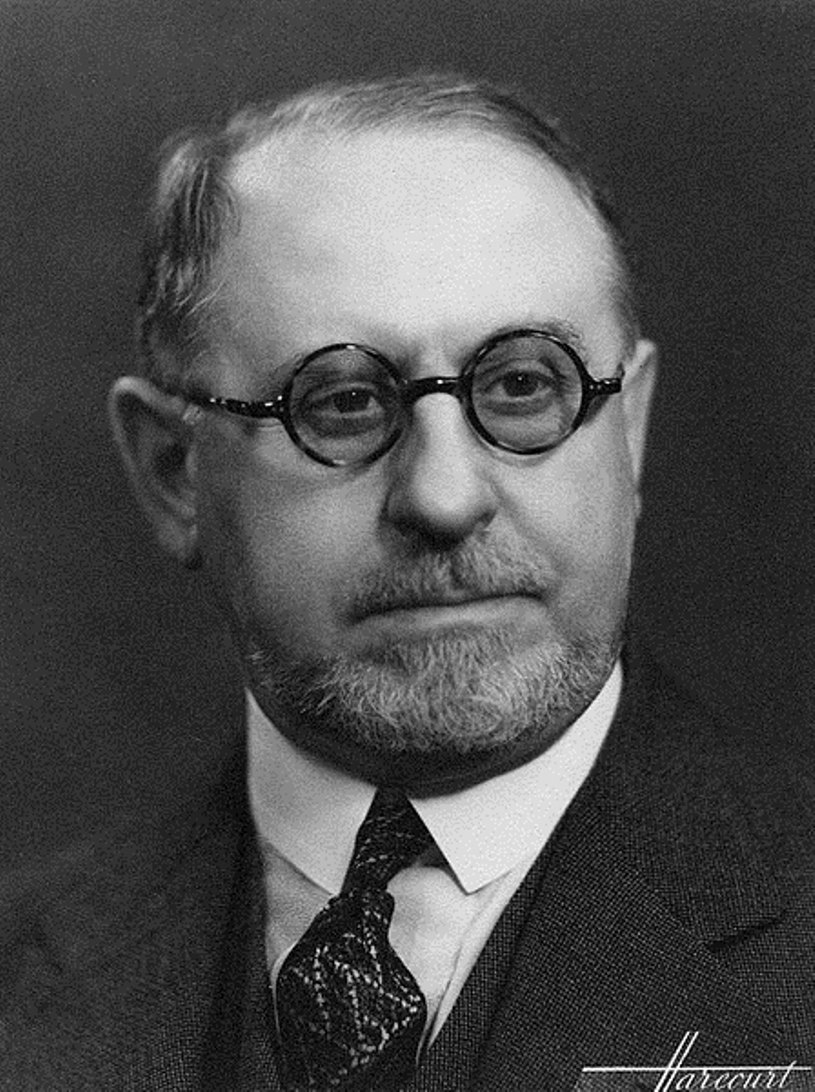

Pierre Paul Jouve was a French painter, sculptor and illustrator.
Paul was the son of painter and ceramicist Auguste Jouve, as a child he frequented the Jardin des Plantes and the Musée de la Histoire Naturelle de Paris and drew wild cats, which he fell in love with throughout his life. He entered the École des Arts Décoratifs and then the École des Beaux-Arts, exhibiting at the Salons from the age of 16. As part of the World Exhibition in 1900, Zhuv was commissioned by the architect René Binet to create a hundred-meter bas-relief frieze depicting wild animals.
In 1905, Marcel Bing organized the first solo exhibition of Paul Jouve, which featured 64 of his works. In 1907 Juve lived at the villa of French artists Abd el-Tif in Algeria, then went to Greece. After World War I he traveled to the Far East, visiting Ceylon, Saigon in the French colony of Cochinchin (now Vietnam), and Phnom Penh in Cambodia. He then explored the jungles of Africa. Paul Jouve became widely known for his paintings and sculptures depicting the animals of Africa. He was the first recipient of the Abd el-Tif Prize in 1907 and then the Indochina Prize in 1921.
Today, Paul Jouve is best remembered for his depictions of big cats and his illustration of an edition of Rudyard Kipling's The Jungle Book in collaboration with engraver F.L. Schmid (1873-1941), which was published in 1919. Juve became a director of the Society of Decorative Artists, and he was elected a member of the French Academy of Fine Arts in 1945. Throughout his long life, the artist continued to travel. He visited the United States and Bermuda, which inspired a panel entitled Poisson, which is now in the collection of the Museum of Fine Arts in Reims.
Paul Jouve died in his studio in Paris in 1973 at the age of 95.


Pierre Paul Jouve was a French painter, sculptor and illustrator.
Paul was the son of painter and ceramicist Auguste Jouve, as a child he frequented the Jardin des Plantes and the Musée de la Histoire Naturelle de Paris and drew wild cats, which he fell in love with throughout his life. He entered the École des Arts Décoratifs and then the École des Beaux-Arts, exhibiting at the Salons from the age of 16. As part of the World Exhibition in 1900, Zhuv was commissioned by the architect René Binet to create a hundred-meter bas-relief frieze depicting wild animals.
In 1905, Marcel Bing organized the first solo exhibition of Paul Jouve, which featured 64 of his works. In 1907 Juve lived at the villa of French artists Abd el-Tif in Algeria, then went to Greece. After World War I he traveled to the Far East, visiting Ceylon, Saigon in the French colony of Cochinchin (now Vietnam), and Phnom Penh in Cambodia. He then explored the jungles of Africa. Paul Jouve became widely known for his paintings and sculptures depicting the animals of Africa. He was the first recipient of the Abd el-Tif Prize in 1907 and then the Indochina Prize in 1921.
Today, Paul Jouve is best remembered for his depictions of big cats and his illustration of an edition of Rudyard Kipling's The Jungle Book in collaboration with engraver F.L. Schmid (1873-1941), which was published in 1919. Juve became a director of the Society of Decorative Artists, and he was elected a member of the French Academy of Fine Arts in 1945. Throughout his long life, the artist continued to travel. He visited the United States and Bermuda, which inspired a panel entitled Poisson, which is now in the collection of the Museum of Fine Arts in Reims.
Paul Jouve died in his studio in Paris in 1973 at the age of 95.


Pierre Paul Jouve was a French painter, sculptor and illustrator.
Paul was the son of painter and ceramicist Auguste Jouve, as a child he frequented the Jardin des Plantes and the Musée de la Histoire Naturelle de Paris and drew wild cats, which he fell in love with throughout his life. He entered the École des Arts Décoratifs and then the École des Beaux-Arts, exhibiting at the Salons from the age of 16. As part of the World Exhibition in 1900, Zhuv was commissioned by the architect René Binet to create a hundred-meter bas-relief frieze depicting wild animals.
In 1905, Marcel Bing organized the first solo exhibition of Paul Jouve, which featured 64 of his works. In 1907 Juve lived at the villa of French artists Abd el-Tif in Algeria, then went to Greece. After World War I he traveled to the Far East, visiting Ceylon, Saigon in the French colony of Cochinchin (now Vietnam), and Phnom Penh in Cambodia. He then explored the jungles of Africa. Paul Jouve became widely known for his paintings and sculptures depicting the animals of Africa. He was the first recipient of the Abd el-Tif Prize in 1907 and then the Indochina Prize in 1921.
Today, Paul Jouve is best remembered for his depictions of big cats and his illustration of an edition of Rudyard Kipling's The Jungle Book in collaboration with engraver F.L. Schmid (1873-1941), which was published in 1919. Juve became a director of the Society of Decorative Artists, and he was elected a member of the French Academy of Fine Arts in 1945. Throughout his long life, the artist continued to travel. He visited the United States and Bermuda, which inspired a panel entitled Poisson, which is now in the collection of the Museum of Fine Arts in Reims.
Paul Jouve died in his studio in Paris in 1973 at the age of 95.
.jpeg)
Jean Dunand was a Swiss and French painter, sculptor, metal craftsman and interior designer during the Art Deco period. He was particularly known for his lacquered screens and other art objects.

Pierre Paul Jouve was a French painter, sculptor and illustrator.
Paul was the son of painter and ceramicist Auguste Jouve, as a child he frequented the Jardin des Plantes and the Musée de la Histoire Naturelle de Paris and drew wild cats, which he fell in love with throughout his life. He entered the École des Arts Décoratifs and then the École des Beaux-Arts, exhibiting at the Salons from the age of 16. As part of the World Exhibition in 1900, Zhuv was commissioned by the architect René Binet to create a hundred-meter bas-relief frieze depicting wild animals.
In 1905, Marcel Bing organized the first solo exhibition of Paul Jouve, which featured 64 of his works. In 1907 Juve lived at the villa of French artists Abd el-Tif in Algeria, then went to Greece. After World War I he traveled to the Far East, visiting Ceylon, Saigon in the French colony of Cochinchin (now Vietnam), and Phnom Penh in Cambodia. He then explored the jungles of Africa. Paul Jouve became widely known for his paintings and sculptures depicting the animals of Africa. He was the first recipient of the Abd el-Tif Prize in 1907 and then the Indochina Prize in 1921.
Today, Paul Jouve is best remembered for his depictions of big cats and his illustration of an edition of Rudyard Kipling's The Jungle Book in collaboration with engraver F.L. Schmid (1873-1941), which was published in 1919. Juve became a director of the Society of Decorative Artists, and he was elected a member of the French Academy of Fine Arts in 1945. Throughout his long life, the artist continued to travel. He visited the United States and Bermuda, which inspired a panel entitled Poisson, which is now in the collection of the Museum of Fine Arts in Reims.
Paul Jouve died in his studio in Paris in 1973 at the age of 95.
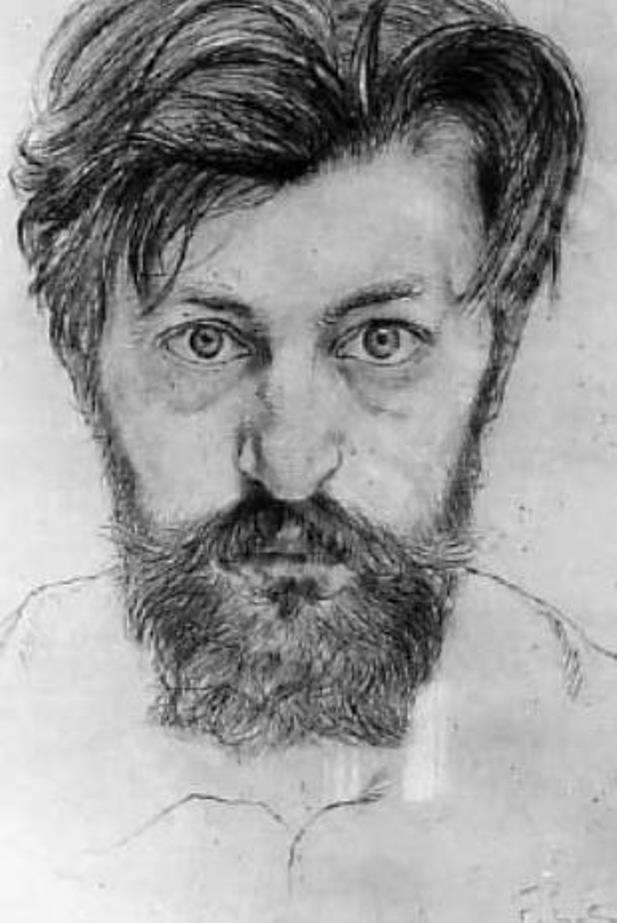


François-Louis Schmied was a French painter, illustrator, wood engraver, printmaker, editor and Art Deco binder.
François-Louis studied wood engraving at the École des Arts industriels in Geneva and painting at the École des Beaux-Arts de Genève. A Swiss, Schmied settled and naturalized in France in 1895. In 1910, he was commissioned to engrave and print Paul Jouve's illustrations for Rudyard Kipling's The Life of the Jungle, which was not published until 1919. For this book, now considered a masterpiece, the master produced about 90 color illustrations. Thanks to the success of this publication, Schmied was able to expand his activity and hire a group of craftsmen to execute his most famous and innovative works.
François-Louis Schmied is considered one of the greatest Art Deco artists and became particularly famous for his beautiful rare books for bibliophiles. Schmied's unique books were very expensive to produce, which required a lot of time and effort, and were always printed in very limited editions, from 20 to 200 copies. During the Great Depression, Schmied's expensive projects could not withstand the competition: the master was forced to sell off almost all his assets and close his workshop and store, and around 1932 he left for Morocco, where he died.
François-Louis Schmied's works are not only aesthetically pleasing, but also express his desire to combine art and literature. The talented artist conveyed with passion and precision the essence of the Art Deco style contemporary to him. Today, Schmied's works, reissued as fine art reproductions, not only convey the aesthetics and precision inherent in each of his originals, but also add a new dimension to them. His son, Theo Schmied, took over François-Louis Schmied's workshop in 1924, reviving its former glory and revitalizing it over time.

Pierre Paul Jouve was a French painter, sculptor and illustrator.
Paul was the son of painter and ceramicist Auguste Jouve, as a child he frequented the Jardin des Plantes and the Musée de la Histoire Naturelle de Paris and drew wild cats, which he fell in love with throughout his life. He entered the École des Arts Décoratifs and then the École des Beaux-Arts, exhibiting at the Salons from the age of 16. As part of the World Exhibition in 1900, Zhuv was commissioned by the architect René Binet to create a hundred-meter bas-relief frieze depicting wild animals.
In 1905, Marcel Bing organized the first solo exhibition of Paul Jouve, which featured 64 of his works. In 1907 Juve lived at the villa of French artists Abd el-Tif in Algeria, then went to Greece. After World War I he traveled to the Far East, visiting Ceylon, Saigon in the French colony of Cochinchin (now Vietnam), and Phnom Penh in Cambodia. He then explored the jungles of Africa. Paul Jouve became widely known for his paintings and sculptures depicting the animals of Africa. He was the first recipient of the Abd el-Tif Prize in 1907 and then the Indochina Prize in 1921.
Today, Paul Jouve is best remembered for his depictions of big cats and his illustration of an edition of Rudyard Kipling's The Jungle Book in collaboration with engraver F.L. Schmid (1873-1941), which was published in 1919. Juve became a director of the Society of Decorative Artists, and he was elected a member of the French Academy of Fine Arts in 1945. Throughout his long life, the artist continued to travel. He visited the United States and Bermuda, which inspired a panel entitled Poisson, which is now in the collection of the Museum of Fine Arts in Reims.
Paul Jouve died in his studio in Paris in 1973 at the age of 95.
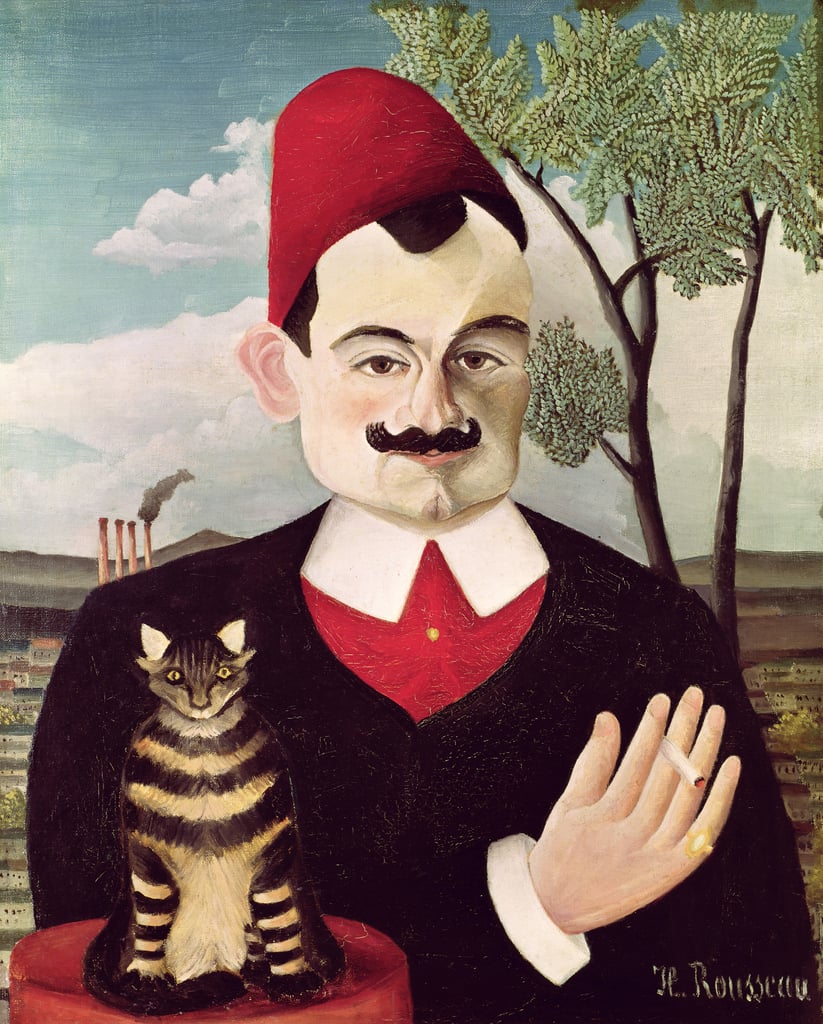

Pierre Loti, real name Louis Marie-Julien Viaud, was a French naval officer and novelist.
At the age of 17 he entered the naval school in Brest, then studied at École navale, the French naval academy. While pursuing a career as an officer in the navy, Louis Viaud began to think about writing. In 1872, he lived in Tahiti for several months and the result was Le Mariage de Loti (The Wedding of Loti), an autobiographical novel that began the fame of the writer Pierre Loti.
During his life he also visited Constantinople, the Holy Land, China, Algeria, British India, and Japan, writing a total of about 40 books. His colonial, mostly sentimental novels of life in exotic countries were very popular in Europe and in the United States, they were staged plays and films. In September 1920, Loti became an honorary citizen of Istanbul. He was also a member of the French Academy, Knight of the Grand Cross of the Legion of Honor.
Pierre Loti was also an avid collector, furnishing his Rochefort home in Orientalist and other styles, which today houses a museum of architectural eclecticism.










