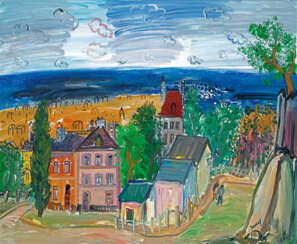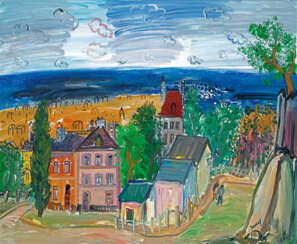a. carlos
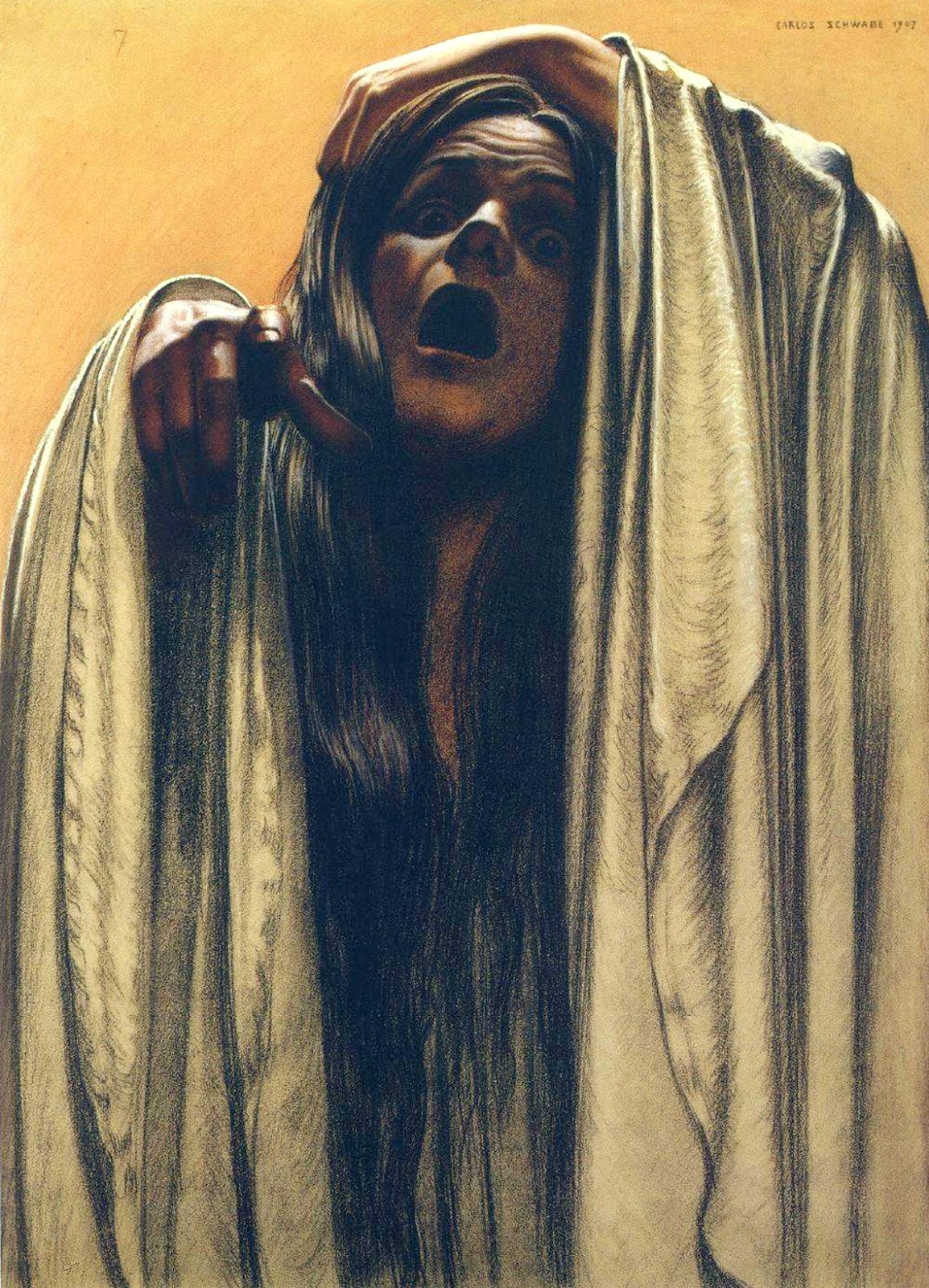

Carlos Schwabe (born Émile Martin Charles Schwab) was a Swiss Symbolist painter and printmaker.

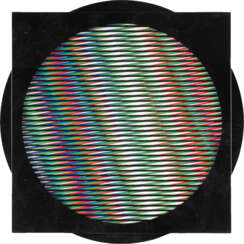
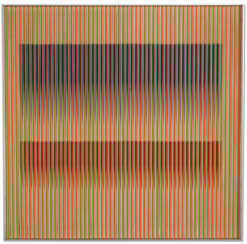
Carlos Cruz-Diez was a Venezuelan artist said by some scholars to have been "one of the greatest artistic innovators of the 20th century."


Carlos Schwabe (born Émile Martin Charles Schwab) was a Swiss Symbolist painter and printmaker.






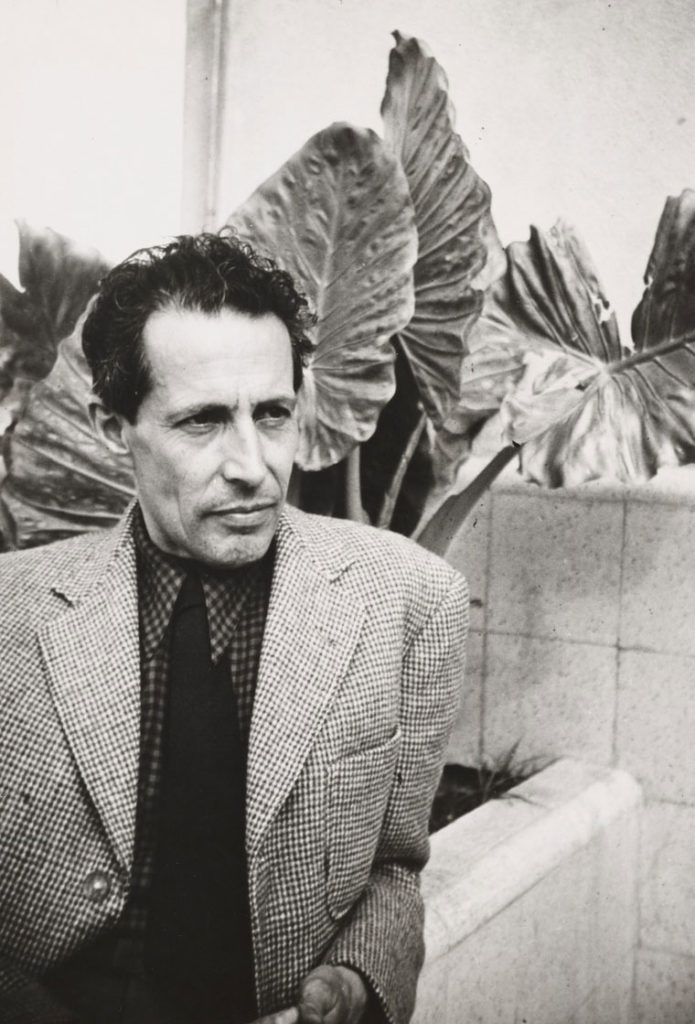
Carlos (Carl) Conrad Grethe was a Uruguayan-born German painter and academician. Grethe was born in Montevideo, Uruguay, but lived in Hamburg from the age of five. He studied at the Fine Arts School of Paul Düyffcke at the Karlsruher Kunstakademie, as well as the Parisian Académie Julian from 1884 to 1886. He interrupted his studies for almost a year to undertake a sea voyage to Mexico in 1888 and 1889. From 1894, Grethe was a member of the Munich Secession, and was also involved in the founding of the Karlsruher Künstlerbundes in 1896, the Stuttgarter Künstlerbundes, (the State Academy of Fine Arts in Stuttgart) in 1901, and the Verein Württembergischer Kunstfreunde. By the turn of the century Grethe had become prominent in representations of man and the sea, as well as of coasts and ports. His artistic style developed from a commitment to modern realism at the beginning of his career to a rather more impressionistic style in his later works.




Carlos Cruz-Diez was a Venezuelan artist said by some scholars to have been "one of the greatest artistic innovators of the 20th century."
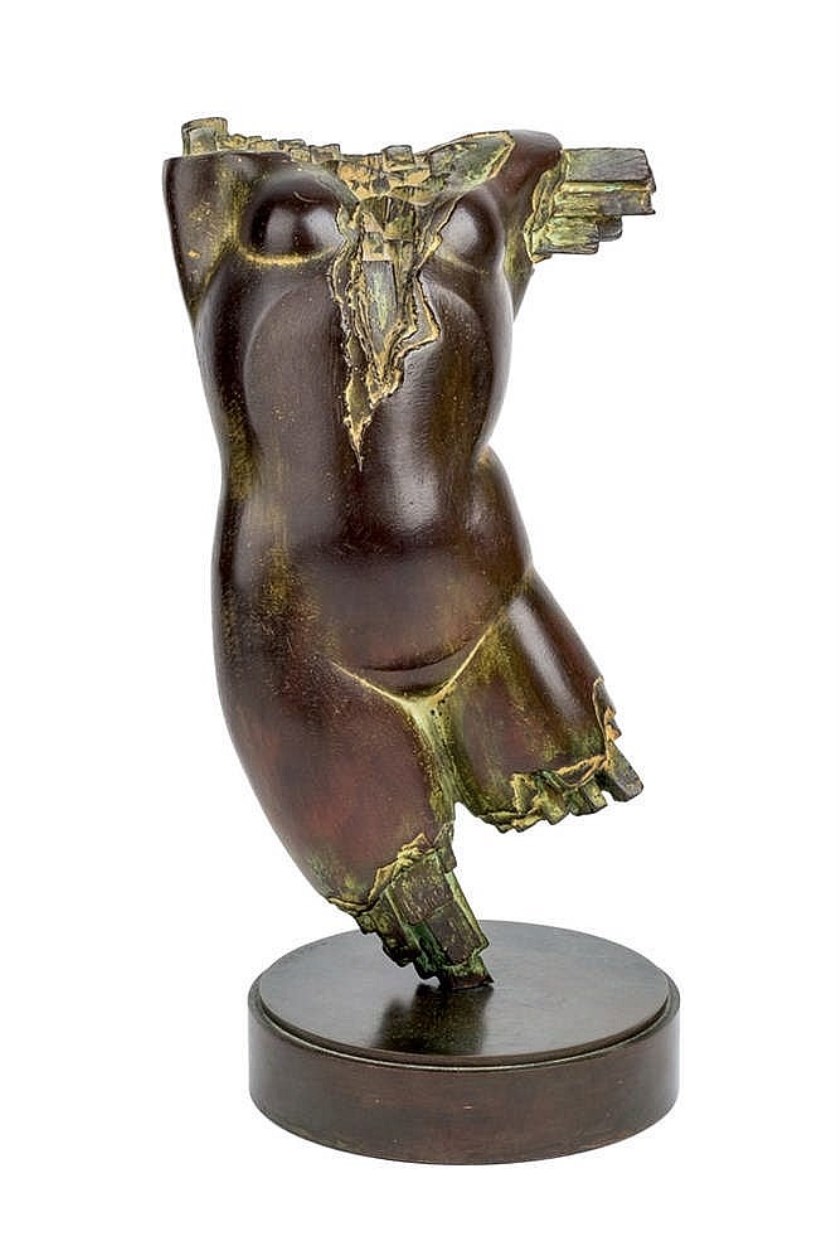


Carlos García Muela is a Spanish sculptor.
Carlos Muela studied at the National School of Fine Arts in Tetouan, Spanish protectorate of Morocco, he moved to Madrid in 1974.
His first sculptures were made of sandstone and were rather crude. Later he began to create more expressionist works in iron or bronze. In 1970, Muela began his series of Torsos of classical character, which became the basis of his work. The sculptor achieved highly expressive figures by breaking and layering them. This was achieved by spreading layers of wax, which broke at the moment of casting in bronze, thus enhancing the effect of the passage of time on the sculptural object.


Carlos Cruz-Diez was a Venezuelan artist said by some scholars to have been "one of the greatest artistic innovators of the 20th century."


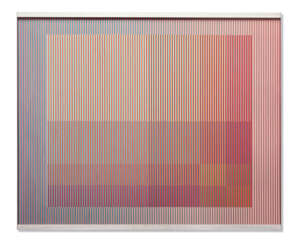
Carlos Cruz-Diez was a Venezuelan artist said by some scholars to have been "one of the greatest artistic innovators of the 20th century."


Carlos Cruz-Diez was a Venezuelan artist said by some scholars to have been "one of the greatest artistic innovators of the 20th century."


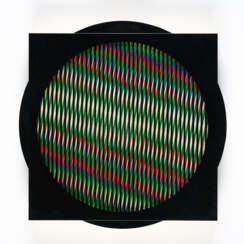
Carlos Cruz-Diez was a Venezuelan artist said by some scholars to have been "one of the greatest artistic innovators of the 20th century."






Carlos Cruz-Diez was a Venezuelan artist said by some scholars to have been "one of the greatest artistic innovators of the 20th century."


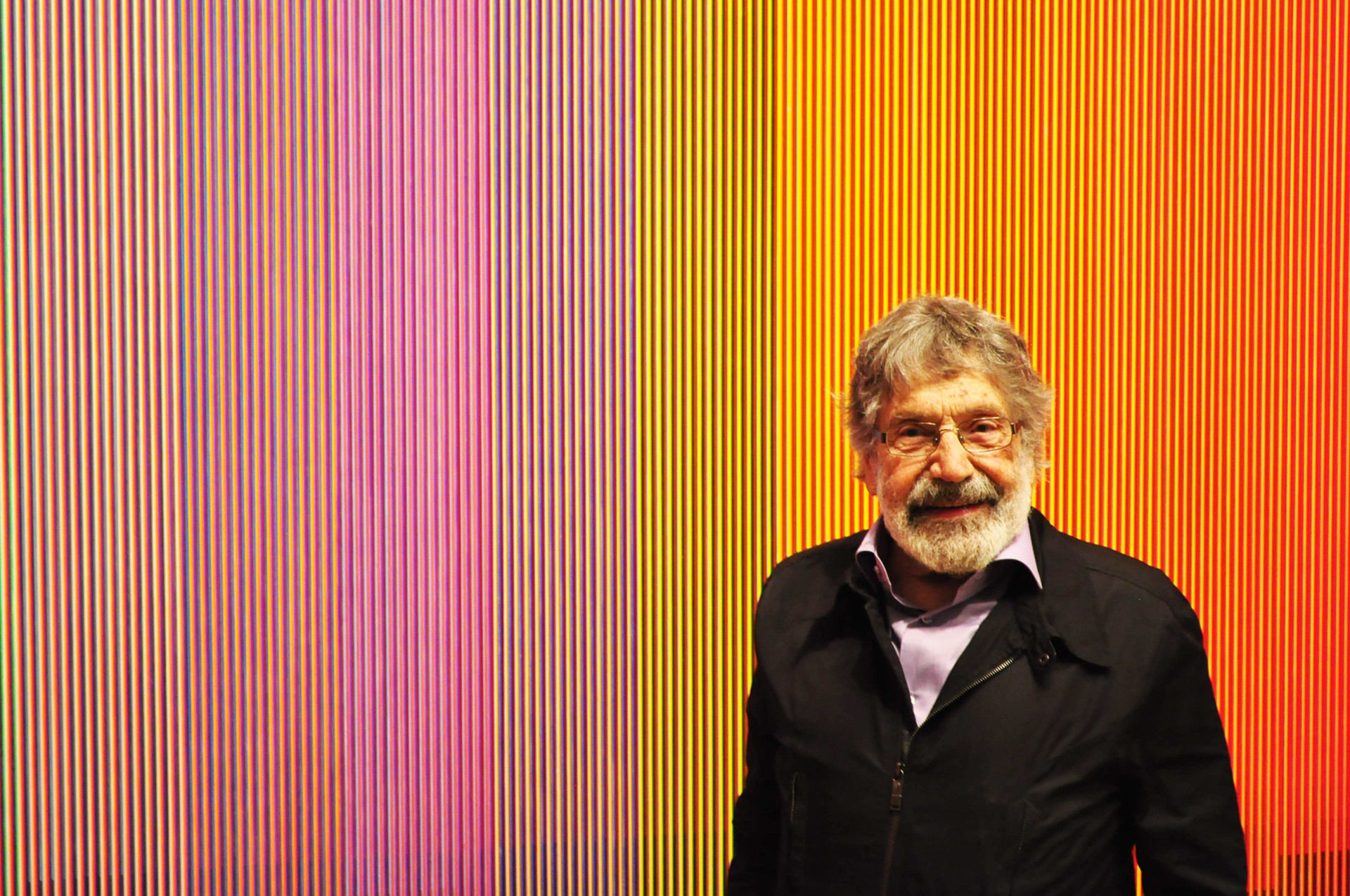
Carlos Cruz-Diez was a Venezuelan artist said by some scholars to have been "one of the greatest artistic innovators of the 20th century."


Carlos Cruz-Diez was a Venezuelan artist said by some scholars to have been "one of the greatest artistic innovators of the 20th century."


Carlos Cruz-Diez was a Venezuelan artist said by some scholars to have been "one of the greatest artistic innovators of the 20th century."


Carlos Cruz-Diez was a Venezuelan artist said by some scholars to have been "one of the greatest artistic innovators of the 20th century."


Carlos Cruz-Diez was a Venezuelan artist said by some scholars to have been "one of the greatest artistic innovators of the 20th century."


Carlos Cruz-Diez was a Venezuelan artist said by some scholars to have been "one of the greatest artistic innovators of the 20th century."