american indians
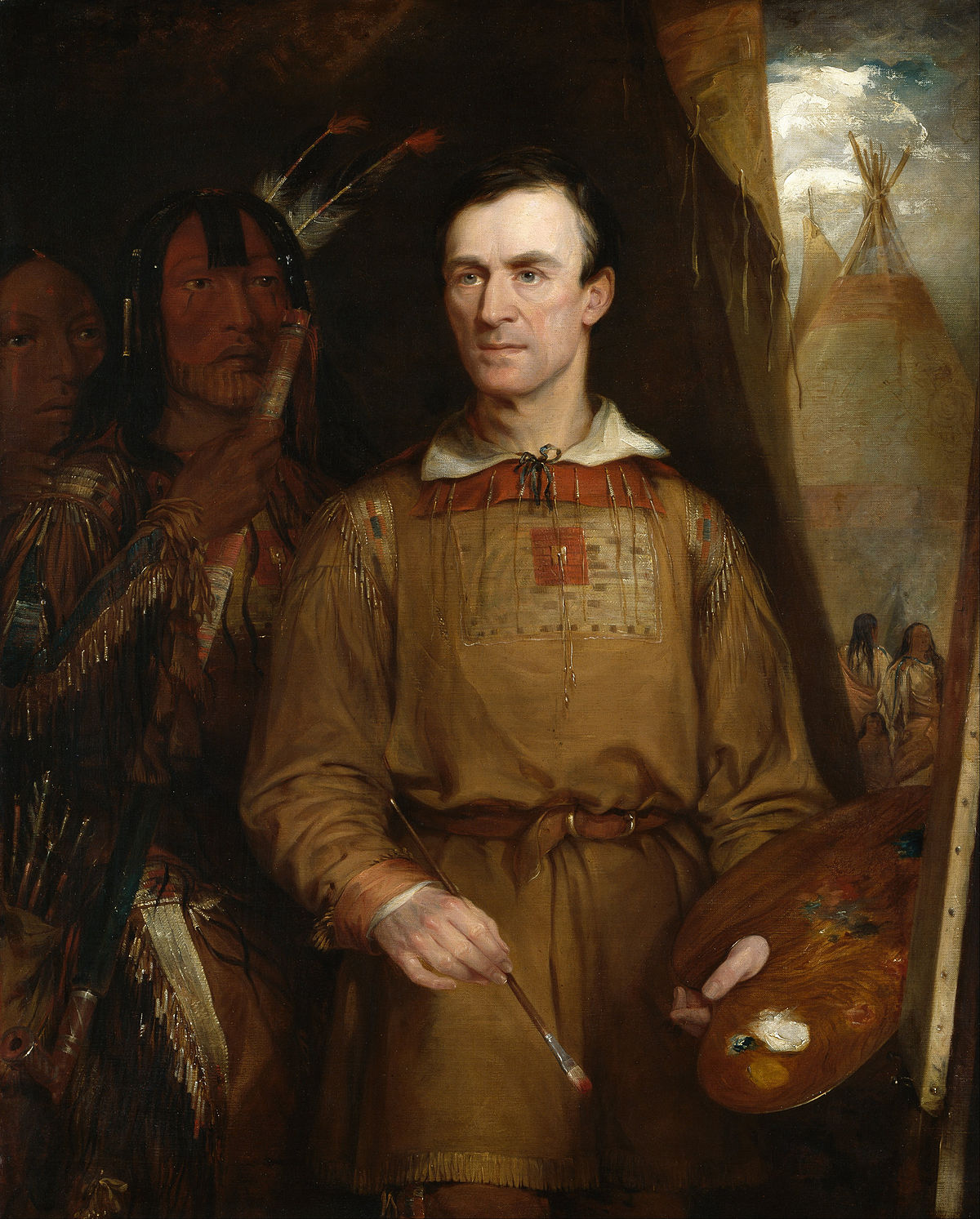

George Catlin was an American painter and writer, renowned for his vivid portrayal of Native American peoples and their cultures. Born in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, Catlin's early fascination with Native Americans grew into a lifelong dedication. His journey to the American West in the 1830s marked the beginning of an ambitious project to capture the disappearing tribes and their ways of life through his art.
Catlin's unique contribution to art and anthropology lies in his extensive collection of paintings, which document the appearance and customs of Native American tribes before the significant impacts of Western expansion. His most notable works, such as the "Buffalo Bull's Back Fat" and "Bird's Eye View of Mandan Village," are celebrated for their detailed representation and vibrant storytelling. These works provide a window into a world that was, at the time, largely misunderstood and misrepresented by mainstream American society.
His dedication led to the creation of the "Indian Gallery," an extensive traveling exhibition of his paintings and artifacts collected during his travels. This collection toured throughout the U.S. and Europe, raising awareness and sparking curiosity about Native American life and culture. For art collectors and experts in antiques, Catlin's works not only offer artistic beauty but also serve as historical documents of immense value.
If you are intrigued by the profound historical and cultural narratives captured in Catlin's paintings, consider signing up for updates on new product sales and auction events related to George Catlin. Stay informed and enrich your collection with pieces of a pivotal era in American history.
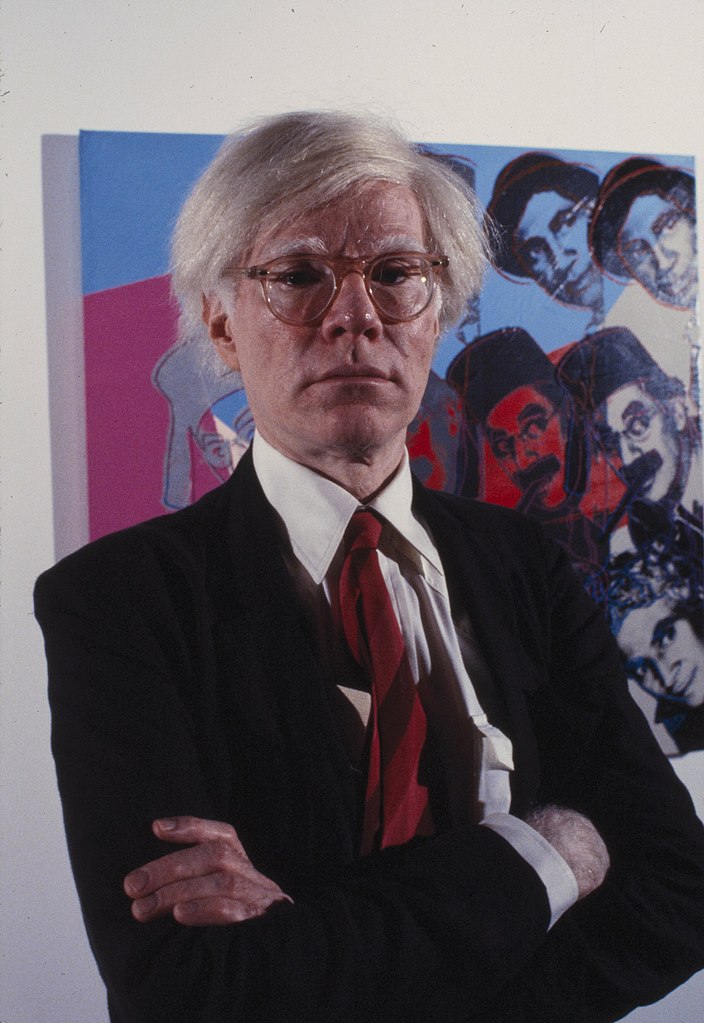


Andy Warhol, born as Andrew Warhola Jr., was an American visual artist, film director, and producer, who played a pivotal role in the development of the Pop Art movement. His art delved into the interplay between artistic expression, advertising, and celebrity culture, especially prevalent in the 1960s. Warhol was renowned for his diverse range of media, which included painting, silkscreening, photography, film, and sculpture.
Warhol's journey began in Pittsburgh, where he was born and raised, initially making a name for himself as a commercial illustrator. His New York studio, "The Factory," became a famous hub for intellectuals, celebrities, and various artistic minds. He was known for creating the notion of "Warhol superstars" and popularized the phrase "15 minutes of fame."
His contribution to the art world is significant, with notable works like "Campbell's Soup Cans" (1962) and "Marilyn Diptych" (1962), as well as his experimental films like "Empire" (1964) and "Chelsea Girls" (1966). These works not only define his career but also underscore the essence of the Pop Art movement.
Warhol's influence extended beyond his artwork. He managed and produced the experimental rock band The Velvet Underground, founded Interview magazine, and wrote several books, including "The Philosophy of Andy Warhol" and "Popism: The Warhol Sixties." Living openly as a gay man before the gay liberation movement, Warhol's personal life was as influential as his professional endeavors.
Tragically, Warhol's life was nearly cut short in 1968 when he was shot by radical feminist Valerie Solanas. He eventually passed away in 1987 due to cardiac arrhythmia following gallbladder surgery. His legacy continues, with The Andy Warhol Museum in Pittsburgh standing as the largest U.S. museum dedicated to a single artist.
Warhol's art remains highly collectible and valuable. His works, like the "Silver Car Crash (Double Disaster)" and "Shot Sage Blue Marilyn," have fetched staggering amounts at auctions, signifying his enduring impact on the art market.
For art collectors and experts, Andy Warhol's work represents a crucial intersection of pop culture and fine art, offering a unique perspective on consumerism and celebrity. His pieces are not just art; they are historical landmarks that capture a transformative era in both art and society.
To stay updated on new products, sales, and auction events related to Andy Warhol, sign up for our updates. This subscription will keep you informed about all things Warhol without overwhelming you with unnecessary information.


Andy Warhol, born as Andrew Warhola Jr., was an American visual artist, film director, and producer, who played a pivotal role in the development of the Pop Art movement. His art delved into the interplay between artistic expression, advertising, and celebrity culture, especially prevalent in the 1960s. Warhol was renowned for his diverse range of media, which included painting, silkscreening, photography, film, and sculpture.
Warhol's journey began in Pittsburgh, where he was born and raised, initially making a name for himself as a commercial illustrator. His New York studio, "The Factory," became a famous hub for intellectuals, celebrities, and various artistic minds. He was known for creating the notion of "Warhol superstars" and popularized the phrase "15 minutes of fame."
His contribution to the art world is significant, with notable works like "Campbell's Soup Cans" (1962) and "Marilyn Diptych" (1962), as well as his experimental films like "Empire" (1964) and "Chelsea Girls" (1966). These works not only define his career but also underscore the essence of the Pop Art movement.
Warhol's influence extended beyond his artwork. He managed and produced the experimental rock band The Velvet Underground, founded Interview magazine, and wrote several books, including "The Philosophy of Andy Warhol" and "Popism: The Warhol Sixties." Living openly as a gay man before the gay liberation movement, Warhol's personal life was as influential as his professional endeavors.
Tragically, Warhol's life was nearly cut short in 1968 when he was shot by radical feminist Valerie Solanas. He eventually passed away in 1987 due to cardiac arrhythmia following gallbladder surgery. His legacy continues, with The Andy Warhol Museum in Pittsburgh standing as the largest U.S. museum dedicated to a single artist.
Warhol's art remains highly collectible and valuable. His works, like the "Silver Car Crash (Double Disaster)" and "Shot Sage Blue Marilyn," have fetched staggering amounts at auctions, signifying his enduring impact on the art market.
For art collectors and experts, Andy Warhol's work represents a crucial intersection of pop culture and fine art, offering a unique perspective on consumerism and celebrity. His pieces are not just art; they are historical landmarks that capture a transformative era in both art and society.
To stay updated on new products, sales, and auction events related to Andy Warhol, sign up for our updates. This subscription will keep you informed about all things Warhol without overwhelming you with unnecessary information.
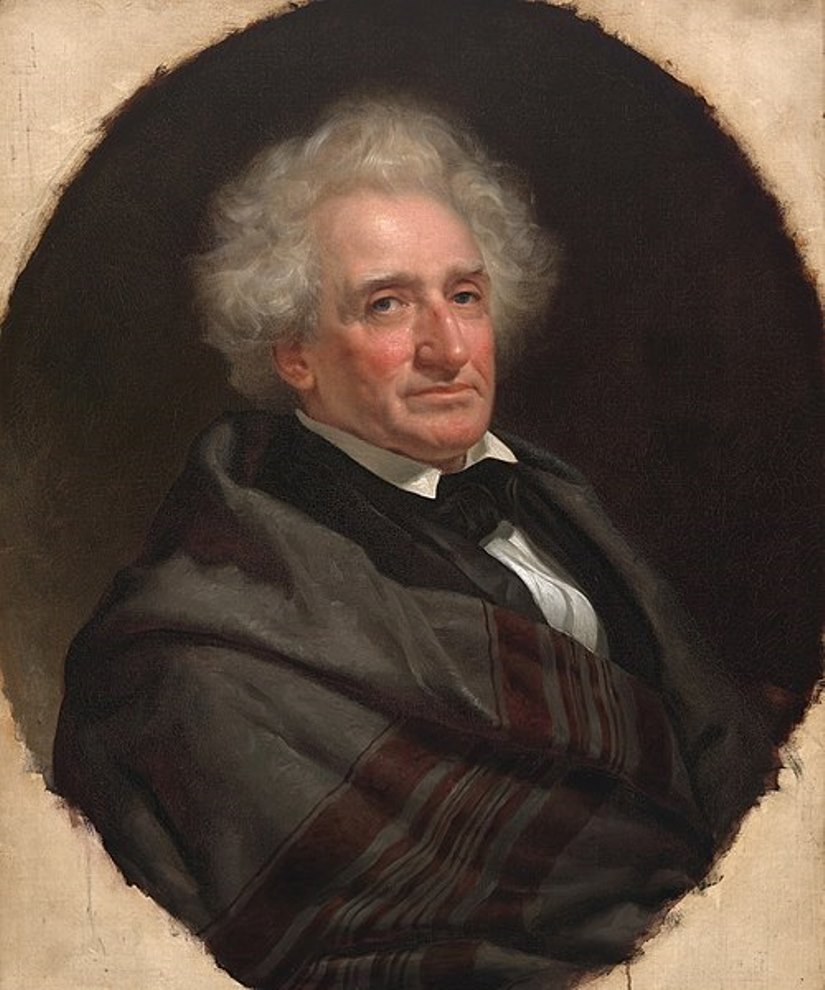


Thomas Loraine McKenney was an American statesman and author.
After the abolition of the U.S. Indian trading program in 1822, then Secretary of War John C. Calhoun established a position in the War Department called Superintendent of Indian Affairs (later to become part of the Bureau of Indian Affairs). McKenney was the first appointed to this position and held it until 1830. Over the years, he worked tirelessly to promote Indian-American relations, advocating for the interests of Indians and striving to preserve the memory of their vanishing culture. Despite his interest in Native American history, McKenney sought to have them assimilated to Euro-American culture through Christian education.
McKenney commissioned leading artists, including Charles Byrd King, to paint portraits of Indian chiefs from more than twenty tribes who visited Washington on official business over a ten-year period. These portraits formed the basis of the government's National Portrait Gallery, first housed in the War Department and later transferred to the Smithsonian Institution. This gallery was featured in part in the three-volume History of the Indian Tribes of North America (1836-1844), with biographical sketches by McKenney, co-authored with Illinois lawyer and writer James Hall.
In 1865, a fire at the Smithsonian Institution destroyed all but a few of the portraits, which are now in the White House. Thus this three-volume book represents the only reliable source on the appearance of many of the most prominent leaders of Indian tribes.
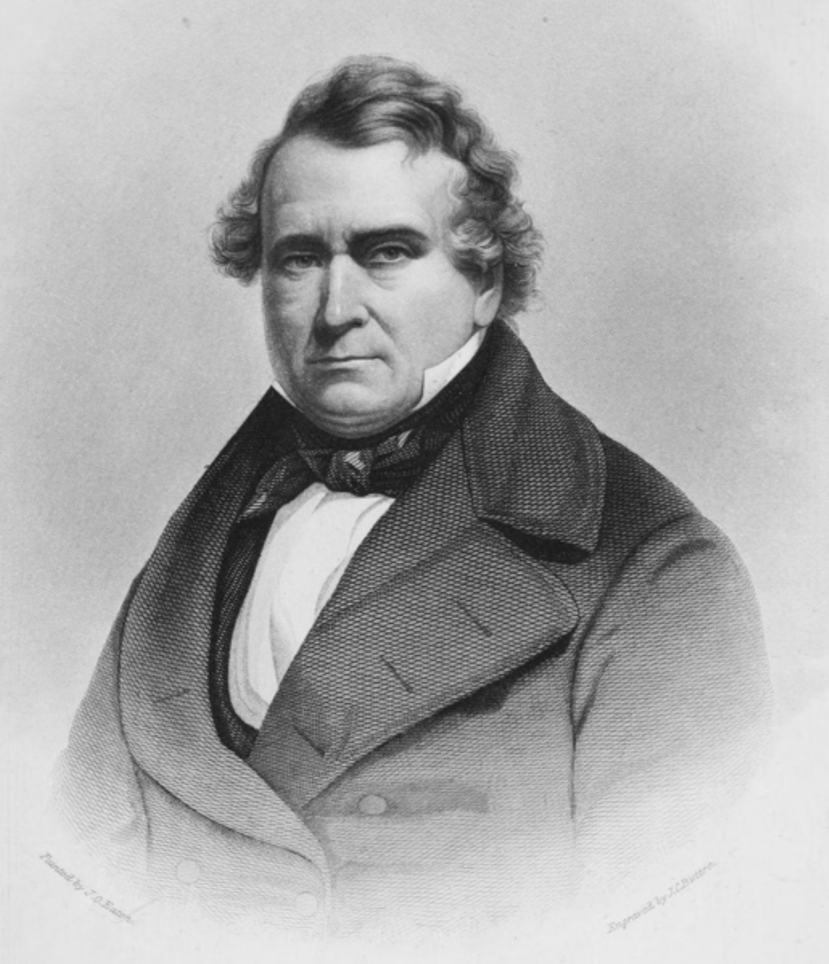

James Hall was an American lawyer, judge, treasurer, and editor.
Hall studied law, fought in the War of 1812, served as a lawyer and circuit judge, newspaper and magazine editor, Illinois state treasurer, and banker in Cincinnati, Ohio. In addition, he was also a historical and fiction writer. In 1828, Hall compiled the first western literary yearbook, Western Souvenir, and edited the Illinois Monthly Magazine. James Hall wrote a travel book, Letters from the West (1828), a novel, The Head of the Harp (1833), and several volumes of short stories.
Hall also contributed to the three-volume History of the Indian Tribes of North America (1836-1844). This book includes portraits of the chiefs of more than twenty Indian tribes, which were painted by noted artists of the day, with biographical sketches by Superintendent of Indian Affairs Thomas L. McKenney.
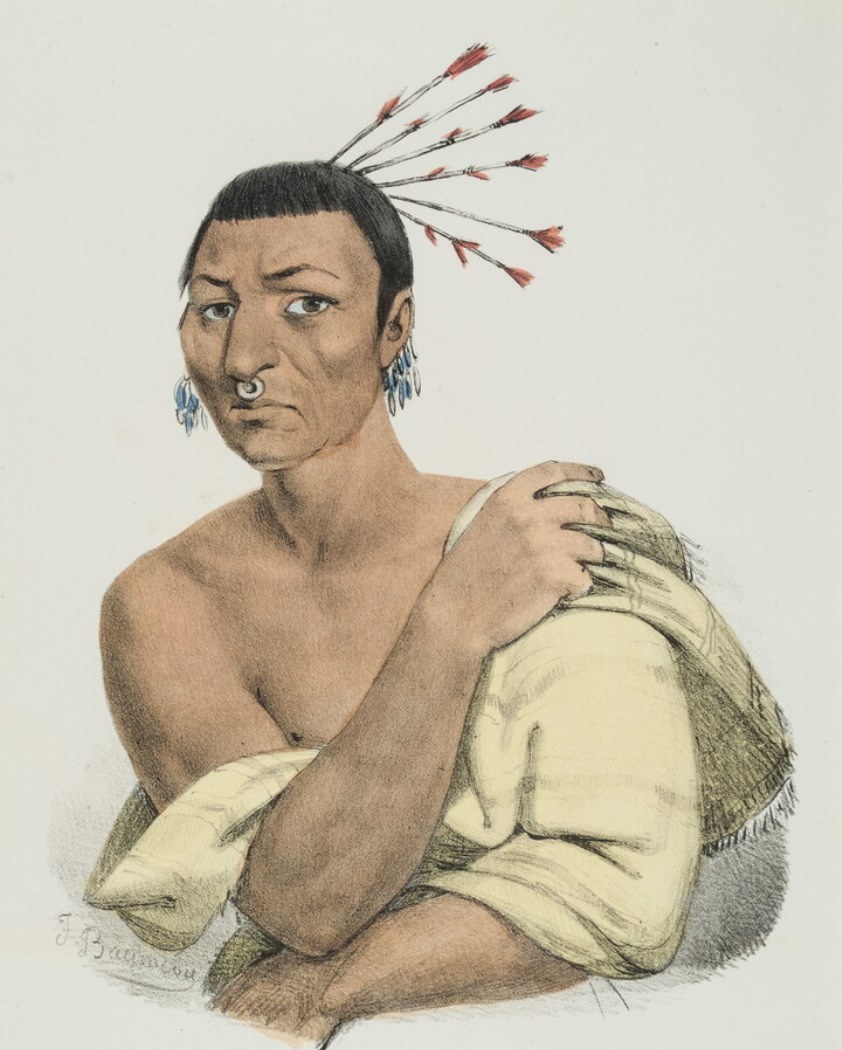
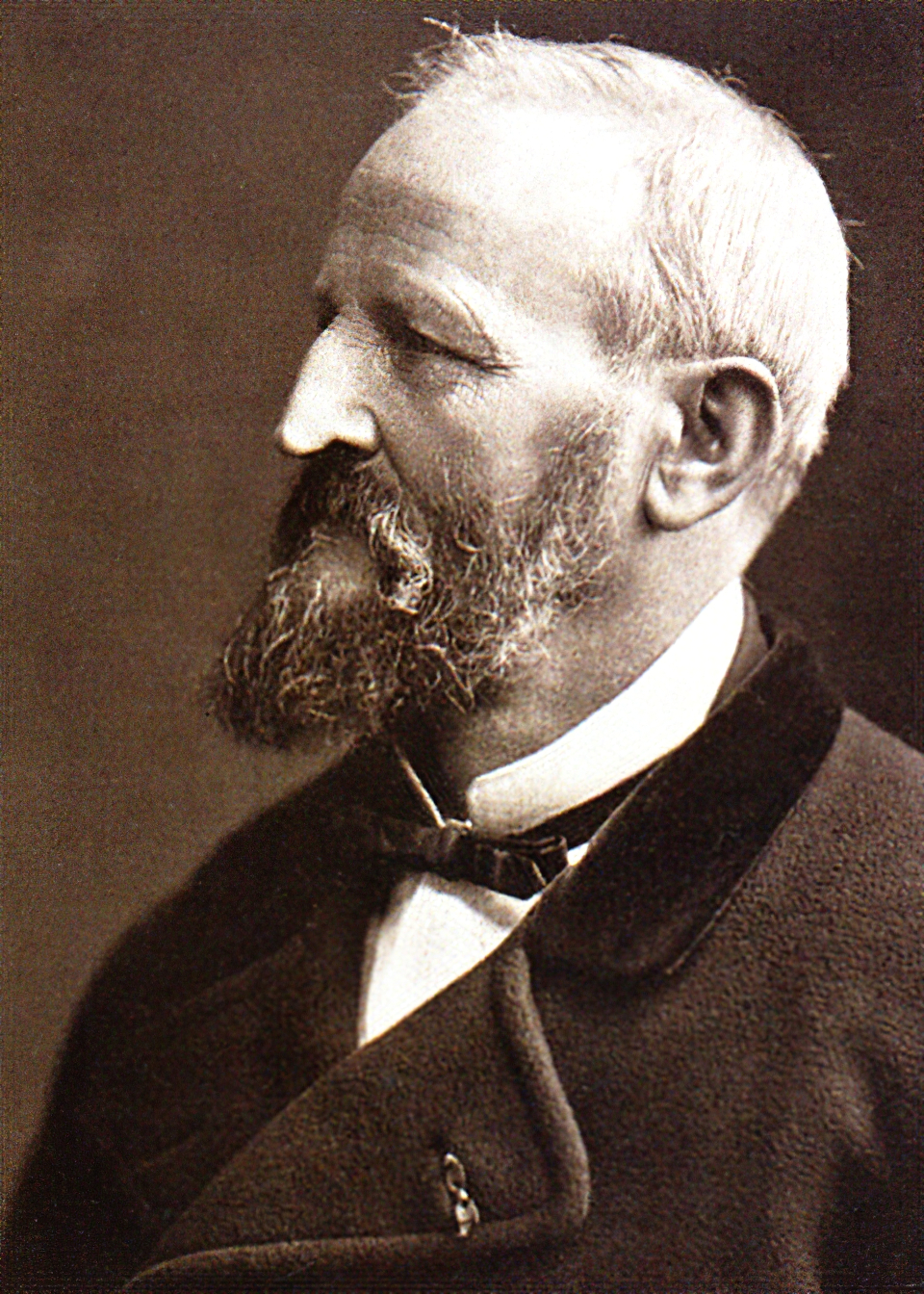





Karl Bodmer was a Swiss-French printmaker, etcher, lithographer, zinc engraver, draughtsman, painter, illustrator and hunter.
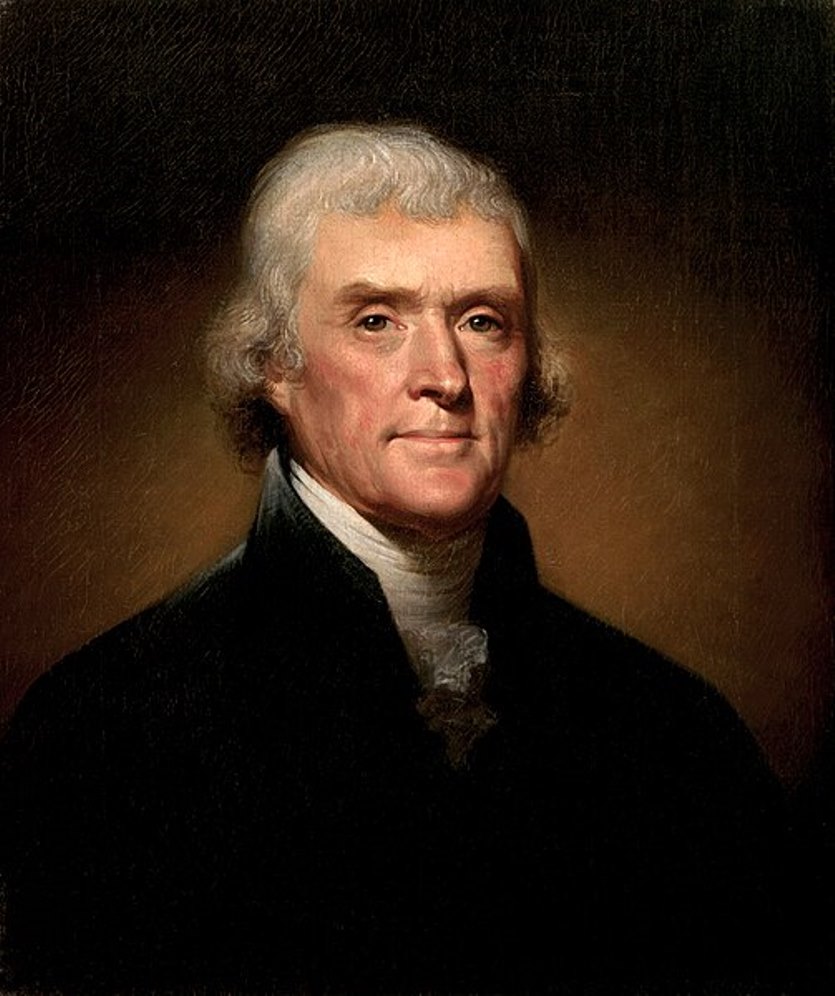


Thomas Jefferson was an American politician and statesman, the third President of the United States (March 4, 1801 - March 4, 1809).
Jefferson was the son of a planter and received a law degree. In 1774, he wrote A Summary of the Rights of British America, which attracted public attention, and he soon gained a reputation as one of the first advocates of American independence from the authority of the British Parliament. In the spring of 1775, the Virginia legislature appointed him a delegate to the Second Conference of the Continental Congress. A year later he was appointed to a committee of five, which also included Adams and Benjamin Franklin, to draft a formal statement of reasons to justify a break with Great Britain. Jefferson thus became one of the authors of the Declaration of Independence. Jefferson succeeded Benjamin Franklin as minister to France in 1785, was secretary of state (1790-1793) under Washington, and vice president (1797-1801) under John Adams.
A Democratic-Republican, Jefferson, who believed that the national government should play a limited role in the lives of citizens, was elected president in 1800. One of the most significant accomplishments of Jefferson's first administration was the purchase of the Louisiana Territory from France for $15 million dollars in 1803 (from the Gulf of Mexico to present-day Canada), effectively doubling the size of the United States. During his second term, Jefferson was focused on trying to keep America out of the Napoleonic Wars in Europe. After his second term as president, he was succeeded by James Madison in 1808.
Upon leaving office, Jefferson retired to his plantation in Virginia, pursued his favorite pastimes, and helped found the University of Virginia. In addition to politics, he is known as a writer, farmer, horticulturist, inventor, book collector, art historian, architect, and scientist. He died at the age of 83 on July 4, 1826, the 50th anniversary of the Declaration of Independence.