beautés

Tim Rollins was an American artist who together with the art collaborative K.O.S. formed the art-group Tim Rollins and K.O.S (Kids of Survival).
Since the founding of the Art & Knowledge Workshop in 1982, Tim Rollins & K.O.S. have produced allegorical paintings, sculptures and drawings by mining the vast wealth of printed matter - from the popular to the arcane, from the minor to the canonical, from legal documents to comic books (areas in no way mutually exclusive in Rollins & K.O.S.'s view) - which are themselves understood as political allegories.



Paul Sérusier was a French Post-Impressionist painter and theorist, notable for his significant contributions to the art movement known as the Nabis. Born in Paris on November 9, 1864, Sérusier's work is characterized by its expressive use of color and pattern, inspired by the techniques of Paul Gauguin. He is best known for his exploration of color, sensation, and abstraction, particularly evident in works like "Le Talisman, the Aven River at the Bois d'Amour" (1888). This painting marks a departure from the Impressionists' more faithful representation of observed reality, focusing instead on translating sensations onto the canvas with vibrant brushstrokes and an emphasis on emotional expression over visual accuracy.
Sérusier's paintings often feature the landscapes and people of Brittany, notable for their contemplative mood achieved through firm contours and blocks of unmodulated color. His style evolved under the influence of Synthetism and Cloisonnism, favoring flattened forms and large swathes of color, as seen in "Farmhouse at le Pouldu" (1890). This approach reflects a decorative organization of objects, emphasizing the craft and execution of the scene.
Some of Sérusier's notable works are housed in prestigious museums such as the Musée d'Orsay in Paris, including "Portrait of Paul Ranson in Nabi Costume" (1890) and "Landscape" (1912). His legacy extends beyond his own artworks; he was a key figure in the formation of the Nabis movement, and his theoretical contributions have had a lasting impact on the art world.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Sérusier's work represents a unique blend of post-impressionist and symbolist styles, making his pieces highly valued both for their historical significance and their aesthetic appeal. To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Paul Sérusier, sign up for our updates. This subscription service is exclusively focused on providing information related to Sérusier's work, ensuring you remain informed about opportunities to acquire pieces by this influential artist.


Paul Sérusier was a French Post-Impressionist painter and theorist, notable for his significant contributions to the art movement known as the Nabis. Born in Paris on November 9, 1864, Sérusier's work is characterized by its expressive use of color and pattern, inspired by the techniques of Paul Gauguin. He is best known for his exploration of color, sensation, and abstraction, particularly evident in works like "Le Talisman, the Aven River at the Bois d'Amour" (1888). This painting marks a departure from the Impressionists' more faithful representation of observed reality, focusing instead on translating sensations onto the canvas with vibrant brushstrokes and an emphasis on emotional expression over visual accuracy.
Sérusier's paintings often feature the landscapes and people of Brittany, notable for their contemplative mood achieved through firm contours and blocks of unmodulated color. His style evolved under the influence of Synthetism and Cloisonnism, favoring flattened forms and large swathes of color, as seen in "Farmhouse at le Pouldu" (1890). This approach reflects a decorative organization of objects, emphasizing the craft and execution of the scene.
Some of Sérusier's notable works are housed in prestigious museums such as the Musée d'Orsay in Paris, including "Portrait of Paul Ranson in Nabi Costume" (1890) and "Landscape" (1912). His legacy extends beyond his own artworks; he was a key figure in the formation of the Nabis movement, and his theoretical contributions have had a lasting impact on the art world.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Sérusier's work represents a unique blend of post-impressionist and symbolist styles, making his pieces highly valued both for their historical significance and their aesthetic appeal. To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Paul Sérusier, sign up for our updates. This subscription service is exclusively focused on providing information related to Sérusier's work, ensuring you remain informed about opportunities to acquire pieces by this influential artist.
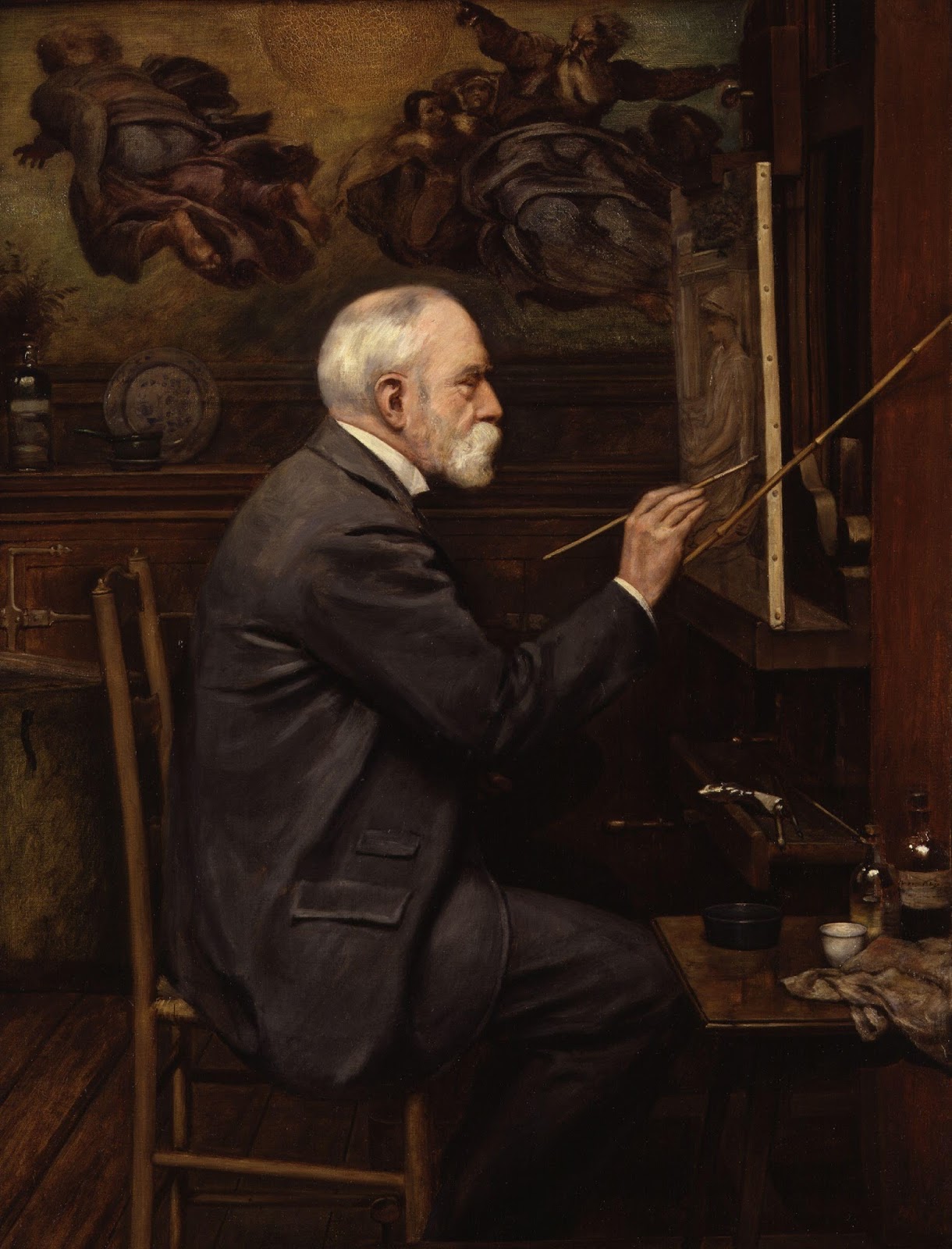

Edward John Poynter was a prominent British painter, known for his historical and mythological artworks that resonate with art collectors and experts. Born in Paris and educated in Britain, Poynter's career flourished with his detailed and evocative paintings, like "Israel in Egypt" and "The Visit of the Queen of Sheba to King Solomon," which reflect his profound historical knowledge and artistic skill. These works are celebrated for their intricate detail and vibrant storytelling, captivating viewers and holding significant positions in galleries and Masonic lodges globally.
Edward John Poynter's dedication to art education was evident through his roles as the Slade Professor at University College London and the principal of the National Art Training School. His contribution extended to administrative roles, notably as the Director of the National Gallery, where he played a pivotal role in the establishment of the Tate Gallery. His legacy in the art world is also marked by his presidency at the Royal Academy, demonstrating his influence and standing in the British art scene.
For those intrigued by Edward John Poynter's mastery and the historical depth of his work, his contributions to art literature, such as "Ten Lectures on Art," offer further insight into his artistic philosophy and approach. These works underscore his commitment to integrating art and archaeology, providing a richer understanding of his creative process and the era he depicted.
For art collectors and enthusiasts interested in Poynter's work and related auction events, staying updated through a subscription service can be invaluable. This ensures you receive timely information on sales and exhibitions featuring Edward John Poynter's art, allowing you to engage deeply with his historical and artistic legacy.
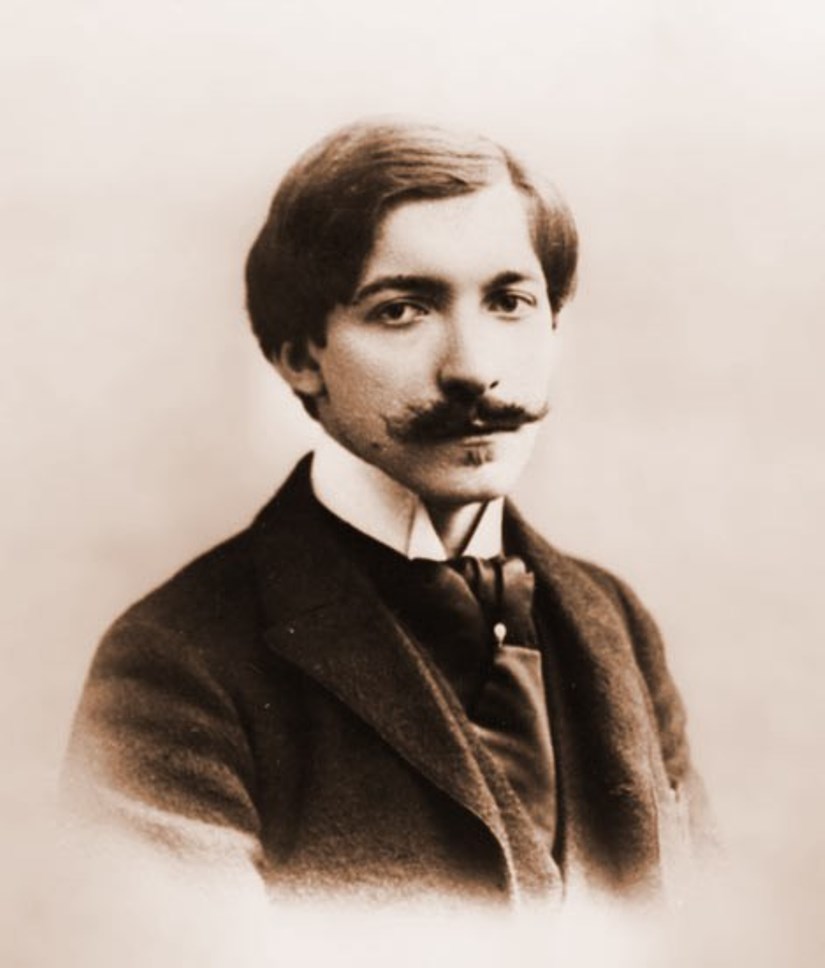


Pierre Louÿs, real name Pierre Félix Louis, was a French poet and writer.
He specialized in erotic and ancient themes in the Art Nouveau style. Louÿs's most famous work is The Songs of Bilitis. It is a collection of erotic poetry with strongly lesbian themes, written in the manner of Sappho. Although Louÿs claimed that these poems had a Greek source, this ultimately proved to be a hoax.
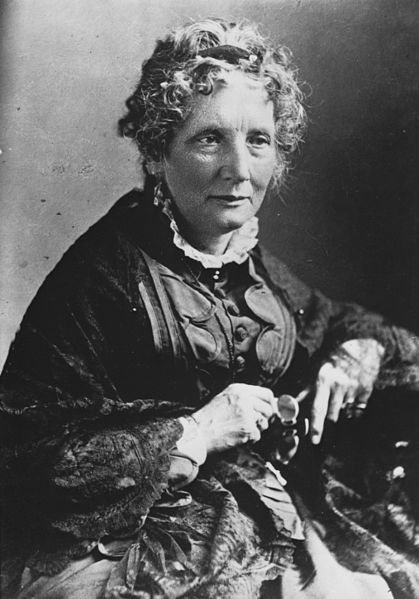



Harriet Beecher Stowe, full name Harriet Elisabeth Beecher Stowe, was an American writer and poet, an activist for the eradication of slavery in the country.
Beecher Stowe is the author of the world-famous novel Uncle Tom's Cabin. Published first in a newspaper and first published as a book in 1852, it aroused widespread anger in the country and galvanized the fight against slavery in the southern United States. This novel was later reprinted many times in all languages of the world and has been screened more than once.
In her youth, Beecher Stowe received an academic education, wrote poetry, notes and essays on social topics. In addition to "The Shack", she wrote several other novels and was engaged in teaching.
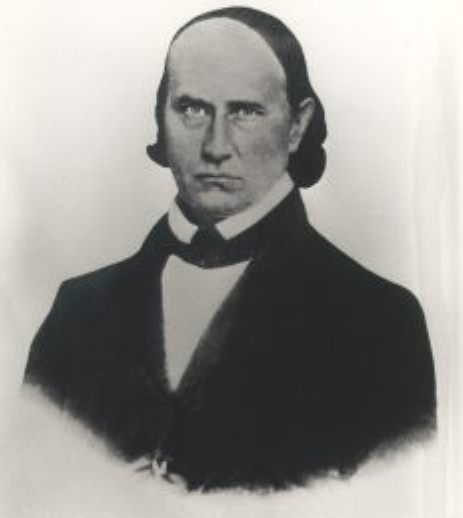



Thomas Holley Chivers was an American physician and poet of the first half of the 19th century.
Chivers earned a medical degree from Transylvania University in Lexington, Kentucky, but rarely practiced medicine. After receiving an inheritance, he was able to live freely and travel. In the early 1830s he traveled extensively throughout the western frontier and the North. He became fascinated with Transcendentalist philosophy as well as slave poetry. A number of Cheevers's poems and plays reflected his ideological views on American Indians and their plight, inspired in part by his interactions with the Cherokee during his frontier wanderings.
During his lifetime, Chivers published eleven volumes of poems, plays, and pamphlets. He also collaborated with the leading literary periodicals and newspapers of the antebellum era, notably the Georgia Citizen, and wrote a biography of Edgar Allan Poe, his friend and soulmate. Nevertheless, the eccentric writer never achieved the critical acclaim he craved all his life.
The friendship between Chivers and Edgar Allan Poe was based on a mutual fascination with metaphysical speculation, as well as on shared literary interests. However, the close cooperation of the two poets was accompanied by a sharp rivalry, in addition, each of them began to consider the artistic borrowings of the other plagiarized. By and large, Chivers is known only for his association with Edgar Poe.
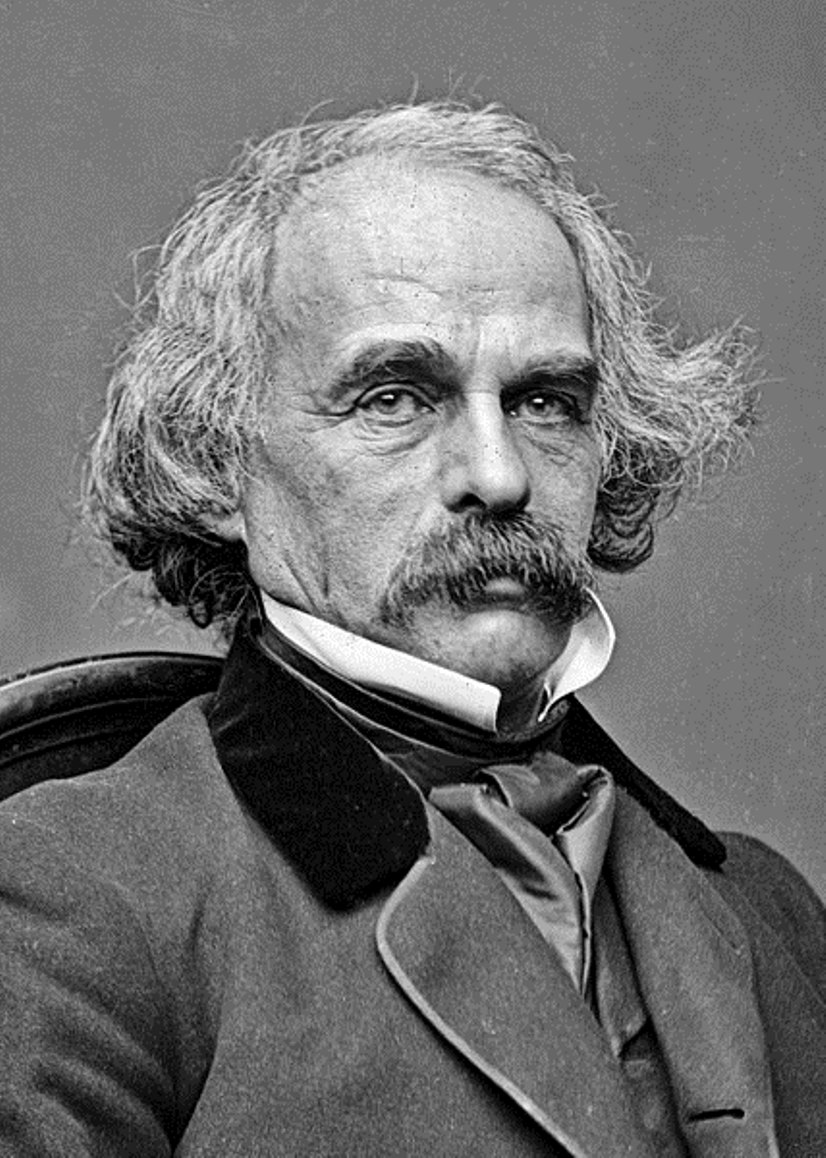



Nathaniel Hawthorne is an American writer and author.
Hawthorne is a recognized short story writer and a master of allegorical and symbolic narrative. One of the first fiction writers in American literature, he is best known for his works The Scarlet Letter (1850) and The House of Seven Gables (1851). Hawthorne's artistic works are considered part of the American Romantic movement and, in particular, of so-called dark Romanticism, a popular mid-19th-century fascination with the irrational, the demonic, and the grotesque.
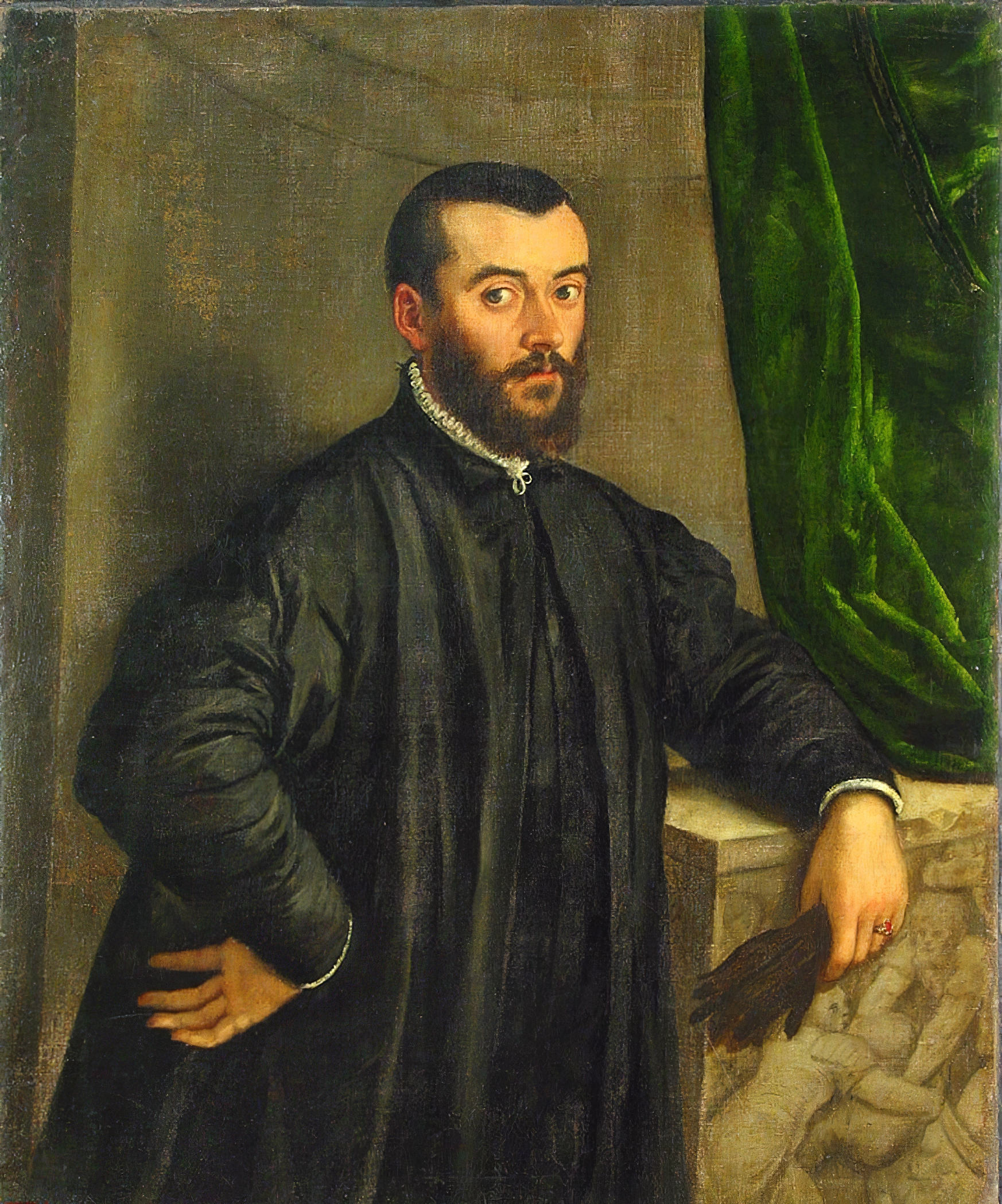


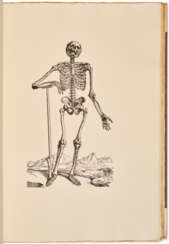
Andreas Vesalius (Dutch: Andries van Wesel) was a Flemish physician, one of the first anatomists of the Renaissance.
Vesalius came from a family of physicians and apothecaries, studied at the Catholic University of Leuven and at the medical school of the University of Paris, where he learned to dissect animals. He also had the opportunity to dissect human cadavers and devoted much time to the study of human bones. He later went to the University of Padua and, after earning his MD degree, was appointed professor of surgery, whose duties included anatomical demonstrations.
Vesalius revolutionized the study of biology and medical practice through his careful description of the anatomy of the human body. Based on observations made by himself, he wrote and illustrated the first complete textbook of anatomy. In 1543 his major work De humani corporis fabrica libri septem ("Seven Books on the Structure of the Human Body"), commonly known as Fabrica, was printed. In this epochal work, Vesalius gave far more extensive and accurate descriptions of the human body than anything that had been done by his predecessors.
In the same year, 1543, the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V appointed him staff physician of his house, and in 1559 Vesalius became physician to the Madrid court of Charles V's son, Philip II.
Vesalius' work made anatomy a scientific discipline with far-reaching implications not only for physiology but for all of biology.