bibliography & printing history


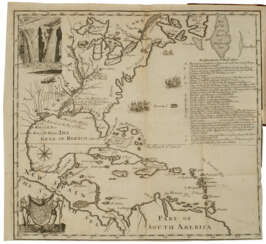
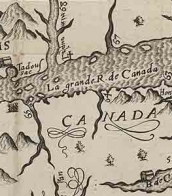
Patrick Browne was an Irish physician and historian, traveler, naturalist and botanist.
Patrick Browne studied medicine in Paris, graduated from the University of Reims, continued his studies in Leiden, and then worked as a doctor at St. Thomas' Hospital in London. Subsequently, he lived for many years in the Caribbean, in Antigua, Santa Cruz, Montserrat and Jamaica, where he practiced medicine. He devoted all his spare time to the study of the natural history of the island. In 1771, Brown returned to Mayo County.
In 1756, Brown published A Civil and Natural History of Jamaica, his most significant work in terms of Carl Linnaeus's botanical nomenclature, which included new names for 104 genera.


Patrick Browne was an Irish physician and historian, traveler, naturalist and botanist.
Patrick Browne studied medicine in Paris, graduated from the University of Reims, continued his studies in Leiden, and then worked as a doctor at St. Thomas' Hospital in London. Subsequently, he lived for many years in the Caribbean, in Antigua, Santa Cruz, Montserrat and Jamaica, where he practiced medicine. He devoted all his spare time to the study of the natural history of the island. In 1771, Brown returned to Mayo County.
In 1756, Brown published A Civil and Natural History of Jamaica, his most significant work in terms of Carl Linnaeus's botanical nomenclature, which included new names for 104 genera.
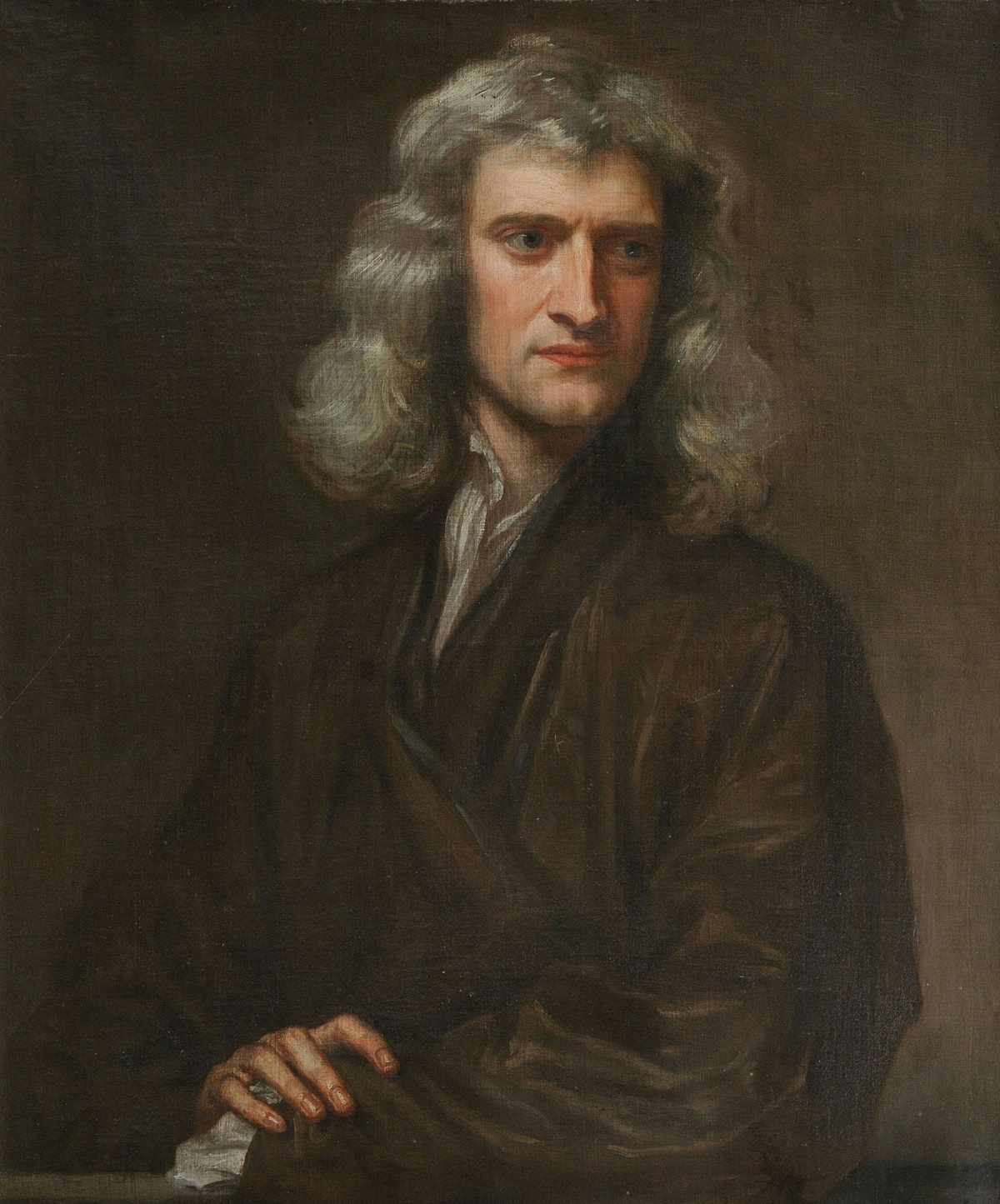









Isaac Newton was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus.
In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for tides, the trajectories of comets, the precession of the equinoxes and other phenomena, eradicating doubt about the Solar System's heliocentricity. He demonstrated that the motion of objects on Earth and celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton's inference that the Earth is an oblate spheroid was later confirmed by the geodetic measurements of Maupertuis, La Condamine, and others, convincing most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over earlier systems.


Isaac Newton was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus.
In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for tides, the trajectories of comets, the precession of the equinoxes and other phenomena, eradicating doubt about the Solar System's heliocentricity. He demonstrated that the motion of objects on Earth and celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton's inference that the Earth is an oblate spheroid was later confirmed by the geodetic measurements of Maupertuis, La Condamine, and others, convincing most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over earlier systems.


Isaac Newton was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus.
In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for tides, the trajectories of comets, the precession of the equinoxes and other phenomena, eradicating doubt about the Solar System's heliocentricity. He demonstrated that the motion of objects on Earth and celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton's inference that the Earth is an oblate spheroid was later confirmed by the geodetic measurements of Maupertuis, La Condamine, and others, convincing most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over earlier systems.
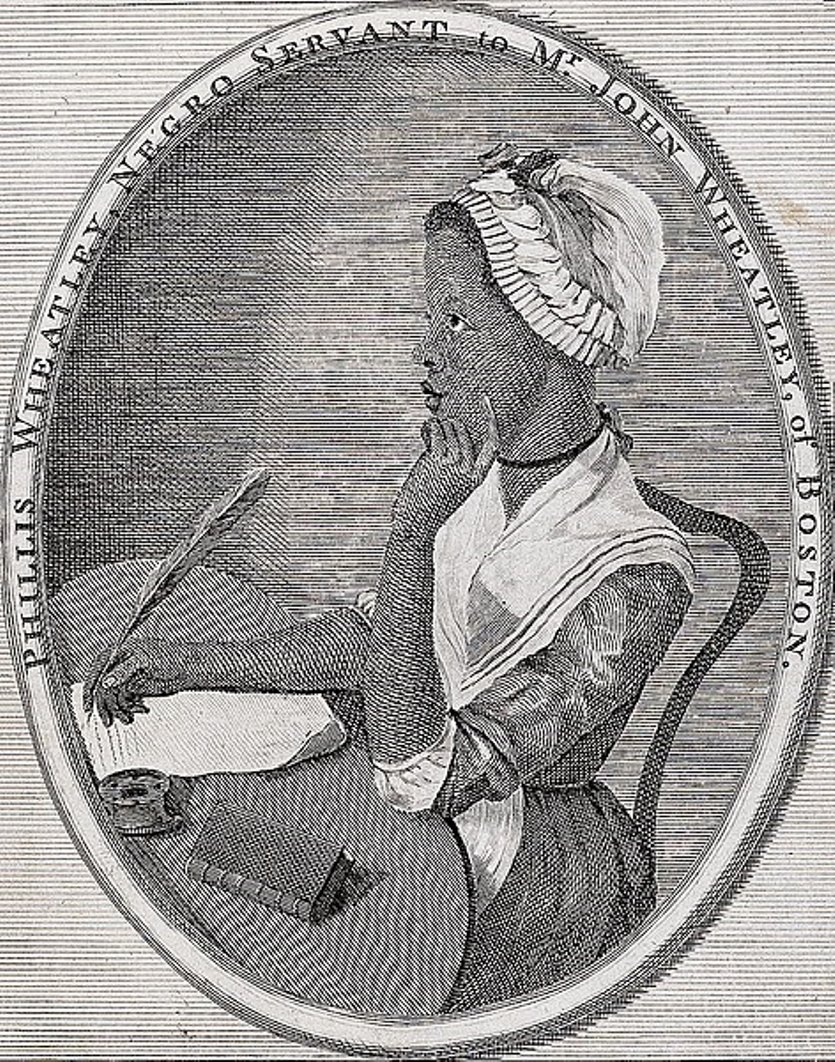


Phillis Wheatley or Phillis Wheatley Peters was an American poet born in Africa.
A native of West Africa, Phillis Wheatley was kidnapped as a young child and sold as a slave in 1761 to John and Susanna Wheatley in Boston. They chose the name Phyllis for her in honor of the ship on which the girl traveled the Middle Passage. The Wheatley family quickly recognized her intellectual abilities and encouraged her study of the classics. Phyllis began writing poems and verses, and some were even published when she was only 14 years old.
However, the 18th-century public had great difficulty accepting a black slave girl as a writer. In May 1773, Wheatley traveled to London with her master's son. There her first book, Poems on Miscellaneous Subjects, Religious and Moral, was published. Wheatley's literary talent and personal qualities contributed to her great social success in London. In the fall of 1773, Phyllis returned to the United States and Wheatley was granted her freedom. She married, but lived only 31 years.
Wheatley's most famous poem today, "On Being Brought from Africa to America" (1768), directly addresses the theme of slavery.
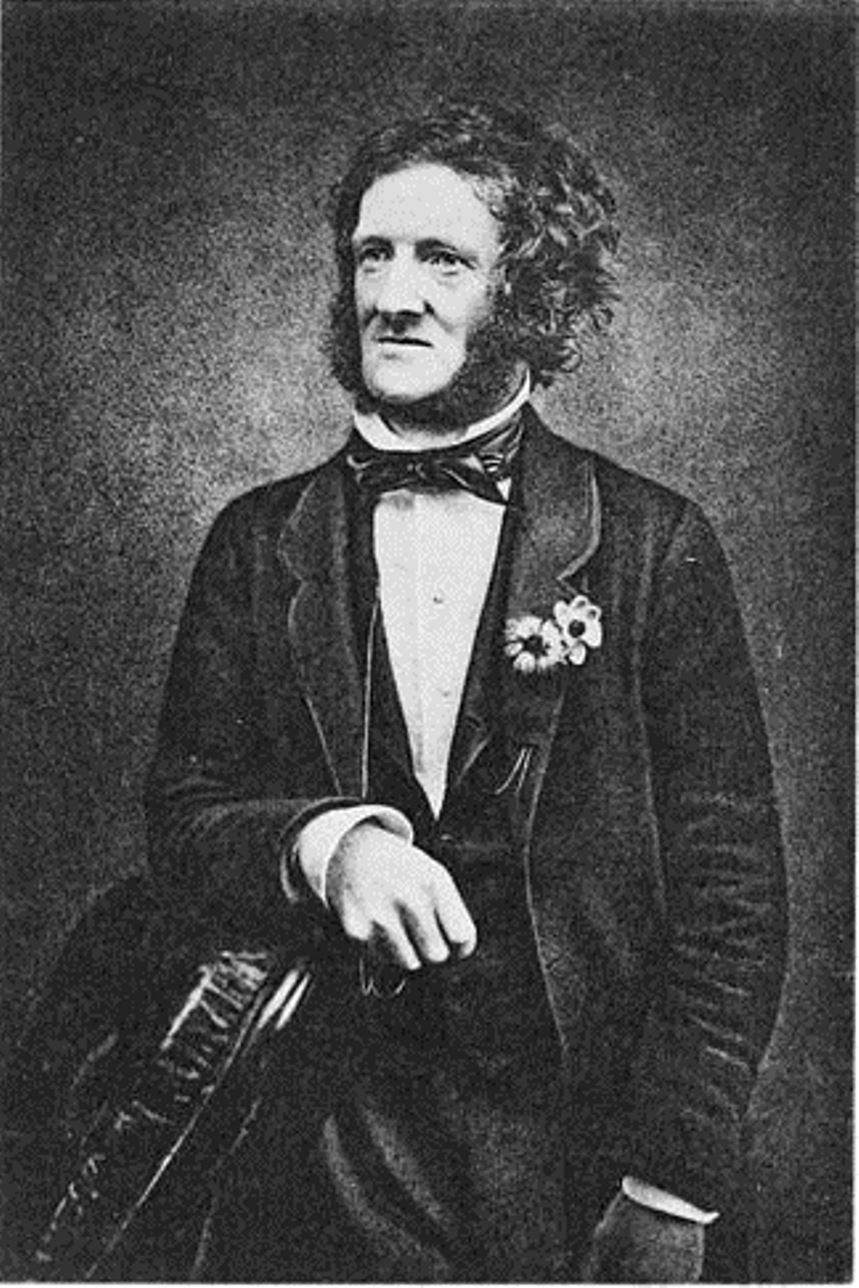


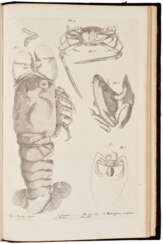
William Chapman Hewitson was a British naturalist, entomologist and artist, a member of the Linnean Society.
After gaining financial independence, Hewitson devoted himself entirely to natural history, particularly the study of scales and birds. His rich collection of exotic butterflies contained over 4,000 species and was considered one of the finest. Hewitson published numerous works on entomology and ornithology and was an accomplished scientific illustrator. His principal work was Illustrations of new species of exotic butterflies, a richly illustrated encyclopedia to which Hewitson devoted the last thirty years of his life, expending enormous personal resources, personally drawing and coloring the figures. At his death he left his entire butterfly collection to the British Museum.
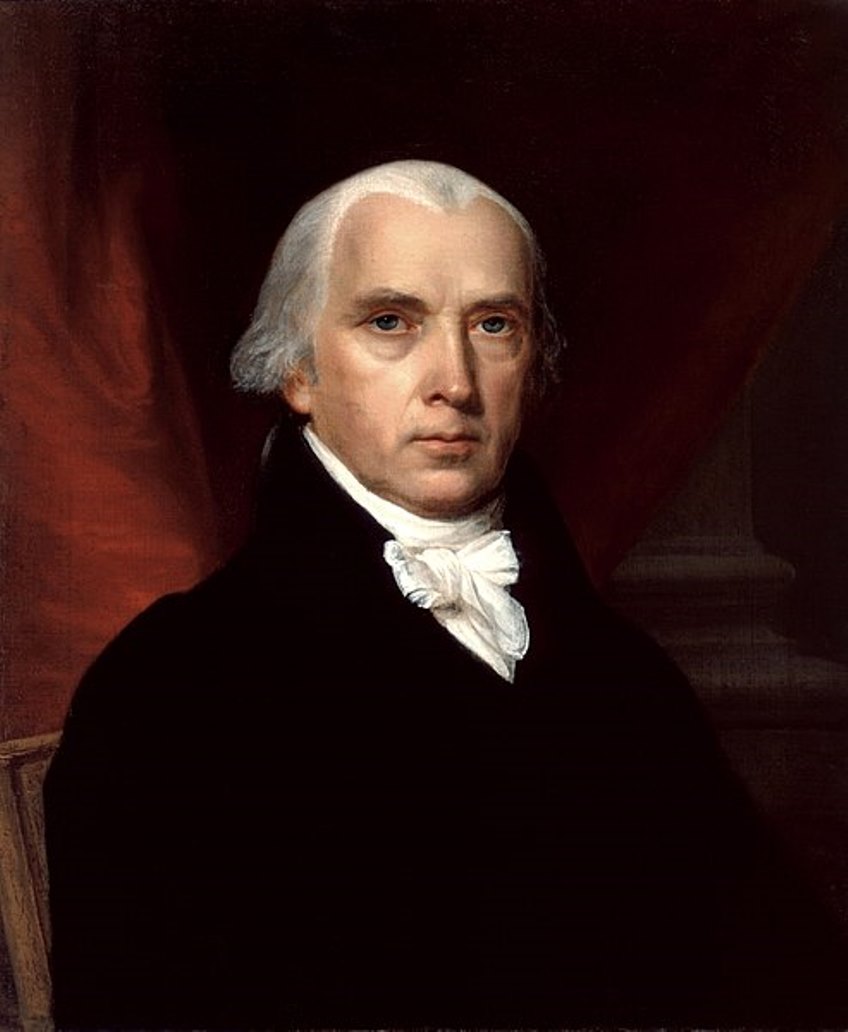




James Madison was an American politician and statesman, the fourth President of the United States (1809-1817).
Madison attended Princeton and studied history, government, and law. He participated in the drafting of the Virginia Constitution in 1776, and in 1780 was chosen to represent Virginia in the Continental Congress (1780-83 and 1786-88). James Madison contributed greatly to the ratification of the Constitution, writing, with Alexander Hamilton and John Jay, The Federalist (1788). He was later called the "father of the Constitution."
In 1792, Madison and Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826) founded the Democratic-Republican Party, which has been called America's first opposition political party. When Jefferson became the third president of the United States, Madison served as his secretary of state. In Congress, he was involved in drafting the Bill of Rights and passing the first revenue legislation. As Secretary of State to President Jefferson (1801-1809), Madison protested to warring France and Great Britain that their seizure of American ships was contrary to international law.
Madison was elected president in 1808, succeeding Jefferson. Continued British interference in shipping, as well as other grievances, led to the War of 1812. During Madison's second term as president, the war was still ongoing, and he and his wife were even forced to flee in the face of advancing British troops who set Washington, D.C. on fire. Despite this, in 1815, the United States declared its victory in the war.
After the end of his second term, Madison remained active in public affairs. He edited his Journal of the Constitutional Convention, was co-chairman of the Virginia Constitutional Convention from 1829-1830, and chancellor of the University of Virginia from 1826-36. He was also Monroe's foreign policy advisor. Although Madison was a slave owner all his life, in the last years of his life he was active in the American Colonization Society, whose mission was to resettle slaves in Africa. James Madison died at the age of 85 in 1836.
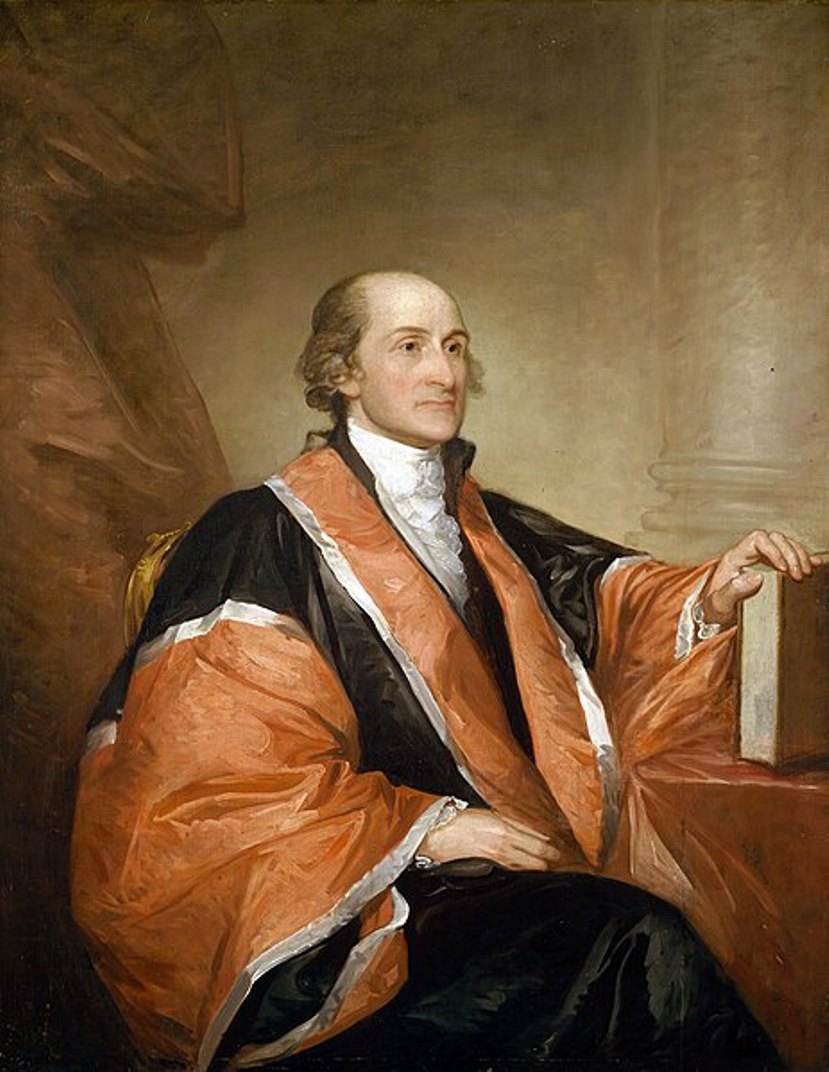

John Jay was an American lawyer and diplomat, statesman, and one of the founding fathers of the United States.
Jay came from French Huguenots, after graduating from King's College (now Columbia University) he entered law school and was admitted to the bar in 1768. After the outbreak of hostilities in the spring of 1775, Jay continued to serve both in New York and in the Continental Congress, which elected him president in late 1778.
In the fall of 1779 he was appointed minister plenipotentiary to Spain, which had recently entered into an alliance with France against England. In May 1782 he traveled to Paris, where a treaty was concluded that formally ended the war with Great Britain in 1783. Before returning to America in July 1784, Jay was appointed secretary of foreign affairs.
In 1788, Jay actively advocated for the ratification of the U.S. Constitution by the state of New York. Together with future President James Madison and economist Alexander Hamilton, he participated in the creation of the famous book The Federalist (1788). Under the new Constitution, President Washington appointed John Jay Chief Justice of the United States in 1789, and in July 1795 he became Governor of New York. After completing his second term as governor in June 1801. Jay retired to his farm in Bedford, New York.
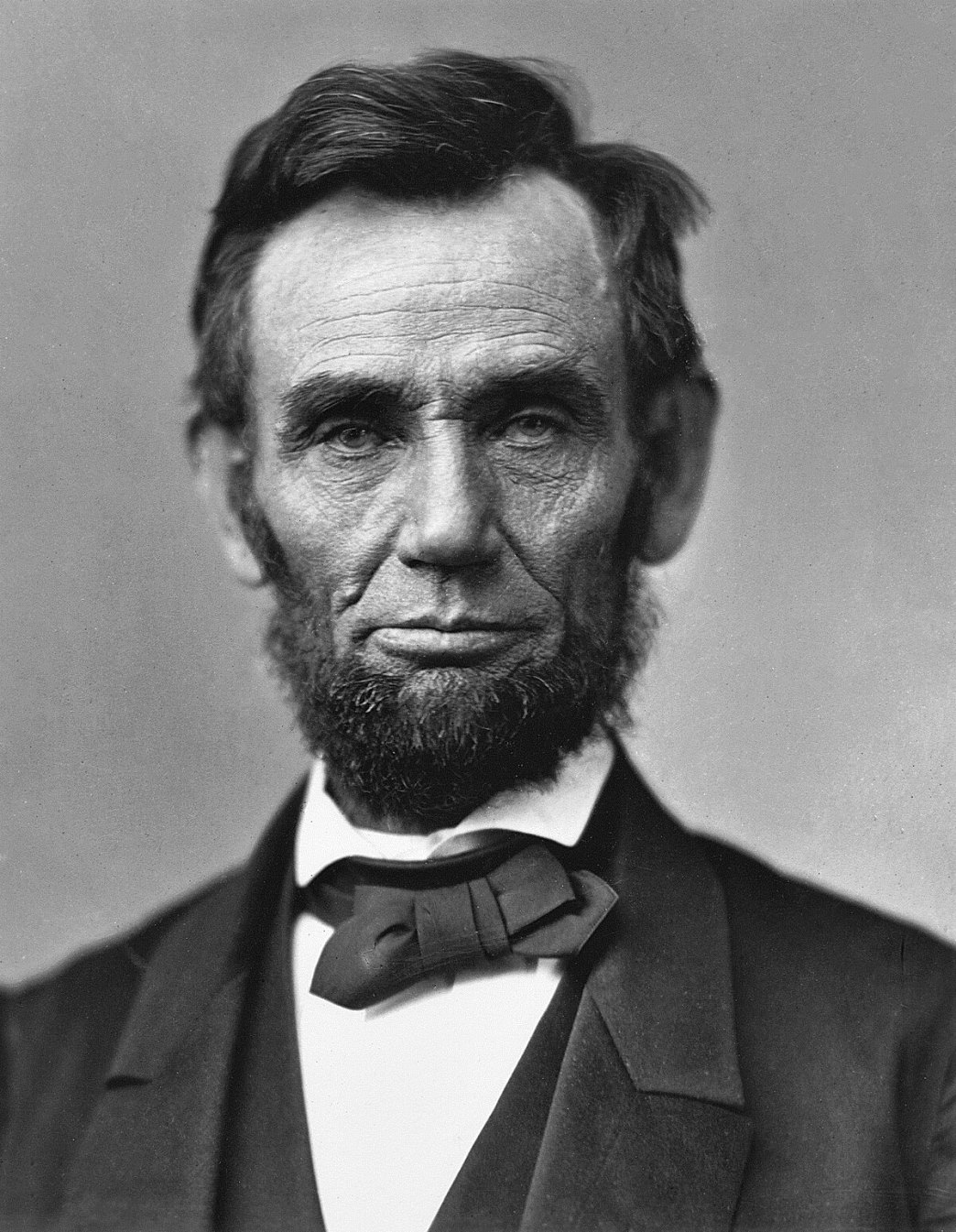


Abraham Lincoln was an American statesman and politician, the 16th President of the United States (March 4, 1861 - April 15, 1865).
The son of a frontiersman and a Kentucky farmer, Lincoln worked hard from an early age and struggled to learn. He was a militiaman in the Indian War, practiced law, and sat in the Illinois legislature for eight years. He was an opponent of slavery and gradually gained a national reputation that earned him victory in the 1860 presidential election.
After becoming the 16th president of the United States, Abraham Lincoln turned the Republican Party into a strong national organization. In addition, he drew most Northern Democrats to the Union side. On January 1, 1863, he issued the Emancipation Proclamation, which declared permanently free those slaves who were in Confederate territory. Lincoln considered secession illegal and was prepared to use force to defend federal law and the Union. Four more slave states joined the Confederacy, but four remained in the Union, and the Civil War of 1861-1865 began.
Lincoln personally directed the military action that led to victory over the Confederacy. Abraham Lincoln was reelected in 1864, and on April 14, 1865, he was fatally shot at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C. by actor John Wilkes Booth.
Abraham Lincoln is a national hero of the American people, he is considered one of the best and most famous presidents of the United States until today.


James Madison was an American politician and statesman, the fourth President of the United States (1809-1817).
Madison attended Princeton and studied history, government, and law. He participated in the drafting of the Virginia Constitution in 1776, and in 1780 was chosen to represent Virginia in the Continental Congress (1780-83 and 1786-88). James Madison contributed greatly to the ratification of the Constitution, writing, with Alexander Hamilton and John Jay, The Federalist (1788). He was later called the "father of the Constitution."
In 1792, Madison and Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826) founded the Democratic-Republican Party, which has been called America's first opposition political party. When Jefferson became the third president of the United States, Madison served as his secretary of state. In Congress, he was involved in drafting the Bill of Rights and passing the first revenue legislation. As Secretary of State to President Jefferson (1801-1809), Madison protested to warring France and Great Britain that their seizure of American ships was contrary to international law.
Madison was elected president in 1808, succeeding Jefferson. Continued British interference in shipping, as well as other grievances, led to the War of 1812. During Madison's second term as president, the war was still ongoing, and he and his wife were even forced to flee in the face of advancing British troops who set Washington, D.C. on fire. Despite this, in 1815, the United States declared its victory in the war.
After the end of his second term, Madison remained active in public affairs. He edited his Journal of the Constitutional Convention, was co-chairman of the Virginia Constitutional Convention from 1829-1830, and chancellor of the University of Virginia from 1826-36. He was also Monroe's foreign policy advisor. Although Madison was a slave owner all his life, in the last years of his life he was active in the American Colonization Society, whose mission was to resettle slaves in Africa. James Madison died at the age of 85 in 1836.
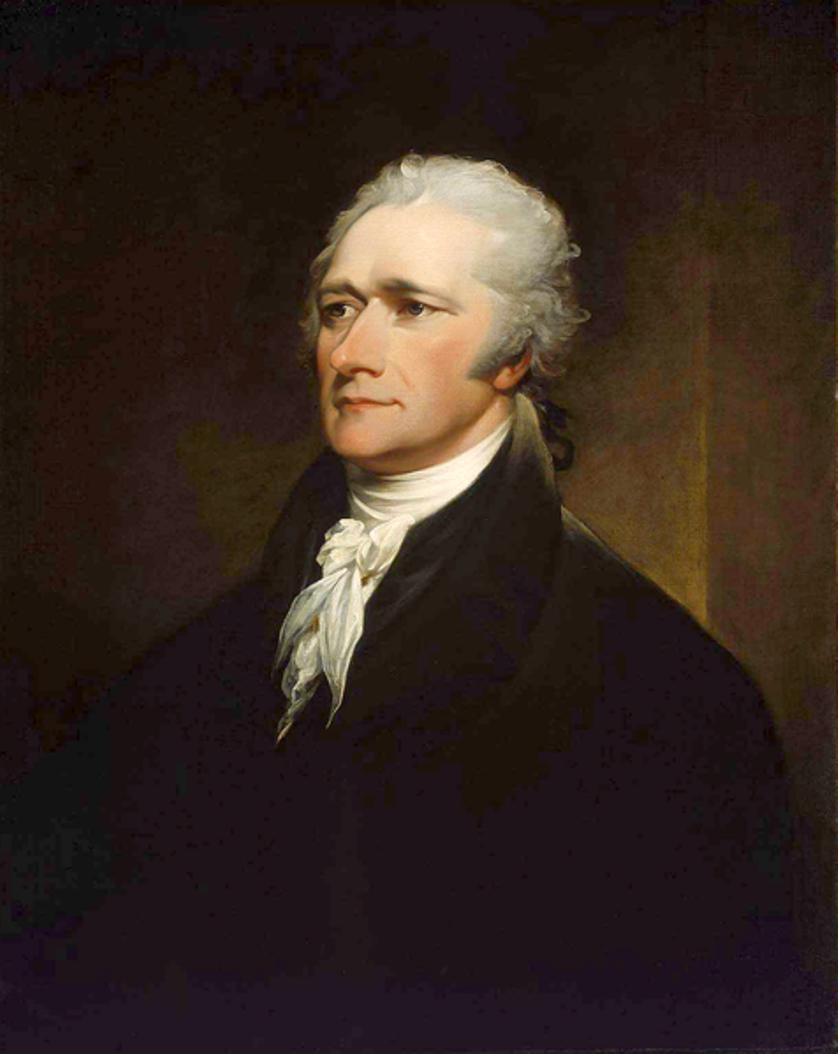

Alexander Hamilton was an American politician and statesman, the founder of the American financial system.
A native of Great Britain, Hamilton arrived in continental America in late 1772 and enrolled at King's College in New York. He became captain of an artillery company in 1776 and fought in the battles of Kips Bay, White Plains, Trenton, and Princeton during the American War of Independence. For four years he served on George Washington's staff as adjutant with the rank of lieutenant colonel. And in 1782, Hamilton was chosen by New York as a delegate to the Confederate Congress.
Alexander Hamilton was also one of New York's delegates to the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in 1787. He was a passionate advocate of the Constitution and, along with future President James Madison and John Jay, contributed to the famous book The Federalist (1788), writing most of the essays for it. After George Washington was elected the nation's first president in 1789, he appointed Hamilton Secretary of the Treasury. As the first Secretary of the Treasury (1789-1795), Hamilton developed plans to finance the national debt, secure federal credit, encourage the expansion of manufacturing, and organize a federal bank. In 1801, Hamilton founded the New York Evening Post newspaper.
On July 11, 1804, Hamilton was mortally wounded in a duel with his personal and political rival, Vice President Aaron Burr. Today, Alexander Hamilton is revered as one of the founding fathers of the United States, he is known for his role in creating America's financial system, and his portrait is on the ten dollar bill.

John Jay was an American lawyer and diplomat, statesman, and one of the founding fathers of the United States.
Jay came from French Huguenots, after graduating from King's College (now Columbia University) he entered law school and was admitted to the bar in 1768. After the outbreak of hostilities in the spring of 1775, Jay continued to serve both in New York and in the Continental Congress, which elected him president in late 1778.
In the fall of 1779 he was appointed minister plenipotentiary to Spain, which had recently entered into an alliance with France against England. In May 1782 he traveled to Paris, where a treaty was concluded that formally ended the war with Great Britain in 1783. Before returning to America in July 1784, Jay was appointed secretary of foreign affairs.
In 1788, Jay actively advocated for the ratification of the U.S. Constitution by the state of New York. Together with future President James Madison and economist Alexander Hamilton, he participated in the creation of the famous book The Federalist (1788). Under the new Constitution, President Washington appointed John Jay Chief Justice of the United States in 1789, and in July 1795 he became Governor of New York. After completing his second term as governor in June 1801. Jay retired to his farm in Bedford, New York.