charles edwards

Charles Edward Conder, an Anglo-British painter, was a pivotal figure in the Australian art scene, known for his significant contributions to the Heidelberg School and the famous 9 x 5 Impressions Exhibition. Born in England in 1868, Conder's artistic journey began in earnest when he moved to Australia, where he immersed himself in the country's landscapes and developed a unique style that melded his natural instinct for color and design with the influences of his contemporaries and the environment.
Charles Edward Conder's time in Australia was marked by collaborative efforts with other notable artists, including Tom Roberts and Arthur Streeton, with whom he shared a studio and participated in the notable 9 x 5 Impressions Exhibition. His work during this period, characterized by a distinctive use of color and form, captured the essence of the Australian landscape while reflecting his personal artistic sensibilities.
In 1890, Charles Edward Conder's artistic pursuits took him to Europe, where he studied in Paris and mingled with prominent artists and writers of the day. His work continued to evolve, embracing the influences of Aestheticism and the Bohemian lifestyle he led. Despite his artistic success, Conder's life was marred by health issues, including the effects of syphilis, which he contracted early in his career. His later years were spent in a struggle with the disease, culminating in his death in a sanatorium in 1909.
Today, Conder's legacy is preserved in his contributions to Australian art and the influence he had on his peers and successors. His works continue to be celebrated for their beauty, emotional depth, and the unique perspective they provide on the landscapes and culture of Australia during his time.
For those interested in delving deeper into the life and works of Charles Edward Conder, his art remains a testament to his skill and vision, offering a window into the vibrant art scene of his era and the landscapes that inspired him.
If you're captivated by the unique blend of Australian landscapes and European artistry in Charles Edward Conder's work, or if you wish to discover more about the Heidelberg School's influence on art and culture, we invite you to sign up for updates. Stay informed about upcoming exhibitions, sales of Conder's works, and exclusive insights into the world of art collecting. Don't miss the opportunity to deepen your appreciation for one of the luminaries of Australian art.





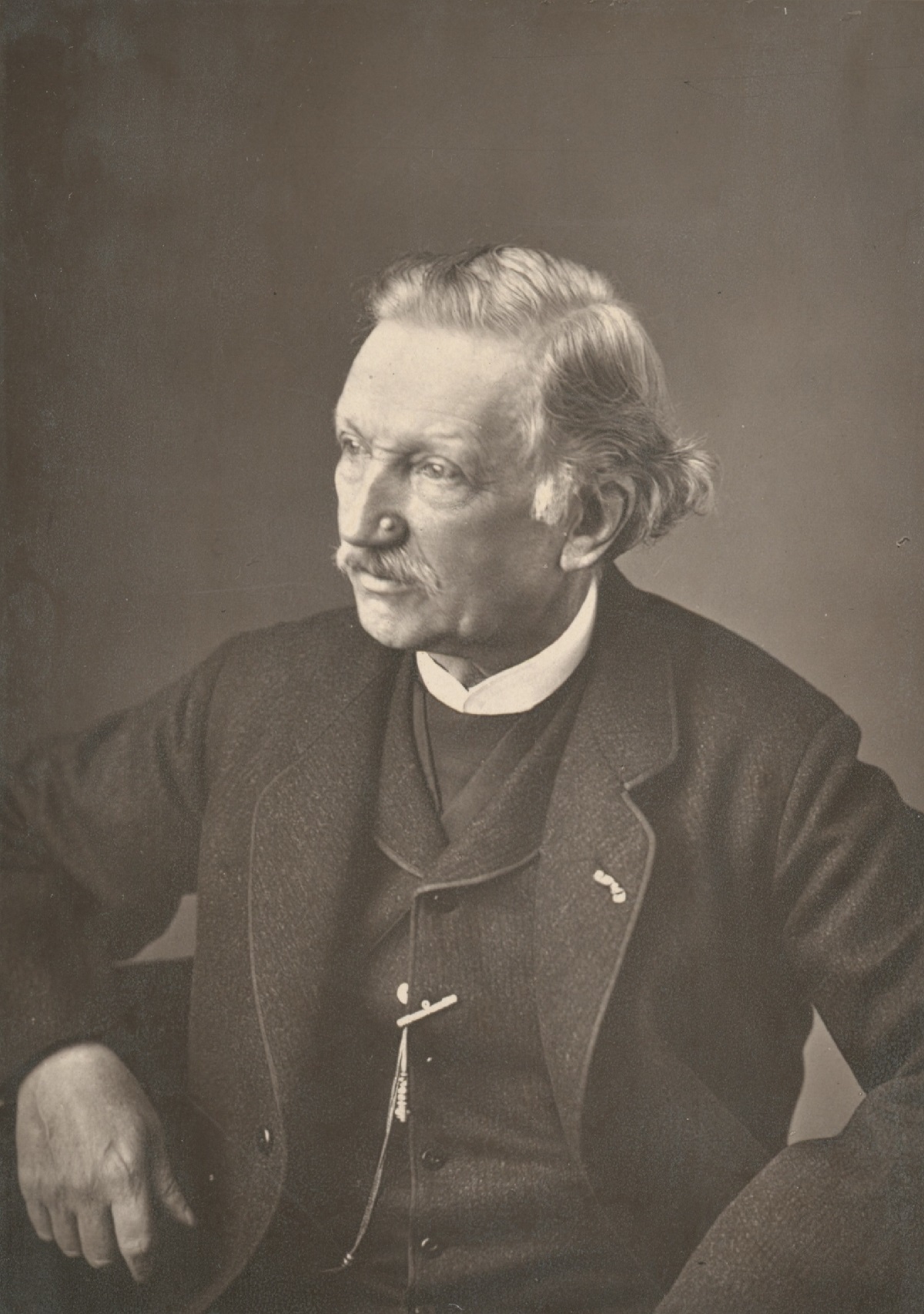
Charles Baker was a British educator, pioneer in deaf education, naturalist and artist.
He became known and honored in Great Britain for having developed the first school textbooks for deaf-blind children, including those based on drawing.
As a young man he became a teacher at the Edgbaston Institute for the Deaf and Dumb in Edgbaston, near Birmingham, and was faced with a complete lack of textbooks for such children. Baker had a passion for entomology, and began directing the attention of his older pupils to the various objects of natural history around them. As a result, in 1828, he authored a small volume of illustrations entitled British Butterflies: their differences, genera and species, with lithographic illustrations of each genus, comprising 33 species, drawn by the children of the Edgbaston School for the Deaf and Dumb."
Charles Baker worked as a teacher of the deaf and headmaster at Doncaster School for forty-five years. During this time he produced many specialized teaching guides and textbooks under the general title "Circle of Knowledge", which were used in Europe and Russia, as well as in China and Japan.


Charles-Emile Jacques was a French painter of Pastoralism and engraver who was, with Jean-François Millet, part of the Barbizon School. He first learned to engrave maps when he spent seven years in the French Army.


Edward John Burra was an English painter, draughtsman, and printmaker, best known for his depictions of the urban underworld, black culture and the Harlem scene of the 1930s.




Edward Lear was an English artist, illustrator, musician, author and poet, who is known mostly for his literary nonsense in poetry and prose and especially his limericks, a form he popularised.


Edward Lear was an English artist, illustrator, musician, author and poet, who is known mostly for his literary nonsense in poetry and prose and especially his limericks, a form he popularised.


Edward Lear was an English artist, illustrator, musician, author and poet, who is known mostly for his literary nonsense in poetry and prose and especially his limericks, a form he popularised.
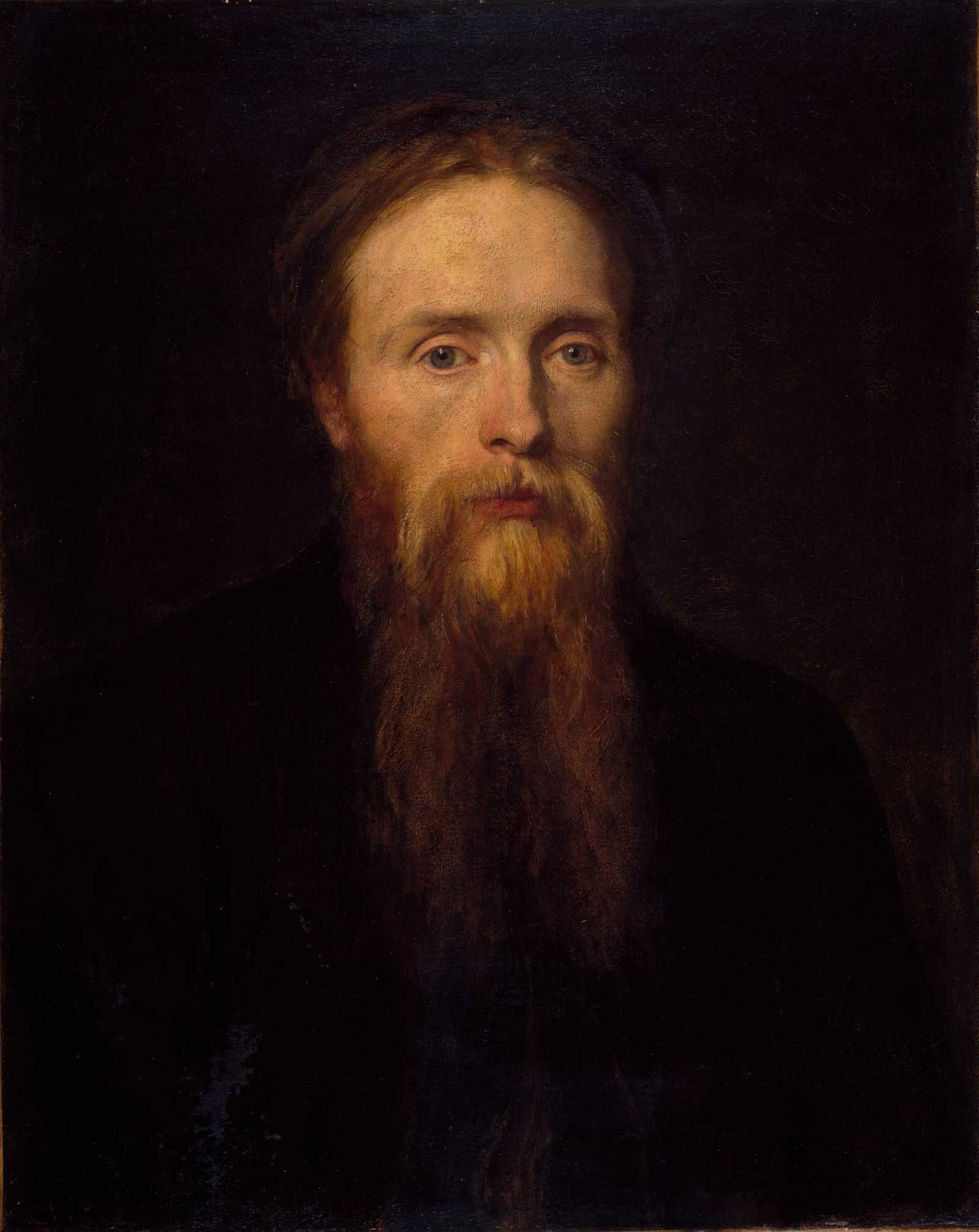
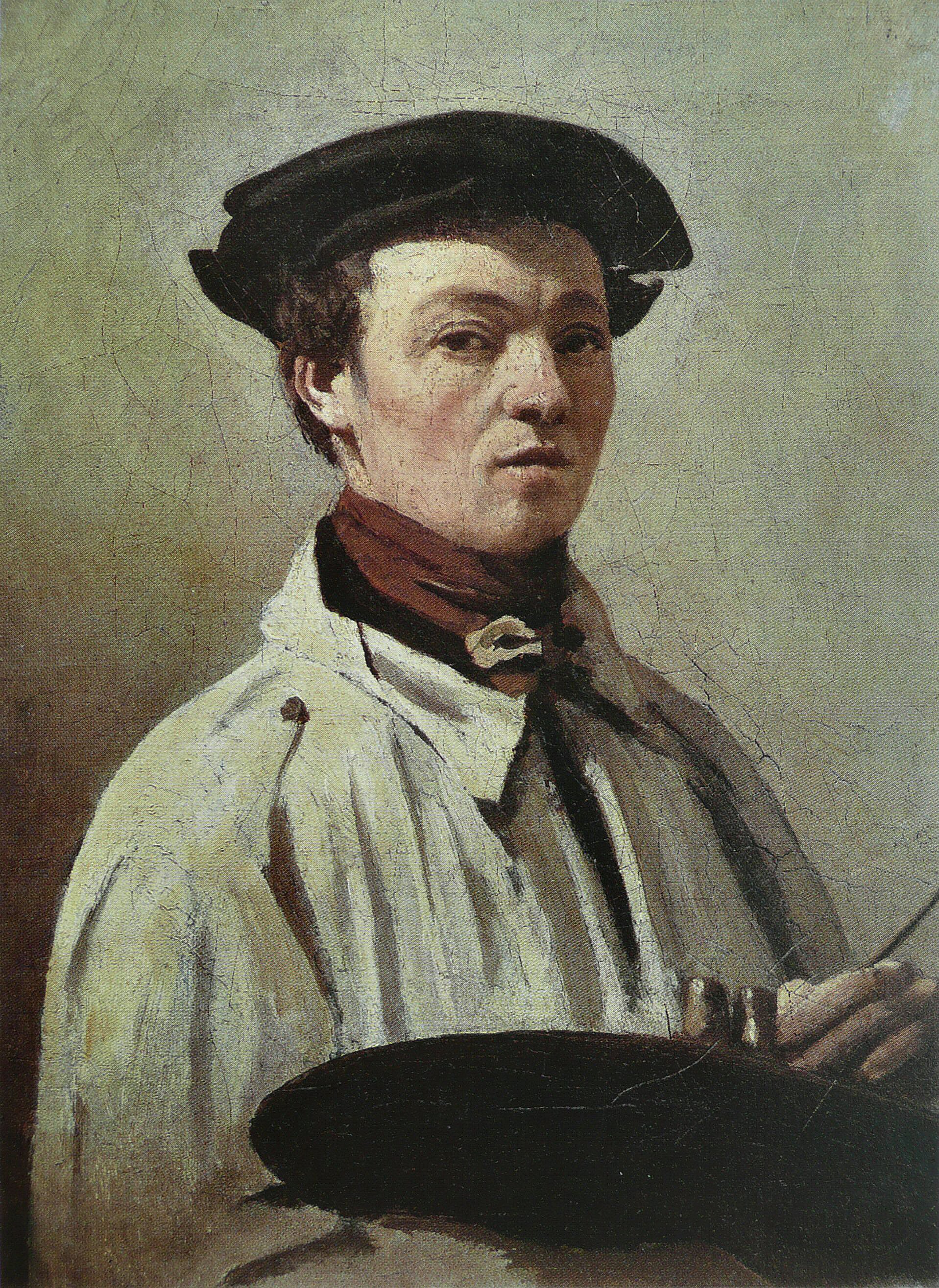






Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot was a French landscape and portrait painter as well as a printmaker in etching. He is a pivotal figure in landscape painting and his vast output simultaneously referenced the Neo-Classical tradition and anticipated the plein-air innovations of Impressionism.
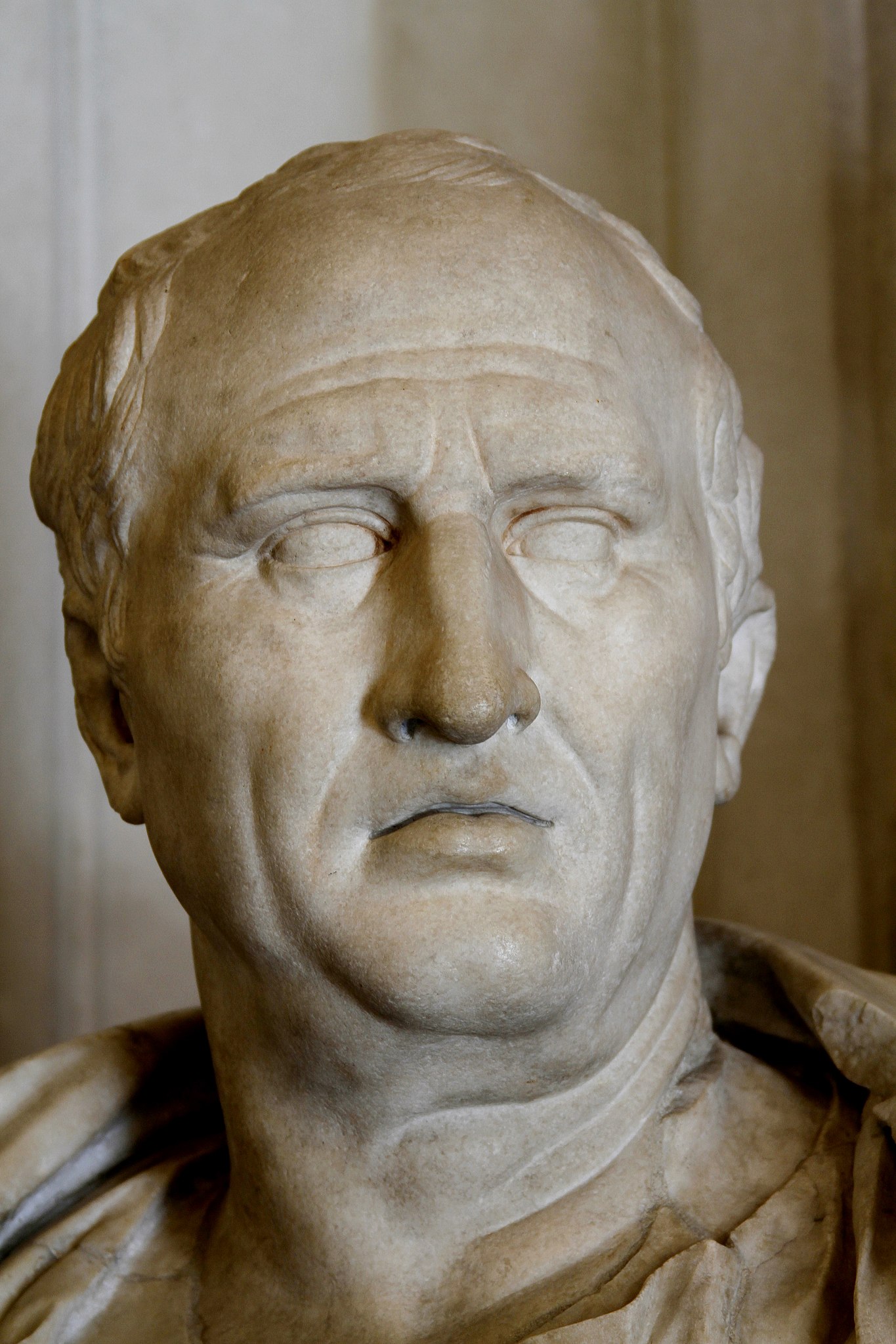







Marcus Tullius Cicero was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the establishment of the Roman Empire. His extensive writings include treatises on rhetoric, philosophy and politics. He is considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the Roman equestrian order, and served as consul in 63 BC.
His influence on the Latin language was immense. He wrote more than three-quarters of extant Latin literature that is known to have existed in his lifetime, and it has been said that subsequent prose was either a reaction against or a return to his style, not only in Latin but in European languages up to the 19th century. Cicero introduced into Latin the arguments of the chief schools of Hellenistic philosophy and created a Latin philosophical vocabulary with neologisms such as evidentia, humanitas, qualitas, quantitas, and essentia, distinguishing himself as a translator and philosopher.
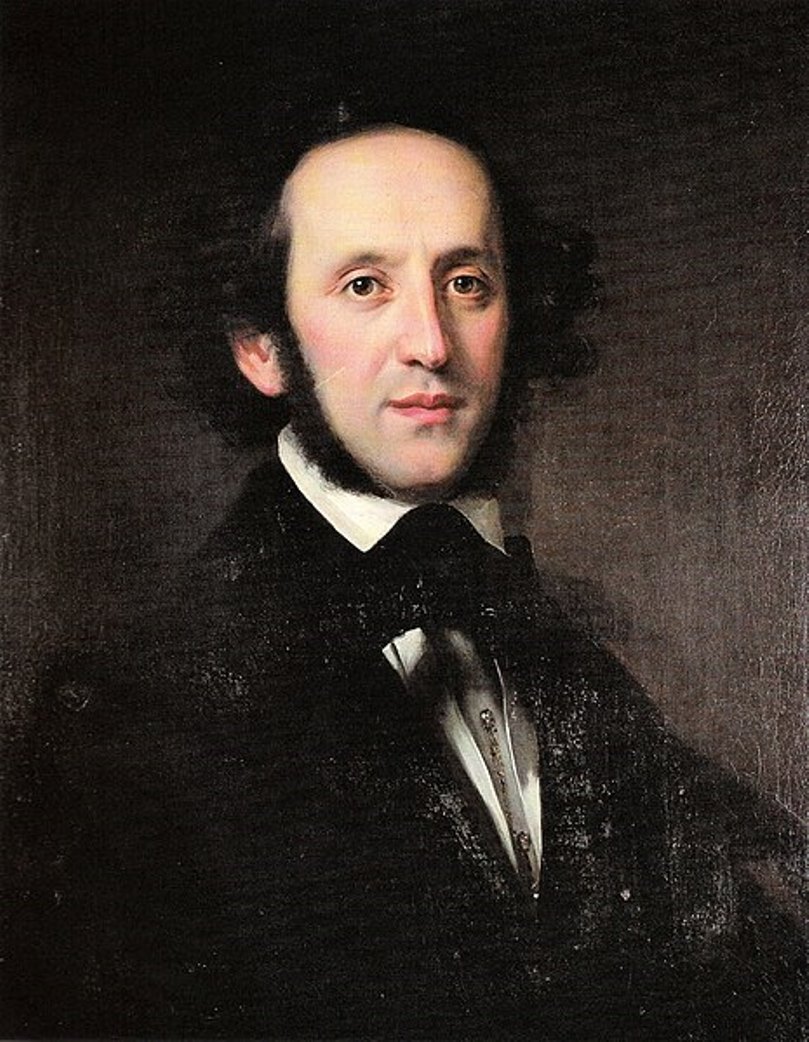


Felix Mendelssohn (full name Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy) was a German composer, pianist, conductor, teacher, and one of the greatest representatives of Romanticism in music.
Felix was born into a Jewish musical family that later converted to Christianity. He received a versatile education and already as a child wrote many musical compositions, including 5 operas, 11 symphonies for string orchestra, concertos, sonatas and fugues. Mendelssohn's first public performance took place in Berlin in 1818, when he was nine years old. In 1821 Mendelssohn was introduced to J.W. von Goethe, for whom he performed works by J.S. Bach and Mozart and to whom he dedicated his Piano Quartet No. 3 in B minor. A friendship developed between the famous wise poet and the 12-year-old musician.
A few years later, the talented musician began conducting in various orchestras in Europe, and became acquainted with Carl Weber. In England, where Mendelssohn visited very often, by the middle of the 19th century his music had become very popular, even with Queen Victoria he was the most favorite composer. He dedicated his Symphony No. 3 in A minor major (Scottish Symphony) to the Queen.
Among Mendelssohn's most famous works are A Midsummer Night's Dream (1826), the Italian Symphony (1833), a violin concerto (1844), two piano concertos (1831, 1837), the oratorio Elijah (1846) and several chamber pieces. The tradition of playing the "Wedding March" from A Midsummer Night's Dream in wedding processions dates back to its performance at the wedding of a royal princess in 1858, already after Mendelssohn's death.
In 1843, Mendelssohn founded a conservatory in Leipzig, where he taught composition with Schumann. Mendelssohn was one of the first great Romantic composers of the nineteenth century.
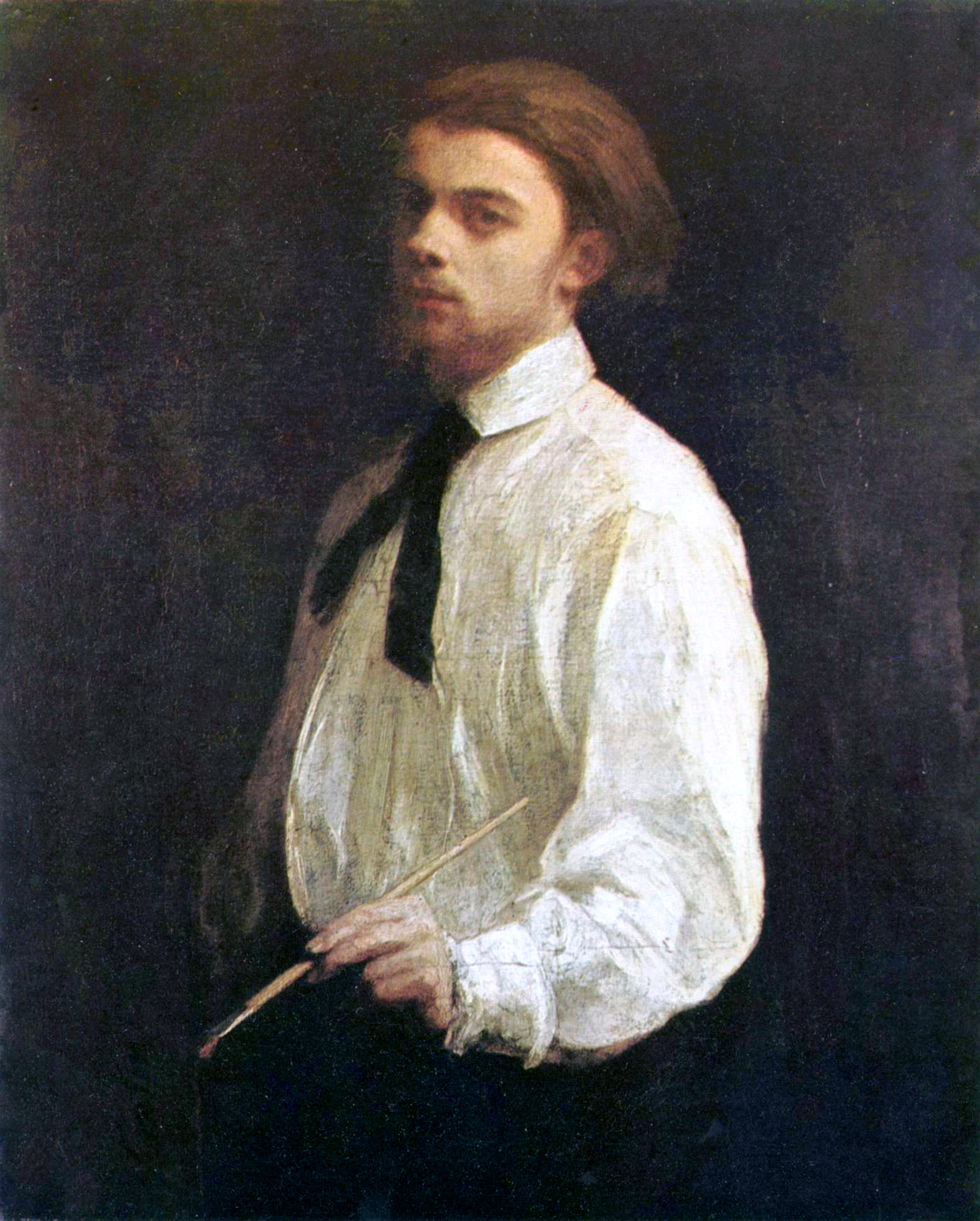


Henri Fantin-Latour was a French painter and lithographer renowned for his exquisite flower paintings and insightful group portraits of Parisian artists and writers. His artistic journey began in Grenoble, where he was born in 1836, but it flourished in Paris, where he moved at a young age to study art. Despite his associations with Impressionists like Édouard Manet and Claude Monet, Fantin-Latour carved his unique path, focusing on still life and portraiture rather than adopting the Impressionist style.
Henri Fantin-Latour's knack for capturing the essence of his subjects is evident in his group portraits, which were not just mere representations but insightful depictions of the artistic and literary circles of his time. His notable works like "A Studio at Les Batignolles" illustrate the camaraderie among artists like Manet, Renoir, and Monet, offering a window into the vibrant Parisian art scene of the 19th century. His still lifes, particularly his flower paintings, are celebrated for their realism and delicate precision, making them a favorite among collectors and art enthusiasts.
In addition to his painting, Henri Fantin-Latour's lithographs, inspired by classical music and imbued with a poetic and symbolic quality, reveal another dimension of his talent, showcasing his ability to transcend the boundaries of realism and delve into the realm of imagination.
For art collectors and experts, Henri Fantin-Latour's works offer a blend of technical mastery and a deep understanding of the interplay between art, music, and literature. His contributions to the art world are remembered and celebrated in museums around the globe, where his works continue to inspire and captivate audiences.
For those interested in exploring more about Henri Fantin-Latour's life and works, visiting exhibitions or keeping abreast of auctions featuring his art can provide valuable insights into his creative genius. To stay updated on related events and opportunities, consider subscribing to updates from art institutions or galleries specializing in 19th-century French art.












![[MARCHAND, Etienne (1755-1793)] and FLEURIEU, Charles Pierre Claret de (1738-1810).](/assets/image/picture_3615476/948e9/5adab94693e4ae36441ca19ea802e8991702422000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[MARCHAND, Etienne (1755-1793)] and FLEURIEU, Charles Pierre Claret de (1738-1810).](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3615476/948e9/5adab94693e4ae36441ca19ea802e8991702422000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)







![[BAKER, Charles (1803-1874)]](/assets/image/picture_2944532/5c632/afac882956434e0e070d6b97c7eb03e91689112800jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[BAKER, Charles (1803-1874)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2944532/5c632/afac882956434e0e070d6b97c7eb03e91689112800jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)