famous

William Shakespeare was a British poet and playwright and writer.
William's father, John Shakespeare, was a merchant and official in Stratford. There are reports that he was a sailor for a time before joining a theater company in London. Beginning in the 1590s, Shakespeare began writing plays, and in 1593 he published a poem, Venus and Adonis, which became popular. He dedicated it to the Duke of Southampton, who was a philanthropist and patron of talent, and soon his business was booming.
From 1592 to 1600 Shakespeare wrote his dramas and romantic comedies "Richard III", "The Taming of the Shrew", "Romeo and Juliet", "A Midsummer Night's Dream" and "The Merchant of Venice", as well as the comedies "Much Ado About Nothing", "Twelfth Night" and the tragedy "Julius Caesar". The playwright's business was so successful that he even bought a large house in Stratford. In 1599, Shakespeare became one of the owners, playwright and actor of the new theater "Globe". In 1603 King James took Shakespeare's troupe under his direct patronage. In the mature period, the great playwright turned to tragedies, there were "Hamlet", "Othello", "King Lear", "Macbeth" and others.
Although in the 19th century researchers had some doubts about the authorship of many of these works, William Shakespeare is considered the greatest English playwright, one of the best playwrights in the world. His plays have been translated into all major languages and to this day form the basis of the world theatrical repertoire, most of them have been screened many times. According to the Guinness Book of Records, Shakespeare remains the world's best-selling playwright, and his plays and poems have sold more than 4 billion copies in the nearly 400 years since his death.


Niccolò di Bernardo Machiavelli was an Italian philosopher, politician and diplomat, historian and Renaissance writer.
As a young man, Niccolò Machiavelli faced financial difficulties due to his father's debts, but had access to a rich library. Machiavelli's early life and career began during a period of political upheaval in Italy. After the expulsion of the Medici family in 1494, for 14 years Niccolo Machiavelli served as a diplomat to the Florentine Republic. During this service, he gained a reputation as a cunning and unconventional thinker. However, when the Medici returned to power in 1512, Machiavelli was dismissed, imprisoned, and temporarily removed from political life.
During this period Machiavelli wrote his famous work The Sovereign, which has become one of the key works in the history of political philosophy. This book epitomizes the Machiavellian approach to politics, where the means justify the end, and where a leader should use any method to consolidate his power. The treatise drew criticism from the Pope, who condemned it for supporting rule through deceit and fear. Nevertheless, The Sovereign is still an important work of political literature, and Machiavelli has come to be called "the father of modern political theory."
Machiavelli lived the rest of his life in a small village near Florence, where he continued his creative endeavors, writing On the Art of War, as well as poems and plays. His literary legacy has become an integral part of the history of political philosophy.


Edmund Spenser was an English poet of the Queen Elizabethan era.
Spenser studied Latin and Greek, as well as literature and religion, at Pembroke Hall, Cambridge University. In 1579 he published his first poetry collection, Shepherd's Calends. He is also the author of a major English epic, The Fairy Queen (1596), a fantastic allegory celebrating the Tudor dynasty and Elizabeth I, and the sonnet cycle Amoretti and Epithalamion (1595).
Alongside his poetry, Spenser pursued a political career, serving as secretary first to the Bishop of Rochester and then to the Earl of Leicester, who introduced him to other poets and artists at Queen Elizabeth's court. In 1580 he was appointed secretary to the Lord Viceroy of Ireland, and later wrote a pamphlet, A View of the Present State of Ireland.
In 1598, during the Nine Years' War, Spenser was banished from his home in Ireland, died in London in 1599, and was buried in Poets' Corner in Westminster Abbey.
Edmund Spenser's poems were characterized by outstanding craftsmanship and lyrical beauty, a style later called the Spenserian stanza. Today his work is widely studied as one of the main representatives of the English literary Renaissance.



Niccolò di Bernardo Machiavelli was an Italian philosopher, politician and diplomat, historian and Renaissance writer.
As a young man, Niccolò Machiavelli faced financial difficulties due to his father's debts, but had access to a rich library. Machiavelli's early life and career began during a period of political upheaval in Italy. After the expulsion of the Medici family in 1494, for 14 years Niccolo Machiavelli served as a diplomat to the Florentine Republic. During this service, he gained a reputation as a cunning and unconventional thinker. However, when the Medici returned to power in 1512, Machiavelli was dismissed, imprisoned, and temporarily removed from political life.
During this period Machiavelli wrote his famous work The Sovereign, which has become one of the key works in the history of political philosophy. This book epitomizes the Machiavellian approach to politics, where the means justify the end, and where a leader should use any method to consolidate his power. The treatise drew criticism from the Pope, who condemned it for supporting rule through deceit and fear. Nevertheless, The Sovereign is still an important work of political literature, and Machiavelli has come to be called "the father of modern political theory."
Machiavelli lived the rest of his life in a small village near Florence, where he continued his creative endeavors, writing On the Art of War, as well as poems and plays. His literary legacy has become an integral part of the history of political philosophy.
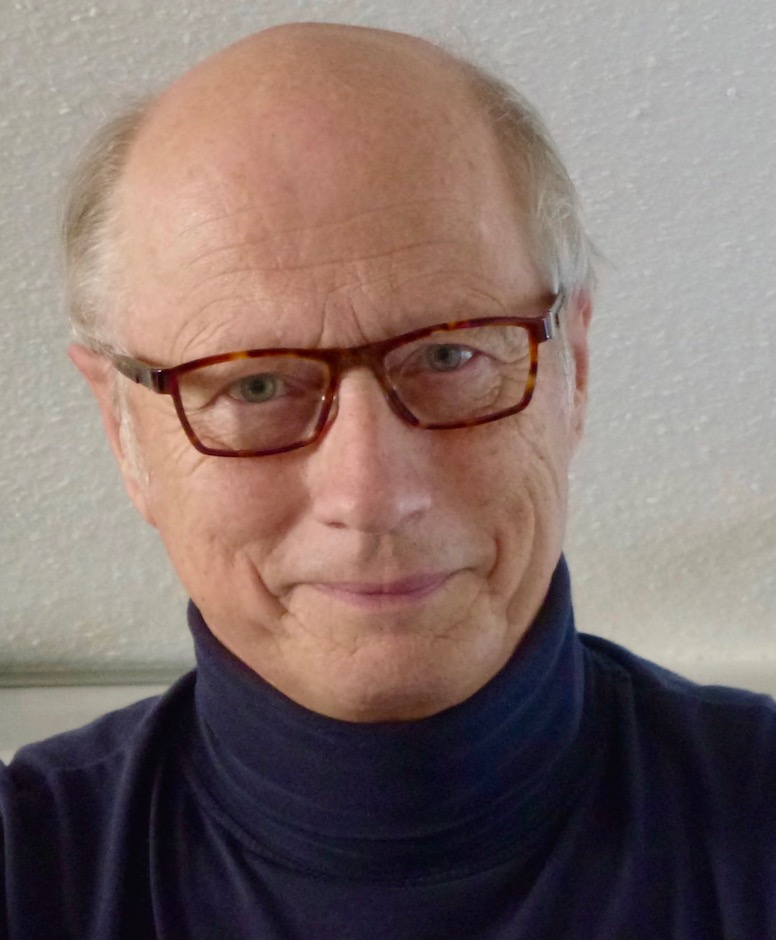





Simon Dittrich is a German painter and graphic artist who lives and works in Stuttgart, Munich, Tuscany and Styria.
Dittrich studied painting at the University of Fine Arts in Berlin, is a member of the Munich and Darmstadt Secession, and a member of the Sudeten-German Academy of Sciences.
Simon Dittrich's early works are dominated by landscapes, animals and still lifes, characterized by varied color and clear lines that emphasize contours. His later works, however, gravitate towards figurative concepts with an abstract tendency.
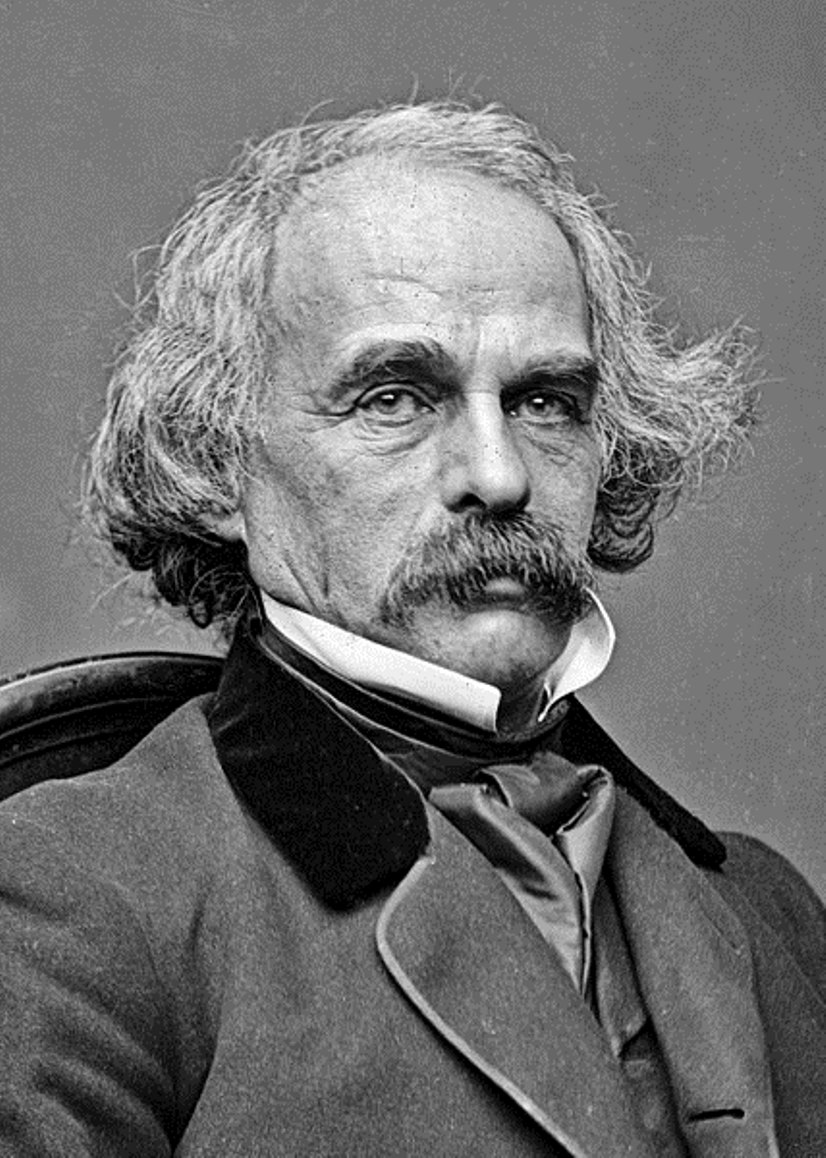


Nathaniel Hawthorne is an American writer and author.
Hawthorne is a recognized short story writer and a master of allegorical and symbolic narrative. One of the first fiction writers in American literature, he is best known for his works The Scarlet Letter (1850) and The House of Seven Gables (1851). Hawthorne's artistic works are considered part of the American Romantic movement and, in particular, of so-called dark Romanticism, a popular mid-19th-century fascination with the irrational, the demonic, and the grotesque.


Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".



Sir Thomas Malory was a British politician, writer, poet and author of The Book of King Arthur.
Malory was born to a noble family in the county of Warwickshire in the early 15th century. As a knight he took part in the War of the Scarlet and White Rose on the side of the Earl of Warwick, in 1444 or 1445 represented his county in the English Parliament. He was convicted several times, spent the last 20 years of his life in prison, where he created his novels.
Malory wrote his book, consisting of eight volumes, while in prison for various crimes, completing it in 1469 AD, and he was released the following year. He called his work "The Whole Book of King Arthur and his Noble Knights of the Round Table," but when published in 1485 the book was titled "The Death of Arthur," which stuck. The only surviving manuscript is in the British Library in London.
The identity of the author of the King Arthur saga is still disputed by researchers. It is possible that another person hides under the name of Malory, but the influence of this medieval work on history and literature is undeniable.