for him
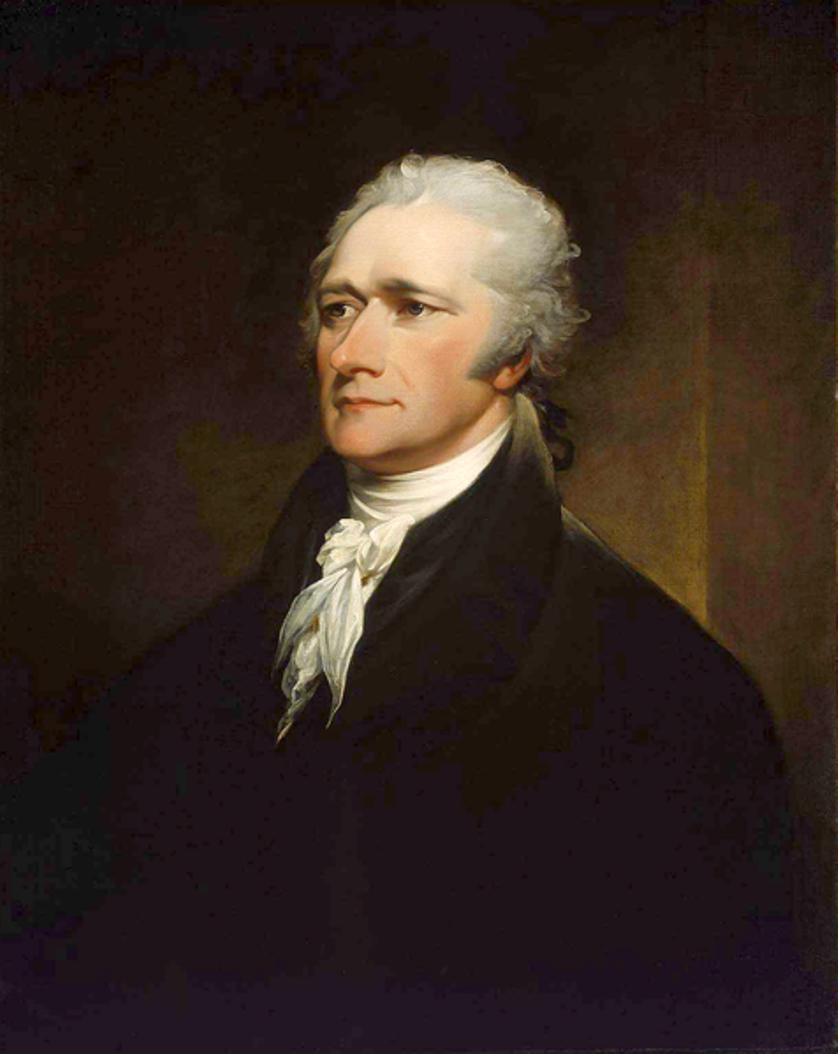

Alexander Hamilton was an American politician and statesman, the founder of the American financial system.
A native of Great Britain, Hamilton arrived in continental America in late 1772 and enrolled at King's College in New York. He became captain of an artillery company in 1776 and fought in the battles of Kips Bay, White Plains, Trenton, and Princeton during the American War of Independence. For four years he served on George Washington's staff as adjutant with the rank of lieutenant colonel. And in 1782, Hamilton was chosen by New York as a delegate to the Confederate Congress.
Alexander Hamilton was also one of New York's delegates to the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in 1787. He was a passionate advocate of the Constitution and, along with future President James Madison and John Jay, contributed to the famous book The Federalist (1788), writing most of the essays for it. After George Washington was elected the nation's first president in 1789, he appointed Hamilton Secretary of the Treasury. As the first Secretary of the Treasury (1789-1795), Hamilton developed plans to finance the national debt, secure federal credit, encourage the expansion of manufacturing, and organize a federal bank. In 1801, Hamilton founded the New York Evening Post newspaper.
On July 11, 1804, Hamilton was mortally wounded in a duel with his personal and political rival, Vice President Aaron Burr. Today, Alexander Hamilton is revered as one of the founding fathers of the United States, he is known for his role in creating America's financial system, and his portrait is on the ten dollar bill.
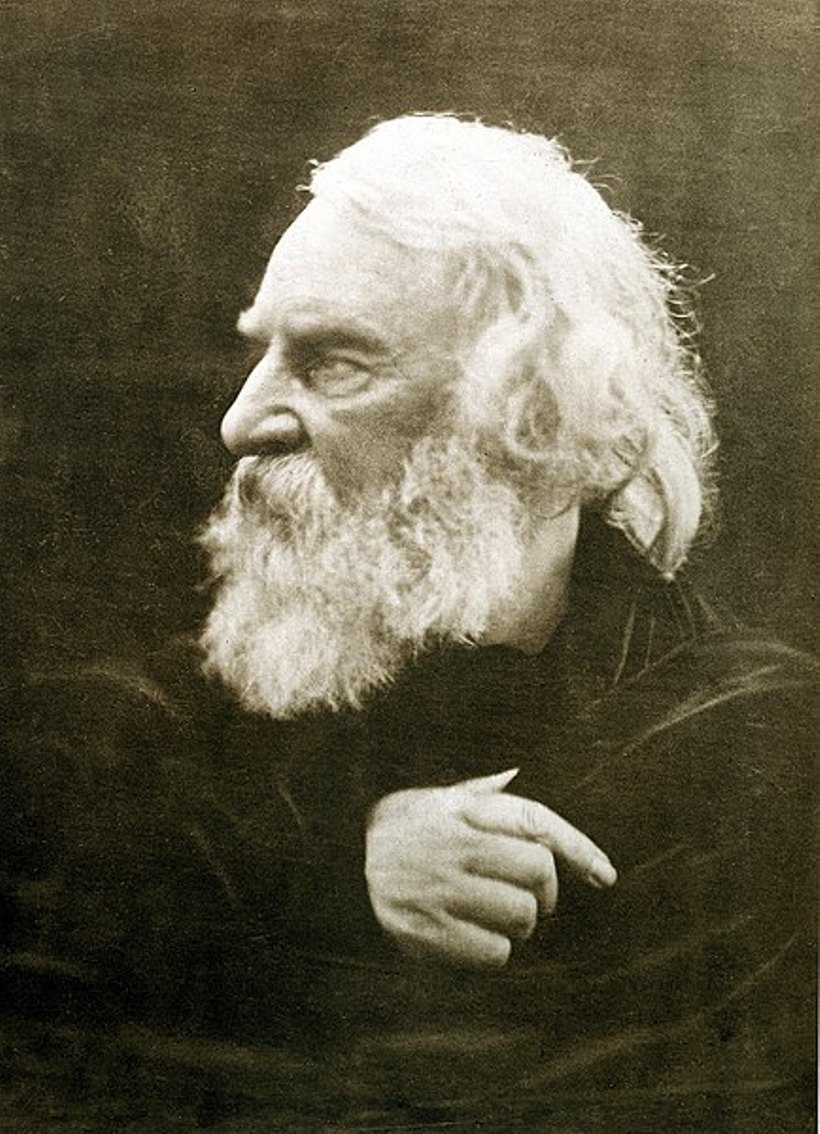


Henry Wadsworth Longfellow was the most popular American poet of the nineteenth century.
Longfellow is one of the most revered poets in the United States. His poems "Paul Revere's Ride", "Evangeline", "The Tale of Acadia" (1847) and "Psalm of Life" were included in elementary and high school curricula and have long been remembered by generations of readers who studied them as children. Longfellow revitalized American literary life by linking American poetry to European traditions outside of England.
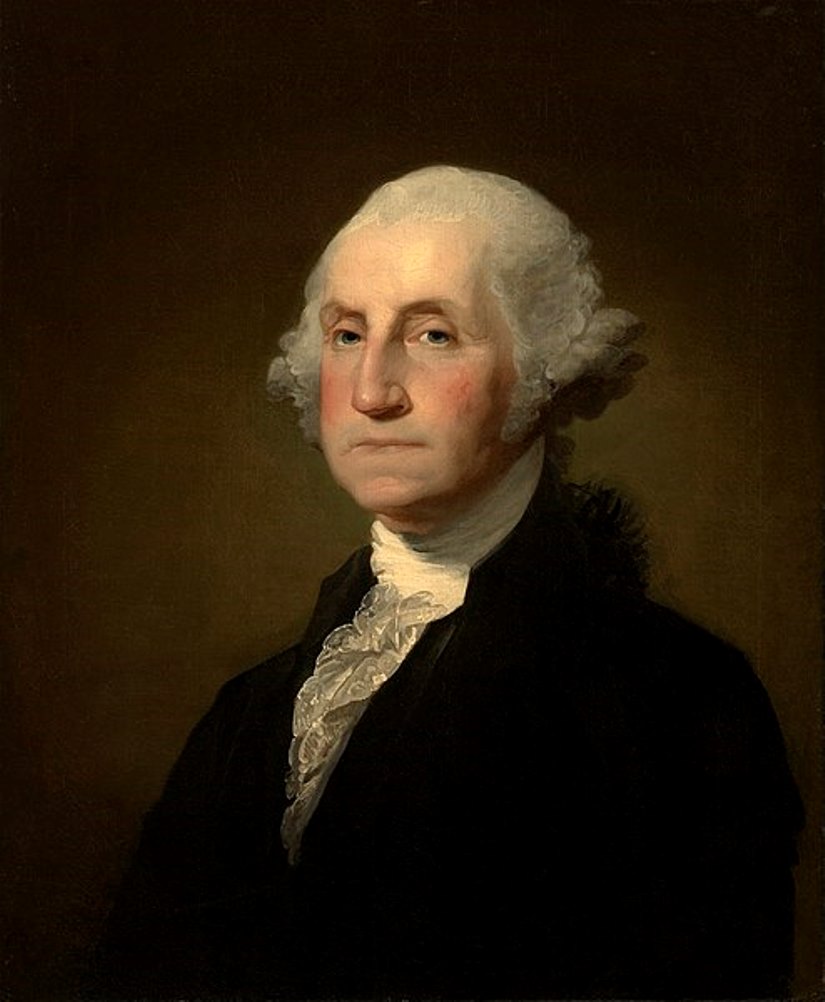


George Washington is the first popularly elected president of the United States of America and one of the founding fathers of the United States.
Born into a noble family in colonial Virginia in February 1732, George Washington served as a Virginian officer with British troops during the French-Indian War (1754-1763) from 1754-1758. This was a territorial war fought largely between the colonies of Britain and France that escalated into a worldwide conflict between the two countries. J. Washington was at the center of the conflicts in the disputed Ohio River Valley area.
In June 1775, he was elected commander-in-chief of the Continental forces in the war already for independence from Great Britain. He commanded American troops throughout the war, becoming famous for his perseverance and bravery.
In 1787, J. Washington represented the state of Virginia as a delegate to the Constitutional Convention. This convention created the Constitution of the United States. In 1789, the Electoral College unanimously elected George Washington president, and in 1792 he was re-elected for a second term. Thus George Washington was in office as President of the United States from April 30, 1789 to March 4, 1797.
As head of state, he helped to strengthen the Union, implement the principles of the Constitution and build the capital of the United States. He was engaged in the formation of the central authorities and system of government, created precedents for the institution of presidents, encouraged the development of the economy, maintained friendly relations with Congress. In foreign policy Washington avoided interference in the affairs of European states.
After leaving the post of president, George Washington lived in Mount Vernon Manor.
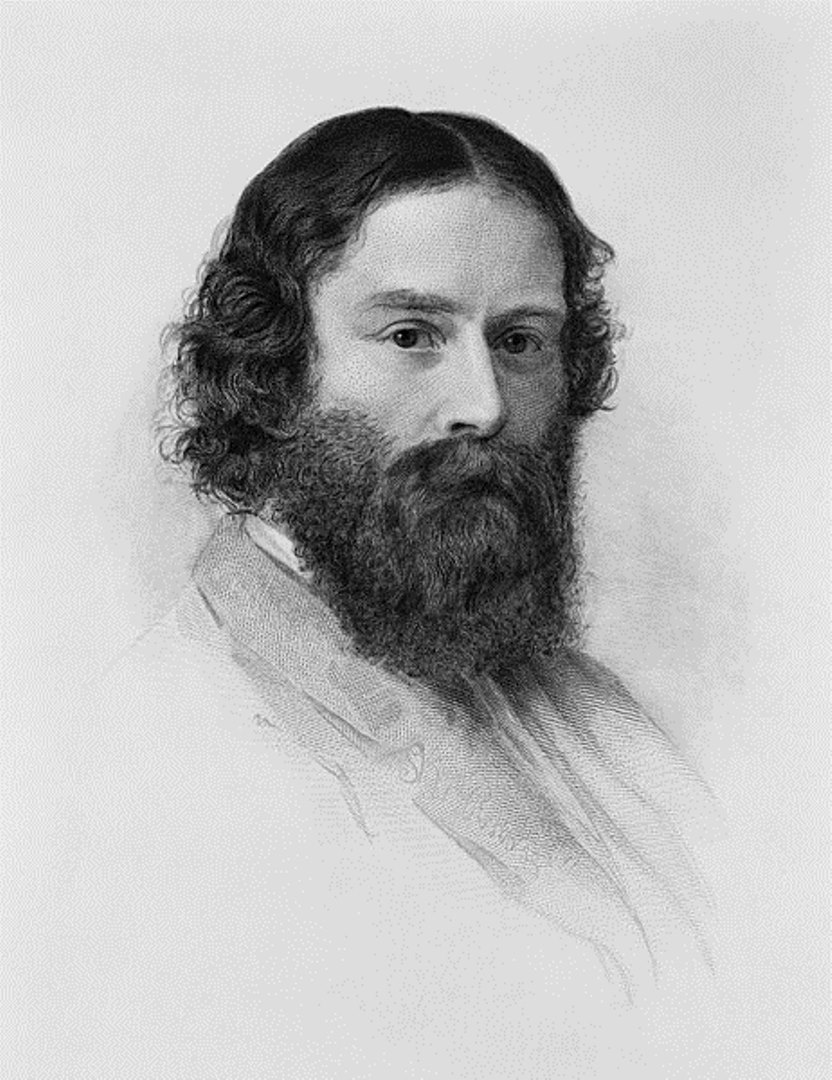


James Russell Lowell was an American poet, educator, and diplomat.
From 1845 to 1850, he wrote about 50 articles against slavery for periodicals. Two of Lowell's other two most important works were also published in 1848: the poem "Sir Launfal's Vision," praising the brotherhood of man, and "A Fable for Critics," a witty appraisal of contemporary American authors. These books, together with the publication in the same year of a second series of his poems, made Lowell the most popular new figure in 19th-century American literature.
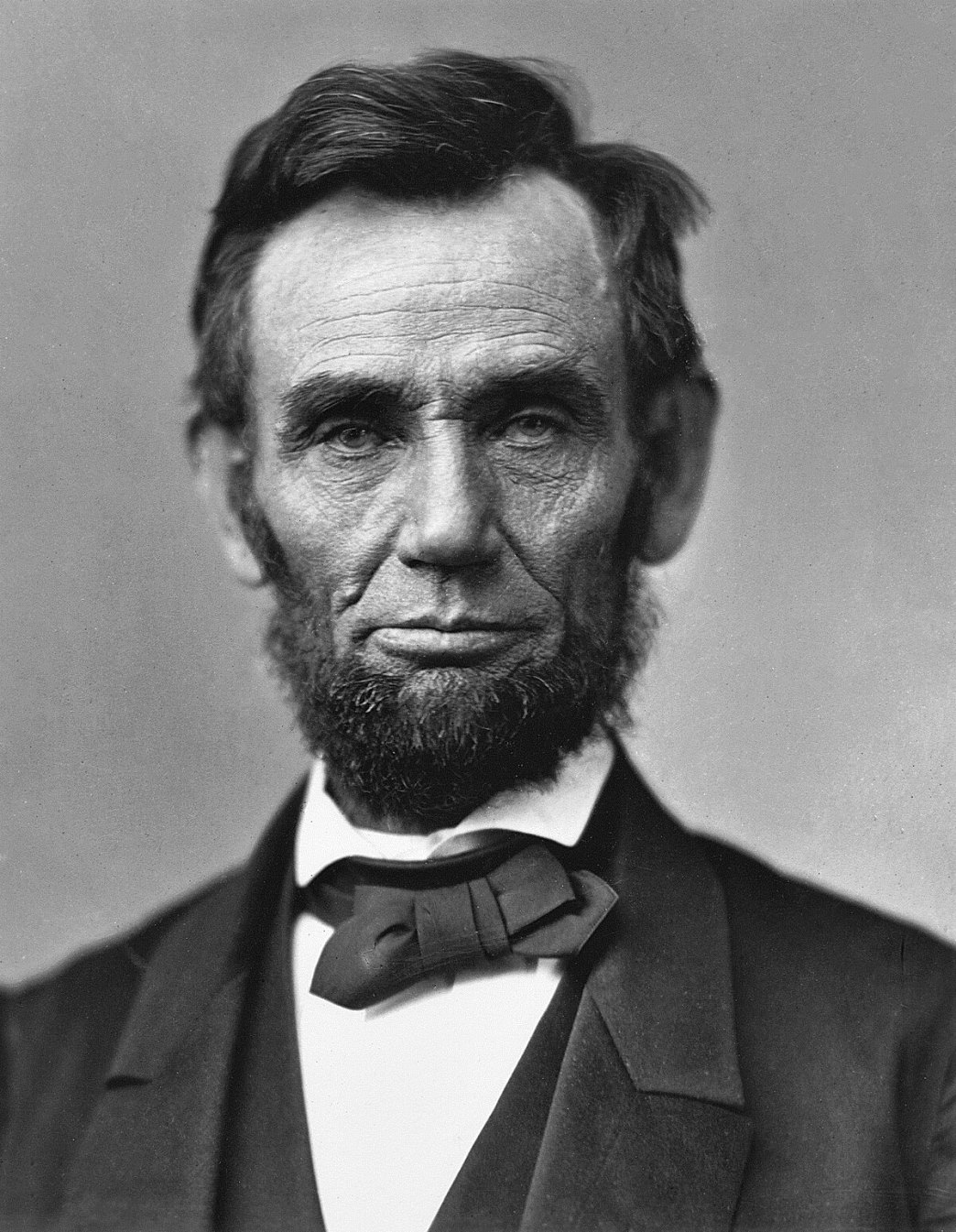


Abraham Lincoln was an American statesman and politician, the 16th President of the United States (March 4, 1861 - April 15, 1865).
The son of a frontiersman and a Kentucky farmer, Lincoln worked hard from an early age and struggled to learn. He was a militiaman in the Indian War, practiced law, and sat in the Illinois legislature for eight years. He was an opponent of slavery and gradually gained a national reputation that earned him victory in the 1860 presidential election.
After becoming the 16th president of the United States, Abraham Lincoln turned the Republican Party into a strong national organization. In addition, he drew most Northern Democrats to the Union side. On January 1, 1863, he issued the Emancipation Proclamation, which declared permanently free those slaves who were in Confederate territory. Lincoln considered secession illegal and was prepared to use force to defend federal law and the Union. Four more slave states joined the Confederacy, but four remained in the Union, and the Civil War of 1861-1865 began.
Lincoln personally directed the military action that led to victory over the Confederacy. Abraham Lincoln was reelected in 1864, and on April 14, 1865, he was fatally shot at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C. by actor John Wilkes Booth.
Abraham Lincoln is a national hero of the American people, he is considered one of the best and most famous presidents of the United States until today.
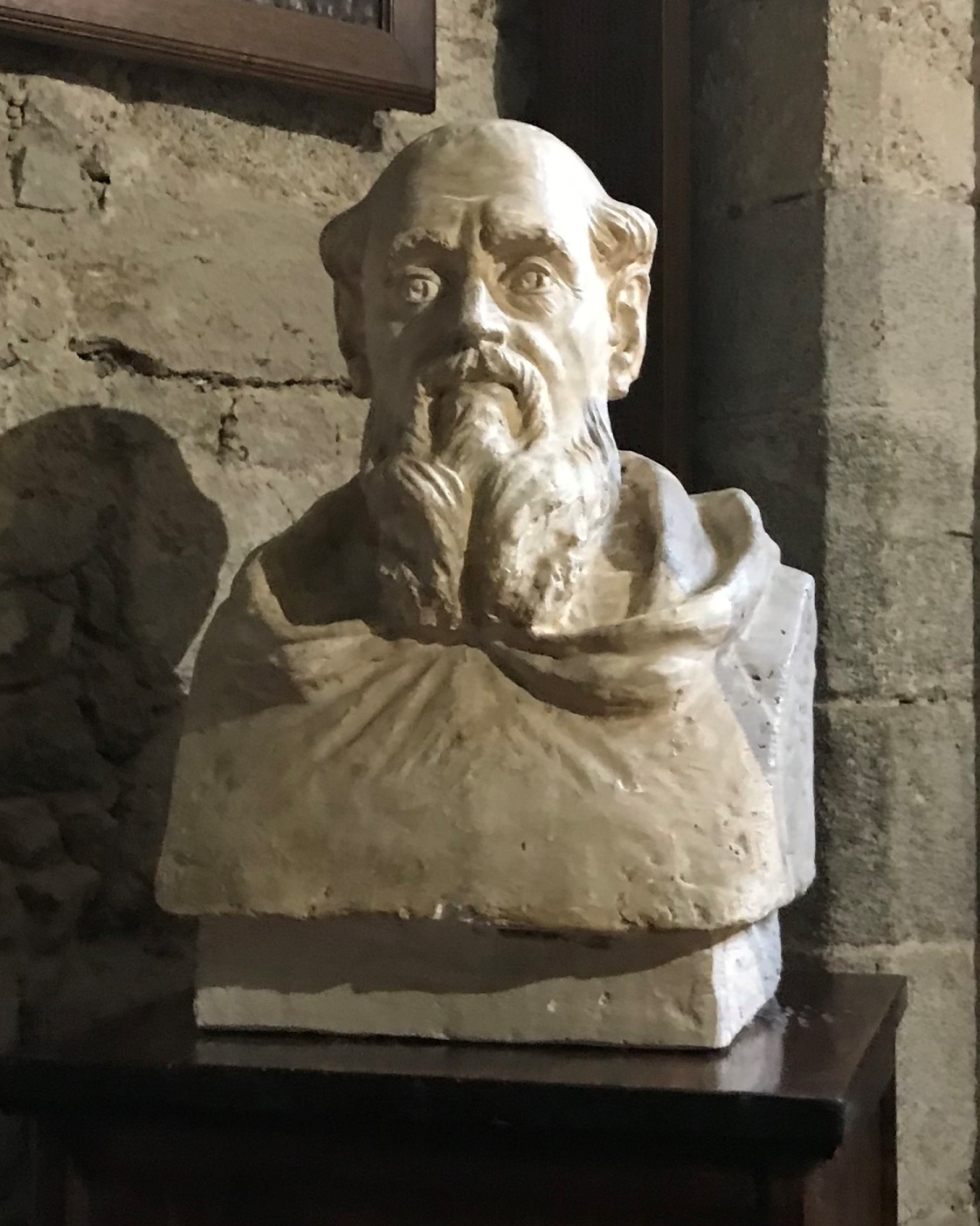


Joachim of Fiore, also known as Joachim de Fiore, and Gioacchino da Fiore, was an Italian mystic, theologian and philosopher of history, a great medieval thinker with a beautiful symbolic imagination.
Fiore was a prolific writer and explored the hidden meaning of the life of the apostles and the scriptures. At the end of the twelfth century Joachim had a high international reputation.
After a pilgrimage to the Holy Land, he became a Cistercian monk and by 1177 had become abbot at Corazzo, Sicily. He retired to the mountains to lead a contemplative life, and in 1196 he founded the Order of San Giovanni in Fiore. In his Book of the Harmony of the New and Old Testaments, Fiore set forth a theory of history and traced correspondences in the Old and New Testaments. In "An Exposition of the Apocalypse" he explored the symbols of the Antichrist, and in "The Ten-String Psalter" he set forth his doctrine of the Holy Trinity. A man of vivid imagination, he was proclaimed a prophet and condemned as a heretic.
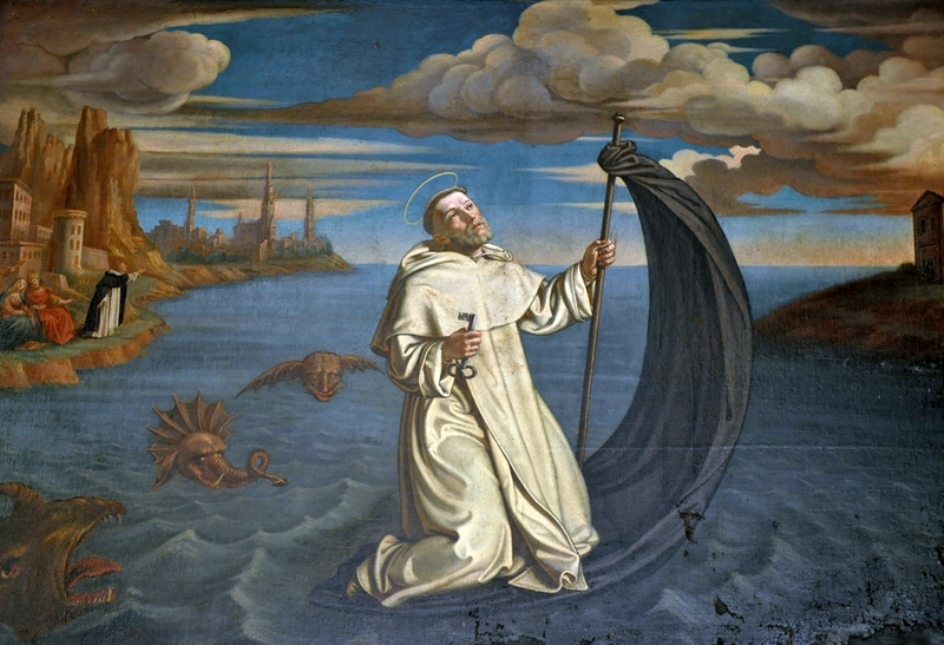


Raymond of Penyafort (Spanish: San Raimundo de Peñafort) was a Spanish theologian, canonist, and Dominican friar who is revered as a saint in the Catholic Church.
Raimondo was an adviser and confessor to the Pope in Rome as well as to kings, particularly James I of Catalonia and Aragon. Together with King James of Aragon and St. Peter Nolasco, he founded the Order of Our Lady of Ransom. The monks of this Order devoted themselves to saving Christians captured by the Moors. One of Raimondo of Peñafort's main goals was the conversion of Jews and Muslims to Christianity, and to achieve this goal he ordered Arabic and Hebrew to be studied and taught in the higher schools run by the Dominicans. He was also among those who founded the Inquisition in Catalonia.
Raimondo died at the age of 100 in Barcelona in 1275 and was canonized by Pope Clement VIII in the same year.

William of Rennes was a 13th-century French Roman Catholic monk, poet, theologian, and expert in canon law.
His commentaries and annotations on the works of the revered Catholic saint Raymond of Peñafort enjoyed almost equal authority in most manuscripts and early editions on academic theology and canon law. William of Rennes also wrote the epic of King Arthur, which is of interest to scholars of literature in that it was the first attempt to transform a medieval hero into a hero of classical eras.




The Master of Bedford was a French miniaturist and manuscript illustrator.
This master of the chapbook worked in Paris from 1405-1435 and is considered one of the most important 15th-century illuminators. He ran an influential workshop in Paris. The artist received his name after his work on two books, which he decorated with illustrations for John Lancaster, Duke of Bedford. One of these, The Bedford Hours, is considered one of the most outstanding illuminated manuscripts extant from the medieval period, with numerous illustrations and extensive decoration, including more than 1,200 decorative medallions that appear in the margins of each page.