poetry

Samuel Kettell was an American writer and editor.
He was an accomplished self-taught linguist and mastered fourteen languages. His humorous publications in the Boston Courier under pseudonyms attracted attention and in 1848 he became the permanent editor-in-chief of this newspaper.
Kettell's major work, however, was Samuel Griswold Goodrich's Samples of American Poetry with Critical and Biographical Notes, which was published in 1829. This comprehensive catalog is the first bibliography of early American poetry, and includes the works of nearly 200 poets before 1829.Kettell provided biographical sketches of each writer, from Cotton Mather to Francis Scott Key, Washington Irving, and Sarah Josepha Hale.
In addition, Kettell published A Personal Narrative of Columbus's First Voyage (1827) and Accounts of the Spanish Inquisition (1828).
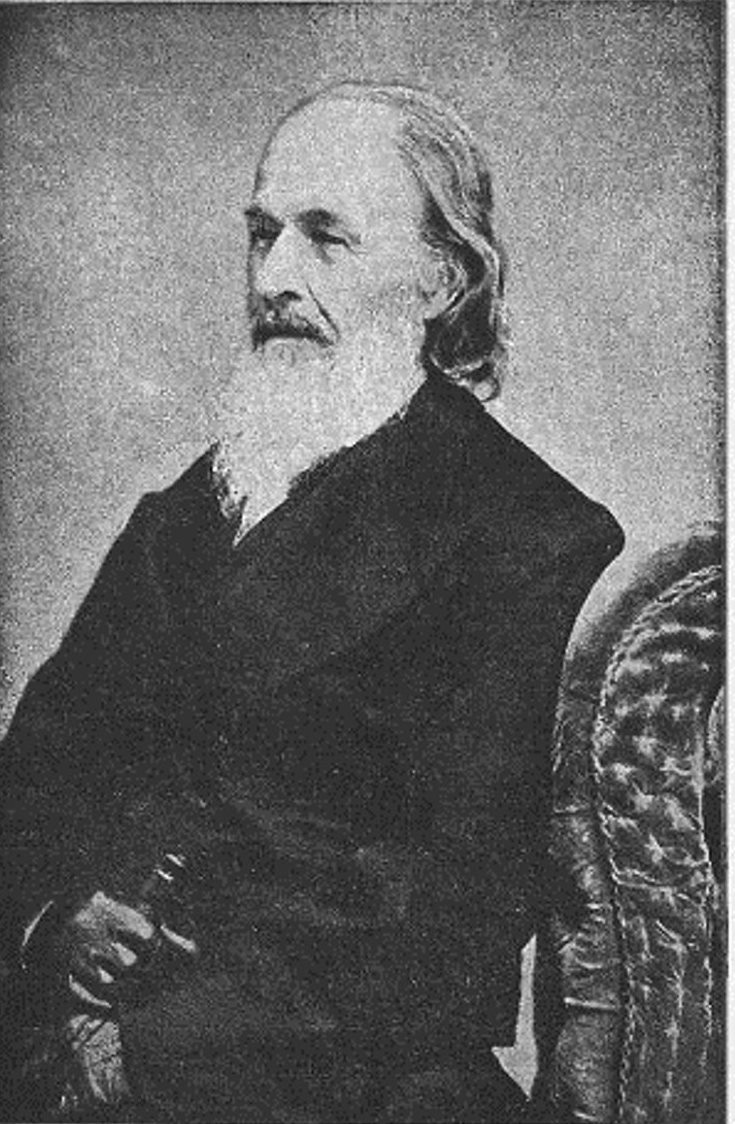


Solyman Brown was an American dentist, creator of the first U.S. National Dental Society and the first U.S. Dental Journal, as well as a poet and artist.
Brown received his bachelor's, master's, and doctor of medicine degrees from Yale University, and also worked as a minister. He wrote many articles explaining dental principles and regulations and became one of the editors of the American Journal and Library of Dental Sciences.
Essentially, in the 19th century, American dentistry was in a terrible state. And Solyman Brown, through all his activism, contributed to the enlightenment and establishment of dentistry in the United States as a true profession and science.
Brown also wrote poetry, articles and essays, and was constantly published in the periodical press. He gained fame and notoriety as a dental poet with his epic "Dentology, a poem on the diseases of the teeth and their proper remedies," which he wrote in 1833. And many more of his poems were devoted to dental diseases, their prevention and treatment. Soliyman Brown, in addition, was a painter and sculptor, painting portraits and creating furniture in wood.
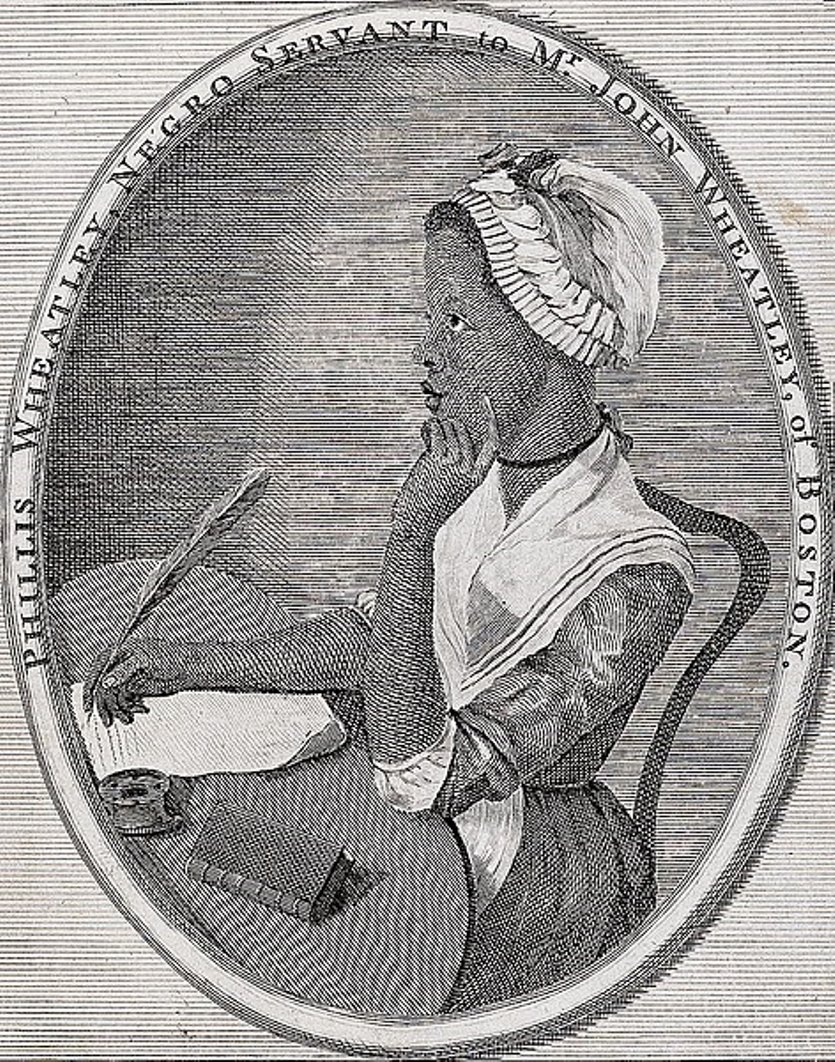




Phillis Wheatley or Phillis Wheatley Peters was an American poet born in Africa.
A native of West Africa, Phillis Wheatley was kidnapped as a young child and sold as a slave in 1761 to John and Susanna Wheatley in Boston. They chose the name Phyllis for her in honor of the ship on which the girl traveled the Middle Passage. The Wheatley family quickly recognized her intellectual abilities and encouraged her study of the classics. Phyllis began writing poems and verses, and some were even published when she was only 14 years old.
However, the 18th-century public had great difficulty accepting a black slave girl as a writer. In May 1773, Wheatley traveled to London with her master's son. There her first book, Poems on Miscellaneous Subjects, Religious and Moral, was published. Wheatley's literary talent and personal qualities contributed to her great social success in London. In the fall of 1773, Phyllis returned to the United States and Wheatley was granted her freedom. She married, but lived only 31 years.
Wheatley's most famous poem today, "On Being Brought from Africa to America" (1768), directly addresses the theme of slavery.

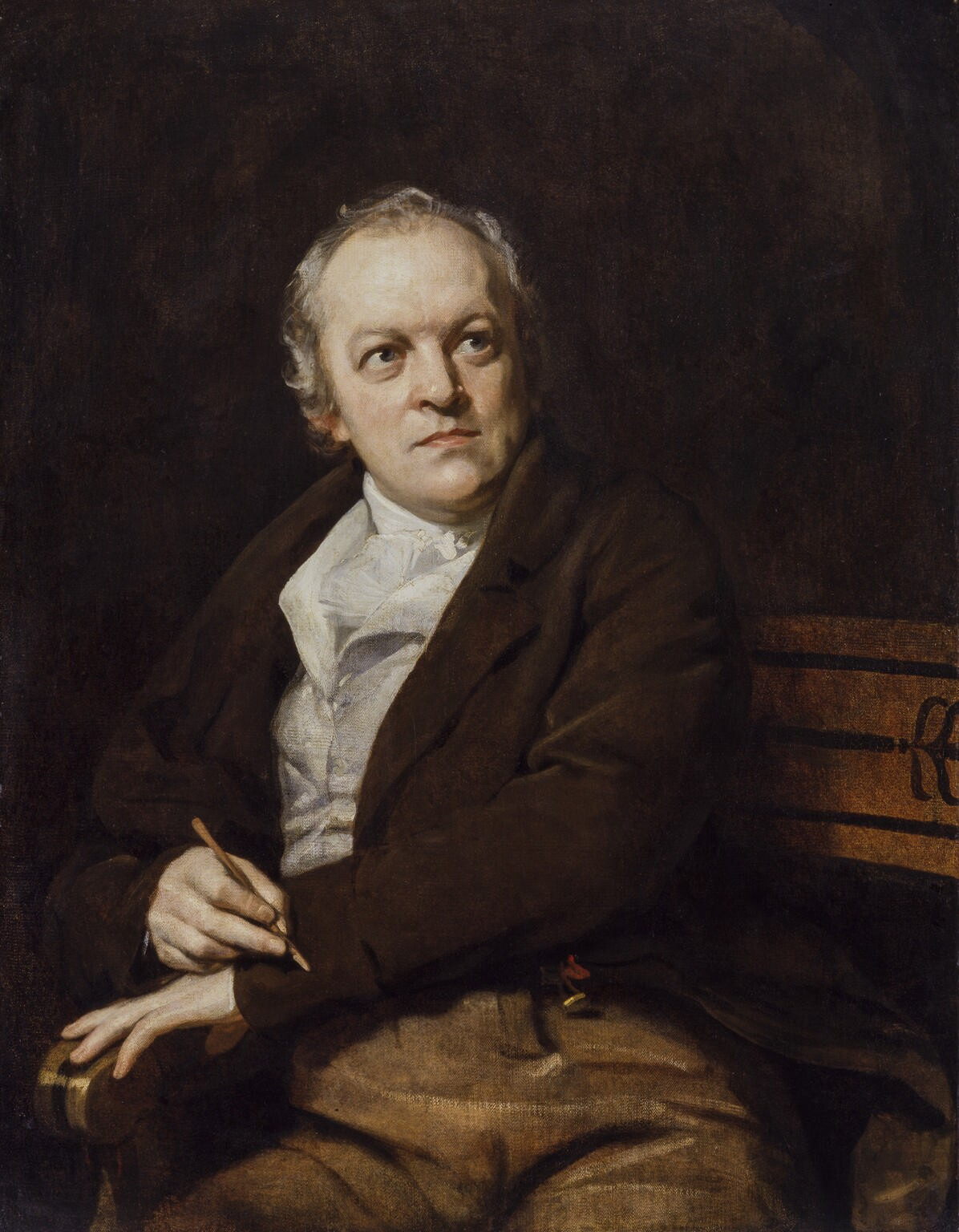
William Blake was an English poet, painter, and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his life, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual art of the Romantic Age. What he called his "prophetic works" were said by 20th-century critic Northrop Frye to form "what is in proportion to its merits the least read body of poetry in the English language". His visual artistry led 21st-century critic Jonathan Jones to proclaim him "far and away the greatest artist Britain has ever produced". In 2002, Blake was placed at number 38 in the BBC's poll of the 100 Greatest Britons. While he lived in London his entire life, except for three years spent in Felpham, he produced a diverse and symbolically rich collection of works, which embraced the imagination as "the body of God" or "human existence itself".
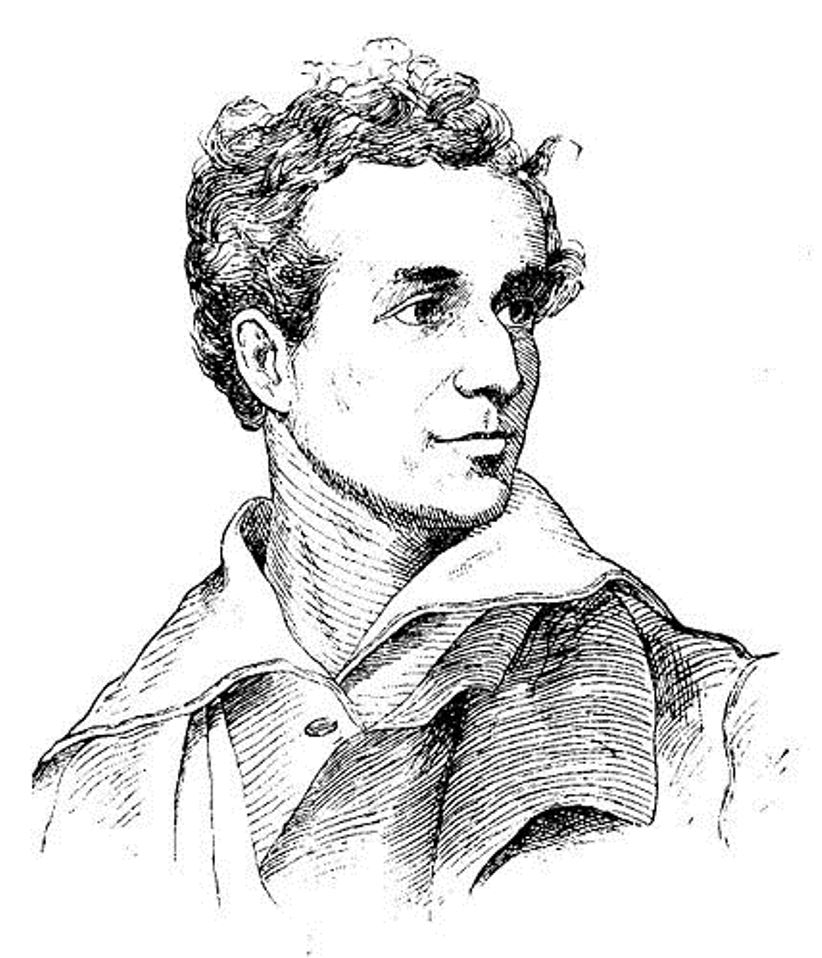


McDonald Clarke was an American outsider poet of the first half of the 19th century.
McDonald Clarke led an eccentric lifestyle and was nicknamed the Mad Poet of Broadway. He suffered periodic bouts of insanity, but was a regular on the New York poetry scene. Clarke was also known for sleeping in cemeteries and imitating Lord Byron. In his many poems, he covered topics ranging from social satire to sentimental romanticism.
Clarke was always virtually penniless and ended his life in a New York prison, where he was taken in another fit. The mad poet was immortalized by Walt Whitman, whom he greatly influenced as a mystical figure and outsider poet. The young Whitman was fascinated by both Clark's works and his eccentric life. Contemporaries describe Clarke as a mad child with aristocratic manners, meek and always happy, and all his oddities did no harm to those around him.
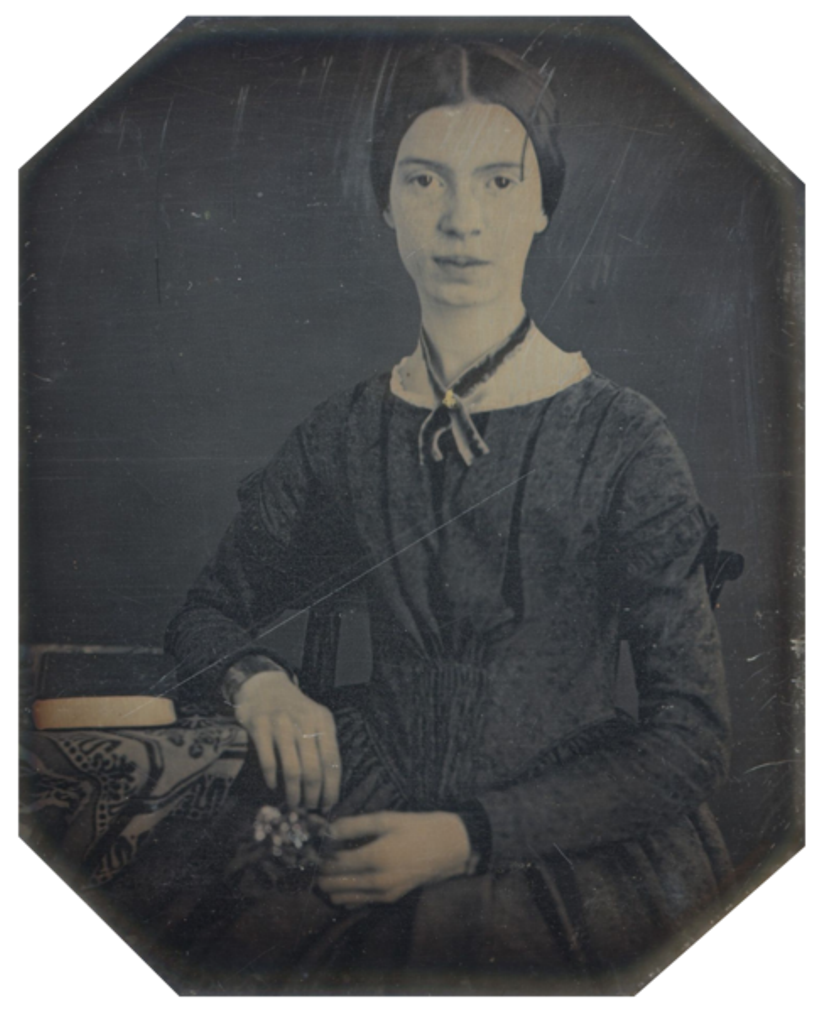


Emily Elizabeth Dickinson was a 19th-century American lyric poet.
Emily led a secluded and rather unusual lifestyle, preferring active correspondence instead of personal communication. In addition to many brilliant and witty letters to her family and friends, she wrote about two thousand poems during her lifetime, but only about ten were published during her lifetime.
Dickinson possessed an extraordinary brilliance of style and integrity of vision and, along with Walt Whitman, is today considered one of the two leading American poets of the nineteenth century. She easily ignored the usual rules of versification and even grammar, and in the intellectual content of her works showed exceptional courage and originality. It is known that the poetess was particularly impressed by the poetry of Ralph Waldo Emerson, and with Charles Wadsworth she corresponded.
Today, the work of Emily Dickinson is evaluated as a bright forerunner of modernism, it is widely studied in educational institutions in the United States and Europe.
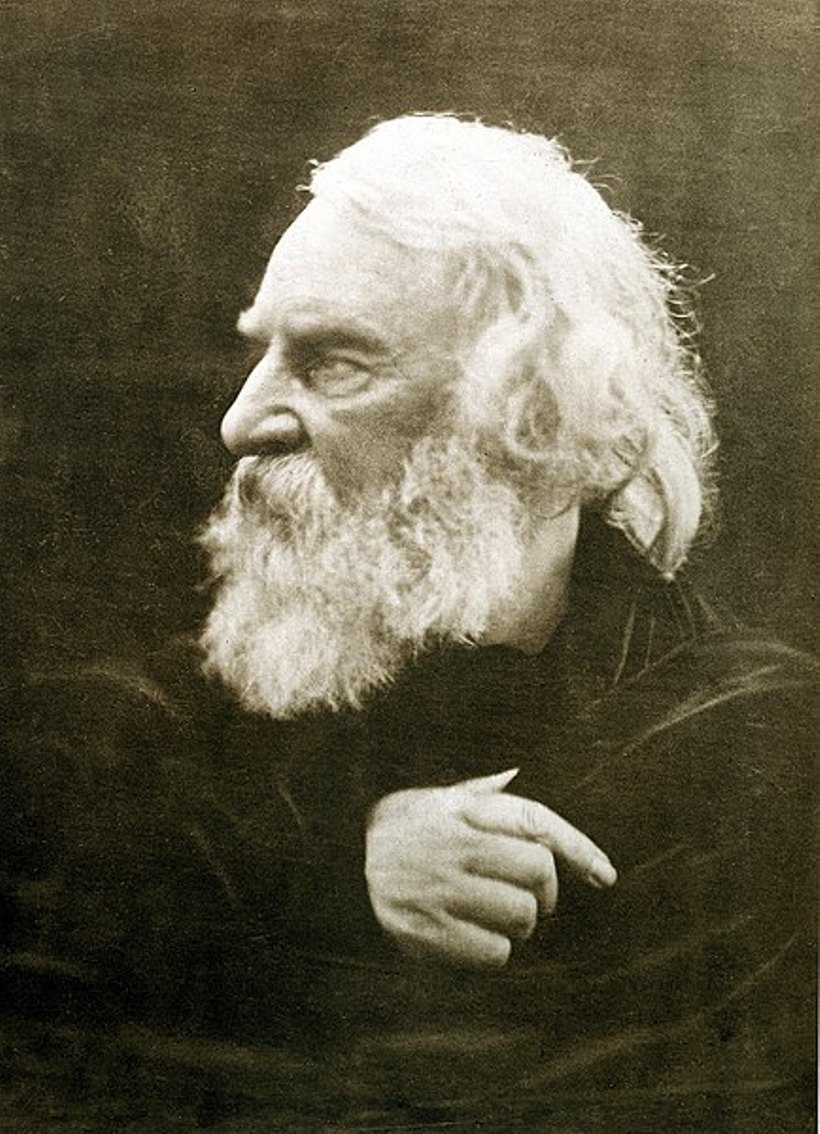


Henry Wadsworth Longfellow was the most popular American poet of the nineteenth century.
Longfellow is one of the most revered poets in the United States. His poems "Paul Revere's Ride", "Evangeline", "The Tale of Acadia" (1847) and "Psalm of Life" were included in elementary and high school curricula and have long been remembered by generations of readers who studied them as children. Longfellow revitalized American literary life by linking American poetry to European traditions outside of England.