roman hur (b. 1993)
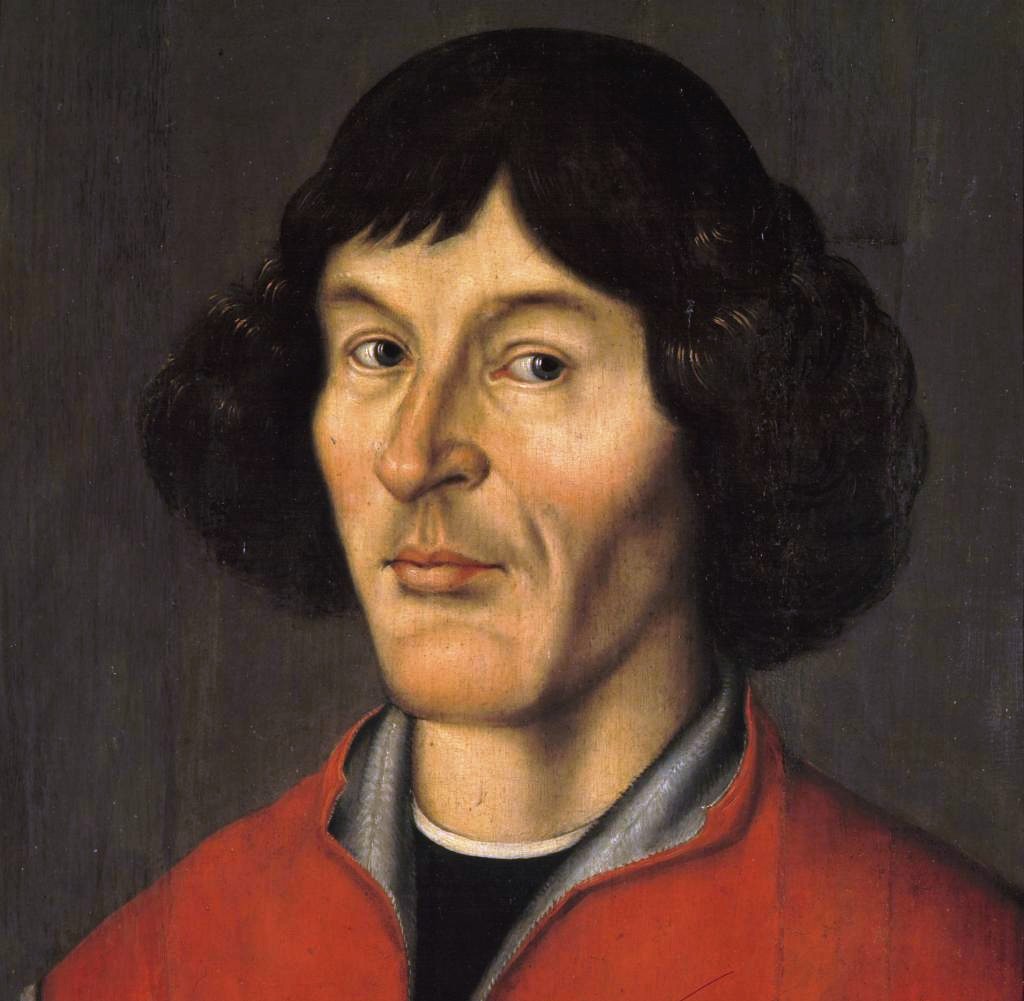











Nicolaus Copernicus (Polish: Mikołaj Kopernik) was a Polish and German scientist, astronomer, mathematician, mechanic, economist, and Renaissance canonist. He was the author of the heliocentric system of the world, which initiated the first scientific revolution.
Copernicus studied the humanities, including astronomy and astrology, at the University of Krakow and at the University of Bologna in Italy. Together with other astronomers, including Domenico Maria de Novara (1454-1504), he was engaged in observing the stars and planets, recording their movements and eclipses. At the time, medicine was closely related to astrology, as the stars were believed to influence the human body, and Copernicus also studied medicine at the University of Padua between 1501 and 1503.
Nicolaus Copernicus, based on his knowledge and observations, was the first to suggest that the Earth is a planet that not only revolves around the sun every year, but also rotates once a day on its axis. This was in the early 16th century when people believed the Earth to be the center of the universe. The scientist also suggested that the Earth's rotation explained the rising and setting of the Sun, the movement of the stars, and that the cycle of the seasons was caused by the Earth's rotation around itself. Finally, he correctly concluded that the Earth's motion in space causes the planets to move backwards across the night sky, the so-called retrograde direction.
Although Copernicus' model was not completely correct, it laid a solid foundation for future scientists, such as Galileo, who developed and improved mankind's understanding of the motion of celestial bodies. Copernicus completed the first manuscript of his book De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium (On the Rotation of the Celestial Spheres) in 1532. In it, the astronomer outlined his model of the solar system and the paths of the planets. However, he published the book only in 1543, just two months before his death, and dedicated it to Pope Paul III. Perhaps for this reason, and also because the subject matter was too difficult to understand, but the church did not finally ban the book until 1616.


Nicolaus Copernicus (Polish: Mikołaj Kopernik) was a Polish and German scientist, astronomer, mathematician, mechanic, economist, and Renaissance canonist. He was the author of the heliocentric system of the world, which initiated the first scientific revolution.
Copernicus studied the humanities, including astronomy and astrology, at the University of Krakow and at the University of Bologna in Italy. Together with other astronomers, including Domenico Maria de Novara (1454-1504), he was engaged in observing the stars and planets, recording their movements and eclipses. At the time, medicine was closely related to astrology, as the stars were believed to influence the human body, and Copernicus also studied medicine at the University of Padua between 1501 and 1503.
Nicolaus Copernicus, based on his knowledge and observations, was the first to suggest that the Earth is a planet that not only revolves around the sun every year, but also rotates once a day on its axis. This was in the early 16th century when people believed the Earth to be the center of the universe. The scientist also suggested that the Earth's rotation explained the rising and setting of the Sun, the movement of the stars, and that the cycle of the seasons was caused by the Earth's rotation around itself. Finally, he correctly concluded that the Earth's motion in space causes the planets to move backwards across the night sky, the so-called retrograde direction.
Although Copernicus' model was not completely correct, it laid a solid foundation for future scientists, such as Galileo, who developed and improved mankind's understanding of the motion of celestial bodies. Copernicus completed the first manuscript of his book De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium (On the Rotation of the Celestial Spheres) in 1532. In it, the astronomer outlined his model of the solar system and the paths of the planets. However, he published the book only in 1543, just two months before his death, and dedicated it to Pope Paul III. Perhaps for this reason, and also because the subject matter was too difficult to understand, but the church did not finally ban the book until 1616.
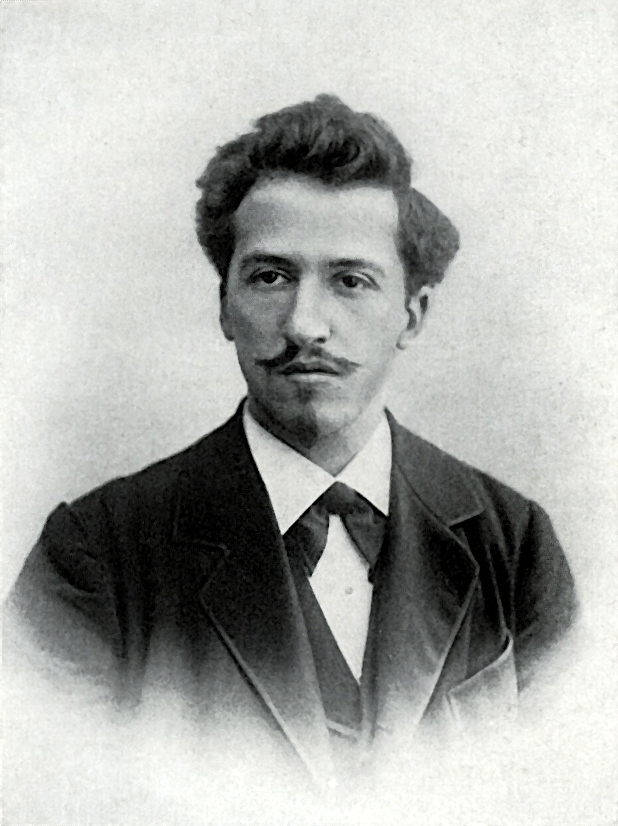


Pieter Cornelis Mondriaan, later known as Piet Mondrian, was a Dutch painter and art theoretician, whose transformation from figurative art to an abstract modernist style revolutionized the visual arts landscape of the 20th century. Born on March 7, 1872, in Amersfoort, Netherlands, and passing away on February 1, 1944, in New York, Mondrian's journey in art began in a devoutly Calvinist home where both art and music were encouraged. His early works were influenced by his surroundings, featuring landscapes in an Impressionist manner, but it was his shift to Paris in 1911 that marked the beginning of his profound evolution towards abstraction.
Mondrian co-founded the De Stijl art movement, aiming to achieve a universal aesthetic through the simplification of visual elements to their essentials: straight lines, right angles, primary colors, and the use of black, white, and gray. This reductionist approach, termed Neoplasticism, was Mondrian's contribution to creating 'universal beauty'. His philosophy extended beyond the canvas, influencing architecture, design, and fashion, encapsulating the modernist ideal and becoming synonymous with Modernism itself.
Some of Mondrian's notable works, such as "Composition with Red, Blue, and Yellow" and "Broadway Boogie Woogie", exemplify his revolutionary style, characterized by an economy of color and a rigorously abstract geometry that aimed to express the dynamic equilibrium of universal forces. These masterpieces, along with his theoretical writings, left a lasting impact on the course of abstract painting and several major art movements including Color Field painting, Abstract Expressionism, and Minimalism.
Mondrian's art is celebrated in museums and galleries worldwide, notably at the Gemeentemuseum Den Haag and the Museum of Modern Art in New York, where his evolution from figuration to geometric abstraction continues to inspire and captivate audiences. His commitment to exploring the spiritual in art through a radical simplification of form and color has cemented his legacy as one of the pioneers of 20th-century abstract art.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Mondrian's works represent not just significant artistic achievements but also pivotal moments in the history of modern art. His influence extends far beyond his own creations, shaping the development of modern aesthetics in numerous fields. If you're intrigued by Mondrian's vision of harmony and order through abstraction, we invite you to sign up for updates. This subscription will keep you informed about new product sales and auction events related to Mondrian's work, ensuring you stay connected to the ever-evolving world of art and design inspired by this iconic figure.
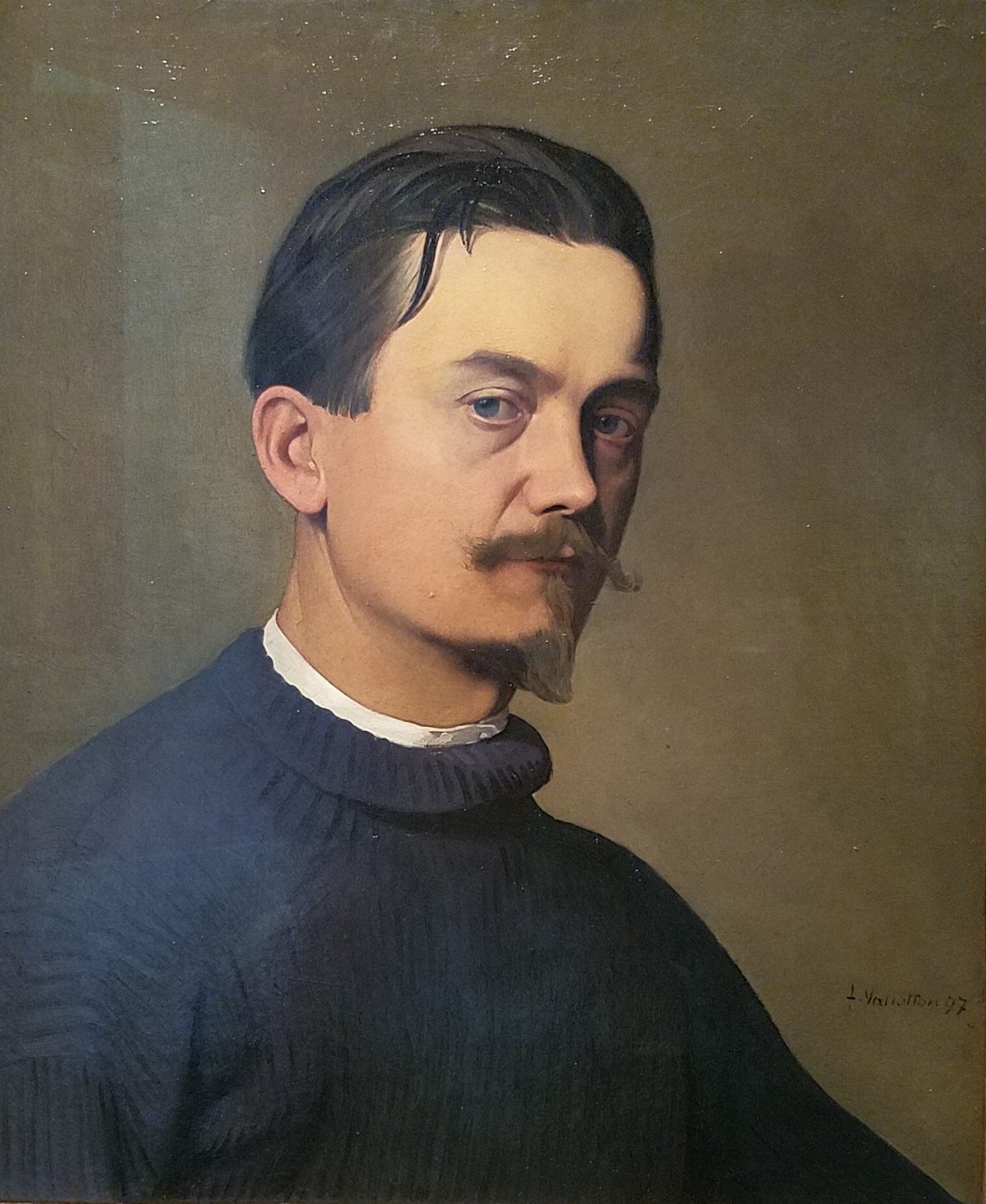


Félix Vallotton, a Swiss-born French graphic artist and painter, is recognized for his distinctive woodcuts and paintings of nudes and interiors. Vallotton's journey into art began in Paris, where he attended the Académie Julian, fostering a unique style that broke from traditional norms. His early works, characterized by extreme realism, were showcased at the Salon des Artistes Français and the Paris Universal Exposition of 1889. This period also marked Vallotton's encounter with Japanese prints, notably those by Hokusai, profoundly influencing his artistic direction.
In 1892, Vallotton joined Les Nabis, a group of avant-garde artists including Pierre Bonnard, Maurice Denis, and Édouard Vuillard, which led to a significant evolution in his style. His paintings from this era, such as "Bathers on a Summer Evening" and "Moonlight," exhibited at the Kunsthaus Zürich and the Musée d'Orsay respectively, reveal a departure from realism towards a more symbolic and abstract representation. The works from this period are characterized by flat areas of color, hard edges, and simplified details, mirroring the style he developed in his woodcuts.
Vallotton's woodcuts, like "Intimités" (Intimacies), a series published in 1898, showcased his mastery in capturing the nuances of human relationships, particularly the tensions between men and women. His graphic art, which included depictions of domestic scenes, bathing women, and street crowds, was not just celebrated in Europe but also influenced artists like Edvard Munch, Aubrey Beardsley, and Ernst Ludwig Kirchner.
Towards the end of his career, Vallotton continued to innovate, combining elements of realism and abstraction, evident in paintings like "La Malade" (The Sick Girl) and "Clair de lune" (Moonlight). His works remain a testament to his ability to merge technical precision with a poignant exploration of human emotions and societal themes.
For art collectors and experts, Vallotton's body of work offers a rich and diverse exploration of early 20th-century art movements, especially his role in the development of modern woodcut techniques and his contribution to the Nabis movement. His works are a study in the fusion of realism and symbolism, marked by a distinctive style that makes his art enduringly relevant and compelling.
For those interested in discovering more about Félix Vallotton and staying updated on related product sales and auction events, signing up for updates is a great opportunity. This subscription will exclusively alert you to new sales and events pertaining to Vallotton's works, ensuring you remain informed in the dynamic world of art and antiques.