Cartographers 17th century


Jan (Joan) Willemsz. Blaeu was a Dutch cartographer, publisher and judge.
Jan was born into the family of the cartographer and publisher Willem Janszoon Blaeu (1571-1638). He studied in Leiden, where he earned a doctorate in law, and in Padua. He then began to assist his father, who was engaged in the manufacture of globes and maps. After his father's death, Jan, together with his brother Cornelius, continued his work, and succeeded him as cartographer for the Dutch East India Company.
In 1651 Blaeu was elected to the Amsterdam city council and later appointed as a judge. At the same time, he was engaged in his publishing business: he continued to publish volumes of Atlas novus, which contained maps of English counties and, for the first time, an atlas of Scotland, as well as one volume of maps of the Far East.
Blaeu did not have time to complete his most ambitious project, but it made him famous as the author of the famous 11-volume Dutch atlas. Based on his previous maps, Blaeu created the Great Atlas (Atlas Maior) - it contained nearly 600 maps and a total of 3,000 pages of Latin text - and was published in 1662. Blaeu's maps were groundbreaking for their time because they were created in accordance with the heliocentric theories of Nicolaus Copernicus.
In 1672, a great fire in Amsterdam destroyed Blaeu's workshop, and the cartographer died a year later, apparently never recovering from this stroke of fate.


Willem Janszoon Blaeu was a Dutch cartographer and map publisher.
Willem studied astronomy and cartography under the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe and even discovered the variable star P Swan in 1600. A little later Blaeu settled in Amsterdam, where he began making globes and also began producing land and sea maps, including a 1605 world map. In 1629 he managed to acquire the printing plates of the cartographer Jodok Hondius, with which he published his own atlas.
In 1633, Willem Blaeu was appointed cartographer of the Dutch Republic, as well as the official cartographer of the Dutch East India Company. Blau built up a large collection of maps and conducted an extensive publishing business. After Willem's death, his sons Jan Blaeu (1596-1673) and Cornelius Blaeu successfully continued his work. But in 1672, during a fire in Amsterdam, Blaeu's workshop was destroyed, and the company founded by Willem Blaeu ceased to exist in 1698.


Joachim Bouvet was a French Jesuit monk and missionary who worked in China.
Joachim Bouvet was one of six Jesuit mathematicians chosen by Louis XIV to travel to China as his envoys and work as missionaries and scholars. In 1687 in Beijing, Bouvet began this work, especially in mathematics and astronomy, and in 1697 the Chinese emperor Kangxi (1654-1722) sent him as ambassador to the French king. Kangxi expressed his wish that Bouvet should bring more missionary scientists with him. Thus, in addition to his scholarly work, Bouvet was also an accomplished diplomat and served as a liaison between the Chinese Emperor Kangxi and King Louis XIV of France.
Bouvet brought to France a manuscript describing Kangxi's life with an eye for diplomatic subtleties, as well as a collection of drawings depicting graceful Chinese figures in traditional and ceremonial dress. The first French edition of The Historical Portrait of the Emperor of China was published in Paris in 1697, and was subsequently translated and published in other languages. And Bouvet returned to China in 1699 with ten new missionaries and a collection of King Louis XIV's engravings for Emperor Kangxi. He remained in China for the rest of his life.
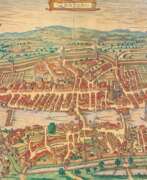

Georg Braun was a German topographical geographer, cartographer and publisher.
Braun was the editor-in-chief of the Civitates orbis terrarum, a groundbreaking atlas of cities, one of the major cartographic achievements of the 16th century. It was the first comprehensive and detailed atlas, with plans of the world's famous cities and bird's-eye views, and became one of the best-selling works of the time.
The book was prepared by Georg Braun in collaboration with the Flemish engraver and cartographer Frans Hoogenberg. Braun, as editor-in-chief, acquired tables, hired artists, and wrote the texts. They drew on existing maps as well as maps based on drawings by the Antwerp artist Joris Hofnagel and his son Jacob. Other authors include Pieter Bruegel the Elder (c. 1525-1569), Jacob van Deventer (c. 1505-1575), and more than a hundred other artists and engravers.


Justus Danckerts I was a Dutch engraver and print publisher who along with other members of the Danckerts family created one of the leading Dutch geographical map and atlas publishing houses. Justus Danckerts was the son of Cornelis Danckerts I (1603-1656), who established the Danckerts cartographic family business in Amsterdam. After producing in the early 1680s over 20 folio-sized atlas maps, he published in 1686-1887 the first Danckerts atlas. In 1690, another 26-sheet geographical atlas was published; between 1698 and 1700, a 60-sheet atlas was completed. Its map sheets and plates were used by various publishers until the middle of the 18th century.
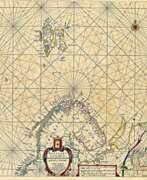
Hendrick Doncker was a Dutch cartographer and publisher of nautical charts, atlases, and books.
An innovator among the first generation of Dutch cartographers, Doncker worked to produce modern nautical charts, which were valued by sailors and a wide audience for their accuracy and precision. Doncker promptly followed geographical discoveries and achieved success by constantly improving and updating old maps, which was a rarity at the time. His major work is the Zee-Atlas (nautical atlas), which was reprinted for 50 years.


Martin Hermann Faber was a German painter, architect, and cartographer. He was also a copper engraver in Rome. He lived and worked most of his life in Emden, where he still remains one of the most respected and significant artistic personalities of the city.


Johann Baptist Homann was a German geographer and cartographer, who also made maps of the Americas. In 1702 he founded his own publishing house. Homann acquired renown as a leading German cartographer, and in 1715 was appointed Imperial Geographer by Emperor Charles VI. In the same year he was also named a member of the Prussian Academy of Sciences in Berlin. In 1716 Homann published his masterpiece Grosser Atlas ueber die ganze Welt (Grand Atlas of all the World). Numerous maps were drawn up in cooperation with the engraver Christoph Weigel the Elder, who also published Siebmachers Wappenbuch.




Hendrik Hondius I was a Flemish-born and trained engraver, cartographer, and publisher who settled in the Dutch Republic in 1597. Hondius was apprenticed in Brussels to Godfried van Ghelder, goldsmith to Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma. He also studied drawing with the engraver Jan Wierix of Antwerp. At this time he started to study engraving. He applied himself to mathematics and studied perspective, architecture and the construction of fortifications. He moved to The Hague by 1597. He obtained his first print privilege for a portrait of Prince Maurits. He dedicated himself to his engraving practice. His work was very well received and he got commissions from many eminent personalities for engravings or drawings. He turned more to publishing rather than engraving and printing in the 1630s. His publications were mainly maps, books about fortifications and official portraits.[5] He also reused original plates and blocks by earlier artists for reprinting and such reprints represented almost a third of his publishing output. In the 1640s he returned to printing concentrating exclusively on etching. One of the most important publications of Hondius was the work Pictorum aliquot celebrium praecipue Germaniae inferioris Effigies (Effigies of some celebrated painters, chiefly of Lower Germany) of 1610, which was a collection of 69 portraits of mainly Netherlandish artists.
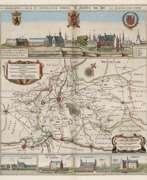



Johannes Janssonius was a Dutch cartographer, printer and publisher.
In 1616 Janssonius created his first maps of France and Italy, and every year he expanded and improved their publishing. The so-called "Great Atlas" already numbered eleven volumes. The editions were printed in Dutch, Latin, French and German.


Conrad Meyer, a Swiss painter, engraver, and medallist, made significant contributions to the art world of his time. Initially a painter of portraits and landscapes, Meyer eventually shifted his focus to copper engraving, producing over a thousand works in his lifetime. Notable among his creations is the map of Switzerland by Conrad Gyger, which he produced in 1657, and his Planisphaerium Coeleste from 1681.
Conrad Meyer's artworks, such as "The Wild Man" (1649), "The Devil's Kitchen Visited by an Angel," and "Allegory of the Transience of Life" (1651), showcase his meticulous technique and are held in high regard, with several pieces housed in the Metropolitan Museum of Art. His work "Parable of the Ungrateful Servant" is part of the Philadelphia Museum of Art's collection, demonstrating his prowess in etching as well.
For art collectors and experts, Conrad Meyer's contributions to Swiss art and engraving offer valuable insights into the 17th-century European art scene, particularly in the context of Zurich. His legacy is encapsulated in the diverse range of subjects he explored, from detailed landscapes to intricate portraits and allegorical scenes, reflecting the cultural and artistic vibrancy of his era.
If you are an enthusiast or collector keen on Conrad Meyer's art, consider signing up for updates related to new sales and auction events concerning his works. This will ensure you stay informed about opportunities to acquire pieces connected to this notable Swiss artist.
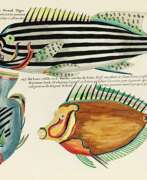

Louis Renard was a Dutch painter, printmaker and book publisher born in France.
Renard published map atlases and illustrated works of natural history popular in 18th-century Europe. In Amsterdam he acquired many cartographic plates by Frederick de Wit, which he combined with minor updates and corrections into an Atlas of Navigation and Commerce and published in 1715. He later sold the plates to R. & J. Ottens, who republished it in 1745.
In 1718 -1719 Renard published the first edition of his most famous multi-volume work, Poissons, écrevisses et crabes... que l'on trouve autour des Isles Moluques, et sur les cotes des Terres Australes ("Fish, crayfish and crabs, of varied colors and unusual forms, which are found around the Moluccas Islands and on the coasts of the southern lands."). This book was the world's first encyclopedia of fish illustrated in color. While working on it, Renard copied drawings by other artists, notably the talented Dutch artist Samuel Fallors. The result was 460 hand-colored copperplate prints.
The creatures in Renard's book are so fanciful that they may seem fictional, but only about 10 percent are, including the depiction of a mermaid. Most likely, these fantasies were included for the sake of attracting buyers. The work is now believed to be an important part of eighteenth-century scientific literature.


Giuseppe Rosaccio was an Italian physician, astronomer, cosmographer and cartographer.
Rosaccio graduated from the University of Padua, studied philosophy, medicine and law, and worked as a physician and judge. He became famous for a series of works that popularized a number of scientific disciplines. Some of his books deal with astrological medicine, specific diseases and their remedies, and the distillation of medicines from plants.
Giuseppe Rosaccio wrote about forty works on various topics of interest to him, but the main one was geography. He wrote an essay on the Muslim religion and treatises on geography, cosmography, astronomy, and astrology, which became very popular and were repeatedly reprinted.
Rosaccio created many atlases and small-format geographical works. Among his works is Ptolemy's Geography, which contains many indexes and is written in Italian (1599). He also authored a large map of the world (1597), and a large map of Italy and Tuscany (1609). His book Journey from Venice to Constantinople includes maps of the route with brief texts, that is, it is essentially an illustrated version of a pilgrimage to the Holy Land.


Nicolas Sanson the Elder (Nicolas Sanson d’Abbeville) was a French cartographer who served under two kings in matters of geography. He has been called the "father of French cartography." He gave lessons in geography both to Louis XIII and to Louis XIV. Active from 1627, Sanson issued his first map of importance, the "Postes de France". After publishing several general atlases himself he became the associate of Pierre Mariette, a publisher of prints. He died in Paris on 7 July 1667. Two younger sons succeeded him as geographers to the king. Sanson's maps were used as a model by his son, Guillaume, and, at least initially, by Duval, his nephew, in his 1664 folio map and 1660 atlas minor map. In 1692 Hubert Jaillot collected Sanson's maps in an Atlas nouveau.
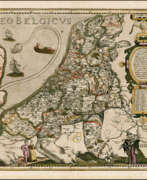
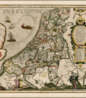
Pieter van der Keere (Latin: Petrus Kaerius) was a Flemish engraver, publisher, cartographer and globe maker.
His father was the master of typefaces Hendrik van der Keere (c. 1540-1580); in 1584 he fled from the Netherlands to London, where he lived most of his life. Pieter van der Keere produced engravings and atlases. From 1603, Kere began to produce large city panoramas, including Utrecht, Cologne, Amsterdam and Paris.
An atlas of the Netherlands was published in 1617, with der Keere's name as publisher and his full signature on several maps. He also produced topographical maps of Amsterdam and Nuremberg, as well as a world map ("Nova totius terrarum orbis..."), which was printed by Jan Janszoon in Amsterdam.
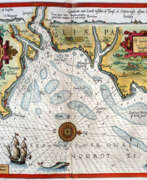
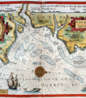
Lucas Waghenaer, full name Lucas Janszoon Waghenaer, was a famous Dutch cartographer, navigator, navigator and writer of the Golden Age.
Between 1550 and 1579, Waghenaer sailed the seas as a senior assistant captain and probably socialized with Portuguese, Spanish, and Italian navigators. The knowledge of nautical charts and the instructions Waghenaer received as a result of these contacts had a great influence on his later work as a cartographer. It is evident that the charts he made had to be based on his observations, and in all his work he had to draw on his own extensive experience of practical navigation. His book Spieghel der Zeevaerdt ("The Navigator's Mirror") or Speculum nauticum super navigatione, first published in 1584, occupies a unique place among the nautical printed works of the sixteenth century, for it is the first printed work with maps.
Moreover, in terms of the magnificent design of the maps and text, it surpasses all other editions of this period and served as a model for pilotage guides and folios with maps even a century later. It is an atlas of nautical charts with instructions for navigation in the western and northwestern coastal waters of Europe. Thanks to the unrivaled skill of engravers Baptiste and Johannes van Deitekom, Waghenaer's original maps were transformed into the most beautiful maps of the time. This book was a huge success, reprinted several times and translated into English, German, Latin and French.
In 1592, Waghenaer's second pilot book Thresoor der zeevaert ("Treasure of Navigation") was published, and in 1598, the third and last publication Enchuyser zeecaertboeck ("Enkhuizen Book of Nautical Charts").