Historians 16th century


Cornelius Gerardi Aurelius, also called Goudanus, was a Dutch humanist scholar, writer, and historian.
Aurelius was a permanent canon (monk) of the Augustinian monastic order and is one of the first humanists of the Netherlands in the 16th century. He wrote poetry, historiography, hagiography, political and theological works. Aurelius also corresponded with many of the famous men of his day, especially Erasmus.


Antonio de San Román de Ribadeneyra, also San Román de Rivadeneira/Ribadeneira, was a Spanish Benedictine monk and historical writer.
He served at the monastery of San Zoil near Carrión de los Condes and wrote several historical books. In particular, an account of King Sebastião I's disastrous invasion of Morocco in 1578 and his death in battle entitled Jornada y muerte del Rey Don Sebastião de Portugal (1603). Antonio de San Román de Ribadeneyra also wrote A General History of Eastern India (1603). This historical work focuses on the Portuguese expeditions to Asia and the Americas, including a description of Christopher Columbus.


Jacopo Filippo di Bergamo, or Giacomo Filippo Forèsti (Latin: Iacobus Philippus Bergomensis) was an Italian Augustinian monk, theologian and chronicler.
Jacopo di Bergamo was born into a noble family, received his ecclesiastical education at the local monastery, and early showed a penchant for literary work. After traveling in Europe, he took the tonsure and was abbot of monasteries, engaged in their improvement.
He is known as the author of a number of significant early printed works, a chronicler and biblical scholar. His Supplementum chronicarum (1483) is a universal chronicle that survived many subsequent editions. And De claris mulieribus, published in 1497, contains the first account of the voyage of the discoverer Columbus.


Niccolò di Bernardo Machiavelli was an Italian philosopher, politician and diplomat, historian and Renaissance writer.
As a young man, Niccolò Machiavelli faced financial difficulties due to his father's debts, but had access to a rich library. Machiavelli's early life and career began during a period of political upheaval in Italy. After the expulsion of the Medici family in 1494, for 14 years Niccolo Machiavelli served as a diplomat to the Florentine Republic. During this service, he gained a reputation as a cunning and unconventional thinker. However, when the Medici returned to power in 1512, Machiavelli was dismissed, imprisoned, and temporarily removed from political life.
During this period Machiavelli wrote his famous work The Sovereign, which has become one of the key works in the history of political philosophy. This book epitomizes the Machiavellian approach to politics, where the means justify the end, and where a leader should use any method to consolidate his power. The treatise drew criticism from the Pope, who condemned it for supporting rule through deceit and fear. Nevertheless, The Sovereign is still an important work of political literature, and Machiavelli has come to be called "the father of modern political theory."
Machiavelli lived the rest of his life in a small village near Florence, where he continued his creative endeavors, writing On the Art of War, as well as poems and plays. His literary legacy has become an integral part of the history of political philosophy.


Sebastian Münster was a German Renaissance scholar, cartographer and cosmographer, historian and linguist-translator.
Münster studied at the University of Tübingen and later taught at the Universities of Basel and Heidelberg. He published several editions of Hebrew grammars and translations from that language, and was the first German to produce an edition of the Hebrew Bible.
In 1544 Münster published his Cosmographia, which was the earliest description of the history, geography, and organization of the world in German. This book was a great success, translated into many European languages and reprinted more than twenty times. "Cosmographia" contained many illustrations and geographical maps of the continents of the world, created by the best engravers of the time.
Among his other works were the "Trilingual Dictionary" (1530) in Latin, Greek, and Hebrew and the "Map of Europe" (1536).


Francisco Pacheco del Río, baptized on November 3, 1564, and passing away on November 27, 1644, was a distinguished Spanish painter. Renowned for his dual role as Diego Velázquez's teacher and father-in-law, Pacheco's influence extends beyond his familial ties, contributing significantly to the arts through his seminal textbook, "Art of Painting." This work remains a crucial resource for understanding 17th-century artistic practices in Spain. Often referred to as the "Vasari of Seville," Pacheco's insights into painting theories and reflections on his contemporaries have left an indelible mark on the history of art, despite criticisms of his conventional execution in painting.
Pacheco's early life was marked by an immersive education in art, learning from Luis Fernandez and drawing inspiration from Italian masters. His journey included a pivotal sojourn to Madrid and Toledo in 1611 to study the works of El Greco, which further enriched his artistic repertoire. Upon his return to Seville, Pacheco opened an art school, laying the groundwork for his future contributions to art education and theory.
His career was notably characterized by his position as the official censor for Seville's Inquisition, which influenced his academic approach to religious subjects. Despite this, his paintings, such as the Last Judgment and Martyrs of Granada, are celebrated for their monumental scale. Pacheco's most enduring legacy, however, may be his influence on Diego Velázquez, whom he mentored for six years. Velázquez's marriage to Pacheco's daughter Juana in 1618 further solidified their personal and professional bonds. Pacheco's "Arte de la pintura" not only provided invaluable biographical information on Spanish painters of his era but also laid down foundational theories on iconography, materials, and technique.
For those interested in exploring Francisco Pacheco del Río's works further, notable pieces can be found in prestigious collections, such as the Museo Nacional del Prado, enriching our understanding of his impact on the art world.
Art enthusiasts, collectors, and experts are encouraged to sign up for updates to stay informed about new product sales and auction events related to Francisco Pacheco del Río, ensuring you remain at the forefront of developments in the fascinating world of art and antiques.


Werner Rolewinck (Latin: Wernerus Rolewinkius) was a German chronicler, historian, and theologian.
Werner Rolewinck was a Cartesian monk. His best known and most important work is Fasciculus temporum, a history from the creation of the world to Pope Sixtus IV. Already during his lifetime this work was republished many times in Latin, French, Dutch, and German. Drawing on major Christian historiographical sources such as Orosius and Eusebius, Fasciculus presents the history of the world in the form of a genealogy, a traditional historiographical structure dating back to late antiquity.
Another famous work by Rolewink is a description of the manners and customs of his homeland entitled De laude veteris Saxsoniæ nunc Westphaliæ dictæ.


Hartmann Schedel was a German humanist, medical scientist, historian and chronicler.
Schedel was the first to compile a world chronicle, the so-called Visual History of the Earth from the Creation of the World to the 1490s, known as Schedelsche Weltchronik (Schedel's World Chronicle). It was published in 1493 in Nuremberg. About 600 woodcuts for this book were created by the artists and engravers Michael Wolgemuth (1434-1519) and Albrecht Dürer (1471-1528). The illustrations depict biblical scenes, family trees, portraits of famous personalities, and fairy tale or legendary creatures. However, the main ones here were maps of the world, Germany and Central Europe.
Hartmann Schedel was one of the first cartographers to use machine printing. He was also a renowned collector of books, artworks and engravings by old masters.


Israël Spach (also Israelis Spachius) was a German and French physician, medical writer and teacher of medicine.
Spach studied at the University of Tübingen, receiving the degree of doctor of medicine, and from 1589 taught medicine and Hebrew at the University of Strasbourg, with the rank of professor of medicine. He was characterized by a high bibliographical education.
Spach was the author of a gynecological encyclopedia, Gynaeciorum sive de mulierum tum communibus, tum gravidarum, parientium, et puerperarum affectibus et morbis, published in Strasbourg in 1597. It was a very significant book for its time.
Israël Spach also wrote Nomenclator scriptorum medicorum..., published in Frankfurt in 1591, which was the first attempt at a bibliography on medical subjects. It was organized under very broad subject headings, with indexes of authors and subjects.


Johannes Stumpf was an early writer on the history and topography of Switzerland as well as a theologian and cartographer.
When he converted to Protestantism, Stumpf had carried over with him most of his parishioners, whom he continued to care for, as the Protestant pastor at Bubikon, till 1543.
Stumpf also published a monograph (very remarkable for the date) about Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor (1556) and a set of laudatory verses about each of the thirteen Swiss cantons.
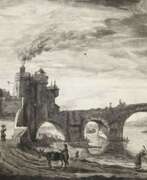

Jacob van der Heyden was a Flemish Baroque painter, sculptor and engraver. According to Houbraken he was a painter from Strasbourg who painted for royalty. According to the RKD he worked in Strasbourg, Frankfurt, and Sweden. and was known for portraits, landscapes and historical allegories. Most of his work that survives today are engravings. He died in Brussels.

































