disc bi
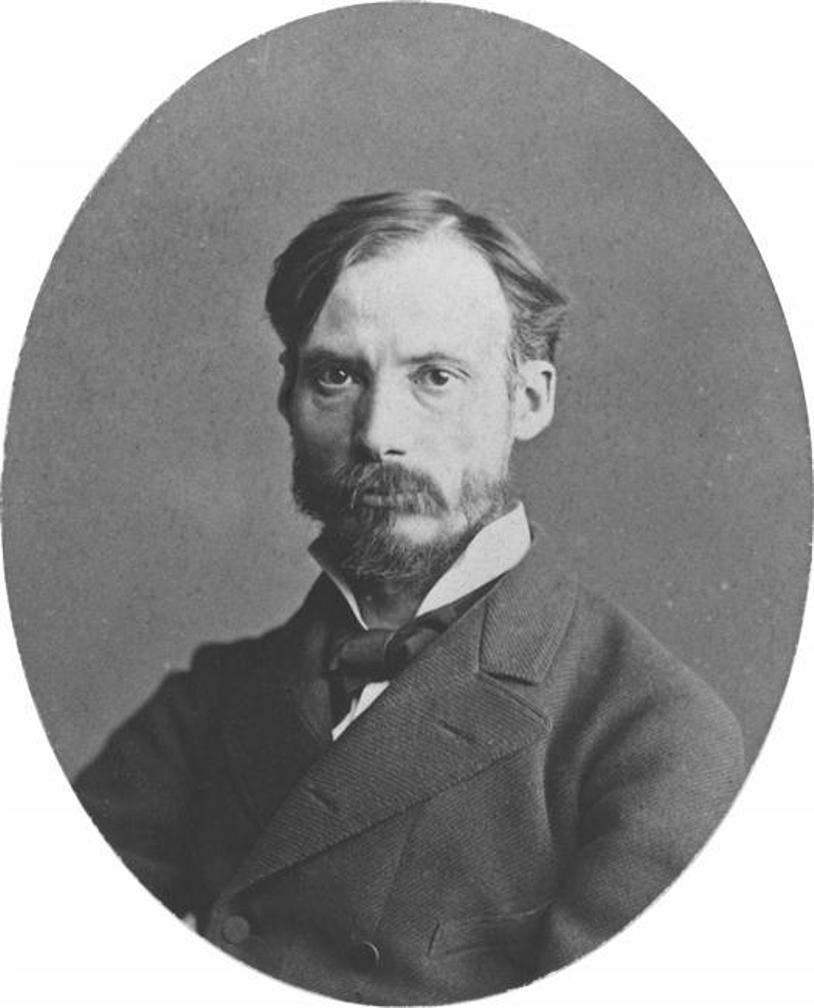



Pierre-Auguste Renoir was a French artist, celebrated as a pivotal figure in the development of the Impressionist movement. Born in Limoges, France, in 1841, Renoir's early experiences in Paris and his apprenticeship as a porcelain painter laid the foundation for his illustrious career in art. His transition to painting was marked by an early fascination with the play of light and color, which became a hallmark of his work. Renoir's paintings are renowned for their vibrant light and saturated color, often focusing on people in intimate and candid compositions. This focus on beauty and a particular affinity for capturing the sensuality of the female form distinguished his work from his contemporaries.
Renoir's contributions to Impressionism were significant, characterized by his use of bright colors and a technique that captured the movement and luminosity of the scene. His evolution as an artist saw him experimenting with a more linear and classical style, especially after his travels to Italy, where he was deeply influenced by the Renaissance masters. Despite facing personal challenges, including severe rheumatoid arthritis in his later years, Renoir's passion for painting never waned. His determination saw him adapting his painting technique to his physical limitations, ensuring that his creative output remained prolific until his death in 1919.
Among Renoir's notable works are "Bal du moulin de la Galette" (1876), "Luncheon of the Boating Party" (1880), and "Girls at the Piano" (1892). These masterpieces exemplify the essence of Impressionist art with their depiction of light, movement, and everyday life. Renoir's works are housed in prestigious museums around the world, serving as a testament to his enduring legacy in the realm of art.
For art collectors and experts, Renoir's oeuvre represents an essential segment of the Impressionist movement, offering insights into the evolution of modern art. His mastery in portraying the beauty of the moment and the depth of human emotion continues to captivate and inspire audiences worldwide.
If you are passionate about collecting or studying the works of Pierre-Auguste Renoir, we invite you to sign up for updates on new product sales and auction events related to this iconic artist. Stay informed about the opportunity to own a piece of art history and deepen your appreciation for the rich tapestry of culture and art that Renoir helped weave.
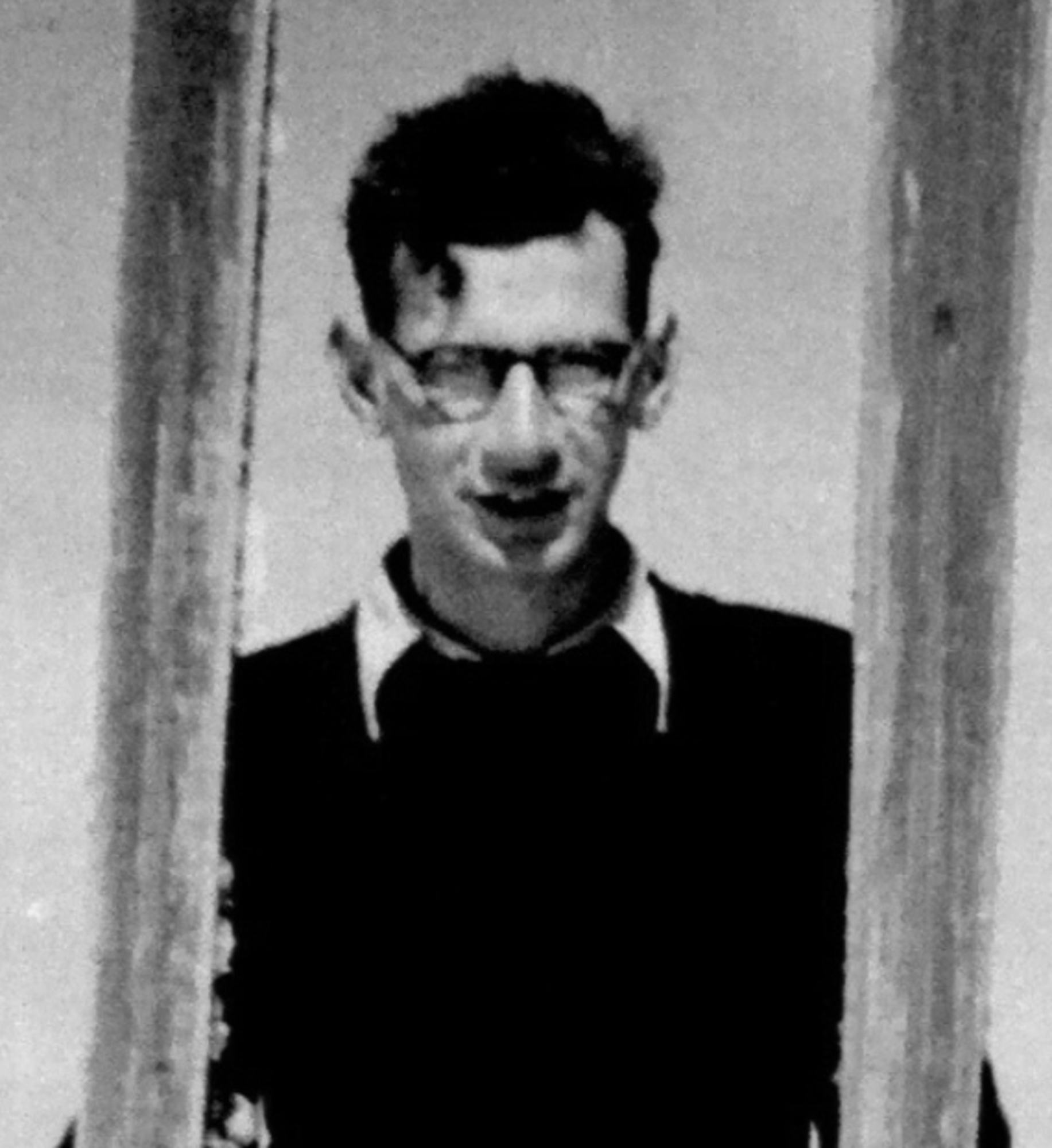


Rudolf Grossmann (German: Rudolf Grossmann, or Großmann), full name Rudolf Wilhelm Walther Grossmann, was a German painter, draftsman, illustrator and graphic artist.
Born into an artistic family, Grossmann began his education in painting and printmaking at the Düsseldorf Academy before continuing his studies in Paris with Lucien Simon and Pouleroz. Among his best-known works are various portrait drawings of celebrities, notably those published in the satirical periodical Simplicissimus; he was also known for his book illustrations. Grossmann began publishing his prints in 1905, and many major publishers in Germany and France commissioned his work. He later concentrated on figurative works and urban scenes, which showed the influence of Cézanne and Pasquin.
From 1928 until Hitler's Nazi Party came to power, Grossmann taught at the Berlin Royal School of Art and was a member of the Berlin Secession and the Deutsche Kunstlerbund. In 1934, his work, like that of many of his colleagues, was stigmatized as degenerate and confiscated by the Nazi government, and he was disbarred from practicing his profession. He soon left for Freiberg im Beisgau, where he died on November 28, 1941.


Rudolf Grossmann (German: Rudolf Grossmann, or Großmann), full name Rudolf Wilhelm Walther Grossmann, was a German painter, draftsman, illustrator and graphic artist.
Born into an artistic family, Grossmann began his education in painting and printmaking at the Düsseldorf Academy before continuing his studies in Paris with Lucien Simon and Pouleroz. Among his best-known works are various portrait drawings of celebrities, notably those published in the satirical periodical Simplicissimus; he was also known for his book illustrations. Grossmann began publishing his prints in 1905, and many major publishers in Germany and France commissioned his work. He later concentrated on figurative works and urban scenes, which showed the influence of Cézanne and Pasquin.
From 1928 until Hitler's Nazi Party came to power, Grossmann taught at the Berlin Royal School of Art and was a member of the Berlin Secession and the Deutsche Kunstlerbund. In 1934, his work, like that of many of his colleagues, was stigmatized as degenerate and confiscated by the Nazi government, and he was disbarred from practicing his profession. He soon left for Freiberg im Beisgau, where he died on November 28, 1941.
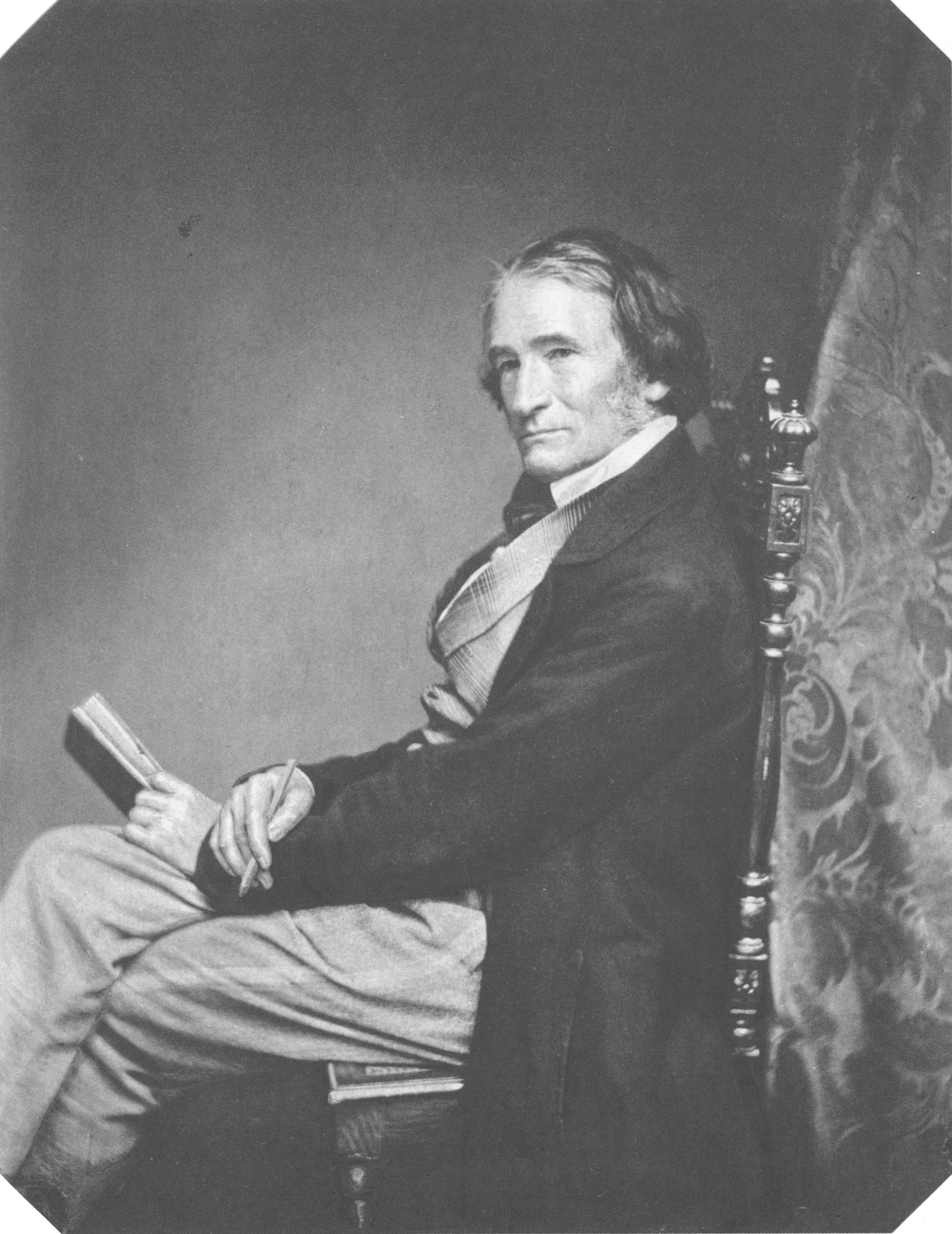


Joseph Karl Stieler was a German painter. From 1820 until 1855 he worked as royal court painter of the Bavarian kings. He is known for his Neoclassical portraits, especially for the Gallery of Beauties at Nymphenburg Palace in Munich, as well as his emblematic portrait of Ludwig van Beethoven, which has become one of his most famous works.

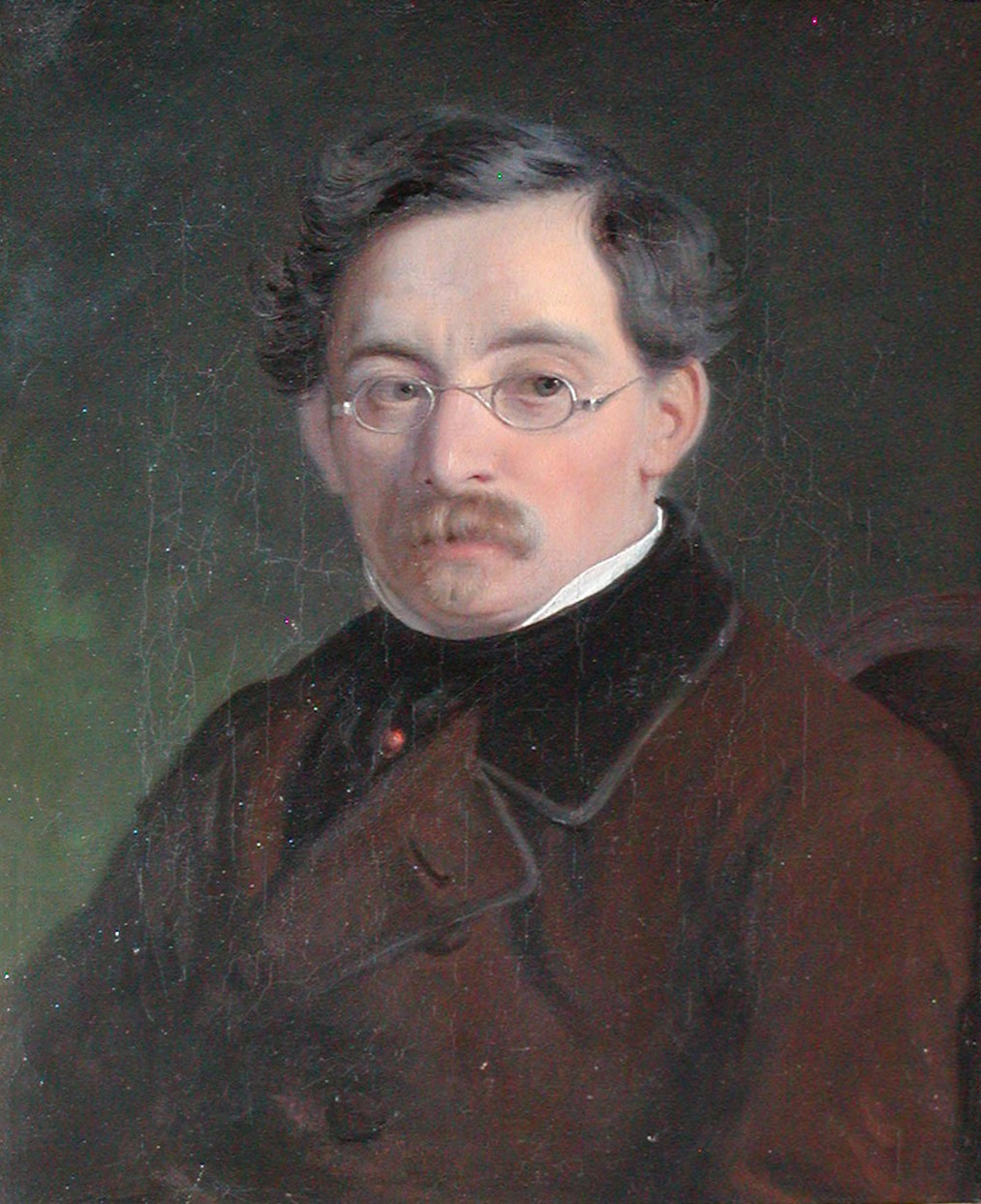
Ernst Meyer was a Danish genre painter of Jewish origin. He studied painting at the Royal Danish Academy of Arts.
Ernst Meyer travelled extensively, living for a time in Germany, France, Switzerland and Italy. It was the colourful street life of Rome that first inspired him to create genre scenes.
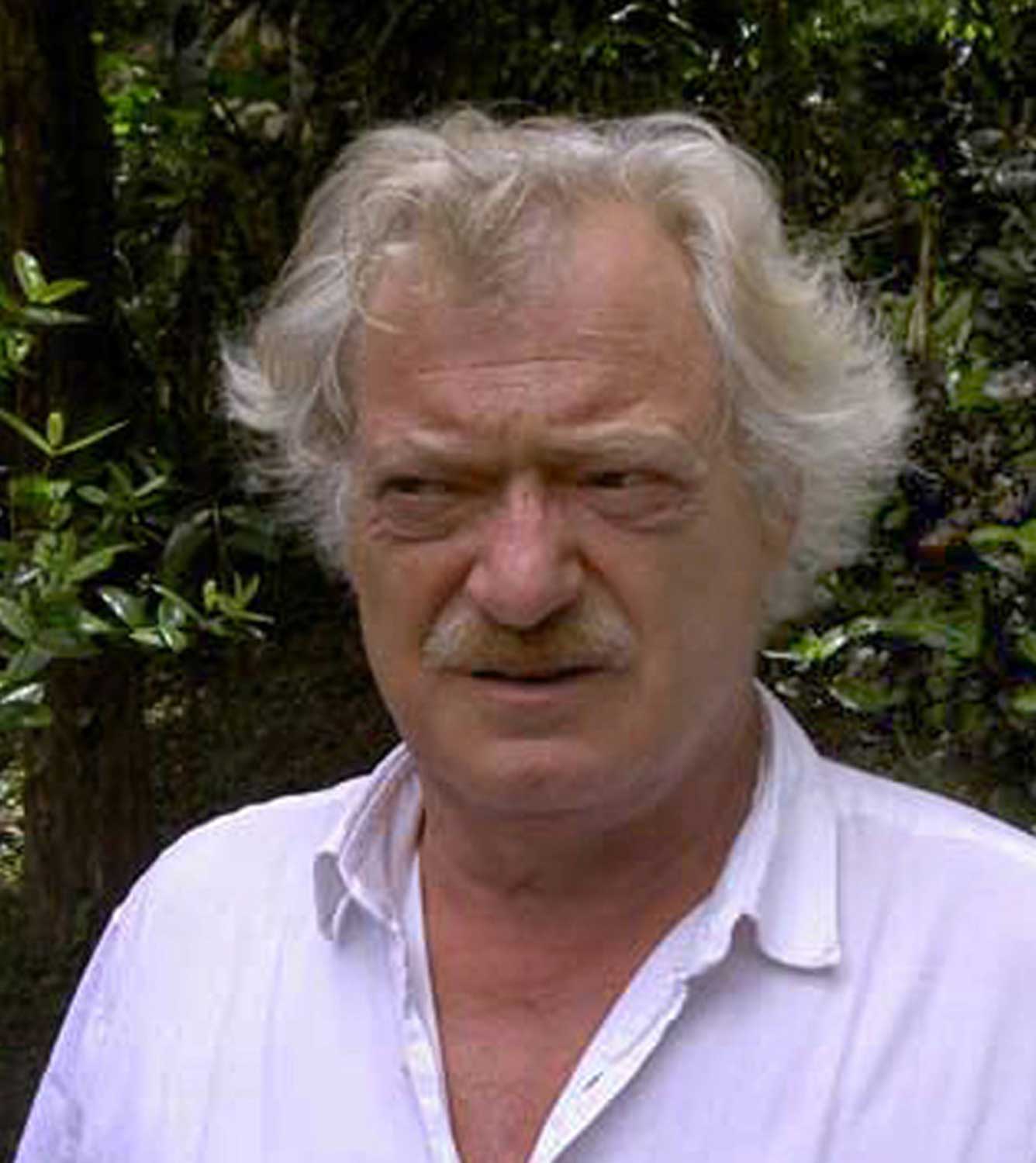


Lambert Maria Wintersberger was a German artist.
With other artists such as Markus Lüpertz, Karl Horst Hödicke, and Bernd Koberling, he helped found the Gallery "Großgörschen 35" in Berlin.
Lambert Maria Wintersberger was the laureate of the Centre Européen d'Actions Artistique Contemporaines in Strasbourg in 1992, and in 2005 and 2006, he was the guest artist at the Majolika Ceramic Factory in Karlsruhe.


Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn, a Dutch Baroque painter and printmaker, was born on July 15, 1606, in Leiden, Netherlands, and died on October 4, 1669, in Amsterdam. He is celebrated as one of the greatest storytellers in art history, acclaimed for his adept portrayal of human emotions and dramatic narratives. Rembrandt's extensive oeuvre includes portraits, self-portraits, landscapes, genre scenes, allegorical, historical, and biblical themes, as well as animal studies. His artistry shined during the Dutch Golden Age, a period marked by cultural and scientific achievements in the Netherlands.
Rembrandt's education in art began around the age of 10 when he left the Latin School in Leiden to train as an artist. He apprenticed with artists like Jacob van Swanenburg and Pieter Lastman, mastering various aspects of painting. He opened his own studio in Leiden around 1624 or 1625, sharing it with his colleague Jan Lievens. By 1631, he had moved to Amsterdam, where he achieved significant success and trained many important Dutch painters.
Among Rembrandt's notable works are "The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp" (1632), "The Night Watch" (1642), and "The Syndics of the Amsterdam Drapers’ Guild" (1662). He was also renowned for his self-portraits, creating around 80 over his lifetime, more than any other artist until the 20th century. These self-portraits were not just artistic endeavors but also experiments with facial expressions and lighting effects. Additionally, Rembrandt was a master etcher, transforming etching from a reproductive technique into an art form.
Rembrandt's painting style is characterized by its dramatic use of light and shadow, known as chiaroscuro. His ability to depict materials realistically was unparalleled; his portrayal of metals and fabrics was so lifelike that they appeared to glow and be tangible. He was also known for his impasto technique, applying paint thickly to the canvas, adding a three-dimensional quality to his works.
Despite his artistic prowess, Rembrandt faced financial difficulties and personal tragedies throughout his life. He declared bankruptcy in 1656, a downfall attributed partly to his extensive collection of art objects and curiosities. His masterpieces, however, continued to garner appreciation and influence generations of artists that followed.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Rembrandt's works represent a pinnacle of artistic achievement in the Dutch Golden Age. His mastery in portraying the human condition and his innovative techniques in painting and etching make his works highly prized and influential in the art world.
To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Rembrandt van Rijn, sign up for our updates. This subscription service is dedicated exclusively to news and events concerning works related to this unparalleled master of the Dutch Golden Age.
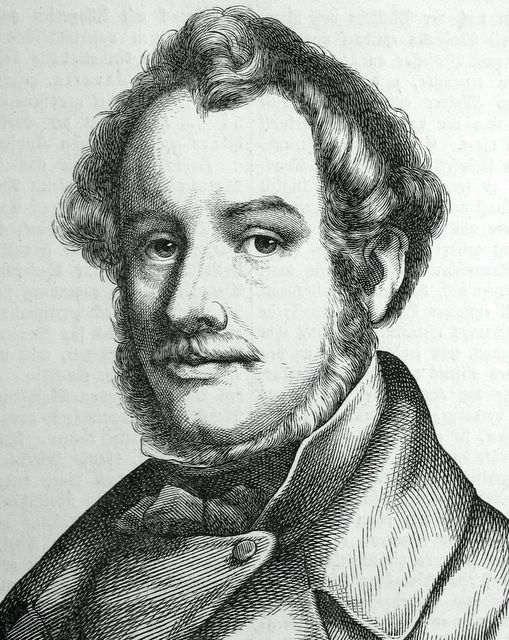


Ludwig Michael Schwanthaler, ennobled as Ritter von Schwanthaler, was a Bavarian sculptor and a key figure in the Classical movement in southern Germany. He was born on 26 August 1802 in Munich to a family that had been involved in sculpture for centuries.
Schwanthaler's journey began under his father's tutelage before he formally trained at the Munich Academy. His talent was so profound that he received commissions from royalty and mentorship from the likes of Peter von Cornelius. He further honed his skills in Rome, where he was influenced by Bertel Thorvaldsen. Returning to Munich, Schwanthaler met the demands for sculpture head-on, collaborating with architects and painters to revive the arts in Bavaria.
Among his many works, the statues in the Neues Palais and the figures in the Alte Pinakothek are notable. His versatility also shone in sacred art, with his contributions to St Ludwig and St Mariahilf churches. The Ruhmeshalle's metopes and the monumental Bavaria statue demonstrate his artistic bravery. Schwanthaler's life was dedicated to his craft, and upon his death on November 14, 1848, he bequeathed his models and studies to the Munich Academy, forming the Schwanthaler Museum.
For art enthusiasts, Schwanthaler's legacy offers a deep dive into classical sculpture's golden age. His works remain a testament to the neoclassical aesthetic and are celebrated for their historical and artistic significance.
Engage with the grandeur of Schwanthaler's art by signing up for updates, and take part in preserving the memory of one of Bavaria's master sculptors.


Ludwig Michael Schwanthaler, ennobled as Ritter von Schwanthaler, was a Bavarian sculptor and a key figure in the Classical movement in southern Germany. He was born on 26 August 1802 in Munich to a family that had been involved in sculpture for centuries.
Schwanthaler's journey began under his father's tutelage before he formally trained at the Munich Academy. His talent was so profound that he received commissions from royalty and mentorship from the likes of Peter von Cornelius. He further honed his skills in Rome, where he was influenced by Bertel Thorvaldsen. Returning to Munich, Schwanthaler met the demands for sculpture head-on, collaborating with architects and painters to revive the arts in Bavaria.
Among his many works, the statues in the Neues Palais and the figures in the Alte Pinakothek are notable. His versatility also shone in sacred art, with his contributions to St Ludwig and St Mariahilf churches. The Ruhmeshalle's metopes and the monumental Bavaria statue demonstrate his artistic bravery. Schwanthaler's life was dedicated to his craft, and upon his death on November 14, 1848, he bequeathed his models and studies to the Munich Academy, forming the Schwanthaler Museum.
For art enthusiasts, Schwanthaler's legacy offers a deep dive into classical sculpture's golden age. His works remain a testament to the neoclassical aesthetic and are celebrated for their historical and artistic significance.
Engage with the grandeur of Schwanthaler's art by signing up for updates, and take part in preserving the memory of one of Bavaria's master sculptors.







































