art for the kitchen
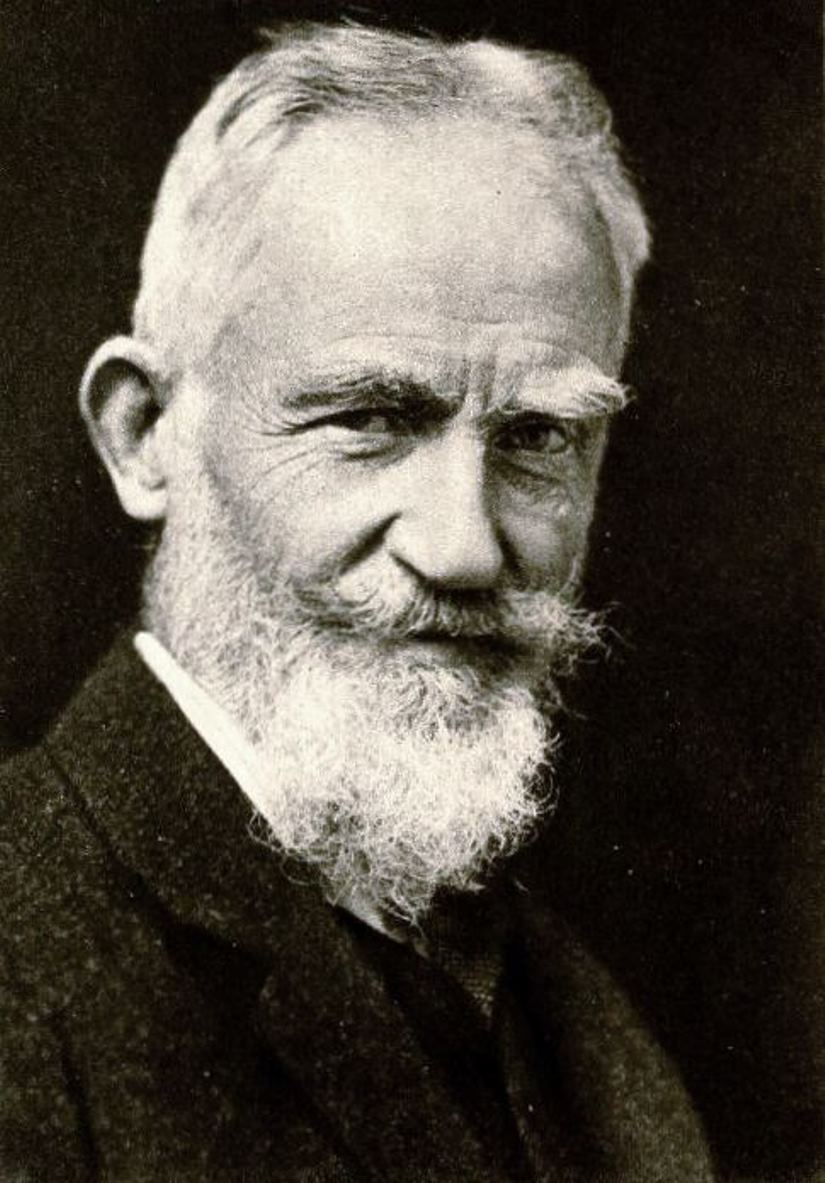
George Bernard Shaw was an Irish playwright, novelist and literary critic, socialist propagandist and journalist, winner of the 1925 Nobel Prize for Literature.
George Bernard was born into a poor noble family and, growing up, suffered greatly from that poverty. After a decade of failure on the literary field, Bernard became an active member of the Fabian Society, a middle-class socialist group founded in 1884, which sought the gradual transformation of English society.
He began working as a journalist and writing plays, which soon enough became popular. In The Man and the Superman, Shaw laid out his philosophy that humanity is the last stage of a purposeful and eternal evolutionary movement of "life force" toward ever higher forms of life. By far his most popular play is Pygmalion, a humane comedy about love and the English class system. But George Bernard Shaw was not only the best comic playwright of his time. Some of his stage works - Caesar and Cleopatra, The Man and Superman, Major Barbara, House of Broken Hearts, and St. Joan - are highly serious and refined in their prose.
Shaw was also a bold pamphleteer, a popular and widely read music and theater critic of his generation, a lecturer and essayist on politics, economics and sociology. In the course of his long and prolific life Bernard Shaw shaped the political, economic and social worldviews of several generations.
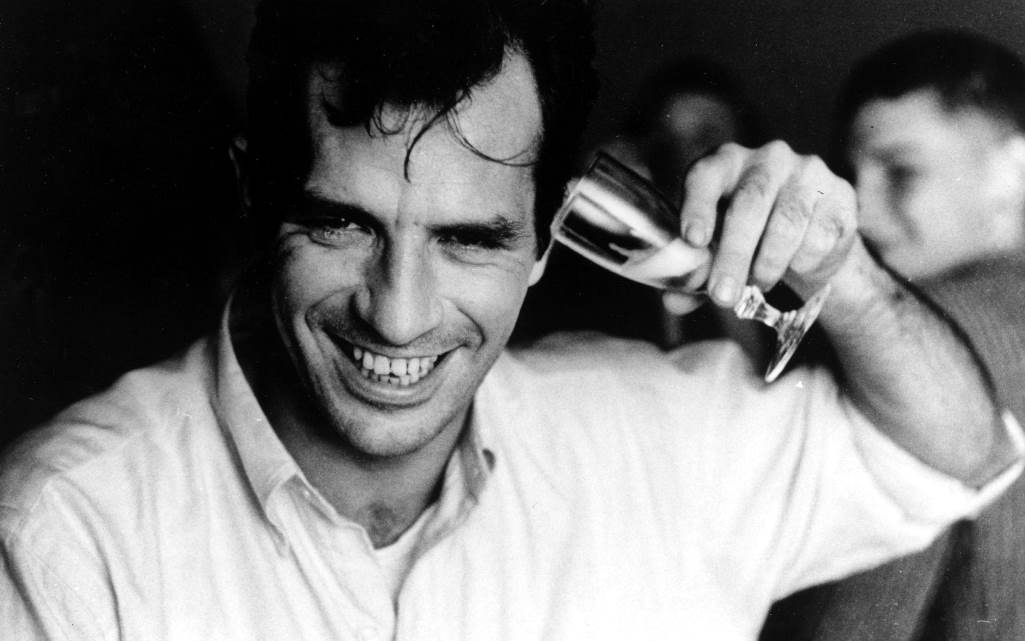
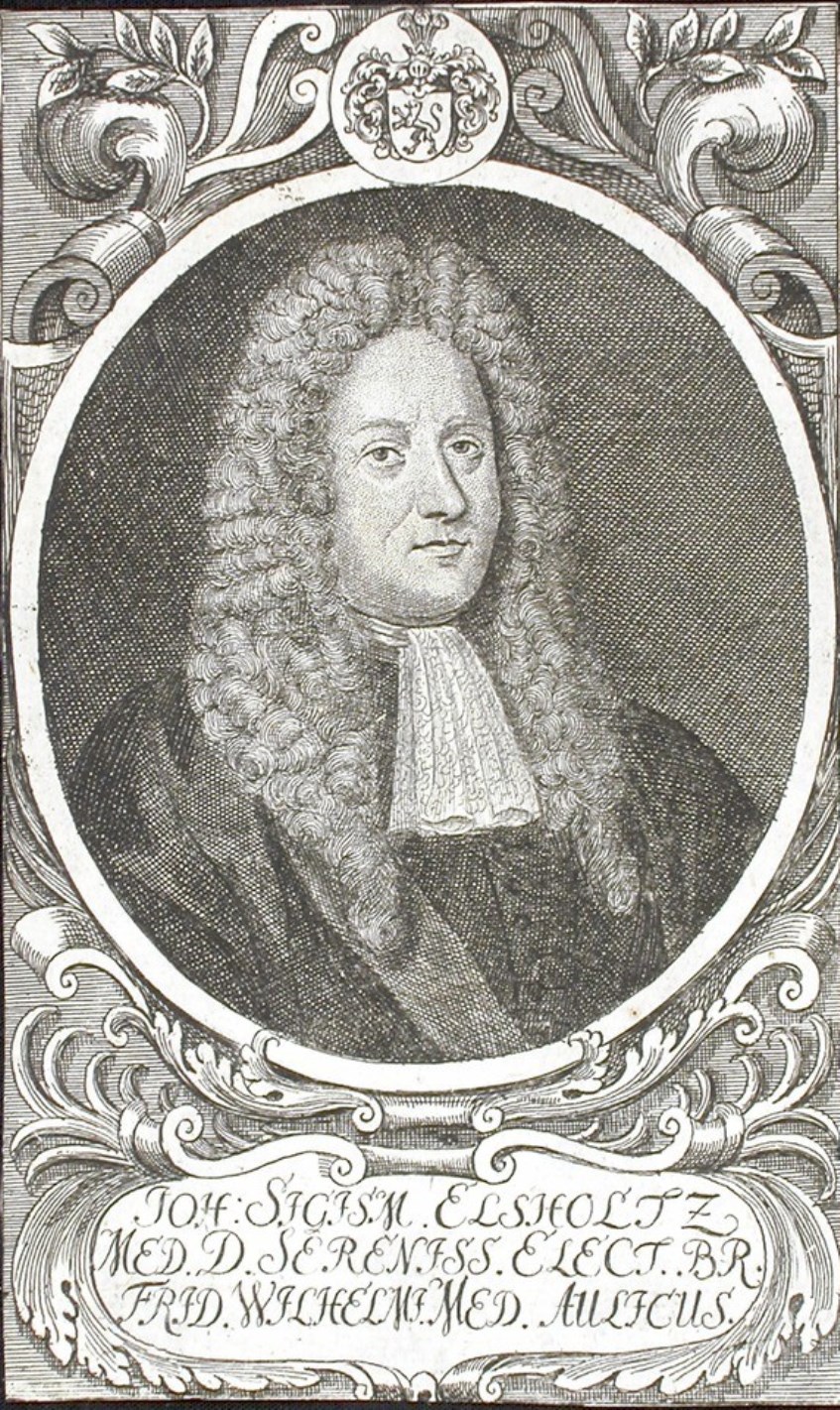








Johann Sigismund Elsholtz (also Elßholtz, Elßholz, Elsholz, Latin Elsholtius) was a German physician, botanist and chemist, a pioneer of hygiene.
Elsholtz studied at the universities of Wittenberg, Königsberg, and Padua, where he received his doctorate. In 1654, he published Anthropometry, written for artists and astrologers as well as students of medicine and physiognomy. The book also explored the supposed relationship between the proportions of the human body and morbidity. Elsholtz was a very versatile scientist and worked in the fields of horticulture, botany, alchemy, astrology, dietetics and medicine, among others.
Elsholtz was later appointed court botanist, alchemist and physician to Elector Friedrich Wilhelm of Brandenburg (1620-1688), and in 1657 was placed in charge of his botanical gardens in Berlin, Potsdam and Oranienburg. In 1672 his treatise Vom Garten-Baw: Oder Unterricht von der Gärtnerey auff das Clima der Chur-Marck Brandenburg was published in Berlin. ("From the Garden Bow or Lessons in Gardening in the Climate of Chur-Marck Brandenburg." It presents the latest gardening techniques for the German climate, discussing flower gardens and their design, vegetable gardens, medicinal gardens, and vineyard care and design.
Elsholtz was a German pioneer in the field of cleanliness and nutrition. Generally speaking, the term "hygiene" first appeared in German in 1682 in his Dietetikon. It is the term he uses to describe the principle of maintaining good health. In his book, the doctor makes recommendations for healthy eating and drinking. He calls for clean water and good air and emphasizes the importance of personal hygiene. Elsholtz was one of the first to administer intravenous injections to people around 1665.
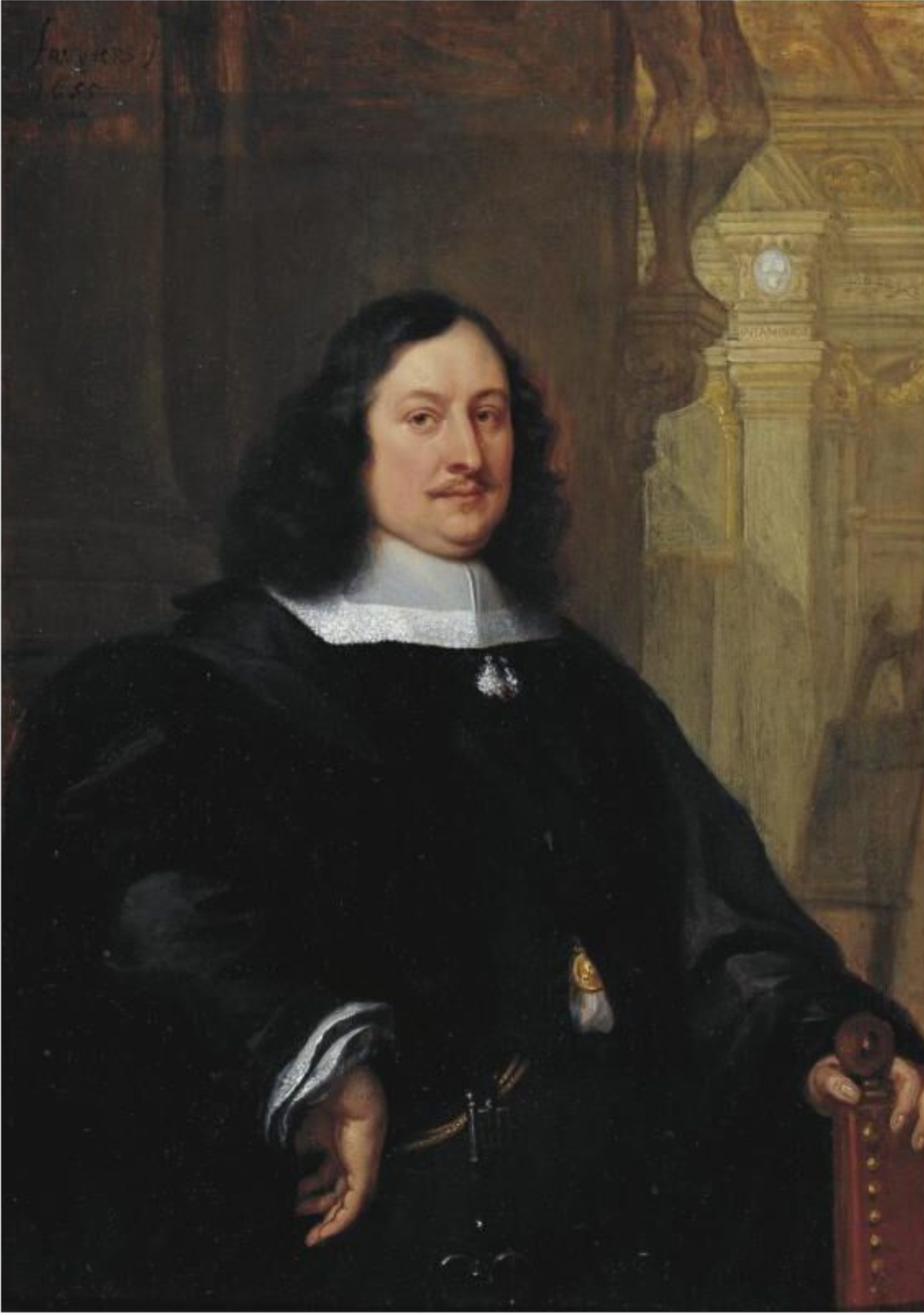





David Teniers the Younger was a Flemish Baroque painter, printmaker, draughtsman, miniaturist painter, staffage painter, copyist and art curator. He was an extremely versatile artist known for his prolific output. He was an innovator in a wide range of genres such as history painting, genre painting, landscape painting, portrait and still life. He is now best remembered as the leading Flemish genre painter of his day. Teniers is particularly known for developing the peasant genre, the tavern scene, pictures of collections and scenes with alchemists and physicians.
He was court painter and the curator of the collection of Archduke Leopold Wilhelm, the art-loving Governor General of the Habsburg Netherlands. He created a printed catalogue of the collections of the Archduke. He was the founder of the Antwerp Academy, where young artists were trained to draw and sculpt in the hope of reviving Flemish art after its decline following the death of the leading Flemish artists Rubens and Anthony van Dyck in the early 1640s. He influenced the next generation of Northern genre painters as well as French Rococo painters such as Antoine Watteau.
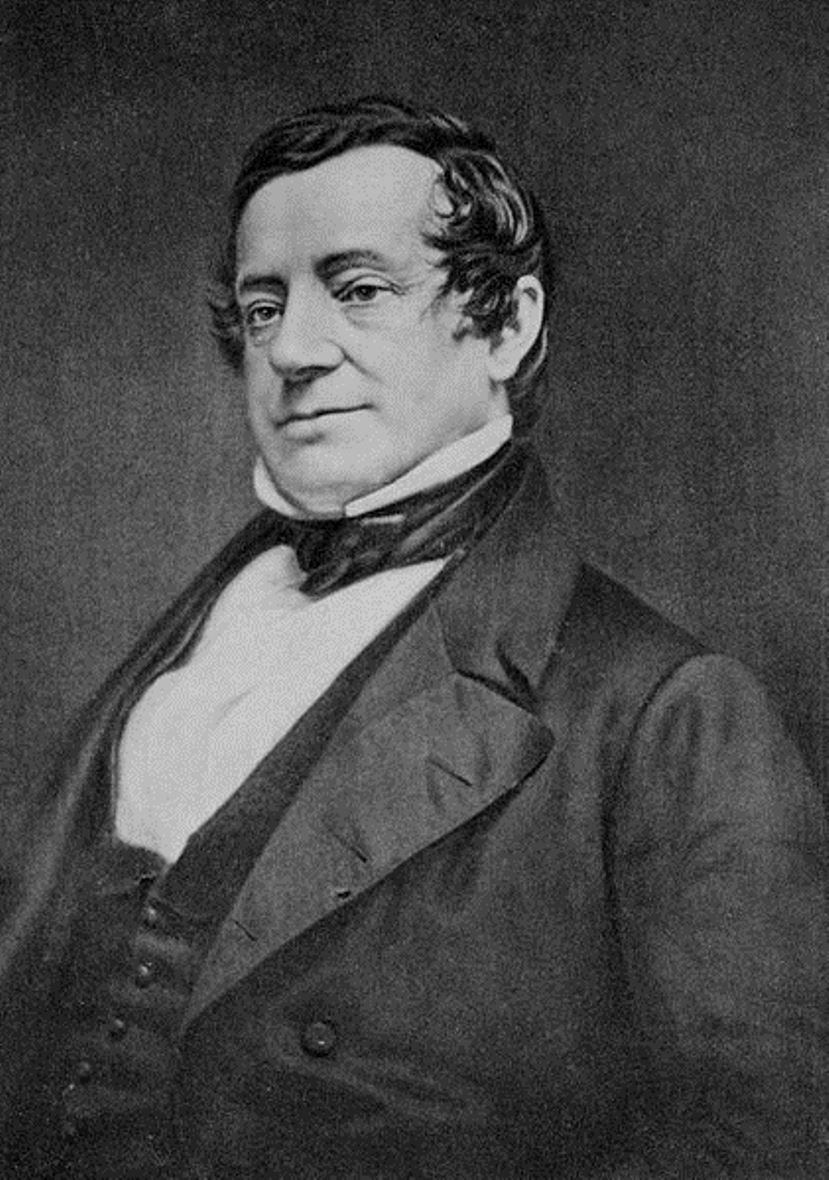


Washington Irving was an American Romantic writer, historian, and diplomat.
Irving has been called "the first American writer" to be recognized in Europe. In 1815, he traveled to England on family business. A huge success in England and the United States was The Sketch Book, published in several installments during 1819-1820, which contained two of the author's most famous works, Rip Van Winkle and The Legend of Sleepy Hollow, and which made him a literary star in both England and the United States.
He continued his literary endeavors and worked at the U.S. Embassy of Great Britain. Returning to the United States in 1832, Irving visited some little-known territories near the western fringes of the country, and this journey inspired his works Journey on the Prairie (1835), Astoria (1836), and The Adventures of Captain Bonneville (1837). Late in life he published several historical and biographical works, including the five-volume Life of George Washington (1855-1859).


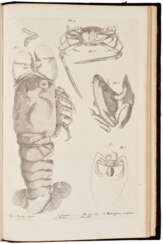
Patrick Browne was an Irish physician and historian, traveler, naturalist and botanist.
Patrick Browne studied medicine in Paris, graduated from the University of Reims, continued his studies in Leiden, and then worked as a doctor at St. Thomas' Hospital in London. Subsequently, he lived for many years in the Caribbean, in Antigua, Santa Cruz, Montserrat and Jamaica, where he practiced medicine. He devoted all his spare time to the study of the natural history of the island. In 1771, Brown returned to Mayo County.
In 1756, Brown published A Civil and Natural History of Jamaica, his most significant work in terms of Carl Linnaeus's botanical nomenclature, which included new names for 104 genera.


Patrick Browne was an Irish physician and historian, traveler, naturalist and botanist.
Patrick Browne studied medicine in Paris, graduated from the University of Reims, continued his studies in Leiden, and then worked as a doctor at St. Thomas' Hospital in London. Subsequently, he lived for many years in the Caribbean, in Antigua, Santa Cruz, Montserrat and Jamaica, where he practiced medicine. He devoted all his spare time to the study of the natural history of the island. In 1771, Brown returned to Mayo County.
In 1756, Brown published A Civil and Natural History of Jamaica, his most significant work in terms of Carl Linnaeus's botanical nomenclature, which included new names for 104 genera.



.jpg)
Jean Elysée Puiforcat was a French silversmith, sculptor and designer. Miller's Antiques Encyclopedia calls Puiforcat the «most important French Art Deco silversmith».
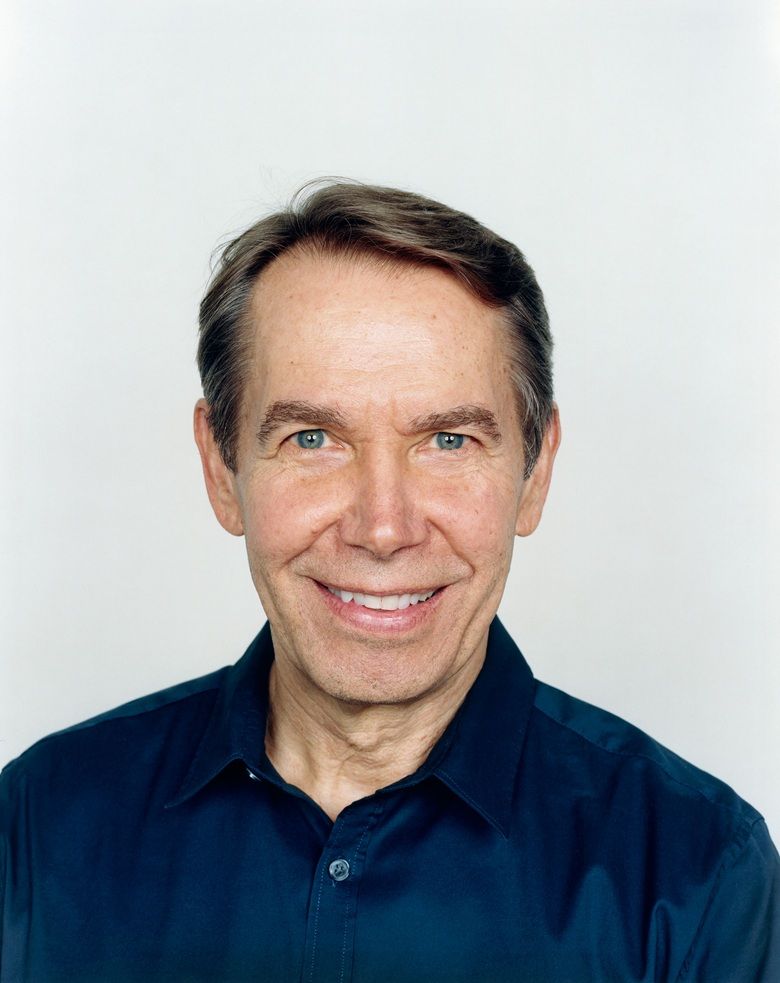
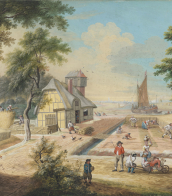



Jeffrey Lynn Koons is an American artist recognized for his work dealing with popular culture and his sculptures depicting everyday objects, including balloon animals produced in stainless steel with mirror-finish surfaces. He lives and works in both New York City and his hometown of York, Pennsylvania. His works have sold for substantial sums, including at least two record auction prices for a work by a living artist: US$58.4 million for Balloon Dog (Orange) in 2013 and US$91.1 million for Rabbit in 2019.
Critics are sharply divided in their views of Koons. Some view his work as pioneering and of major art-historical importance. Others dismiss his work as kitsch, crass, and based on cynical self-merchandising. Koons has stated that there are no hidden meanings and critiques in his works.