art oriental

Frederick Arthur Bridgman was an American artist. He was known for his paintings in the Orientalist style.
Frederick Arthur Bridgman studied art at the Brooklyn Art Association and the National Academy of Design in New York. In 1866 he went to Paris to continue his studies at the École des Beaux-Arts. There he worked in the studio of Jean-Léon Gérôme, who at the time was a leading Orientalist painter. Bridgeman painted scenes of everyday life in the area, as well as historical and religious subjects. His paintings were notable for their vivid colours, attention to detail and dramatic compositions.


Frederick Arthur Bridgman was an American artist. He was known for his paintings in the Orientalist style.
Frederick Arthur Bridgman studied art at the Brooklyn Art Association and the National Academy of Design in New York. In 1866 he went to Paris to continue his studies at the École des Beaux-Arts. There he worked in the studio of Jean-Léon Gérôme, who at the time was a leading Orientalist painter. Bridgeman painted scenes of everyday life in the area, as well as historical and religious subjects. His paintings were notable for their vivid colours, attention to detail and dramatic compositions.


Frederick Arthur Bridgman was an American artist. He was known for his paintings in the Orientalist style.
Frederick Arthur Bridgman studied art at the Brooklyn Art Association and the National Academy of Design in New York. In 1866 he went to Paris to continue his studies at the École des Beaux-Arts. There he worked in the studio of Jean-Léon Gérôme, who at the time was a leading Orientalist painter. Bridgeman painted scenes of everyday life in the area, as well as historical and religious subjects. His paintings were notable for their vivid colours, attention to detail and dramatic compositions.
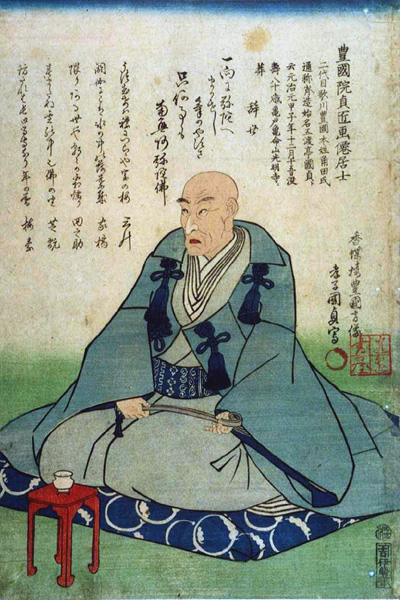


Utagawa Kunisada (Jap. 歌川 国貞, also known as Utagawa Toyokuni III (Jap. 三代歌川豊国)) is the largest Japanese artist and master of color graphics (woodcuts) of the Edo period.
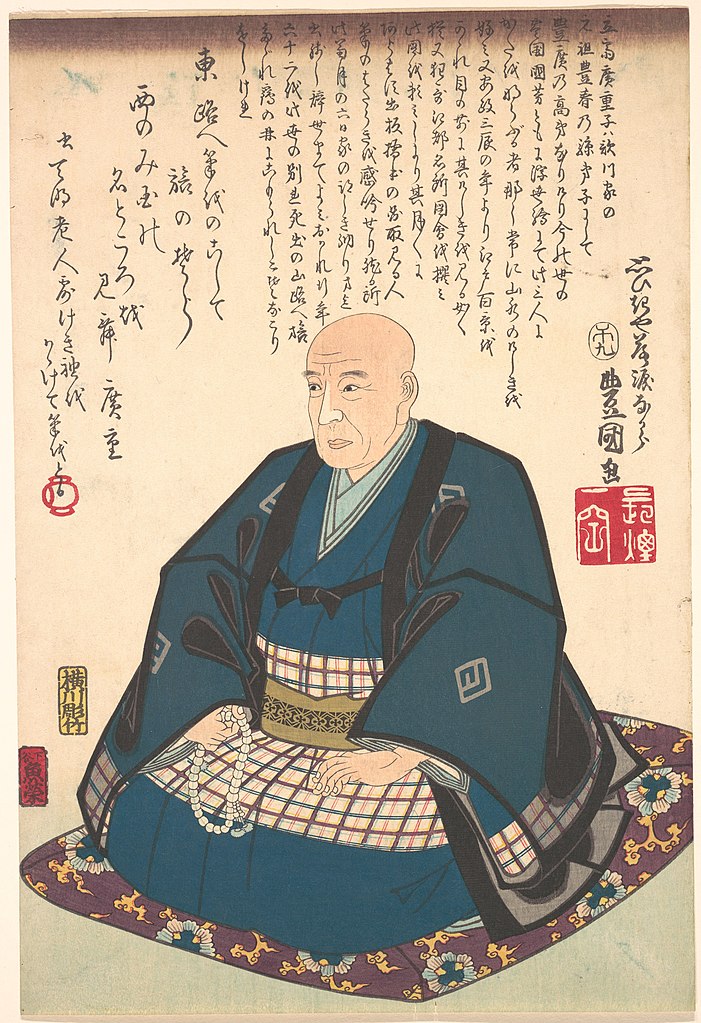

Utagawa Hiroshige (Japanese: 歌川 広重) was a Japanese ukiyo-e artist, considered the last great master of that tradition. Hiroshige is best known for his horizontal-format landscape series The Fifty-three Stations of the Tōkaidō and for his vertical-format landscape series One Hundred Famous Views of Edo. The subjects of his work were atypical of the ukiyo-e genre, whose typical focus was on beautiful women, popular actors, and other scenes of the urban pleasure districts of Japan's Edo period (1603–1868). The popular series Thirty-six Views of Mount Fuji by Hokusai was a strong influence on Hiroshige's choice of subject, though Hiroshige's approach was more poetic and ambient than Hokusai's bolder, more formal prints. Subtle use of color was essential in Hiroshige's prints, often printed with multiple impressions in the same area and with extensive use of bokashi (color gradation), both of which were rather labor-intensive techniques.