energy

Kim Yusob is a South Korean artist who lives and works in Berlin, Germany and Seoul, South Korea. After graduating from the Department of Fine Art at Chosun University, Gwangju, in 1983 Kim Yusob moved to Berlin. There he studied both at the Kunsthochschule Weissensee in East Berlin and at the Western Universität der Künste (University of the Arts). 1995 he became Meisterschüler (Master Disciple) of Wolfgang Petrick. Since 1996 Kim has been teaching at Chosun University, where he completed Graduate School in 2001. From 2007 on he has been teaching at the Universität der Künste (University of the Arts). In 2014 he became Professor of Painting at Chosun University. Within his oeuvre Kim Yusob aims at providing new impulses for abstract expressionism. His process of painting unites religious, philosophical and Anthroposophical aspects. Due to Kim’s background it is also rooted in Daoism and the I Ching. Furthermore, Kim obtains a typical effect by applying special technique of decelerating the colours’ drying.


Kim Yusob is a South Korean artist who lives and works in Berlin, Germany and Seoul, South Korea. After graduating from the Department of Fine Art at Chosun University, Gwangju, in 1983 Kim Yusob moved to Berlin. There he studied both at the Kunsthochschule Weissensee in East Berlin and at the Western Universität der Künste (University of the Arts). 1995 he became Meisterschüler (Master Disciple) of Wolfgang Petrick. Since 1996 Kim has been teaching at Chosun University, where he completed Graduate School in 2001. From 2007 on he has been teaching at the Universität der Künste (University of the Arts). In 2014 he became Professor of Painting at Chosun University. Within his oeuvre Kim Yusob aims at providing new impulses for abstract expressionism. His process of painting unites religious, philosophical and Anthroposophical aspects. Due to Kim’s background it is also rooted in Daoism and the I Ching. Furthermore, Kim obtains a typical effect by applying special technique of decelerating the colours’ drying.


Kim Yusob is a South Korean artist who lives and works in Berlin, Germany and Seoul, South Korea. After graduating from the Department of Fine Art at Chosun University, Gwangju, in 1983 Kim Yusob moved to Berlin. There he studied both at the Kunsthochschule Weissensee in East Berlin and at the Western Universität der Künste (University of the Arts). 1995 he became Meisterschüler (Master Disciple) of Wolfgang Petrick. Since 1996 Kim has been teaching at Chosun University, where he completed Graduate School in 2001. From 2007 on he has been teaching at the Universität der Künste (University of the Arts). In 2014 he became Professor of Painting at Chosun University. Within his oeuvre Kim Yusob aims at providing new impulses for abstract expressionism. His process of painting unites religious, philosophical and Anthroposophical aspects. Due to Kim’s background it is also rooted in Daoism and the I Ching. Furthermore, Kim obtains a typical effect by applying special technique of decelerating the colours’ drying.


Kim Yusob is a South Korean artist who lives and works in Berlin, Germany and Seoul, South Korea. After graduating from the Department of Fine Art at Chosun University, Gwangju, in 1983 Kim Yusob moved to Berlin. There he studied both at the Kunsthochschule Weissensee in East Berlin and at the Western Universität der Künste (University of the Arts). 1995 he became Meisterschüler (Master Disciple) of Wolfgang Petrick. Since 1996 Kim has been teaching at Chosun University, where he completed Graduate School in 2001. From 2007 on he has been teaching at the Universität der Künste (University of the Arts). In 2014 he became Professor of Painting at Chosun University. Within his oeuvre Kim Yusob aims at providing new impulses for abstract expressionism. His process of painting unites religious, philosophical and Anthroposophical aspects. Due to Kim’s background it is also rooted in Daoism and the I Ching. Furthermore, Kim obtains a typical effect by applying special technique of decelerating the colours’ drying.


Kim Yusob is a South Korean artist who lives and works in Berlin, Germany and Seoul, South Korea. After graduating from the Department of Fine Art at Chosun University, Gwangju, in 1983 Kim Yusob moved to Berlin. There he studied both at the Kunsthochschule Weissensee in East Berlin and at the Western Universität der Künste (University of the Arts). 1995 he became Meisterschüler (Master Disciple) of Wolfgang Petrick. Since 1996 Kim has been teaching at Chosun University, where he completed Graduate School in 2001. From 2007 on he has been teaching at the Universität der Künste (University of the Arts). In 2014 he became Professor of Painting at Chosun University. Within his oeuvre Kim Yusob aims at providing new impulses for abstract expressionism. His process of painting unites religious, philosophical and Anthroposophical aspects. Due to Kim’s background it is also rooted in Daoism and the I Ching. Furthermore, Kim obtains a typical effect by applying special technique of decelerating the colours’ drying.
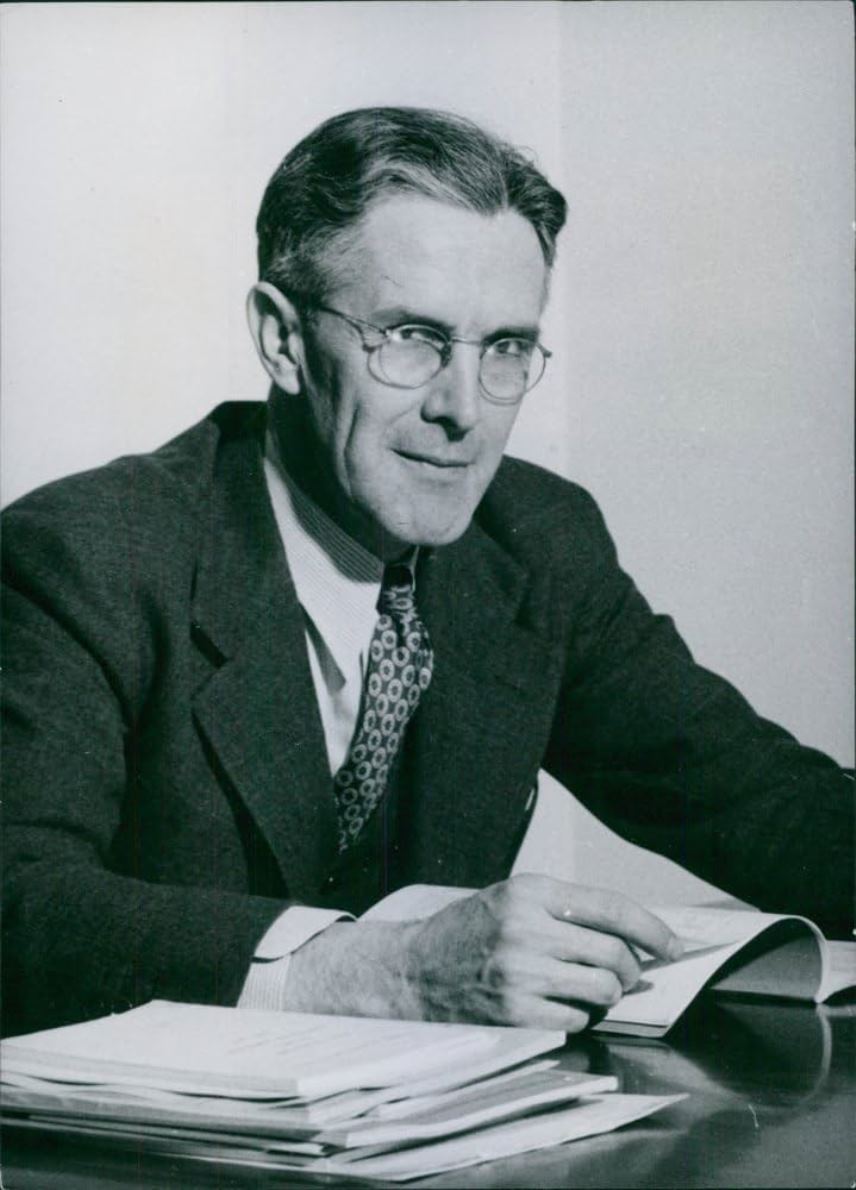


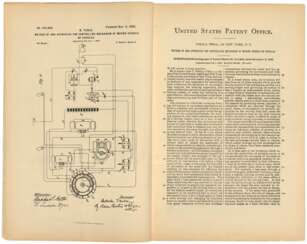
Henry DeWolf Smyth was an American scientist, nuclear physicist, and diplomat.
Smyth studied at Princeton and Cambridge Universities, taught in Princeton's physics department from 1924 to 1966, and chaired the department for many years. At first he investigated the ionization of gases, but from the mid-1930s he turned his attention to nuclear physics. During World War II, Smith was a member of the uranium section of the National Defense Research Committee. He also proposed electromagnetic techniques that were used to enrich the first samples of U-235 during the Manhattan Project. Smith worked as a consultant on this project from 1943 to 1945 and served as deputy director of the Metallurgical Laboratory at the University of Chicago.
In 1944, General Leslie Groves appointed Henry Smith to the Committee on Postwar Policy to propose a public policy for research and development of atomic energy after the war. He wrote the official public report on the bomb, which became known as the Smith Report and was widely distributed throughout the country.
After the war, Henry DeWolf Smith served as commissioner of the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission and as the U.S. representative to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). In 1953, he was President Eisenhower's chief advisor on Ike's "Atoms for Peace" speech and received the Atoms for Peace Award in 1968.



Max Ackermann was a German painter and graphic artist. He was a pupil of Adolf Hölzel and is considered a pioneer of abstract painting.


Max Ackermann was a German painter and graphic artist. He was a pupil of Adolf Hölzel and is considered a pioneer of abstract painting.


Max Ackermann was a German painter and graphic artist. He was a pupil of Adolf Hölzel and is considered a pioneer of abstract painting.


Max Ackermann was a German painter and graphic artist. He was a pupil of Adolf Hölzel and is considered a pioneer of abstract painting.


Timothy Chapman is an American wildlife artist living and working in Phoenix, Arizona.
He holds bachelor's degrees in biology (Occidental College) and printmaking (Arizona State University), and a master's degree in printmaking (Southern Illinois University in Edwardsville). And now he works at the Cattletrack Art Complex and calls his work "invented natural history."
Timothy Chapman has two passions in life - animals and art. He paints wild, striking images of animals, such as flying zebras and giraffes with floral patterns. Finding charm in whimsical ideas is what made Chapman an artist, and it's what he's known for today. He admires the balance between magical realism and the quiet surrealism of Frida Kahlo. And then there are the natural history illustrators, often anonymous, who took creative liberties with their drawings.


Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".


Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".


Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".
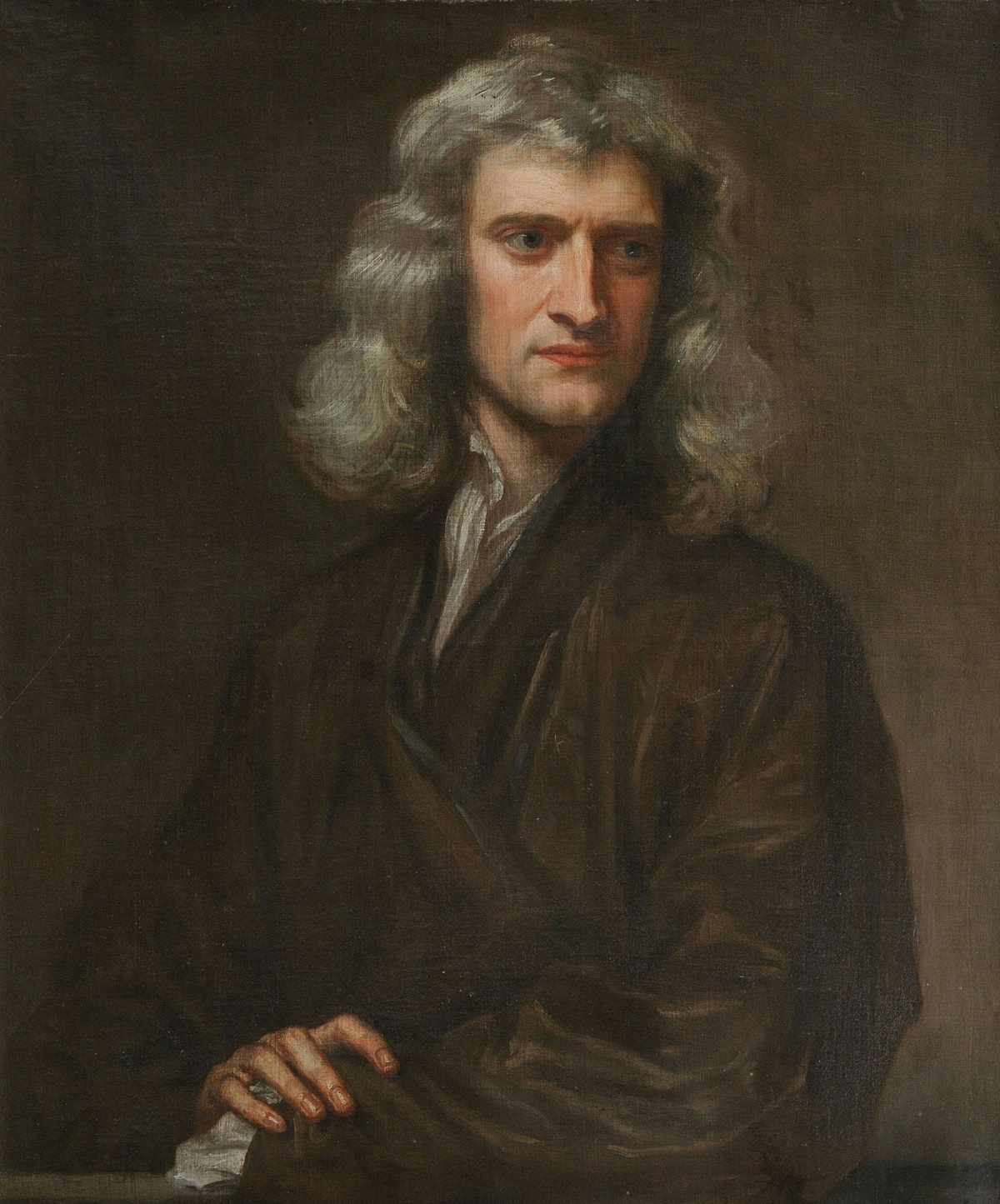


Isaac Newton was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus.
In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for tides, the trajectories of comets, the precession of the equinoxes and other phenomena, eradicating doubt about the Solar System's heliocentricity. He demonstrated that the motion of objects on Earth and celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton's inference that the Earth is an oblate spheroid was later confirmed by the geodetic measurements of Maupertuis, La Condamine, and others, convincing most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over earlier systems.


Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".
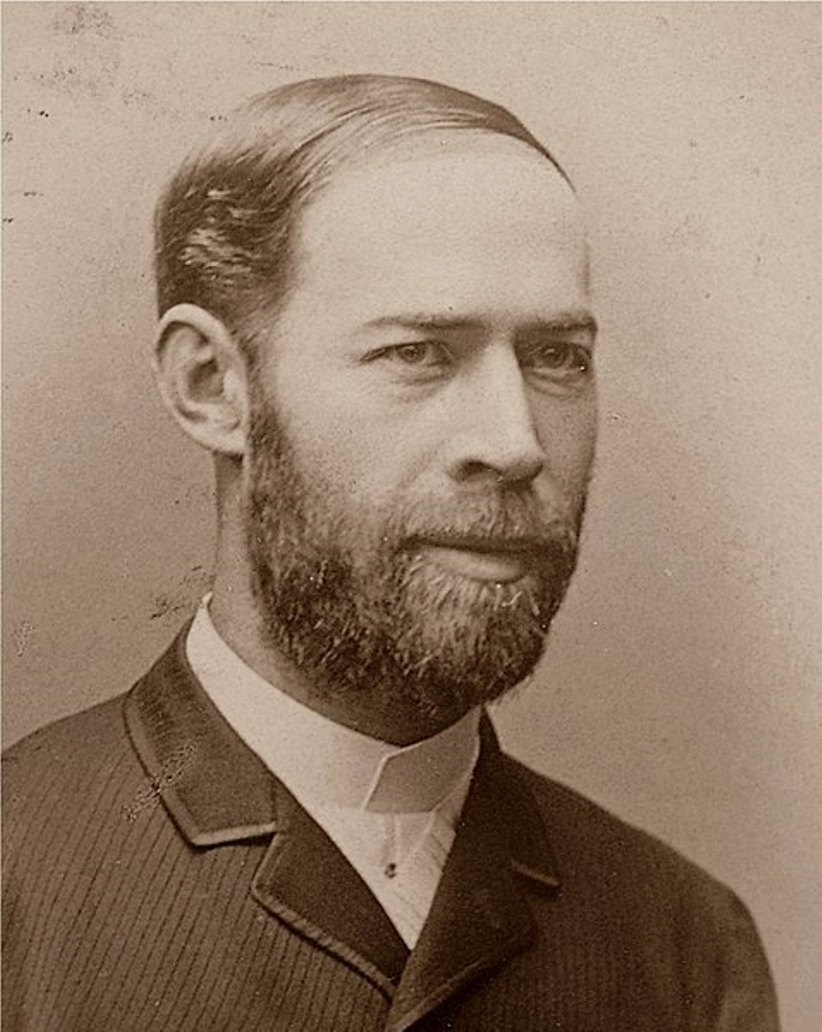


Heinrich Rudolf Hertz was a German physicist and inventor of radio waves.
Hertz graduated from the University of Berlin, studying under Hermann von Helmholtz and Gustav Kirchhoff, then was a professor of physics at the University of Karlsruhe, and from 1889 became a professor of physics at the University of Bonn.
A tireless experimenter, Hertz conducted various experiments with electric waves. Hertz reported his first discovery at the end of 1887 in a treatise "On the electromagnetic effects caused by electrical perturbations in insulators," which he sent to the Berlin Academy. For a time the waves he discovered were called Hertzian waves, but today they are known as radio waves. Hertz's discovery was a confirmation of James Clerk Maxwell's electromagnetic theory and paved the way for numerous advances in communication technology.
Hertz is also known for the discovery of the photoelectric effect, which occurred during his research on electromagnetic waves. Hertz was only 37 years old at the time of his death and many of his experiments and work remained unfinished, but his discovery of radio waves had a huge impact on the world in the 20th century, paving the way for the development of radio, television and radar.