graphique du livre
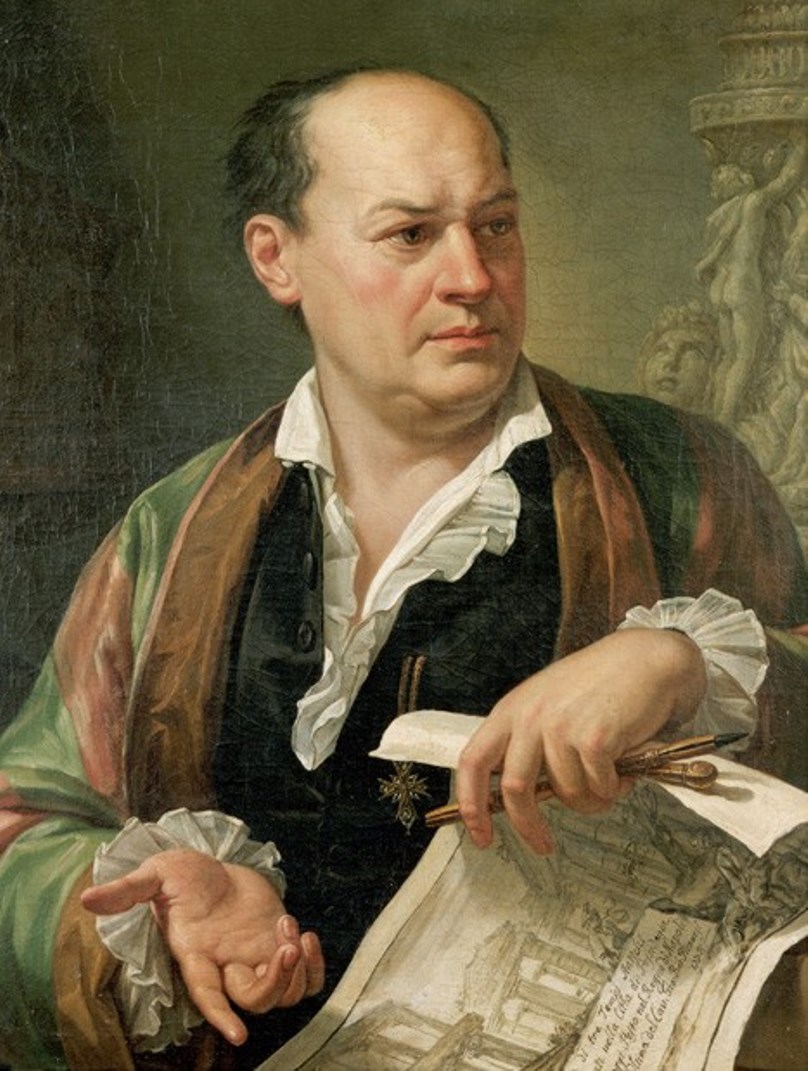



Giovanni Battista Piranesi was an 18th-century Italian painter, engraver, architect, and archaeologist who represented Neoclassicism and Romanticism. He was famous for creating a lot of original etchings with images of antique architecture monuments.
Giovanni Piranesi created hundreds of drawings and drafts in which he depicted the reconstructed ruins of ancient Roman buildings. His works are still used as teaching aids in the education of architectural students in many prestigious European universities. Piranesi periodically printed voluminous books with dozens of his own engravings depicting modified ancient architectural masterpieces - "graphic fantasies". His works were in demand among professional architects, who borrowed Piranesi's original ideas for their designs.
The peak of Piranesi's career came in the 1760s when, in recognition of his merits, he became an honorary member of the Guild of St. Luke and received from the Pope the title of Knight of the Golden Spur.
More than 700 of the master's original etchings have survived, printed in scholarly works.


Giovanni Battista Piranesi was an 18th-century Italian painter, engraver, architect, and archaeologist who represented Neoclassicism and Romanticism. He was famous for creating a lot of original etchings with images of antique architecture monuments.
Giovanni Piranesi created hundreds of drawings and drafts in which he depicted the reconstructed ruins of ancient Roman buildings. His works are still used as teaching aids in the education of architectural students in many prestigious European universities. Piranesi periodically printed voluminous books with dozens of his own engravings depicting modified ancient architectural masterpieces - "graphic fantasies". His works were in demand among professional architects, who borrowed Piranesi's original ideas for their designs.
The peak of Piranesi's career came in the 1760s when, in recognition of his merits, he became an honorary member of the Guild of St. Luke and received from the Pope the title of Knight of the Golden Spur.
More than 700 of the master's original etchings have survived, printed in scholarly works.
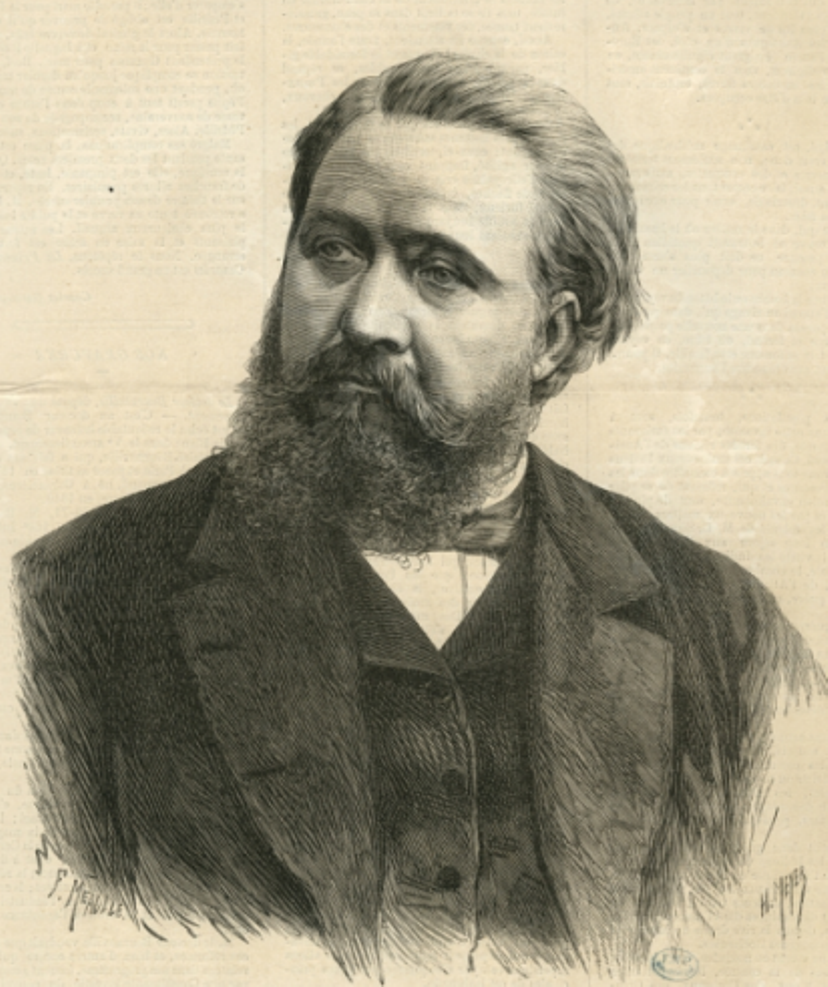







Désiré-Magloire Bourneville was a French physician, neurologist, innovator and educator, and statesman.
Born into a modest family, Bourneville began his medical education in 1860 and for about ten years worked as an assistant to Jean-Martin Charcot, where, together with Paul Régnard, he supervised the publication of "Photographic Iconography of Salpetriere". During the Franco-Prussian War, he served as both surgeon and physician's assistant. Appointed physician at Bissetre, Borneville devoted himself to the medical and educational care of "idiots and epileptics" for whom he organized a service, and later directed the Fondation Vallée in Gentilly until his death. He is considered one of the earliest child psychiatrists.
In 1876, Bourneville was elected a municipal councilor of Paris, three years later he became a general councilor of the Seine, and then a deputy. In this capacity, Bourneville carried out several health reforms: he became the rapporteur for the public assistance budget and the budget for psychiatric asylums, achieved the creation of the first special classes for mentally retarded children, and the first municipal nursing school in Salpêtrière.
Bourneville had many very different talents. Very early on he became interested in medical journalism, where he made a name for himself through the vividness of his articles. In 1873, he founded the journal Progrès Médical, which promoted the tenets of avant-garde medicine, open to pioneering scientific developments (Bourneville published Charcot's lessons) and social issues. He fully developed the theoretical and practical foundations of teaching for the nursing profession. Outraged by the lack of practitioners' professional knowledge of obstetrics, he worked to create a new medical specialty, gynecology. But his main purpose in life was to educate and nurture those who were labeled "idiots" and mentally retarded.
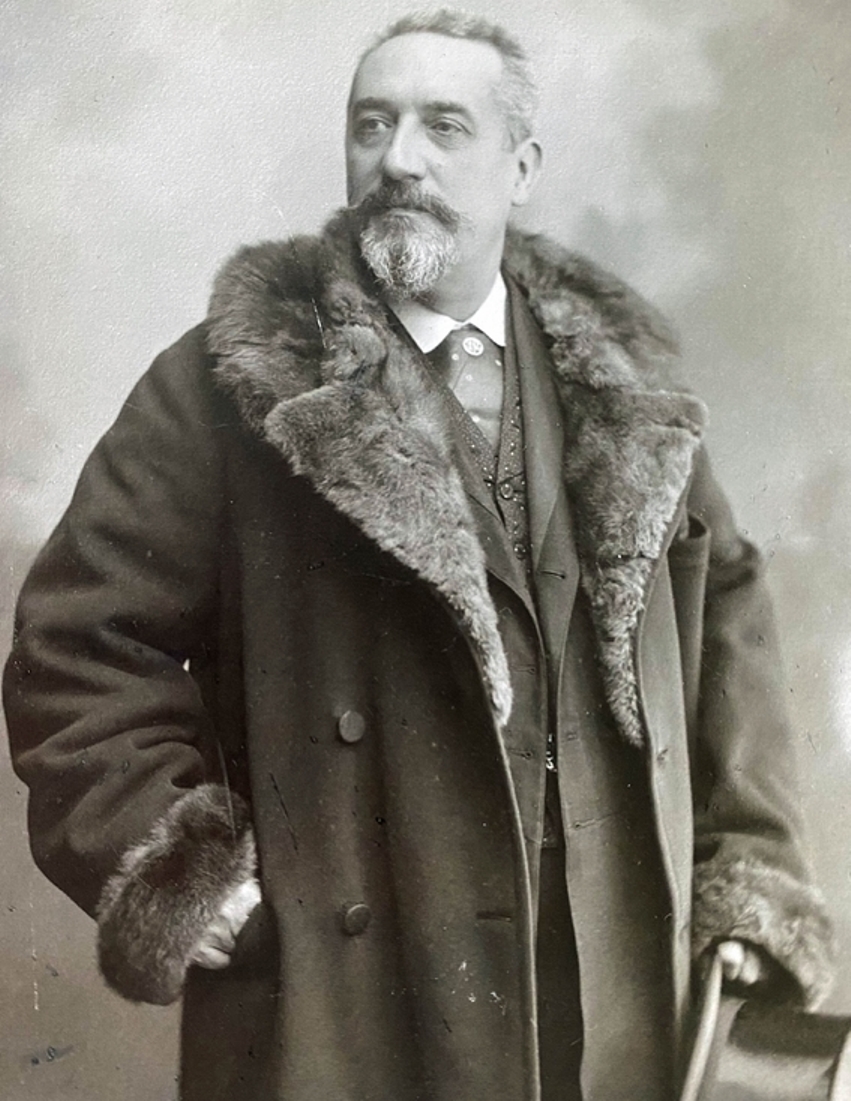

Paul Regnard, full name Paul Marie Léon Regnard, was a French physician, physiologist and photographer, and teacher.
He became a trainee at the hospital in 1874 and received his MD degree in 1878. Paul Regnard was deputy director of the Hautes Etudes Laboratories, and from 1878 taught general physiology at the newly founded National Agronomic Institute and later became its director (1902). He was also from 1895 a member of the Academy of Medicine in the section of biological sciences.
Regnard was one of the first practitioners of medical photography, particularly photographs of the mentally ill. Together with Désiré-Magloire Borneville, he directed the photographic service at the Salpêtrière Hospital of Paris, established by the psychiatrist J.C. Charcot (1825-1893). Numerous photographs were published in the book Iconographie Photographyique de la Salpêtrière. Regnard was a tireless researcher. He was one of the first naturalists to study the effects of atmospheric pressure on microbial metabolism. The scientist made a detailed historical and bibliographical survey of descriptions of possession and witchcraft through the ages, focusing on well-documented cases.
Regnar was particularly interested in the physical manifestations described by contemporaries: fainting spells, tetany, paresthesias, signs that could only be interpreted as diabolical or at least miraculous. All these signs Regnard had already observed, photographed, and treated at the Salpêtrière Hospital in the department of J.M. Charcot, to whom he dedicated this work, and so it was from the perspective of nascent psychiatry that Regnard analyzed these historical cases.
For his services, Regnard was made a Chevalier of the Legion of Honor in 1884, then an officer in 1900.
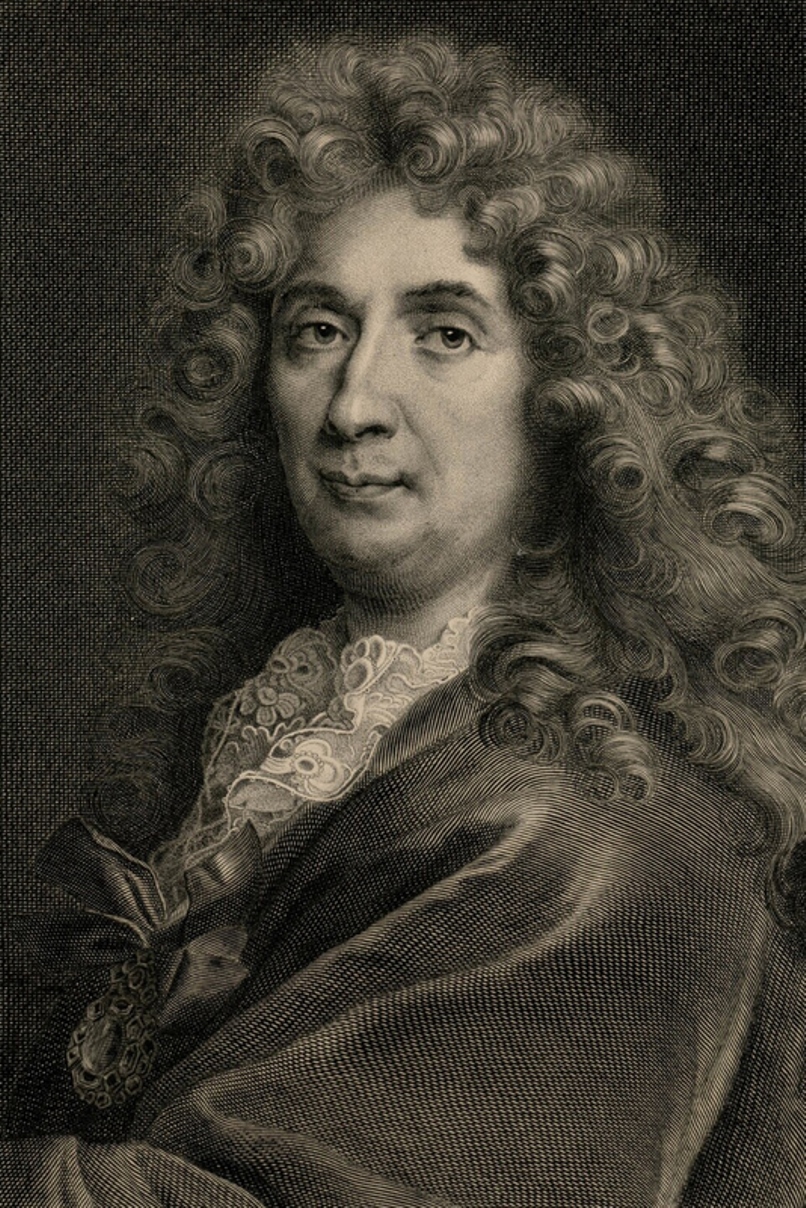


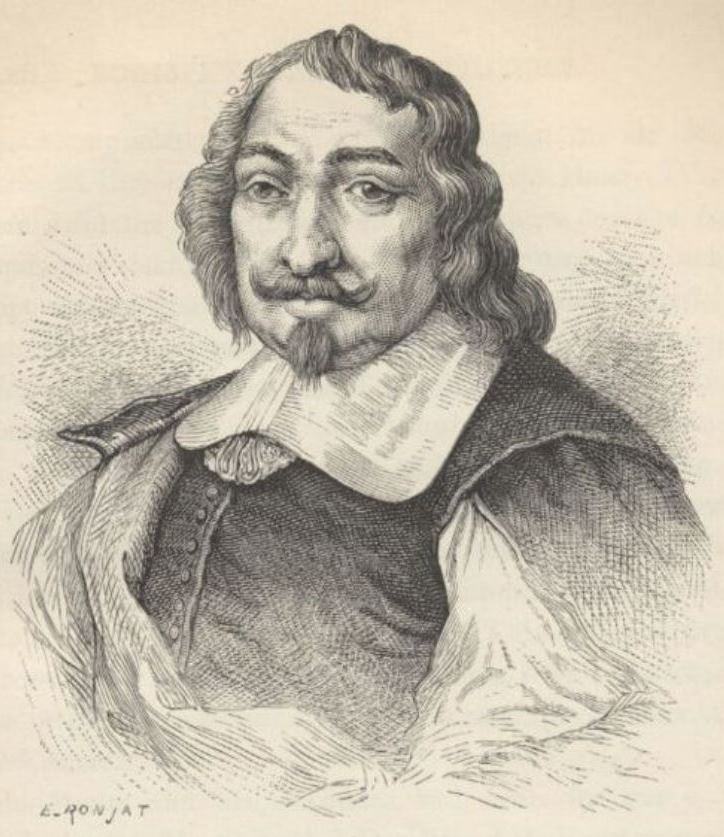
Charles Le Brun was a French painter, draftsman and chief decorator of the Palace of Versailles.
Charles came from an educated and respected family, trained in painting in Italy and very soon his talents were appreciated in the highest circles of France. In 1660 Le Brun painted "The Family of Darius before Alexander", which brought him the reputation of a brilliant French painter, and in 1664 he received the position of the first painter of the king. Thereafter he received more and more commissions and more honors.
From 1662 Le Brun controlled all the artistic projects of the royal court. In the Palace of Versailles, Lebrun created beautiful decorations: the Ambassadors' Staircase, the Hall of Mirrors, the Peace Room and the War Room. In each of his designs, he emphasized the king's achievements. He was also responsible for the decoration of the State Apartments, which was entrusted to the greatest artists of the time, who worked from his drawings. Le Brun also designed most of the statues in the park at Versailles. This enormous work cemented his reputation as a true seventeenth-century genius, as well as one of the founders, ideologues, and chief representatives of the classicist "grand style" of King Louis XIV's era.
In 1648 Le Brun became a founding member of the Royal Academy of Painting and Sculpture, and in 1663 - the manager of the Manufacture of tapestries.
Charles Le Brun was not only the creator of the "grand style", but also contributed to the rebirth of classicism into academism.
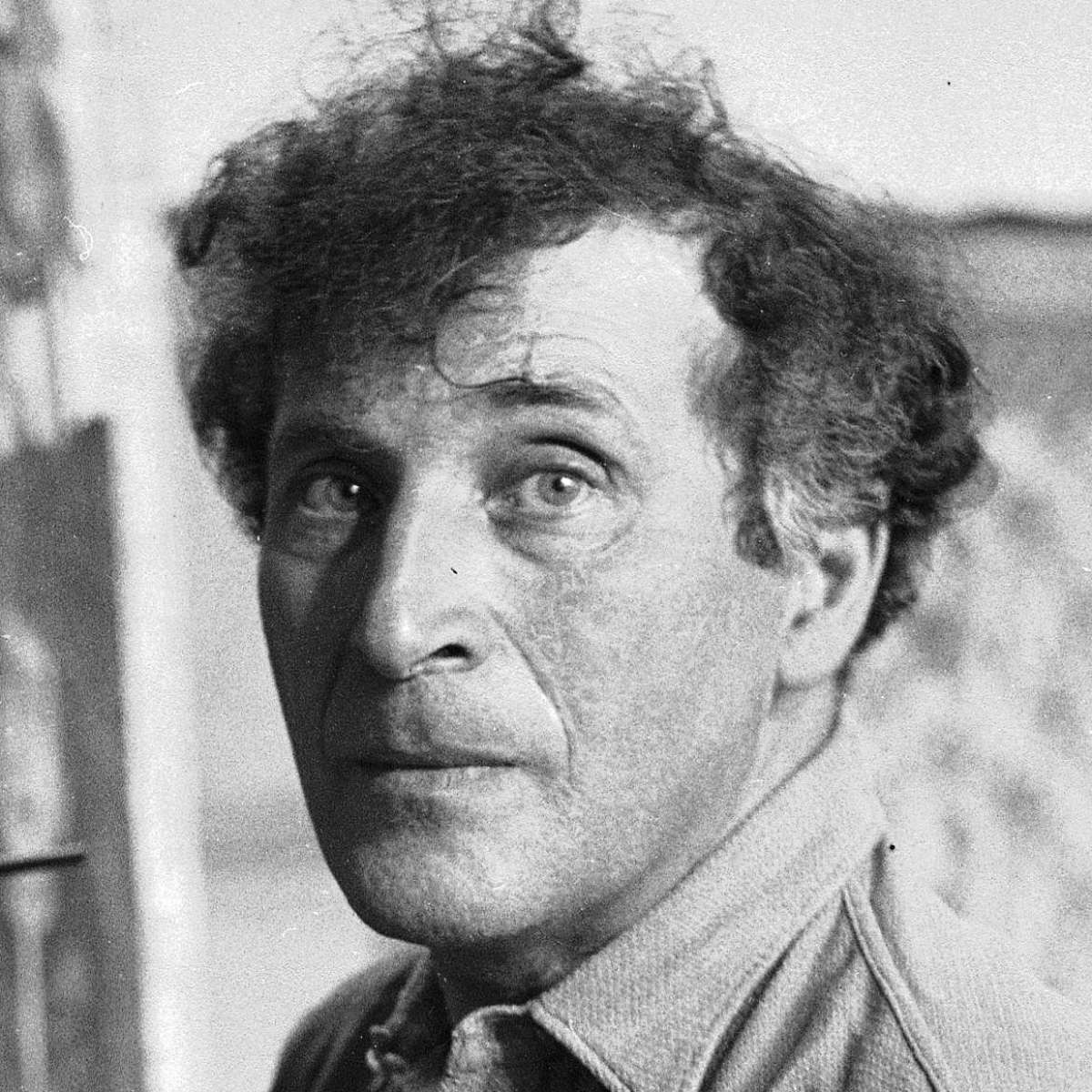




Marc Chagall (Russian: Марк Заха́рович Шага́л), born Moishe Shagal in 1887 near Vitebsk, Belarus (then part of the Russian Empire), was a Belarusian and French artist celebrated for his pivotal role in the avant-garde movement and his unique integration of Eastern European Jewish culture into modern art. His contributions spanned several artistic formats including painting, stained glass, stage sets, ceramics, tapestries, and fine art prints. Chagall's early modernist tendencies were enriched by his experiences across Saint Petersburg, Paris, and Berlin before World War I, leading to a distinctive style that melded Cubism, Symbolism, and Fauvism with his Jewish heritage.
Chagall's work is recognized for its emotional depth, often exploring themes of love, memory, and Jewish folklore through vibrant colors and dreamlike imagery. Notably, art critic Robert Hughes described him as "the quintessential Jewish artist of the twentieth century," a sentiment echoed by art historian Michael J. Lewis who regarded Chagall as a significant figure within European modernism and as the world's preeminent Jewish artist of his time.
Among Chagall's famed contributions are his stained-glass windows for the cathedrals of Reims and Metz, the UN, and the Jerusalem Windows in Israel. His monumental paintings include parts of the ceiling of the Paris Opéra and works that explore biblical themes, a hallmark of his oeuvre that underscores his enduring engagement with spiritual and religious motifs.
For art collectors and antiques experts, Chagall's works are notable not only for their artistic innovation but also for their rich cultural and historical significance. His art is housed in many prestigious museums worldwide, including the Marc Chagall National Museum in Nice, France, which focuses on his works inspired by religion and houses the series of paintings illustrating the biblical message.
For those interested in exploring Chagall's legacy and the vibrant intersection of culture, art, and history his work represents, signing up for updates on new product sales and auction events related to Marc Chagall can provide invaluable insights and opportunities. This is an invitation to engage more deeply with the world of art and culture that Chagall so uniquely encapsulated in his work.









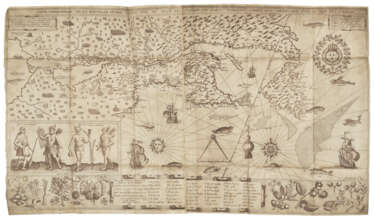
![DU BARTAS, Guillaume de Saluste (1544-1590). Les Œuvres de G. de Saluste seigneur Du Bartas Reveues et augmentees par l’auteur. S.l. [Genève] : Guillaume de Laimarie pour Jacques Chouet, 1582. [relié avec] La Sepmaine, ou creation du monde, de G](/assets/image/picture_1320933/25255/a05b47b738ff75226095f9a04d7527fb1616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![DU BARTAS, Guillaume de Saluste (1544-1590). Les Œuvres de G. de Saluste seigneur Du Bartas Reveues et augmentees par l’auteur. S.l. [Genève] : Guillaume de Laimarie pour Jacques Chouet, 1582. [relié avec] La Sepmaine, ou creation du monde, de G](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_1320933/25255/a05b47b738ff75226095f9a04d7527fb1616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)

























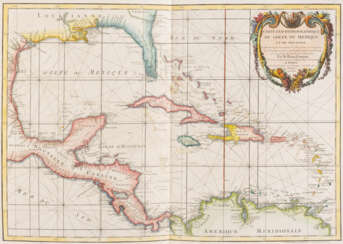
![[CABINET DU ROI]](/assets/image/picture_3566952/29da4/fb231fa3112a5ab8e44a4c50ebdcaa131700607600jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[CABINET DU ROI]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3566952/29da4/fb231fa3112a5ab8e44a4c50ebdcaa131700607600jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
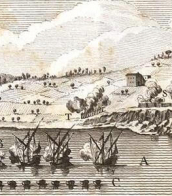
















![Charles Le Brun | Grand escalier du chateau de Versailles. Paris, [1725], from the library of the Duchesse de Berry](/assets/image/picture_3553008/ec9f0/uetj65gqqo2ruc9jwwadbwuz3io4pimo93nkrxgxopcbddyau3e7vp6zhjxxem1699092113jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Charles Le Brun | Grand escalier du chateau de Versailles. Paris, [1725], from the library of the Duchesse de Berry](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3553008/ec9f0/uetj65gqqo2ruc9jwwadbwuz3io4pimo93nkrxgxopcbddyau3e7vp6zhjxxem1699092113jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Low Countries | Le grand théâtre profane du duché de Brabant [bound uniformly with] Le grand théâtre sacré du duché de Brabant, The Hague, 1730, 1734](/assets/image/picture_3553024/e511c/3pxzidpqncdewbfvj6izl9ztdbwxrlcszxo02ukckkfm1ip-iuwlupupyz-plx-1699092718jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Low Countries | Le grand théâtre profane du duché de Brabant [bound uniformly with] Le grand théâtre sacré du duché de Brabant, The Hague, 1730, 1734](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3553024/e511c/3pxzidpqncdewbfvj6izl9ztdbwxrlcszxo02ukckkfm1ip-iuwlupupyz-plx-1699092718jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)







