important russian art
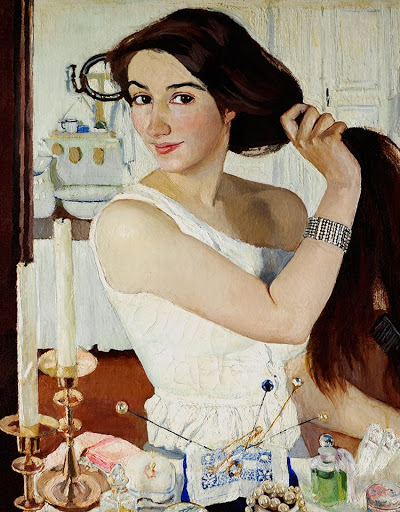

Zinaida Yevgenyevna Serebriakova (Russian: Зинаида Евгеньевна Серебрякова) was a Russian painter known for her lifelike portraits and depictions of rural life, which resonate with warmth and a profound sense of humanity. Born into the distinguished Benois family in 1884, her early life was immersed in art, guided by notable figures like her grandfather, Alexandre Benois, and influenced by her study trips to Italy and under the mentorship of Ilya Repin and Osip Braz. Her marriage to Boris Serebriakov further enriched her artistic environment, enabling her to produce works that captured the simple joys and the intrinsic beauty of her surroundings.
Serebriakova's art gained significant attention with her self-portrait "At the Dressing-Table" (1909) and continued with notable works like "Peasants" (1914–1915) and "Bleaching Cloth" (1917), highlighting her exceptional skill in portraying the Russian countryside and its inhabitants with a blend of grandeur and intimacy. Her ability to imbue her canvases with the spirit of her subjects, whether through the dignified depictions of peasant life or the intimate portrayals of her family, set her apart in the Russian art scene of the early 20th century.
The October Revolution of 1917 marked a turning point in Serebriakova's life, leading to personal tragedies and a shift in her artistic medium due to financial constraints. Despite these challenges, her resilience and dedication to art remained steadfast, evident in her works from this period that include poignant family portraits and explorations of new subjects in the realm of theatre and ballet.
In 1924, Serebriakova moved to Paris, where her art evolved through influences from travels, notably her trips to Morocco, capturing the vibrancy of landscapes and local cultures. Yet, the essence of her work—characterized by a celebration of beauty and life—remained consistent throughout her career. Although separated from her homeland for many years, the recognition of her art in the Soviet Union before her death in 1967 affirmed her lasting impact on Russian and French art.
Zinaida Serebriakova's legacy is a testament to her indomitable spirit and artistic prowess, making her one of the most cherished painters of her time. Her works continue to be celebrated for their technical brilliance, emotional depth, and the unique perspective she offered on the beauty of everyday life.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Serebriakova's works offer a window into the soul of early 20th-century Russia and France, embodying the universal themes of family, work, and the natural world with unparalleled sensitivity and grace. To stay updated on sales and auction events featuring Zinaida Yevgenyevna Serebriakova's works, signing up for updates is a step toward owning a piece of this exceptional artistic legacy.
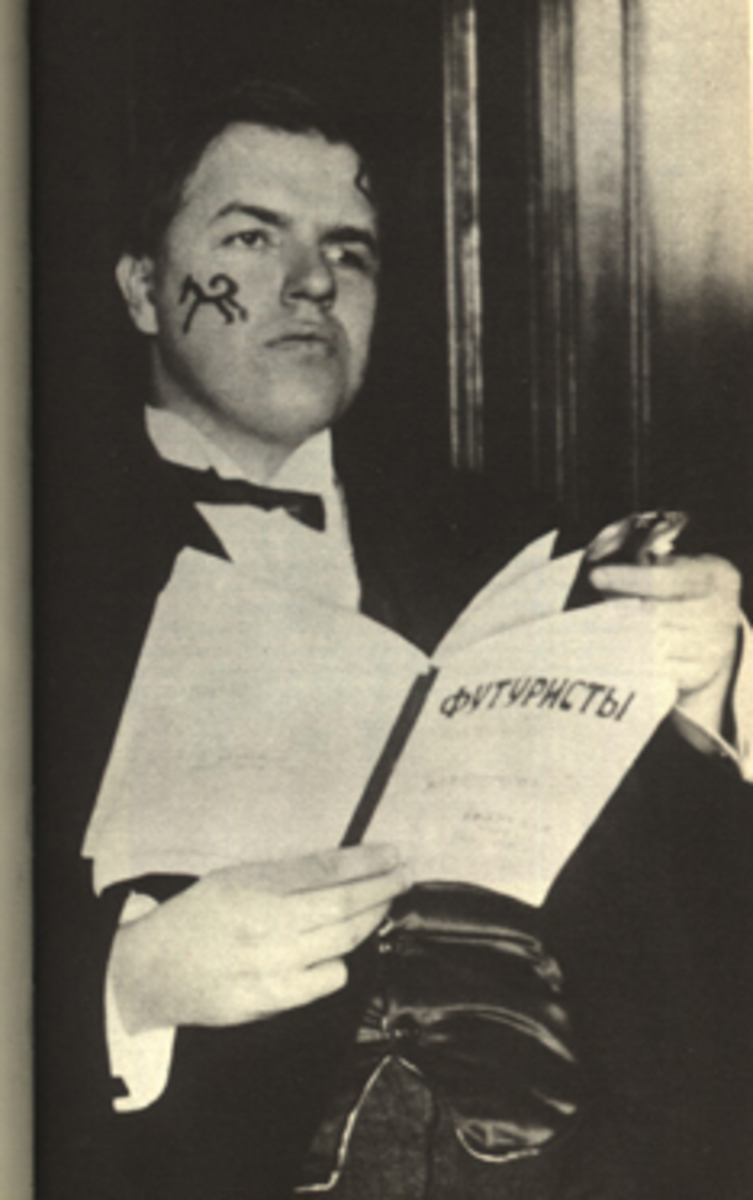


David Davidovich Burliuk (Russian: Давид Давидович Бурлюк), a pioneering figure of the Russian Futurist movement, was a Ukrainian poet, artist, and publicist, born in 1882 in Semirotovshchina, Kharkov, Ukraine, and died in 1967 on Long Island, N.Y., U.S. Known for his eclectic contributions that spanned poetry, painting, criticism, and publishing, Burliuk's work was instrumental in introducing the Russian avant-garde to Europe and the United States. Despite having a lesser volume of work in poetry and painting compared to his contemporaries, Burliuk's knack for discovering talent and promoting it was unparalleled. He was among the first to publish the works of Velimir Khlebnikov and to recognize the genius of Vladimir Mayakovsky, significantly contributing to their renown.
Burliuk's artistic journey was marked by his involvement with the Futurist and Neo-Primitivist movements. His early work, including an exhibition with the group Zveno ("The Link") in Kiev in 1908 and his participation in the Hylaea group, set the stage for his later achievements. He was a co-author of the influential Futurist manifesto "A Slap in the Face of Public Taste" in 1912, advocating for a break from traditional art forms and the embrace of modernity. Burliuk's commitment to Futurism was evident in his publishing endeavors and his collaborations with notable artists of the time.
In his later years, after emigrating to the United States in 1922, Burliuk continued to engage with the art world, contributing to pro-Soviet groups and publishing his works and those of his contemporaries. His efforts were recognized in several exhibitions, including a significant show at the Brooklyn Museum's 1926 International Exhibition of Modern Art. Despite facing challenges, such as being denied permission to visit his homeland by the Soviet government, Burliuk's influence remained steadfast. His legacy as a central figure in Russian Futurism and his contributions to the broader art movement are celebrated to this day.
To stay informed about updates and events related to David Davidovich Burliuk, including sales of his works and auction events, sign up for our newsletter. This subscription will ensure you're the first to know about new discoveries and opportunities to engage with Burliuk's enduring legacy.
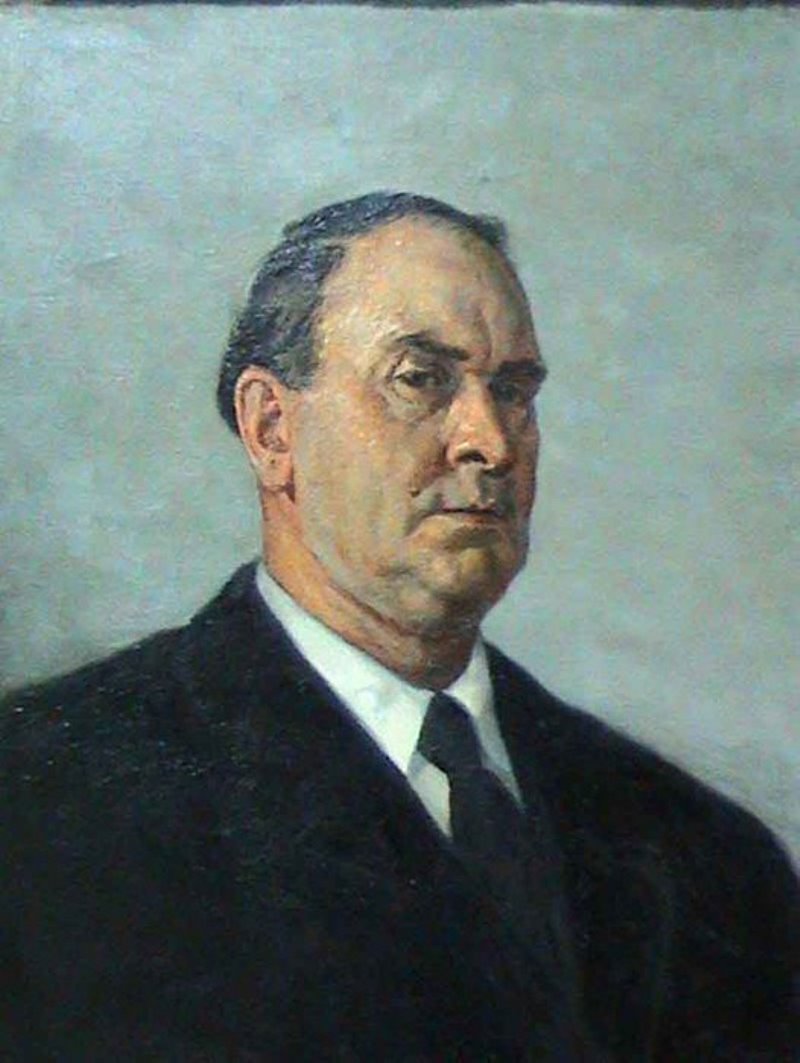


Pavel Petrovich Sokolov-Skala (Russian: Павел Петрович Соколов-Скаля) was a prominent Russian artist, celebrated for his contributions to Soviet art and culture. Born in 1899, Sokolov-Skala's artistic journey was marked by his affiliation with the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, reflecting the political landscape of his time through his work. His legacy includes receiving prestigious awards like the Stalin Prize and the Medal "For Valiant Labour in the Great Patriotic War 1941–1945", acknowledging his influence and contribution to Russian art and history.
Sokolov-Skala's oeuvre is notable for its diversity, ranging from monumental historical paintings to poignant war posters, demonstrating his versatility and mastery across different mediums. His works, such as "The Clear Glade" and "A Heroic Deed of Captain Gastello," are celebrated for their powerful portrayal of Soviet themes, capturing the spirit and challenges of his era. These pieces not only underscore Sokolov-Skala's artistic prowess but also his commitment to depicting the Soviet Union's ideals and narratives.
His paintings and posters, often characterized by their bold use of color and dramatic compositions, provide insight into the socio-political context of the 20th century Soviet Union, making him a key figure in Russian art history. Despite his significant role, Sokolov-Skala's work invites audiences to explore the nuanced intersections of art, politics, and history, offering a complex portrait of Soviet life.
Collectors and experts in art and antiques have continuously shown interest in Sokolov-Skala's works, highlighting their historical value and artistic merit. His contributions remain a focal point of study and appreciation within both Russian and international art circles.
For enthusiasts looking to delve deeper into the world of Pavel Petrovich Sokolov-Skala or to add a piece of his legacy to their collection, signing up for updates can provide exclusive access to new product sales and auction events featuring his work. This is a unique opportunity to engage with the rich history and profound impact of Sokolov-Skala's art on contemporary culture.
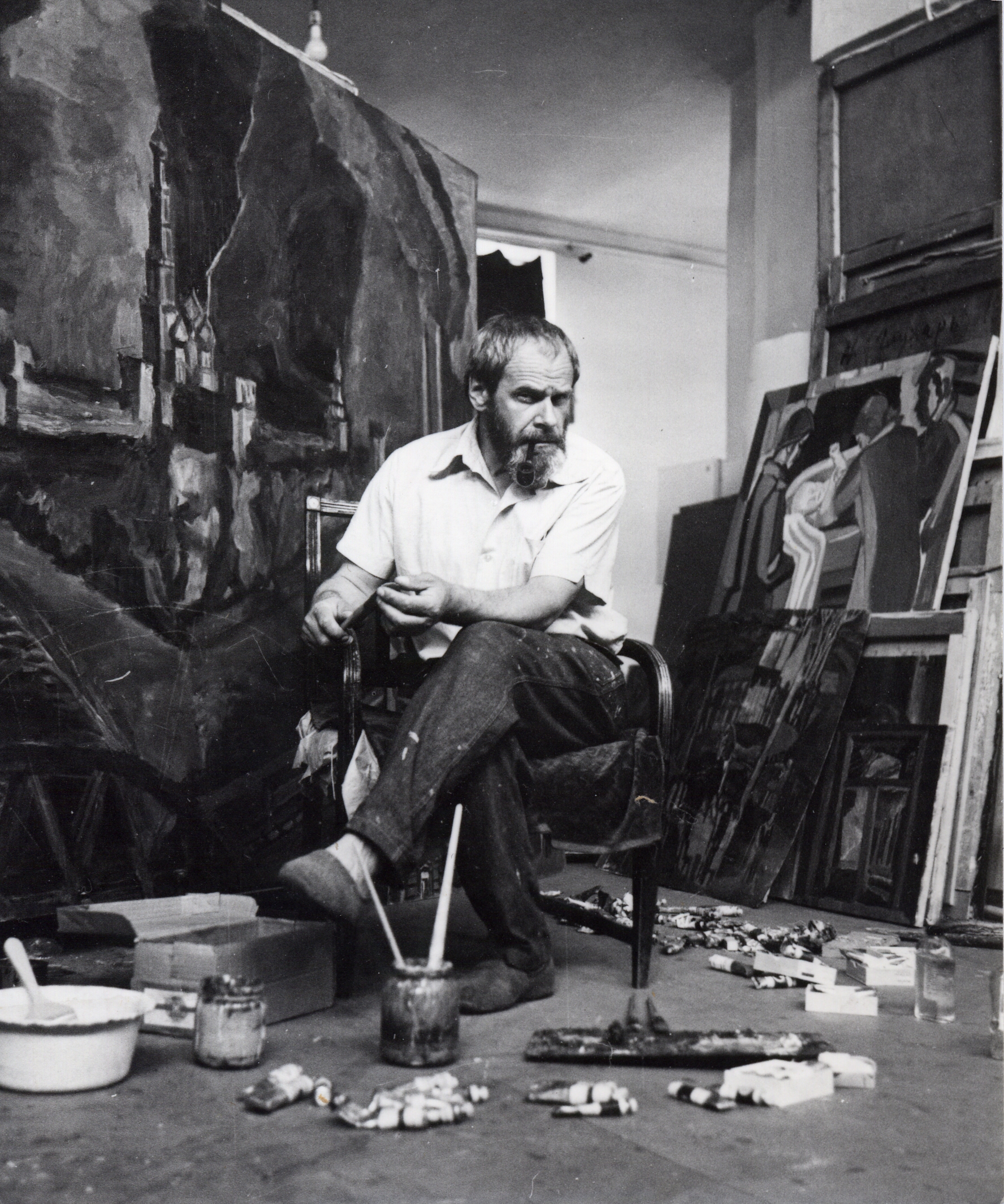


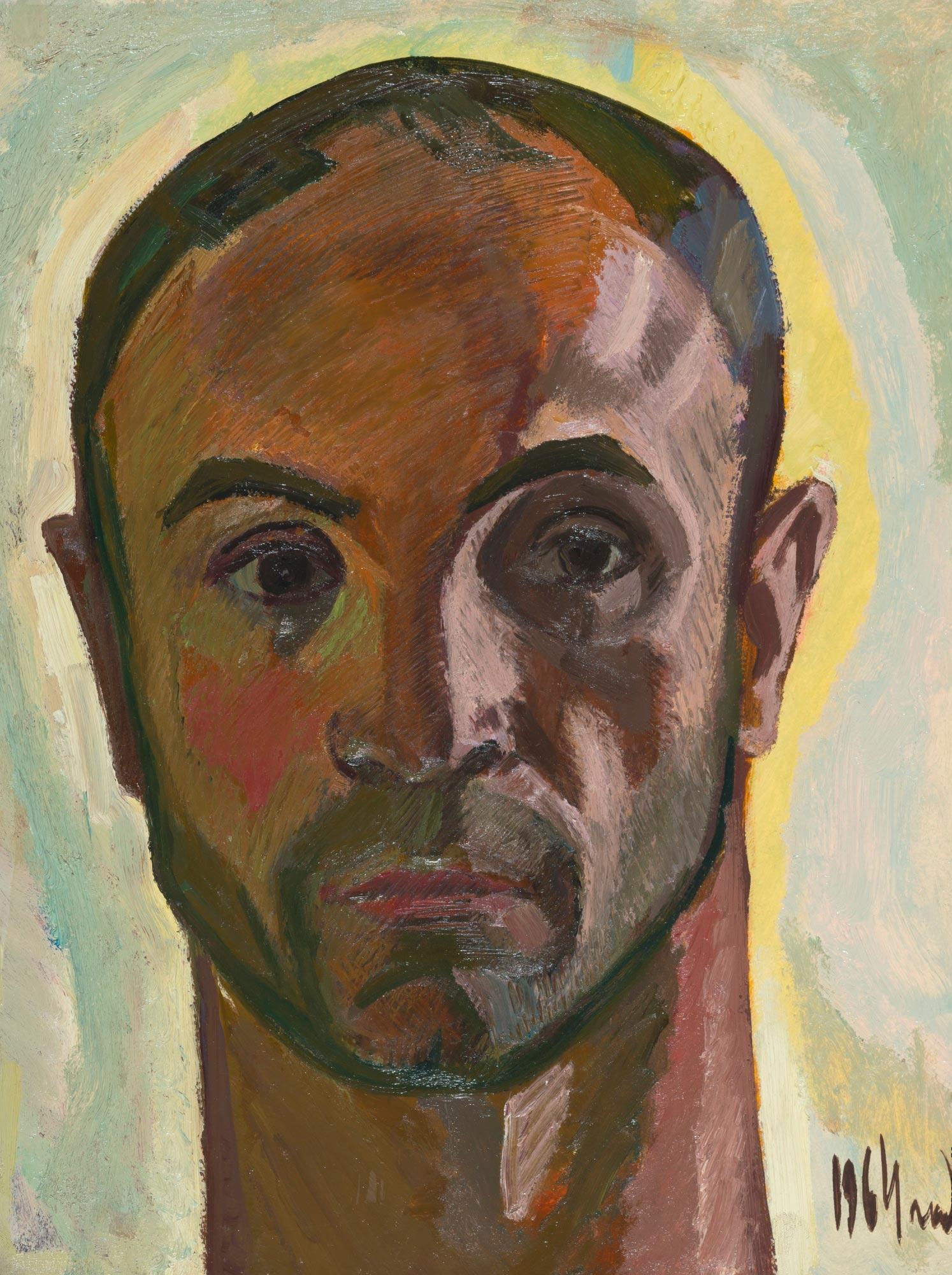
Nikolai Ivanovich Andronov (Russian: Николай Иванович Андронов) was a Soviet artist of the second half of the twentieth century. He is known as a painter, muralist and teacher, considered one of the founders of the "severe style" in the art of the USSR.
Nikolai Andronov actively worked to liberalize the Soviet art scene. At the beginning of his career, he created thematic paintings, later focusing on landscapes. The artist was also involved in the decoration of buildings, including the clubhouse of the Soviet Embassy in the United States, the Paveletsky Railway Station and subway stations in Moscow. From 1992, he taught at the Surikov Moscow Art Institute and headed the composition department.
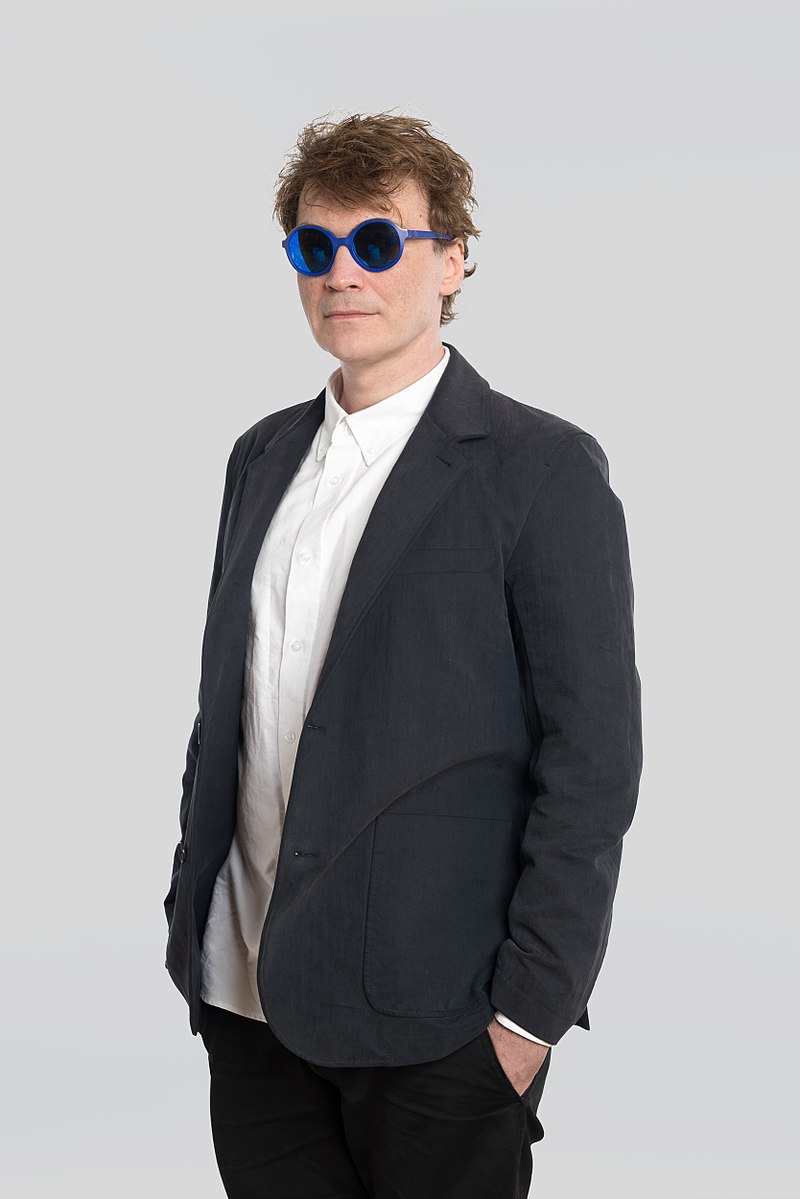


Pavel Vitalievich Pepperstein (birth name Pivovarov) is a Russian writer, artist, contemporary art theorist and one of the founders of the art group Inspection Medical Hermeneutics.
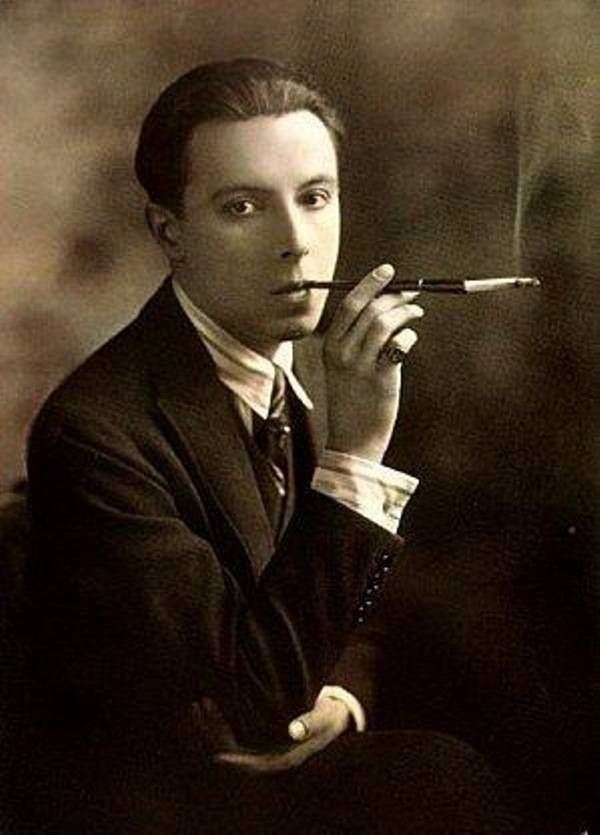


Roman Petrovich Tirtoff, pseudonym Erté, was a Russian-born artist, graphic artist, illustrator, stage designer, fashion designer and sculptor of the Art Deco era who worked in Paris and Hollywood. His pseudonym, which he took "so as not to disgrace his family", was made up of the first letters of his first and last name.
Herthe is best known for his elegant fashion illustrations, costume designs and set designs for the theatre.
Erte's work was not limited to the realm of fashion and theatre. He created jewellery, perfume bottles, furniture and furnishings, infusing them with his unique sense of style and elegance. His work often utilised elements of Egyptian, Byzantine and Oriental art, combining historical traditions with contemporary aesthetics


Roman Petrovich Tirtoff, pseudonym Erté, was a Russian-born artist, graphic artist, illustrator, stage designer, fashion designer and sculptor of the Art Deco era who worked in Paris and Hollywood. His pseudonym, which he took "so as not to disgrace his family", was made up of the first letters of his first and last name.
Herthe is best known for his elegant fashion illustrations, costume designs and set designs for the theatre.
Erte's work was not limited to the realm of fashion and theatre. He created jewellery, perfume bottles, furniture and furnishings, infusing them with his unique sense of style and elegance. His work often utilised elements of Egyptian, Byzantine and Oriental art, combining historical traditions with contemporary aesthetics


Roman Petrovich Tirtoff, pseudonym Erté, was a Russian-born artist, graphic artist, illustrator, stage designer, fashion designer and sculptor of the Art Deco era who worked in Paris and Hollywood. His pseudonym, which he took "so as not to disgrace his family", was made up of the first letters of his first and last name.
Herthe is best known for his elegant fashion illustrations, costume designs and set designs for the theatre.
Erte's work was not limited to the realm of fashion and theatre. He created jewellery, perfume bottles, furniture and furnishings, infusing them with his unique sense of style and elegance. His work often utilised elements of Egyptian, Byzantine and Oriental art, combining historical traditions with contemporary aesthetics


Roman Petrovich Tirtoff, pseudonym Erté, was a Russian-born artist, graphic artist, illustrator, stage designer, fashion designer and sculptor of the Art Deco era who worked in Paris and Hollywood. His pseudonym, which he took "so as not to disgrace his family", was made up of the first letters of his first and last name.
Herthe is best known for his elegant fashion illustrations, costume designs and set designs for the theatre.
Erte's work was not limited to the realm of fashion and theatre. He created jewellery, perfume bottles, furniture and furnishings, infusing them with his unique sense of style and elegance. His work often utilised elements of Egyptian, Byzantine and Oriental art, combining historical traditions with contemporary aesthetics


Roman Petrovich Tirtoff, pseudonym Erté, was a Russian-born artist, graphic artist, illustrator, stage designer, fashion designer and sculptor of the Art Deco era who worked in Paris and Hollywood. His pseudonym, which he took "so as not to disgrace his family", was made up of the first letters of his first and last name.
Herthe is best known for his elegant fashion illustrations, costume designs and set designs for the theatre.
Erte's work was not limited to the realm of fashion and theatre. He created jewellery, perfume bottles, furniture and furnishings, infusing them with his unique sense of style and elegance. His work often utilised elements of Egyptian, Byzantine and Oriental art, combining historical traditions with contemporary aesthetics


Ivan Pavlovich Pokhitonov (Russian: Иван Павлович Похитонов) was a Russian artist of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. He is known as a painter and graphic artist, a master of landscape, who lived and worked in Europe for much of his career.
Ivan Pokhitonov created mainly miniature landscapes, made with a small brush on planks of red or lemon wood, treated and primed with a special technology. He worked mostly in plein air. The most common motif of his miniature paintings during the years of emigration were city and seascapes of France. In his works, always built on a combination of the finest shades of color, the artist organically combined the techniques of Barbizon, of which he was a fan, and the traditions of the Russian landscape school. He also turned to the genre of still life and portraiture.



Vasily Dmitrievich Polenov (Russian: Васи́лий Дми́триевич Поле́нов) was a distinguished Russian painter, celebrated for his contribution to landscape and historical painting. Born into an enlightened family in St. Petersburg in 1844, Polenov's artistic journey was nurtured by both his heritage and formal education at the Imperial Academy of Arts. His mastery in capturing the serene beauty of the Russian countryside and his innovative approach to biblical themes have cemented his place in the annals of art history.
Polenov's artistry was marked by his pioneering use of plein air painting, a technique that brought a fresh vibrancy and realism to his landscapes. Works such as "Moscow Courtyard" (1878) and "Overgrown Pond" (1879) not only showcase his technical prowess but also reflect his profound connection to Russian rural life and nature. His depiction of biblical scenes, notably in "Christ and the Sinner" (1886–87), broke new ground by intertwining these sacred stories with his love for landscapes, imbuing them with a unique sense of place and time.
A notable period in Polenov's career was his travels in Europe, where encounters with artists and cultures deeply influenced his work. Despite these influences, it was his Russian vistas that garnered the most acclaim, demonstrating his ability to infuse landscapes with a deeply personal and nationalistic sentiment. His commitment to art was intertwined with his belief in its power to evoke happiness and joy, a philosophy that guided his teaching career at the Moscow School of Painting, Sculpture and Architecture, where he mentored future luminaries of Russian art.
Polenov's legacy extends beyond his paintings. His estate, Polenovo, near Tarusa, has been transformed into a national art museum, ensuring that his contributions to Russian art and culture continue to inspire future generations. This dedication to the arts was recognized by his appointment as a People's Artist of the USSR in 1926, a testament to his enduring impact on the cultural landscape.
For art collectors and experts, Polenov's work represents not just aesthetic beauty but a rich narrative of Russia's cultural and natural heritage. His paintings, held in prestigious galleries like the State Tretyakov Gallery and the State Russian Museum, offer a window into the soul of Russian art, marked by a quest for harmony and a deep reverence for the natural world.
For those interested in exploring the works and legacy of Vasily Dmitrievich Polenov further, signing up for updates on new product sales and auction events related to his art can provide valuable insights into his enduring influence. This subscription is an opportunity to stay connected with the world of one of Russia's most beloved artists, ensuring access to the latest offerings and scholarly research surrounding his oeuvre.
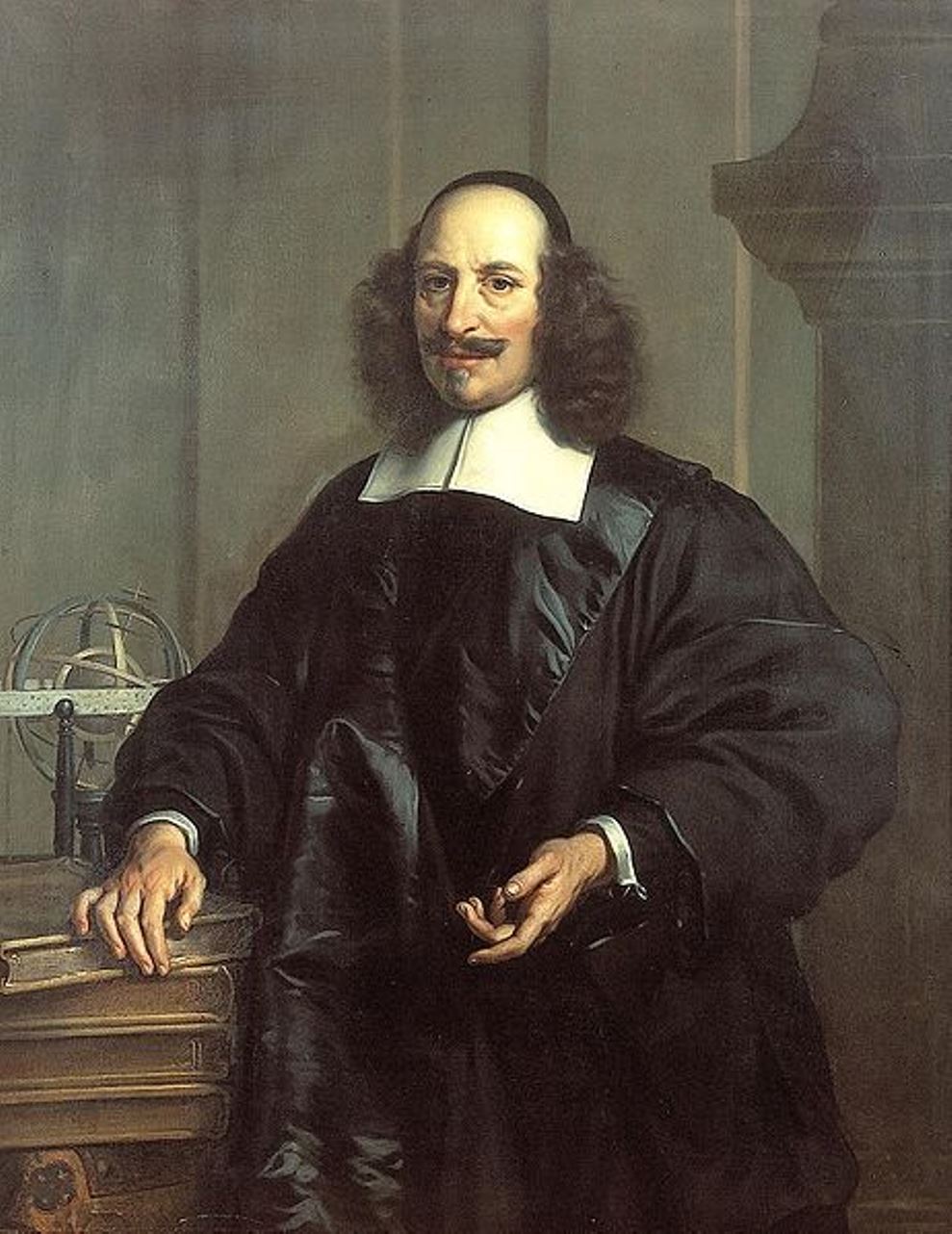


Jan (Joan) Willemsz. Blaeu was a Dutch cartographer, publisher and judge.
Jan was born into the family of the cartographer and publisher Willem Janszoon Blaeu (1571-1638). He studied in Leiden, where he earned a doctorate in law, and in Padua. He then began to assist his father, who was engaged in the manufacture of globes and maps. After his father's death, Jan, together with his brother Cornelius, continued his work, and succeeded him as cartographer for the Dutch East India Company.
In 1651 Blaeu was elected to the Amsterdam city council and later appointed as a judge. At the same time, he was engaged in his publishing business: he continued to publish volumes of Atlas novus, which contained maps of English counties and, for the first time, an atlas of Scotland, as well as one volume of maps of the Far East.
Blaeu did not have time to complete his most ambitious project, but it made him famous as the author of the famous 11-volume Dutch atlas. Based on his previous maps, Blaeu created the Great Atlas (Atlas Maior) - it contained nearly 600 maps and a total of 3,000 pages of Latin text - and was published in 1662. Blaeu's maps were groundbreaking for their time because they were created in accordance with the heliocentric theories of Nicolaus Copernicus.
In 1672, a great fire in Amsterdam destroyed Blaeu's workshop, and the cartographer died a year later, apparently never recovering from this stroke of fate.
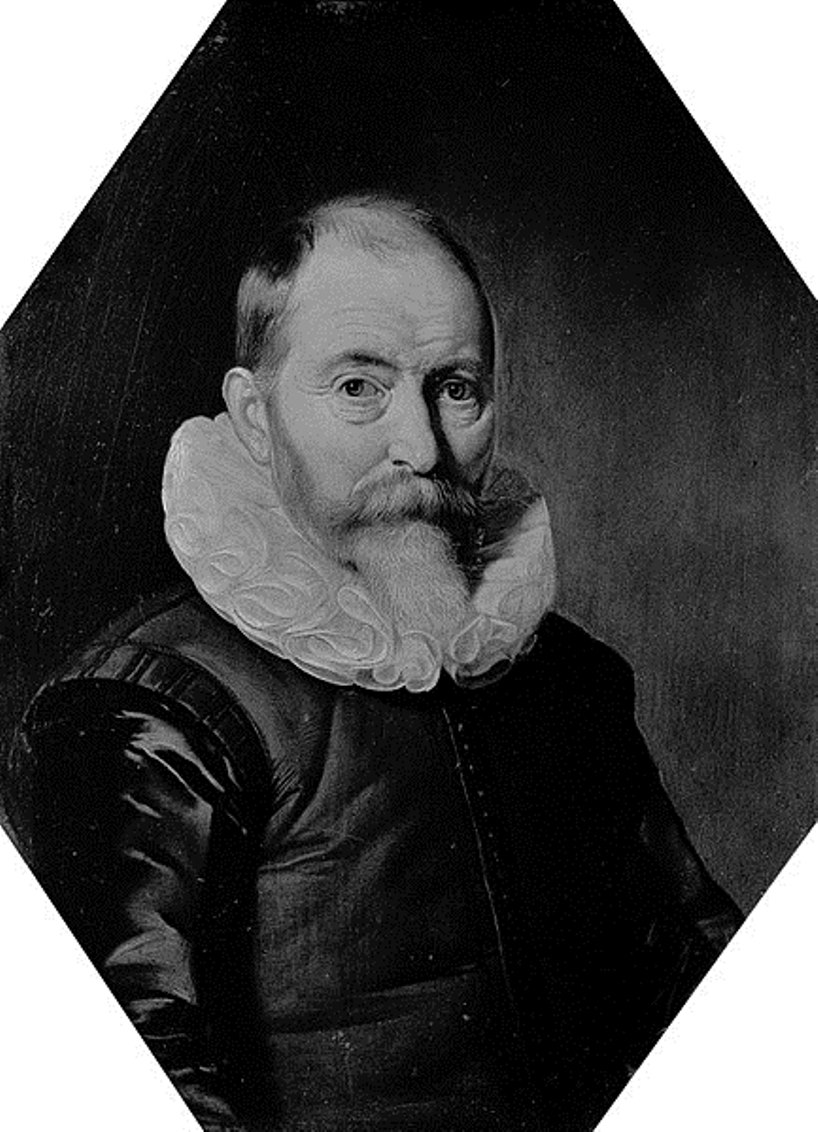

Willem Janszoon Blaeu was a Dutch cartographer and map publisher.
Willem studied astronomy and cartography under the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe and even discovered the variable star P Swan in 1600. A little later Blaeu settled in Amsterdam, where he began making globes and also began producing land and sea maps, including a 1605 world map. In 1629 he managed to acquire the printing plates of the cartographer Jodok Hondius, with which he published his own atlas.
In 1633, Willem Blaeu was appointed cartographer of the Dutch Republic, as well as the official cartographer of the Dutch East India Company. Blau built up a large collection of maps and conducted an extensive publishing business. After Willem's death, his sons Jan Blaeu (1596-1673) and Cornelius Blaeu successfully continued his work. But in 1672, during a fire in Amsterdam, Blaeu's workshop was destroyed, and the company founded by Willem Blaeu ceased to exist in 1698.