metaphysical art
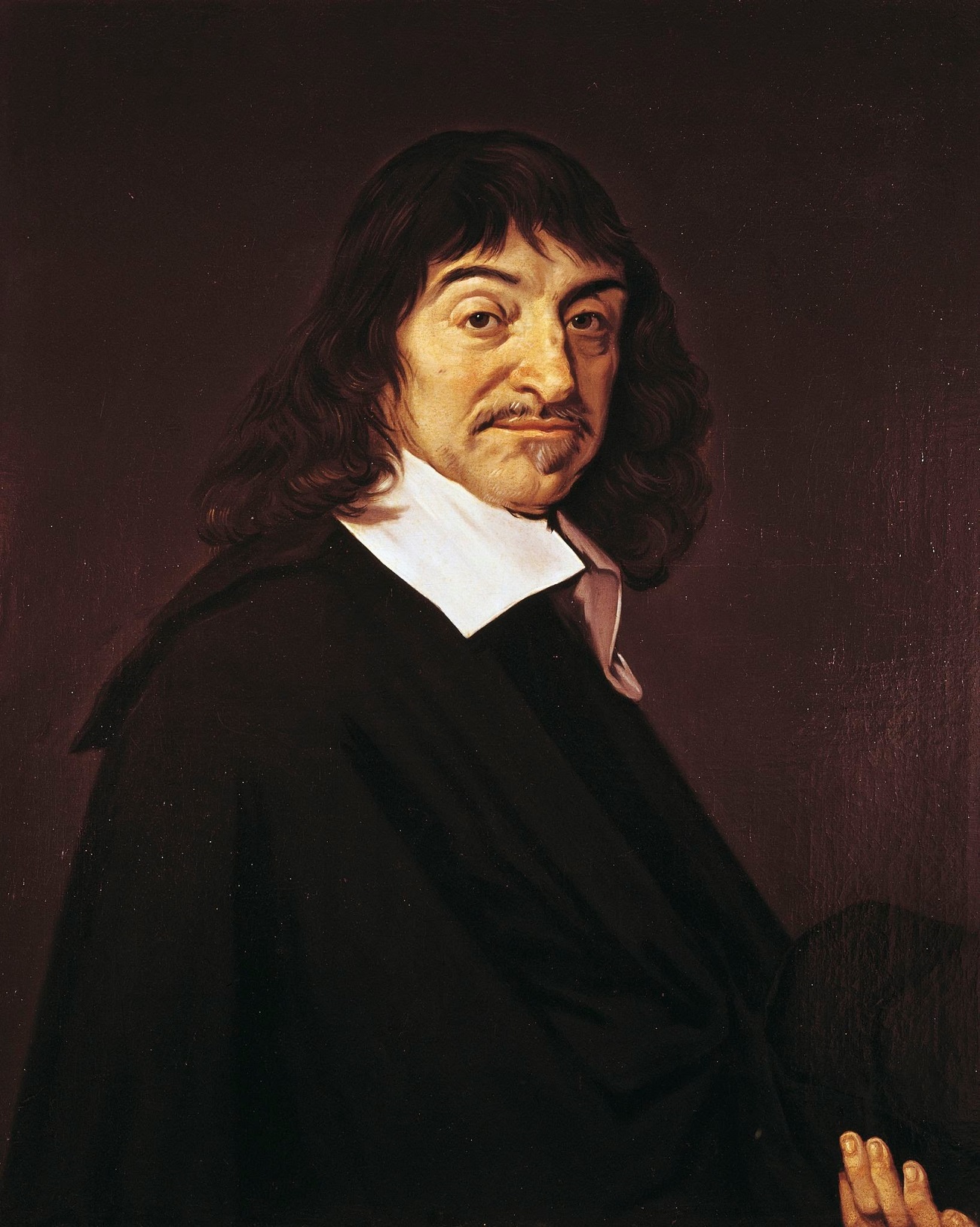

René Descartes was a French philosopher, mathematician, and natural scientist who is considered the founder of modern philosophy.
Descartes was a very versatile scientist: besides numerous philosophical reflections, he wrote works on optics, meteorology and geometry. Contemporaries noted his extensive knowledge in many sciences. Descartes owns the famous saying "I think, therefore I exist" (best known in the Latin formulation "Cogito, ergo sum", although it was originally written in French: "Je pense, donc je suis").
He developed a metaphysical dualism that radically distinguished between mind, whose essence is thought, and matter, whose essence is extension in three dimensions. Descartes' metaphysics is rationalistic, based on the postulation of innate ideas of mind, matter, and God, but his physics and physiology, based on sense experience, are mechanistic and empirical.
Unlike his scientific predecessors, who felt a holy awe at the incomprehensibility of the divine essence of the universe, Descartes admired the ability of the human mind to understand the cosmos and to generate happiness itself, and rejected the view that human beings were inherently unhappy and sinful. He believed that it was inappropriate to pray to God to change the state of things and the world; it was much more productive to change oneself.



Paul Nash was a British surrealist painter and war artist, as well as a photographer, writer and designer of applied art. Nash was among the most important landscape artists of the first half of the twentieth century. He played a key role in the development of Modernism in English art.


Athanasius Kircher was a German scholar, inventor, professor of mathematics and oriental studies, and a friar of the Jesuit order.
Kircher knew Greek and Hebrew, did scientific and humanities research in Germany, and was ordained in Mainz in 1628. During the Thirty Years' War he was forced to flee to Rome, where he remained for most of his life, serving as a kind of intellectual and information center for cultural and scientific information drawn not only from European sources but also from an extensive network of Jesuit missionaries. He was particularly interested in ancient Egypt and attempted to decipher hieroglyphics and other riddles. Kircher also compiled A Description of the Chinese Empire (1667), which was long one of the most influential books that shaped the European view of China.
A renowned polymath, Kircher conducted scholarly research in a variety of disciplines, including geography, astronomy, mathematics, languages, medicine, and music. He wrote some 44 books, and more than 2,000 of his manuscripts and letters have survived. He also assembled one of the first natural history collections.
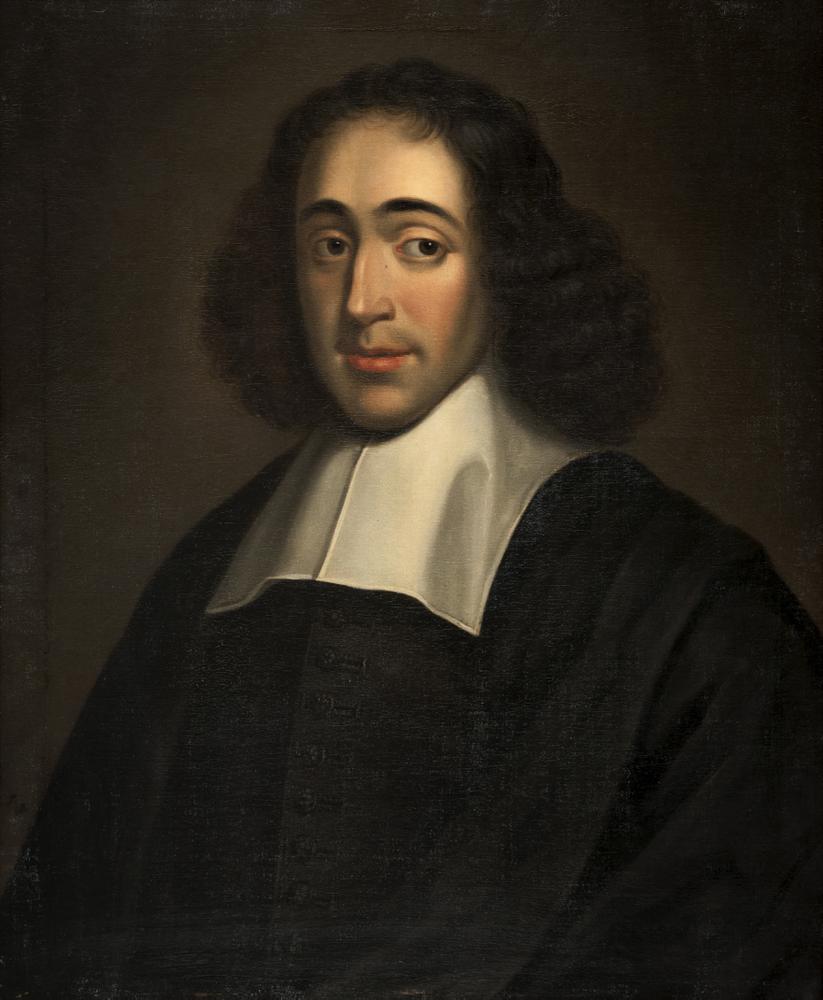


Benedictus Spinoza (Spanish: Baruj Espinosa) at birth Baruch Spinoza is a Dutch philosopher-rationalist of Jewish origin, a bright representative of the Age of Enlightenment.
Spinoza was born into a family of Portuguese Jews in Amsterdam, who converted to Christianity but returned to Judaism. As a young man, he was considered an outstanding Talmudic scholar and a promising religious scholar. But, inspired by the philosophical writings of René Descartes and Francis Bacon, the young philosopher soon fell outside the orthodox tradition because of his radical views. In 1656 he was severely excommunicated for heresy.
For the rest of his life, Spinoza spent his modest life grinding lenses and privately teaching philosophy, but he also wrote anonymously published philosophical treatises and secretly exchanged letters with many philosophically inclined luminaries of the wider European Enlightenment. Spinoza's only book, published in 1663 in Amsterdam under his own name, was Renati Des Cartes Principiorum Philosophiae Pars I, & II, More Geometrico demonstrate (Principles of Cartesian Philosophy). These principles served as a preparatory work for many metaphysical views in his most important treatise, Ethics (1677).
Benedict Spinoza defended the philosophical life from religious persecution and advocated a new, liberal, democratic regime to support that life. Although Spinoza was often persecuted as an atheist in his time, his writings played an important role in shaping philosophy, theology, and politics in the centuries to come. Of all the philosophers of the seventeenth century, Spinoza is one of the most relevant today.
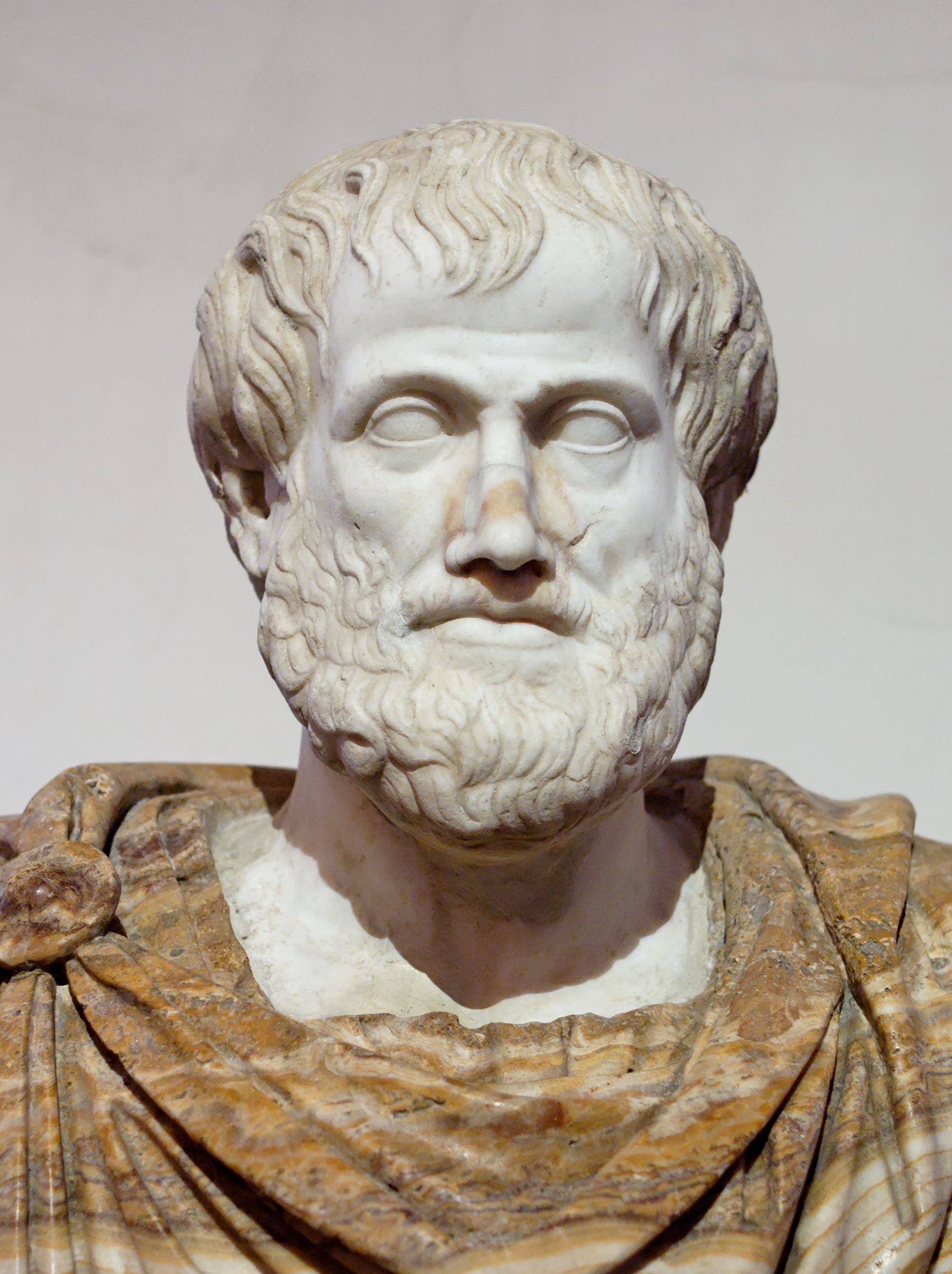


Aristotle (Greek: Ἀριστοτέλης) was an Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath, renowned for his profound impact on Western philosophy and science. Born in Stagira, Chalcidice, Aristotle's intellectual ventures spanned a multitude of subjects, including but not limited to physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology.
Educated in Plato's Academy in Athens, Aristotle distinguished himself as a scholar of vast knowledge and influence. His foundational works laid the groundwork for the development of modern science, while his teachings on logic and the syllogistic method continue to resonate in the realm of philosophy. As the tutor of Alexander the Great and the founder of the Lyceum in Athens, Aristotle's legacy extends beyond his prolific writings, with his teachings shaping medieval scholarship and influencing both Judeo-Islamic and Christian theologies.
Among Aristotle's notable works, his treatises such as "Nicomachean Ethics," "Politics," "Metaphysics," and "Poetics" have been studied for centuries. His concept of the "Golden Mean," advocating for a balanced and moderate approach to life, remains a cornerstone of ethical philosophy. His ideas on the "Prime Mover" and empirical evidence as a basis for understanding the world laid the foundation for scientific inquiry. Although only about a third of his original output has survived, Aristotle's contributions continue to be a subject of academic study and admiration.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, the philosophical and scientific principles of Aristotle's works are not just historical artifacts but living ideas that continue to shape our understanding of the world and our place within it. His insights into the "good life" and the pursuit of happiness are as relevant today as they were in ancient Greece.
If you wish to stay informed about new product sales and auction events related to Aristotle, sign up for updates. This subscription is your gateway to the latest scholarly works, collections, and auctions connected to the great philosopher's legacy.


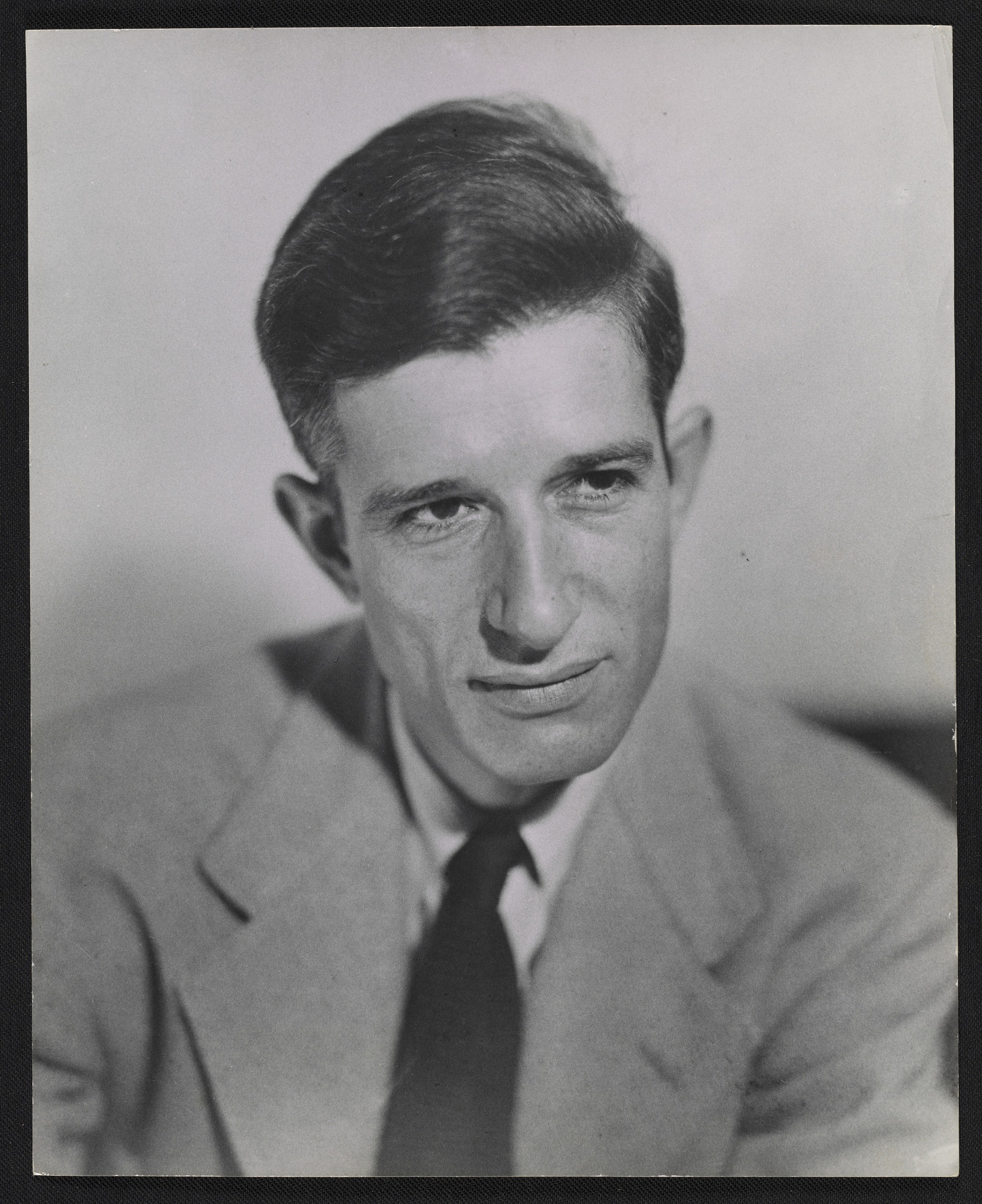
René Descartes was a French philosopher, mathematician, and natural scientist who is considered the founder of modern philosophy.
Descartes was a very versatile scientist: besides numerous philosophical reflections, he wrote works on optics, meteorology and geometry. Contemporaries noted his extensive knowledge in many sciences. Descartes owns the famous saying "I think, therefore I exist" (best known in the Latin formulation "Cogito, ergo sum", although it was originally written in French: "Je pense, donc je suis").
He developed a metaphysical dualism that radically distinguished between mind, whose essence is thought, and matter, whose essence is extension in three dimensions. Descartes' metaphysics is rationalistic, based on the postulation of innate ideas of mind, matter, and God, but his physics and physiology, based on sense experience, are mechanistic and empirical.
Unlike his scientific predecessors, who felt a holy awe at the incomprehensibility of the divine essence of the universe, Descartes admired the ability of the human mind to understand the cosmos and to generate happiness itself, and rejected the view that human beings were inherently unhappy and sinful. He believed that it was inappropriate to pray to God to change the state of things and the world; it was much more productive to change oneself.


René Descartes was a French philosopher, mathematician, and natural scientist who is considered the founder of modern philosophy.
Descartes was a very versatile scientist: besides numerous philosophical reflections, he wrote works on optics, meteorology and geometry. Contemporaries noted his extensive knowledge in many sciences. Descartes owns the famous saying "I think, therefore I exist" (best known in the Latin formulation "Cogito, ergo sum", although it was originally written in French: "Je pense, donc je suis").
He developed a metaphysical dualism that radically distinguished between mind, whose essence is thought, and matter, whose essence is extension in three dimensions. Descartes' metaphysics is rationalistic, based on the postulation of innate ideas of mind, matter, and God, but his physics and physiology, based on sense experience, are mechanistic and empirical.
Unlike his scientific predecessors, who felt a holy awe at the incomprehensibility of the divine essence of the universe, Descartes admired the ability of the human mind to understand the cosmos and to generate happiness itself, and rejected the view that human beings were inherently unhappy and sinful. He believed that it was inappropriate to pray to God to change the state of things and the world; it was much more productive to change oneself.
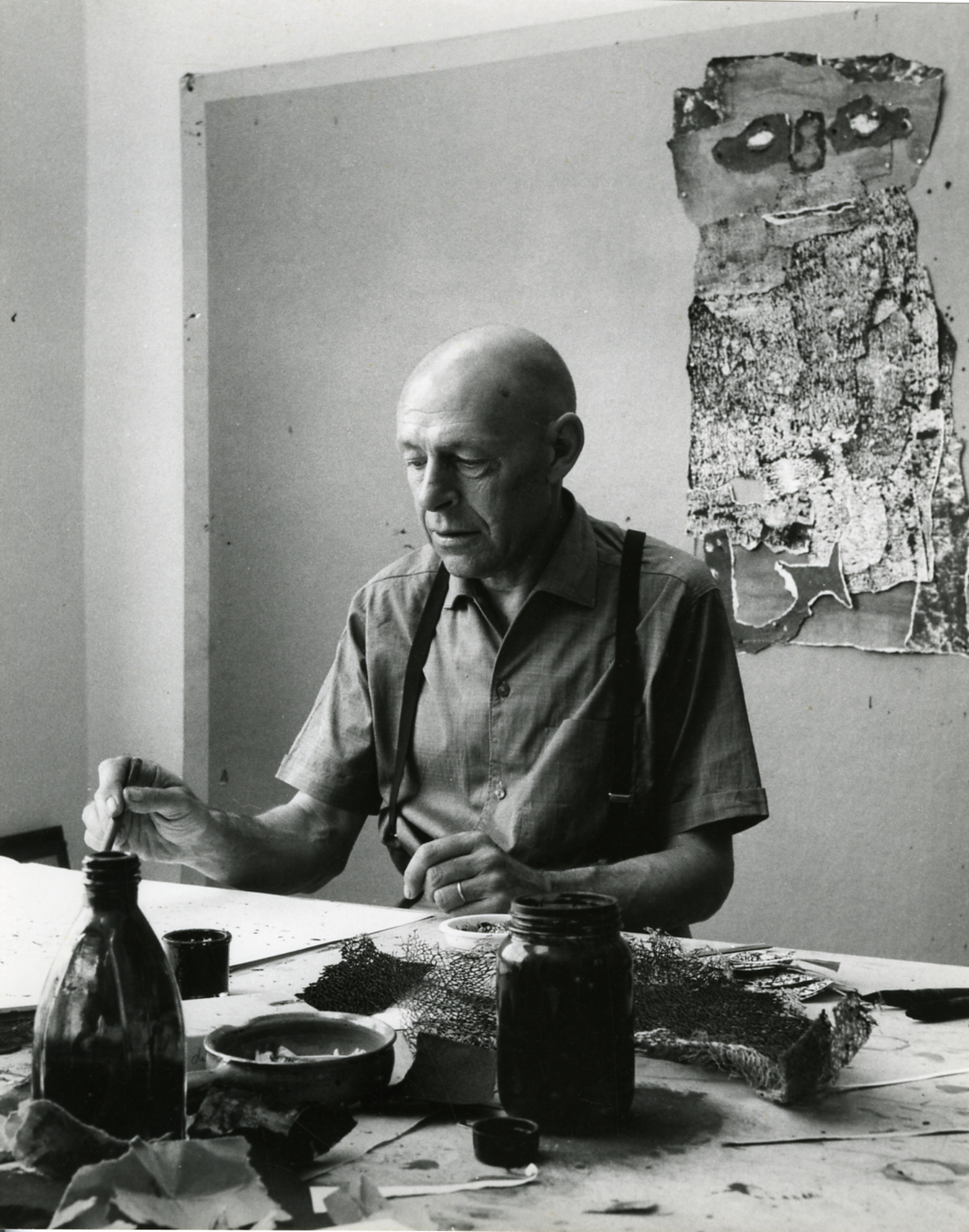


Jean Philippe Arthur Dubuffet, a pioneering French painter and sculptor, revolutionized the post-war art scene with his radical Matterism movement. He defied the conventional aesthetics of his time, championing "low art" and propelling a more genuine, humanistic image-making approach.
Dubuffet, born in Le Havre, France, in 1901, was a prominent figure at the Ecole de Paris and an advocate for Art Brut, or "raw art", which sought to capture art's purest form. His works were characterized by a rough, unrefined aesthetic, which eschewed academic norms in favor of spontaneity and authenticity.
Art enthusiasts and experts can view Dubuffet's innovative works at institutions like the Museum of Modern Art, where his legacy as a groundbreaking artist continues to be celebrated. His Matterism philosophy has left an indelible mark on the art world, inspiring generations of artists to embrace the beauty in the unconventional.
For those interested in the avant-garde and the legacy of Jean Philippe Arthur Dubuffet, sign up for our exclusive updates. This service is designed for connoisseurs and professionals in the art and antique sector, promising alerts on new insights and events strictly related to Dubuffet's profound influence.
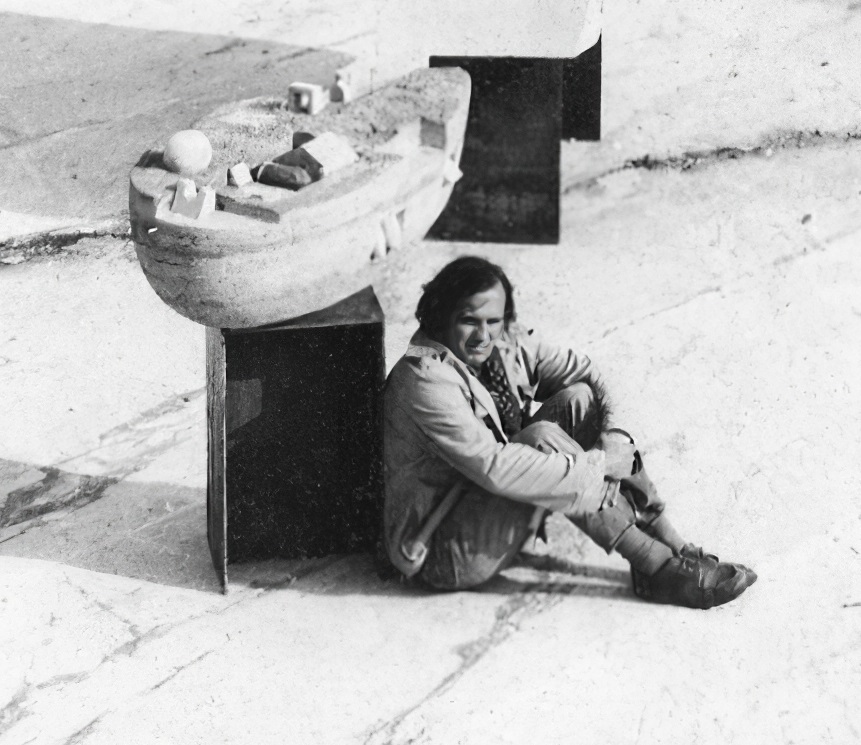


Gonzalo Fonseca was a Uruguayan artist known for his stone sculpting. He originally studied to be an architect at the University of Montevideo, but discovered modern art in 1942 after working in the Taller Torres-Garcia workshop. He studied painting in the workshop until 1949, and became interested in pre-Columbian art during that time. Fonseca is frequently associated with the movement Universal Constructivism.
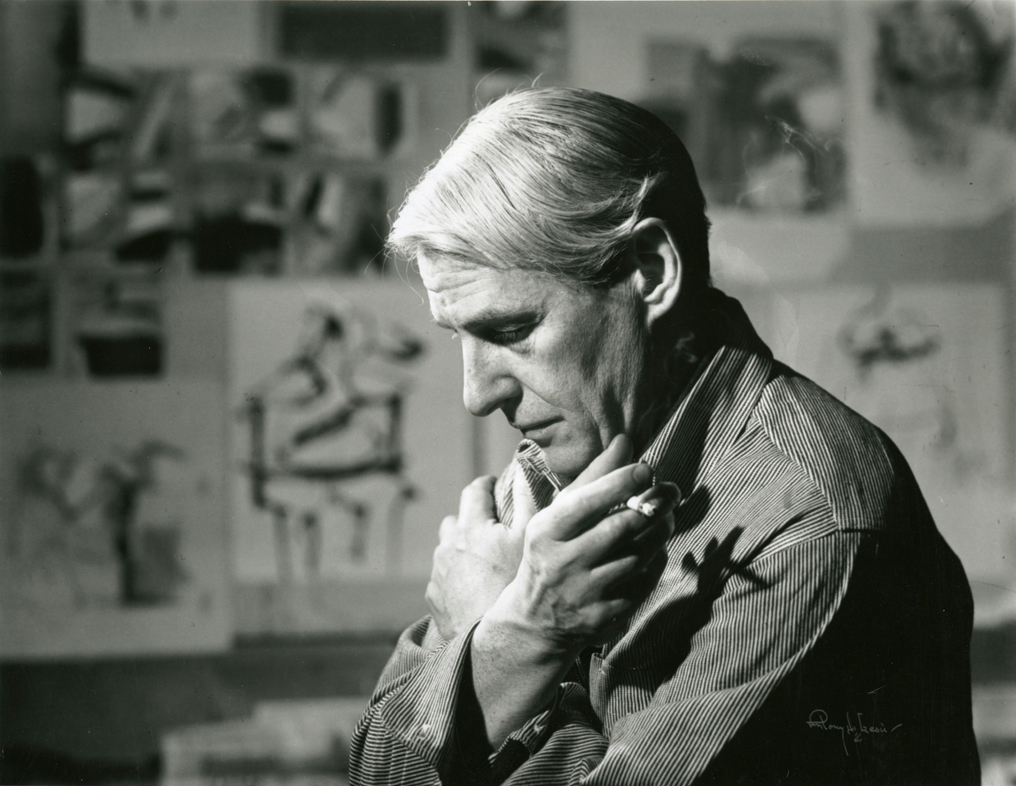


Willem de Kooning was a Dutch-American abstract expressionist painter. Born in Rotterdam, Netherlands, he moved to the United States in 1926, becoming a U.S. citizen in 1962. He was a leading figure in the Abstract Expressionism movement, known for his dramatic and often energetic style. He gained prominence between 1948 and 1953, creating some of his most iconic works, including the Woman series.
De Kooning's paintings combined abstraction with elements of Cubism, Surrealism, and Expressionism. His style evolved over time, with works that ranged from figurative to more abstract pieces. Among his most notable works are "Woman I" (1950-52) and "Excavation" (1950), which reflect his unique approach to painting, characterized by vigorous brushstrokes, bold colors, and complex textures.
Despite his success, de Kooning faced challenges, including personal struggles with alcoholism and deteriorating health due to Alzheimer's disease in his later years. His artwork has had a lasting impact on modern art, and his pieces can be found in major museums and galleries worldwide, such as the Museum of Modern Art (MoMA) and the Smithsonian American Art Museum.
Stay updated on new releases and auction events featuring works by Willem de Kooning by signing up for our exclusive email notifications. Get insider information and never miss a chance to add to your art collection.
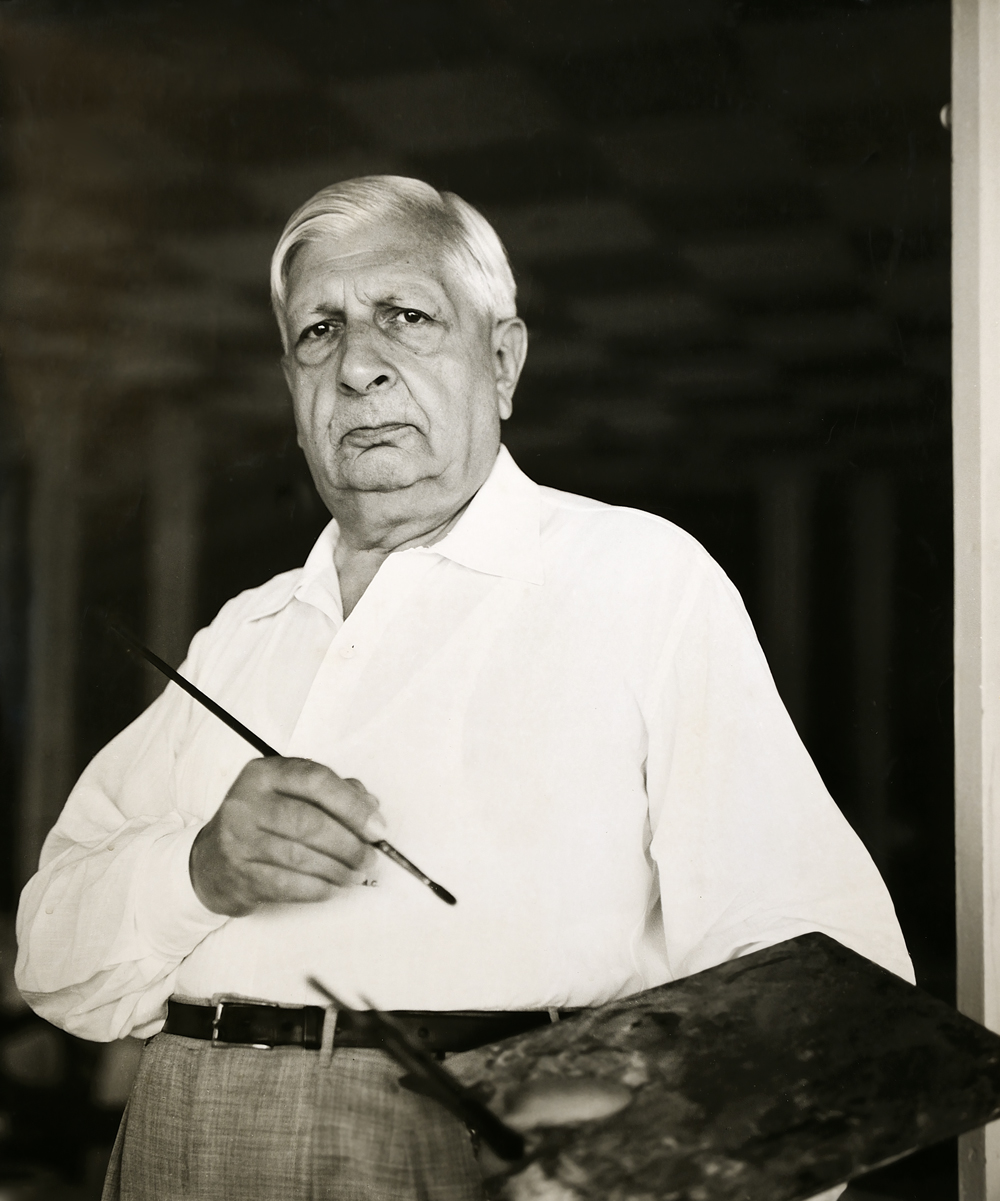


Giuseppe Maria Alberto Giorgio de Chirico, an Italian artist renowned for his profound influence on the Surrealist movement, stands as a seminal figure in 20th-century art. Born in Volos, Greece, in 1888, de Chirico was a visionary painter, sculptor, and writer whose works profoundly altered the landscape of modern art. His paintings, characterized by their dreamlike quality, enigmatic compositions, and the juxtaposition of classical and modern elements, delve into the mysteries of the subconscious, exploring themes of nostalgia, metaphysics, and the uncanny.
De Chirico's art is distinguished by its unique blend of classical motifs with surreal, dreamlike atmospheres, creating a sense of profound mystery and unease. His most famous works, such as "The Enigma of an Autumn Afternoon" and "The Melancholy of Departure," exhibit deserted cityscapes filled with elongated shadows, enigmatic figures, and classical architecture, which became hallmarks of his style. These paintings not only prefigured the Surrealist movement but also influenced countless artists with their exploration of the psyche, the distortion of space, and the play of light and shadow.
His impact on culture and art is undeniable, with his works housed in prestigious museums and galleries worldwide, including the Museum of Modern Art in New York and the Tate Modern in London. De Chirico's ability to evoke the mysterious interconnection between the ancient and the modern through his art continues to captivate collectors and experts in the fields of art and antiques. His innovative approach to painting and sculpture has solidified his position as a key figure in the development of modern art.
For collectors and enthusiasts keen on exploring the depths of 20th-century art and the enigmatic world of Giuseppe Maria Alberto Giorgio de Chirico, staying informed about new discoveries, auction events, and sales of his works is essential. We invite you to sign up for updates to ensure you never miss an opportunity to engage with the enduring legacy of this remarkable Artist. This subscription is your gateway to the latest news related to de Chirico, focusing exclusively on product sales and auction events associated with his influential oeuvre.

Samuel Lewis Francis, an American painter and printmaker, was known for his pivotal role in postwar American painting and his contributions to the Abstract Expressionism and Color Field painting movements. Born in San Mateo, California, Francis' early life was marked by a deep personal loss and a significant injury during his service in the Army Air Corps, which led him to pursue painting while recovering in a hospital. His work, characterized by splashes of bright contrasting colors against expansive white canvases, drew international acclaim, particularly in Europe and Japan, underscoring his influence on the global art scene.
Francis' art evolved through various phases, from monochromatic works to vibrant, large-scale pieces, and was deeply influenced by his time in Paris and Japan, reflecting elements of Tachisme and possibly Zen Buddhism. Notable for creating large murals and his "Edge" series, Francis also founded The Lapis Press, further contributing to the art community by producing visually compelling texts. Despite facing health challenges towards the end of his life, he remained prolific, leaving behind a legacy celebrated through the Sam Francis Foundation, which aims to perpetuate his creative legacy.
Francis' artworks are held in prestigious collections worldwide, including The Metropolitan Museum of Art, The Museum of Modern Art, New York, and the Centre Pompidou-Musee National d'Art Moderne, Paris, highlighting his enduring influence on contemporary art. His auction records and continued recognition in solo exhibitions posthumously underscore the lasting impact of his work on both collectors and the art community.
For those passionate about modern art and its history, staying informed about Samuel Lewis Francis' contributions and the ongoing exhibitions of his works can be enriching. Sign up for updates related to Francis to ensure you don't miss out on new sales and auction events showcasing his vibrant legacy.
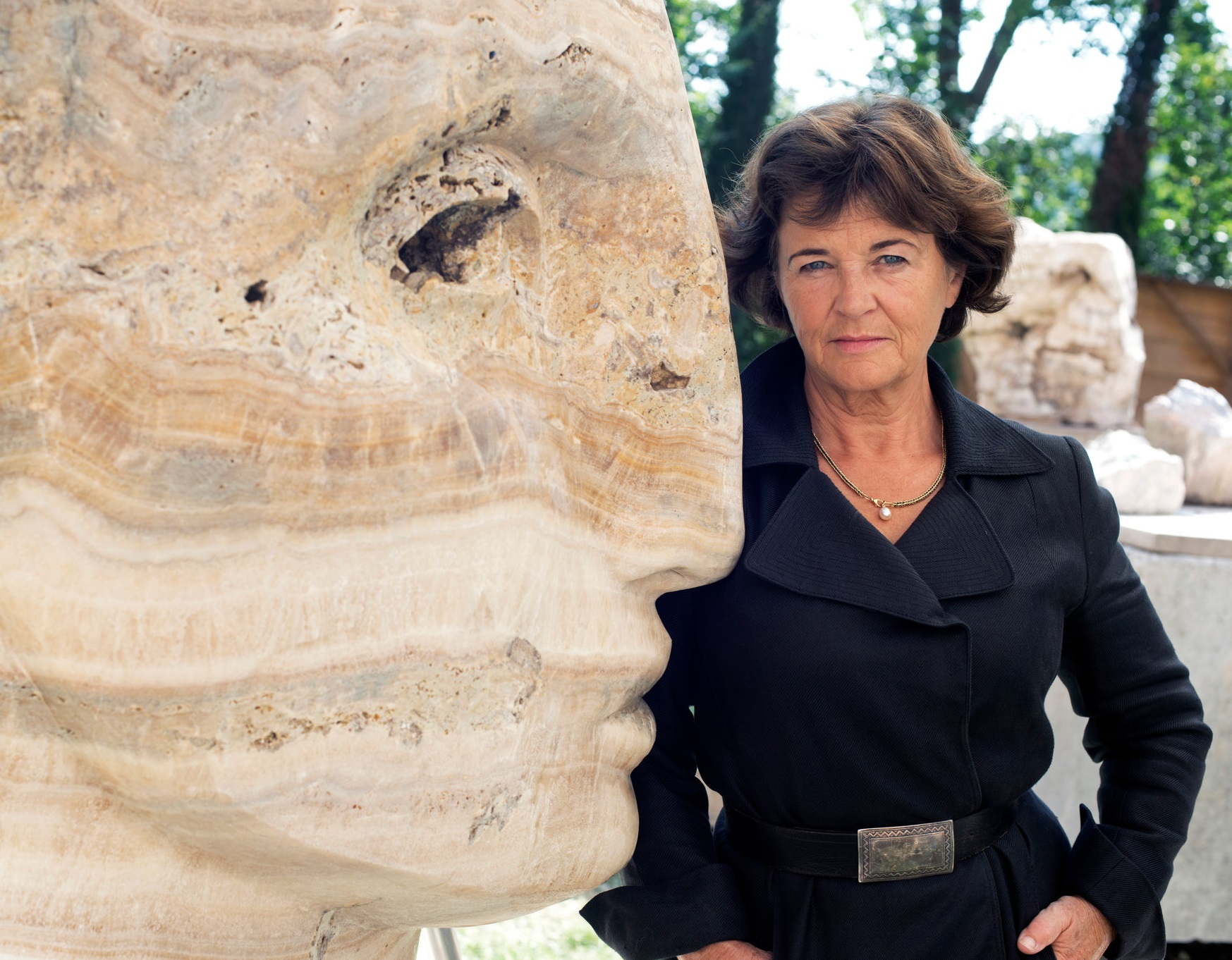


Emily Young is a sculptor, who has been called «Britain's greatest living stone sculptor». She was born in London into a family of artists, writers and politicians. She currently divides her time between studios in London and Italy.
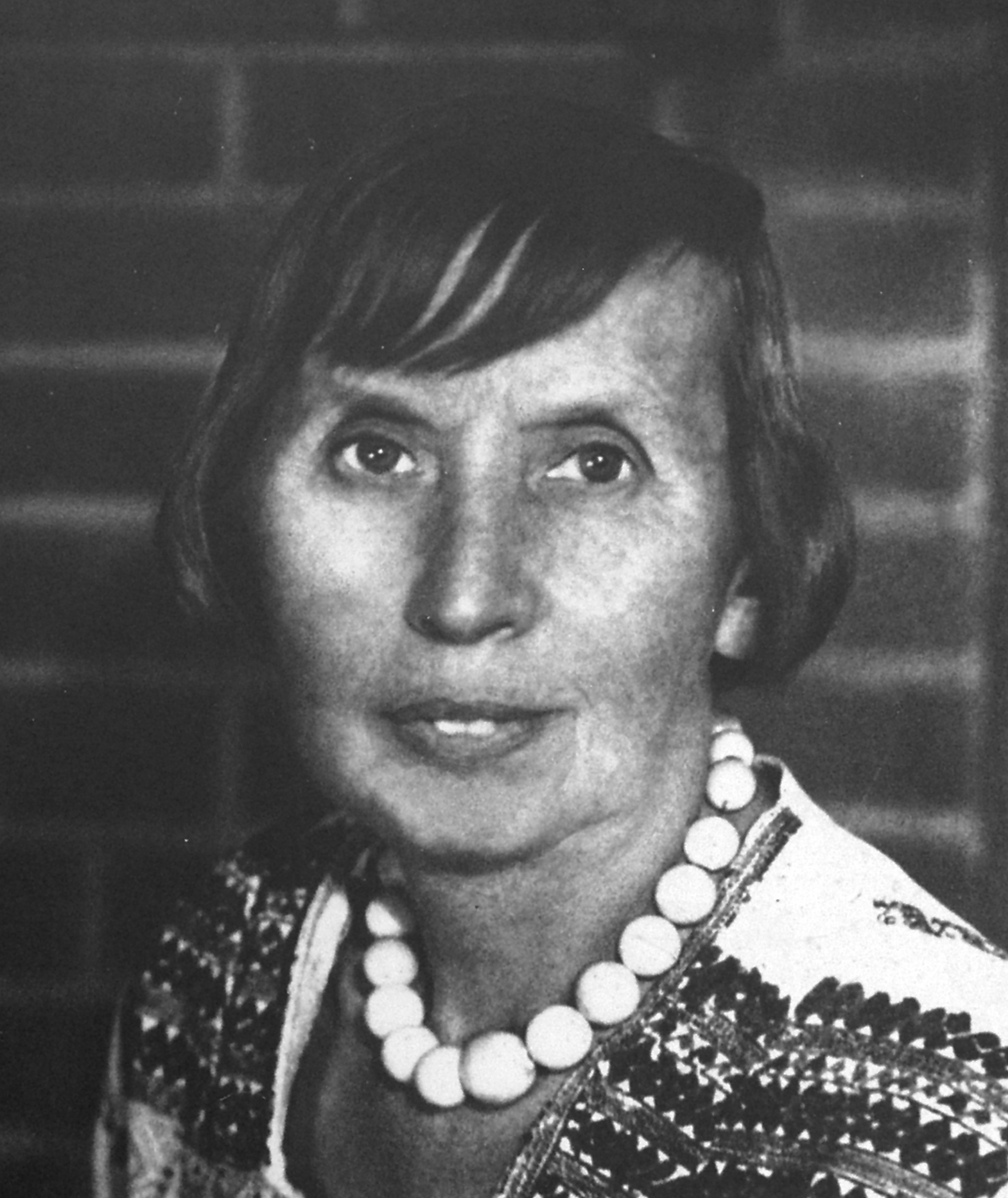


Ida Kerkovius was a Baltic German painter and weaver from Latvia.
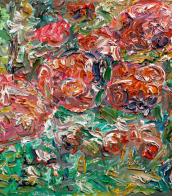
Samuel Lewis Francis, an American painter and printmaker, was known for his pivotal role in postwar American painting and his contributions to the Abstract Expressionism and Color Field painting movements. Born in San Mateo, California, Francis' early life was marked by a deep personal loss and a significant injury during his service in the Army Air Corps, which led him to pursue painting while recovering in a hospital. His work, characterized by splashes of bright contrasting colors against expansive white canvases, drew international acclaim, particularly in Europe and Japan, underscoring his influence on the global art scene.
Francis' art evolved through various phases, from monochromatic works to vibrant, large-scale pieces, and was deeply influenced by his time in Paris and Japan, reflecting elements of Tachisme and possibly Zen Buddhism. Notable for creating large murals and his "Edge" series, Francis also founded The Lapis Press, further contributing to the art community by producing visually compelling texts. Despite facing health challenges towards the end of his life, he remained prolific, leaving behind a legacy celebrated through the Sam Francis Foundation, which aims to perpetuate his creative legacy.
Francis' artworks are held in prestigious collections worldwide, including The Metropolitan Museum of Art, The Museum of Modern Art, New York, and the Centre Pompidou-Musee National d'Art Moderne, Paris, highlighting his enduring influence on contemporary art. His auction records and continued recognition in solo exhibitions posthumously underscore the lasting impact of his work on both collectors and the art community.
For those passionate about modern art and its history, staying informed about Samuel Lewis Francis' contributions and the ongoing exhibitions of his works can be enriching. Sign up for updates related to Francis to ensure you don't miss out on new sales and auction events showcasing his vibrant legacy.
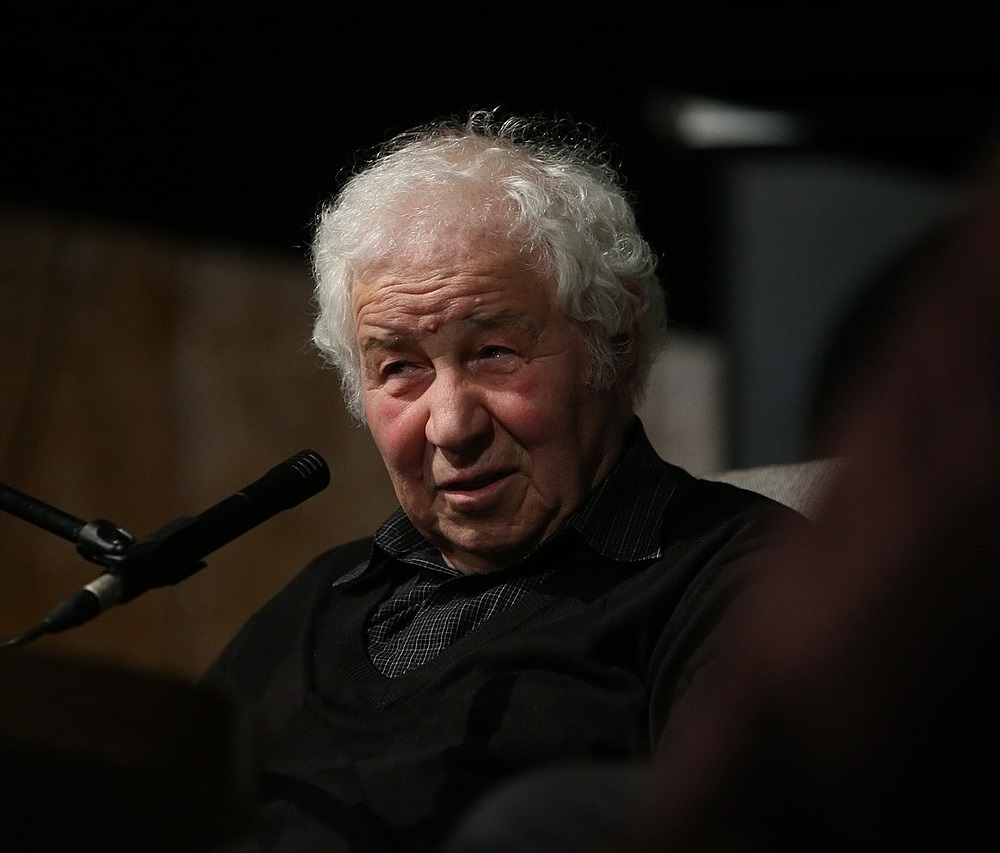

Ilya Iosifovich Kabakov (Russian: Илья́ Ио́сифович Кабако́в) was a seminal Russian-American conceptual artist, celebrated for his profound contributions to the art world, particularly through installations that critically examined Soviet life and the broader themes of human existence. Born on September 30, 1933, in Dnipropetrovsk, Ukrainian SSR, Kabakov's early life during the tumultuous World War II era and subsequent education at the V.I. Surikov State Art Institute in Moscow shaped his perspective and artistic expression. His nuanced critiques of the Soviet regime, combined with his exploration of utopian projects—including capitalism—through his art, positioned him as a pivotal figure in the dialogue between Eastern and Western artistic traditions.
Kabakov's partnership with Emilia Kanevsky, who later became his wife, led to a dynamic collaboration that spanned decades, producing influential exhibitions globally, including notable showcases at the Documenta in 1992, the Venice Biennale in 1993, and the Tate Modern in 2017. Their work is characterized by the use of fictional narratives, which often drew upon Kabakov's personal experiences to explore the life cycle of the Soviet Union, positioning it not merely as a failed socialist experiment but as one among many utopian visions susceptible to the authoritarian will to power.
Throughout his career, Kabakov never shied away from the complexity of the human condition, as evidenced by his installations like "The Man Who Flew Into Space From His Apartment" and "The Toilet," which resonate with viewers for their depth and the universality of their themes. His artworks are part of the collections of prestigious institutions such as the Museum of Modern Art, the Centre Pompidou, and the State Hermitage Museum, underscoring his significant impact and enduring legacy in the art world.
Kabakov's death on May 27, 2023, at the age of 89, marked the end of a prolific career that left an indelible mark on the landscape of conceptual art. His work continues to inspire and provoke thought, bridging the gap between personal narrative and global history, and inviting viewers to reconsider their perspectives on society, history, and the role of art in reflecting and shaping human experience.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques interested in staying updated on exhibitions and auctions related to Ilya Iosifovich Kabakov, signing up for updates can provide exclusive insights and opportunities to engage with his impactful body of work. This subscription ensures that enthusiasts are well-informed about new sales and events, allowing them to deepen their appreciation for Kabakov's artistic contributions.