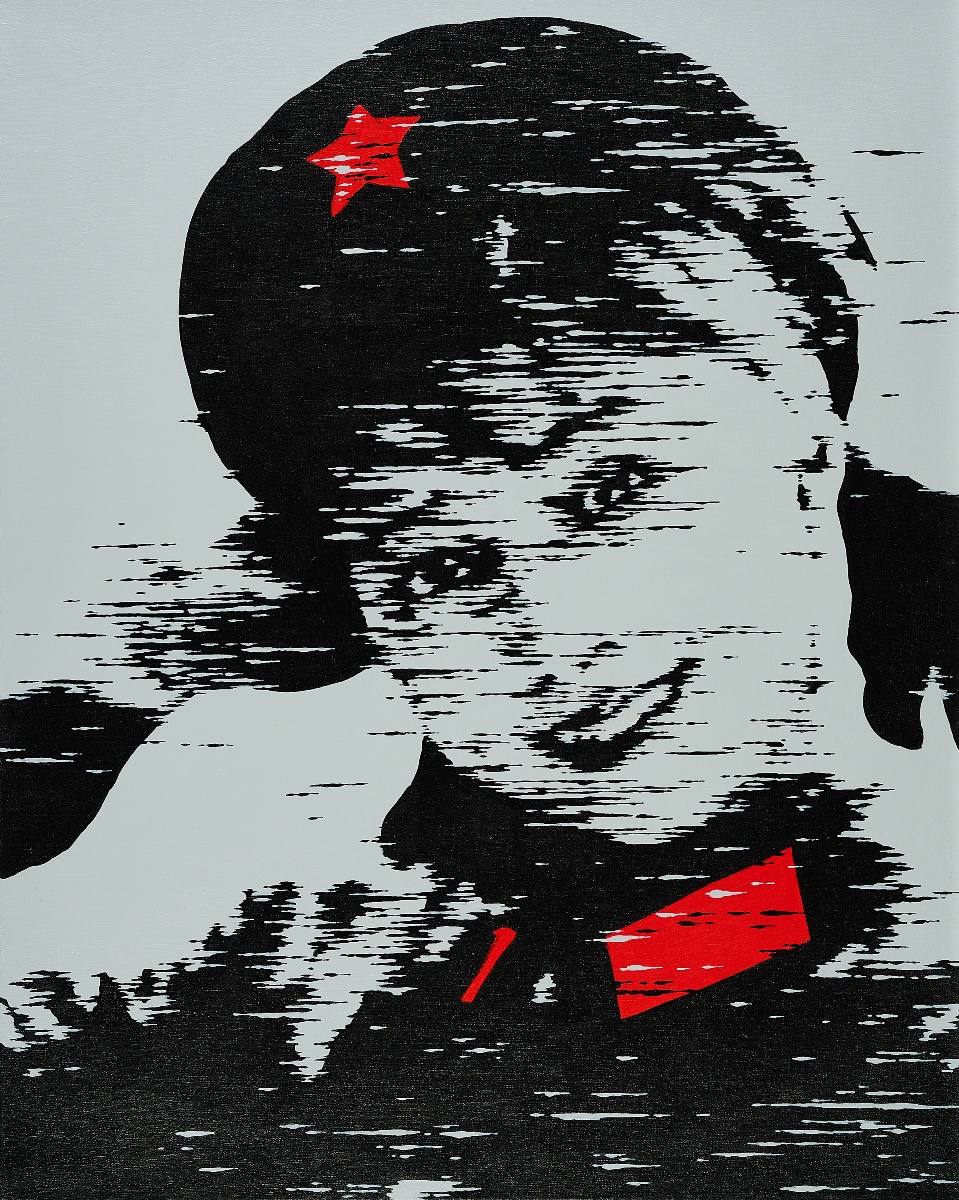
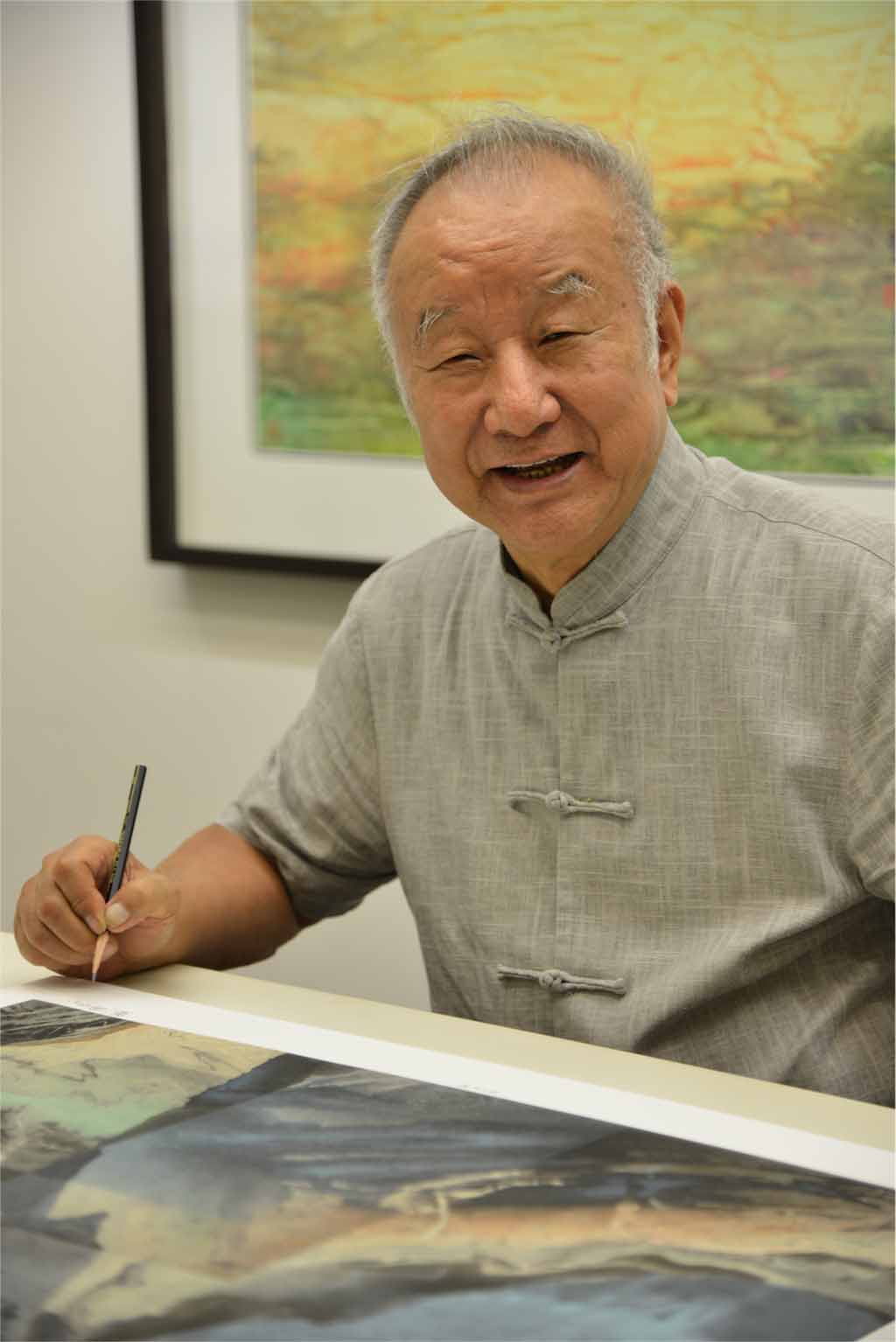
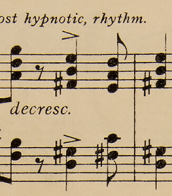song ying
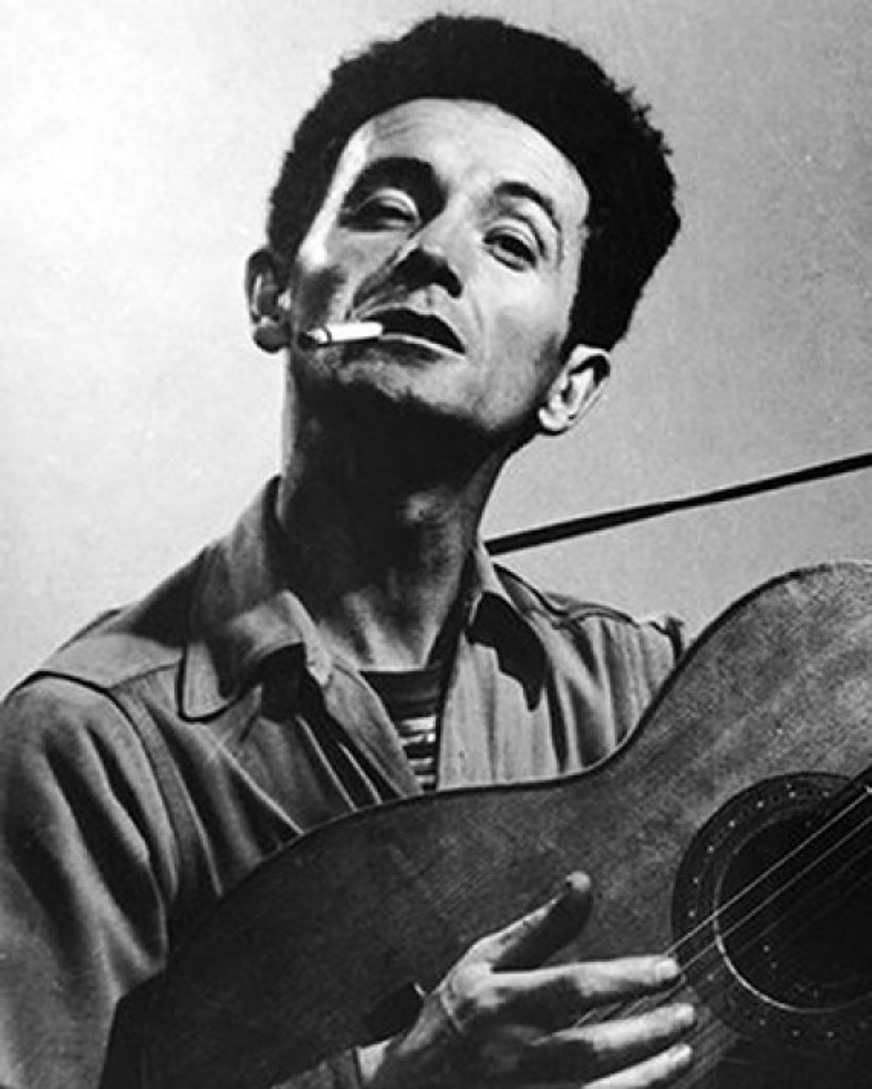

Woodrow Wilson Guthrie or Woody Guthrie is an American folk and country singer and musician.
Guthrie was born in difficult economic times in the United States. At first, he earned a living as a sign painter in different cities, traveling by hitchhiking. At the age of 20, he began learning to play guitar, playing in saloons and labor camps during the Great Depression. In his travels, the musician absorbed and performed many of the old folk ballads he heard around him and wrote many new songs reflecting the everyday joys and hardships of the ordinary people he met in his travels.
Guthrie was a major influence on folk and rock musicians from Bob Dylan to Wilco. Among Guthrie's best-known songs are Pastures of Plenty, Bound for Glory, and This Land is Your Land, the latter of which, due to its popularity, has become something of an "alternative national anthem" in the United States. In 1940, he recorded four hours of songs and stories for the Archive of American Folk Song at the Library of Congress (now the Archive of Folk Culture, American Folklife Center). Throughout the 1940s and 1950s, Guthrie had a high-profile career in radio broadcasting and recording.
Woody was a very prolific composer, writing thousands of songs. He also wrote an autobiographical novel, On the Road to Fame, and drew thousands of pen and ink drawings, many of which are now in the Ralph Rinzler Center's Folklife Archives and Collections.
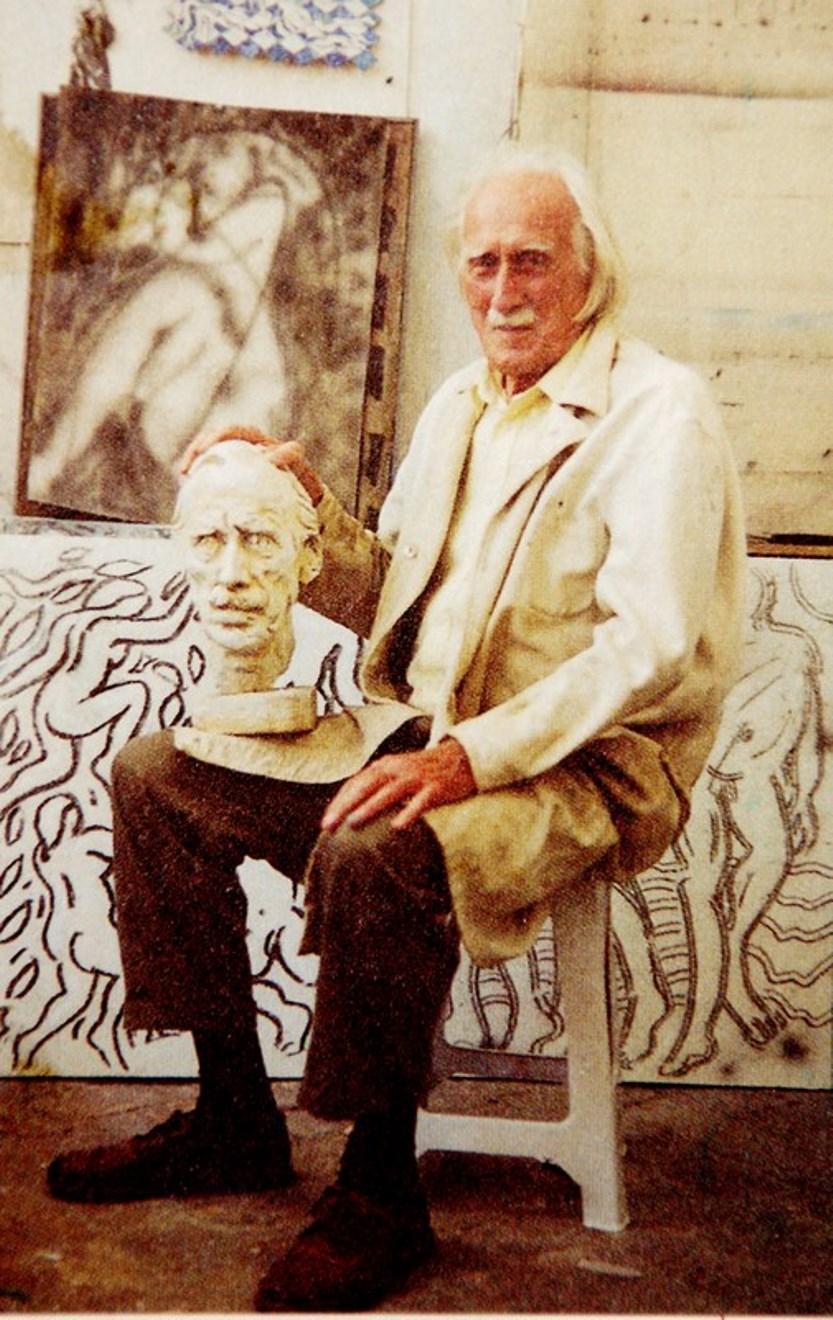

Harold Ambellan is an American painter and sculptor.
He studied sculpture and fine art in Buffalo before moving to New York City. The human figure is central to Harold Ambellan's work. He created monumental figures and drew extensively, leaving thousands of drawings. Ambellan was one of the participants in Roosevelt's Federal Art Project, which hired hundreds of artists during the Great Depression who collectively created more than 100,000 paintings and over 18,000 sculptures.
Ambellan remained committed to figuration in both his sculpture and painting. He was elected president of the Sculptors Guild of America in 1941, and that same year his work was exhibited in group shows at the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York and the Academy of Fine Arts in Philadelphia.
In 1944, Ambellan participated in the liberation of Normandy as part of the U.S. Navy, then taught three-dimensional art at the Workshop School in New York City. In 1954, for political reasons, Ambellan moved to France and remained there for the rest of his life, working and exhibiting throughout Europe.


Woodrow Wilson Guthrie or Woody Guthrie is an American folk and country singer and musician.
Guthrie was born in difficult economic times in the United States. At first, he earned a living as a sign painter in different cities, traveling by hitchhiking. At the age of 20, he began learning to play guitar, playing in saloons and labor camps during the Great Depression. In his travels, the musician absorbed and performed many of the old folk ballads he heard around him and wrote many new songs reflecting the everyday joys and hardships of the ordinary people he met in his travels.
Guthrie was a major influence on folk and rock musicians from Bob Dylan to Wilco. Among Guthrie's best-known songs are Pastures of Plenty, Bound for Glory, and This Land is Your Land, the latter of which, due to its popularity, has become something of an "alternative national anthem" in the United States. In 1940, he recorded four hours of songs and stories for the Archive of American Folk Song at the Library of Congress (now the Archive of Folk Culture, American Folklife Center). Throughout the 1940s and 1950s, Guthrie had a high-profile career in radio broadcasting and recording.
Woody was a very prolific composer, writing thousands of songs. He also wrote an autobiographical novel, On the Road to Fame, and drew thousands of pen and ink drawings, many of which are now in the Ralph Rinzler Center's Folklife Archives and Collections.

Harold Ambellan is an American painter and sculptor.
He studied sculpture and fine art in Buffalo before moving to New York City. The human figure is central to Harold Ambellan's work. He created monumental figures and drew extensively, leaving thousands of drawings. Ambellan was one of the participants in Roosevelt's Federal Art Project, which hired hundreds of artists during the Great Depression who collectively created more than 100,000 paintings and over 18,000 sculptures.
Ambellan remained committed to figuration in both his sculpture and painting. He was elected president of the Sculptors Guild of America in 1941, and that same year his work was exhibited in group shows at the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York and the Academy of Fine Arts in Philadelphia.
In 1944, Ambellan participated in the liberation of Normandy as part of the U.S. Navy, then taught three-dimensional art at the Workshop School in New York City. In 1954, for political reasons, Ambellan moved to France and remained there for the rest of his life, working and exhibiting throughout Europe.