table bibliothèque
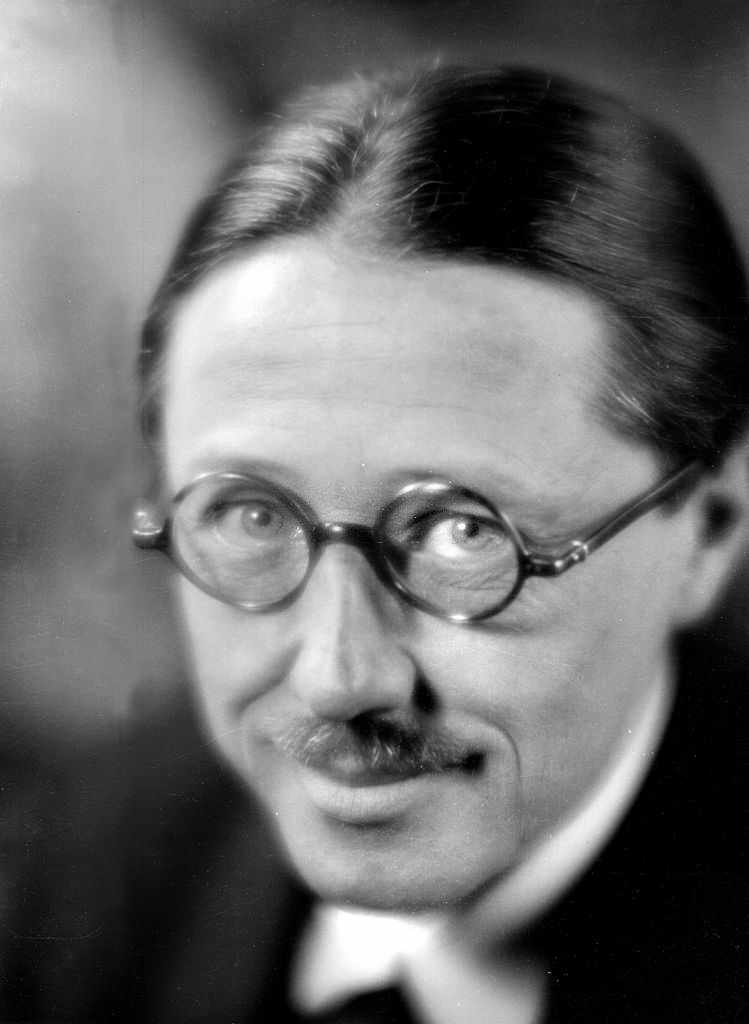

Émile-Jacques Ruhlmann, (sometimes called Jacques-Émile Ruhlmann), was a French furniture designer and interior decorator, who was one of the most important figures in the Art Deco movement. His furniture featured sleek designs, expensive and exotic materials and extremely fine craftsmanship, and became a symbol of the luxury and modernity of Art Deco. It also produced a reaction from other designers and architects, such as Le Corbusier, who called for simpler, functional furniture.
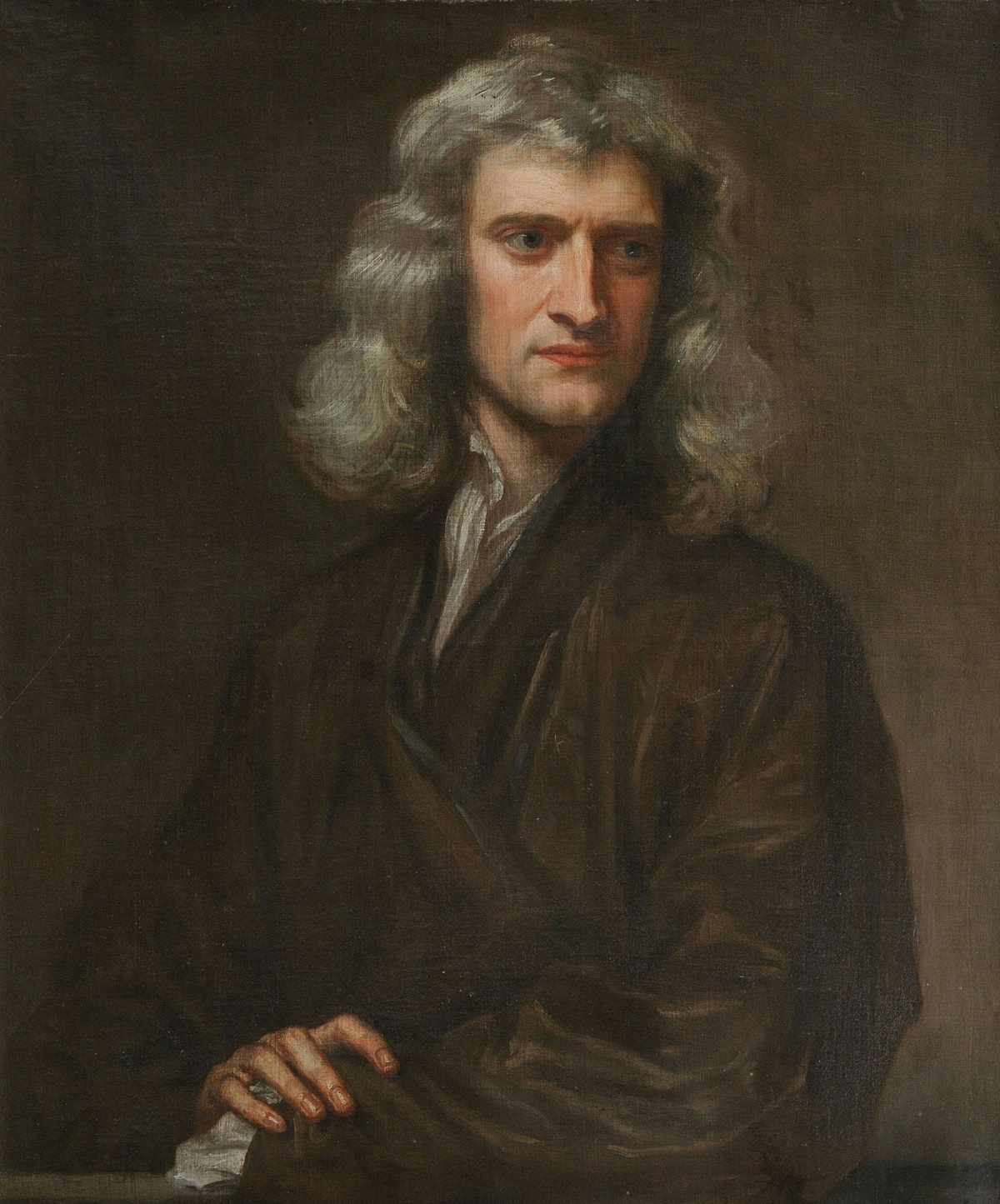



Isaac Newton was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus.
In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for tides, the trajectories of comets, the precession of the equinoxes and other phenomena, eradicating doubt about the Solar System's heliocentricity. He demonstrated that the motion of objects on Earth and celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton's inference that the Earth is an oblate spheroid was later confirmed by the geodetic measurements of Maupertuis, La Condamine, and others, convincing most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over earlier systems.





Émile-Jacques Ruhlmann, (sometimes called Jacques-Émile Ruhlmann), was a French furniture designer and interior decorator, who was one of the most important figures in the Art Deco movement. His furniture featured sleek designs, expensive and exotic materials and extremely fine craftsmanship, and became a symbol of the luxury and modernity of Art Deco. It also produced a reaction from other designers and architects, such as Le Corbusier, who called for simpler, functional furniture.

Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.
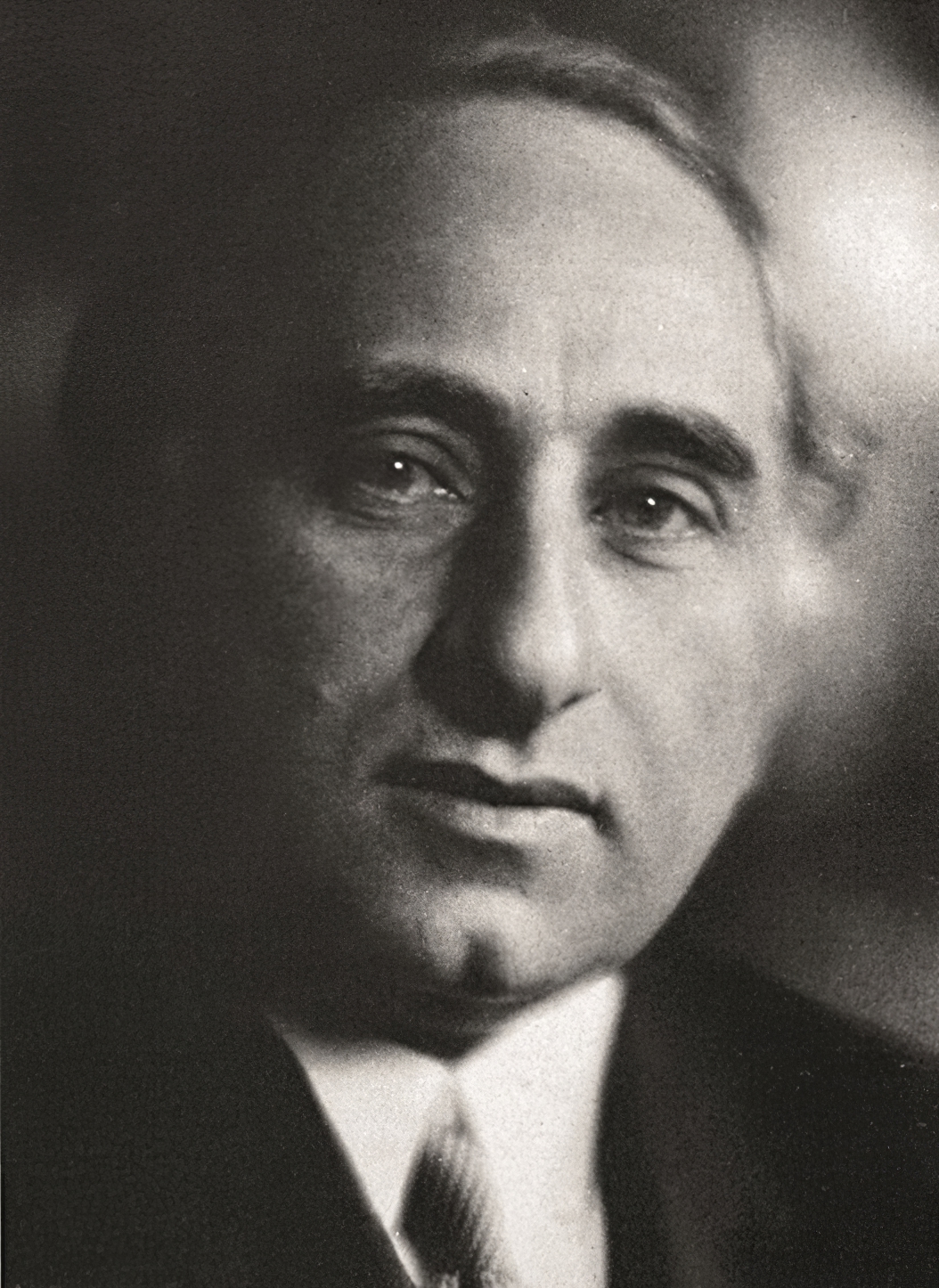


Pierre Chareau was a French architect and designer.
Chareau designed the first house in France made of steel and glass, the Maison de Verre.
Chareau was a member of Congrès International d'Architecture Moderne.
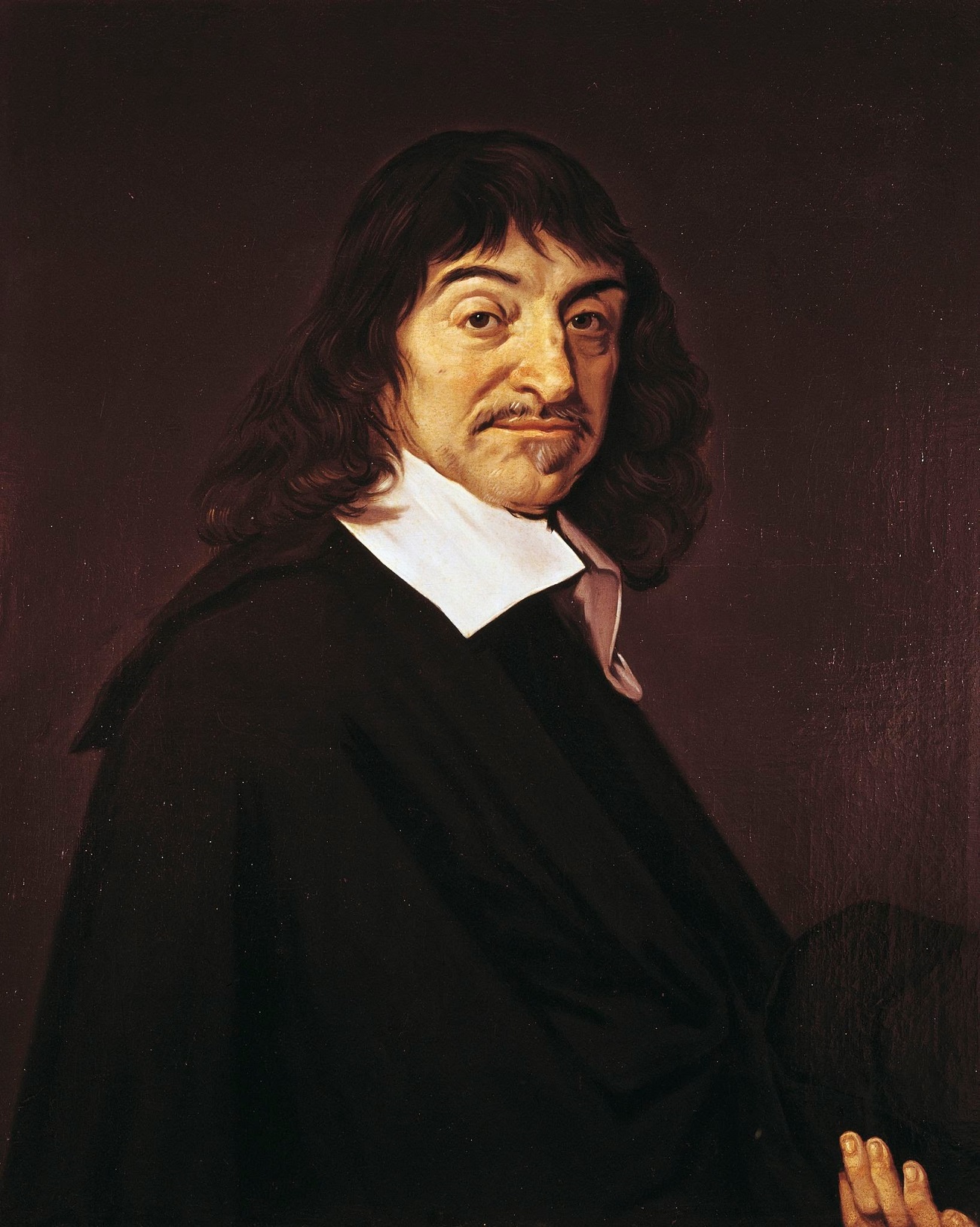


René Descartes was a French philosopher, mathematician, and natural scientist who is considered the founder of modern philosophy.
Descartes was a very versatile scientist: besides numerous philosophical reflections, he wrote works on optics, meteorology and geometry. Contemporaries noted his extensive knowledge in many sciences. Descartes owns the famous saying "I think, therefore I exist" (best known in the Latin formulation "Cogito, ergo sum", although it was originally written in French: "Je pense, donc je suis").
He developed a metaphysical dualism that radically distinguished between mind, whose essence is thought, and matter, whose essence is extension in three dimensions. Descartes' metaphysics is rationalistic, based on the postulation of innate ideas of mind, matter, and God, but his physics and physiology, based on sense experience, are mechanistic and empirical.
Unlike his scientific predecessors, who felt a holy awe at the incomprehensibility of the divine essence of the universe, Descartes admired the ability of the human mind to understand the cosmos and to generate happiness itself, and rejected the view that human beings were inherently unhappy and sinful. He believed that it was inappropriate to pray to God to change the state of things and the world; it was much more productive to change oneself.












![[PASQUIER, Étienne (1529-1615)]. La Main ou OEuvres poétiques faits sur la Main de Estienne Pasquier, Advocat au Parlement de Paris. Paris : Michel Gadouleau, 1584.](/assets/image/picture_1321011/12f17/4e5a4ee6f2802a1e1adddce24f5bd5ca1616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[PASQUIER, Étienne (1529-1615)]. La Main ou OEuvres poétiques faits sur la Main de Estienne Pasquier, Advocat au Parlement de Paris. Paris : Michel Gadouleau, 1584.](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_1321011/12f17/4e5a4ee6f2802a1e1adddce24f5bd5ca1616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)


![[AUBIGNÉ, Théodore Agrippa d' (1552-1630)]. Les Tragiques. Donnez au public par le larcin de Prométhée. Au Dezert par L.B.D.D, [château de Maillé : Jean Moussat], 1616.](/assets/image/picture_1320898/3976f/cbf089ad2351e04118152eab6351a58d1616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[AUBIGNÉ, Théodore Agrippa d' (1552-1630)]. Les Tragiques. Donnez au public par le larcin de Prométhée. Au Dezert par L.B.D.D, [château de Maillé : Jean Moussat], 1616.](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_1320898/3976f/cbf089ad2351e04118152eab6351a58d1616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)


![ÉNOC DE LA MESCHINIÈRE, Pierre (1550- vers 1597). Opuscules Poétiques de Pierre Énoc. D. G. A Monsieur Dorsaine, Siegneur de Tizay, Lieutenant General pour le Roy a Yssoudun. [Genève :], Jacob Stoer, 1572.](/assets/image/picture_1320941/87c40/fe57837c9d5d4ee3f50dac7eb2955ee01616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![ÉNOC DE LA MESCHINIÈRE, Pierre (1550- vers 1597). Opuscules Poétiques de Pierre Énoc. D. G. A Monsieur Dorsaine, Siegneur de Tizay, Lieutenant General pour le Roy a Yssoudun. [Genève :], Jacob Stoer, 1572.](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_1320941/87c40/fe57837c9d5d4ee3f50dac7eb2955ee01616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)


































![[PASCAL, Blaise (1623-1662)]](/assets/image/picture_2500960/130be/3cdb73731e903f3be16eddb0cd4f51011667984400jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[PASCAL, Blaise (1623-1662)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2500960/130be/3cdb73731e903f3be16eddb0cd4f51011667984400jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)









![[DESCARTES, René (1596-1650)]](/assets/image/picture_2500811/a67fb/9ee6c1d6009ac0da55c5104d2c2f17ad1667984400jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[DESCARTES, René (1596-1650)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2500811/a67fb/9ee6c1d6009ac0da55c5104d2c2f17ad1667984400jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)






![FIBONACCI, Leonardo [c.1170-c.1250]; BOETHIUS, Anicius Manlius Severinus [c.480-524], GROSSETESTE, Robert [1175-1253]; [DE PULCHRO RIVO, Johannes, attrib.]](/assets/image/picture_2279440/69ac3/5672d49f6fe2176fe5b0465502ca1a9b1657663200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![FIBONACCI, Leonardo [c.1170-c.1250]; BOETHIUS, Anicius Manlius Severinus [c.480-524], GROSSETESTE, Robert [1175-1253]; [DE PULCHRO RIVO, Johannes, attrib.]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2279440/69ac3/5672d49f6fe2176fe5b0465502ca1a9b1657663200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)