thomas johnson



Martin Johnson Heade was an American painter known for his salt marsh landscapes, seascapes, and depictions of tropical birds (such as hummingbirds), as well as lotus blossoms and other still lifes. His painting style and subject matter, while derived from the romanticism of the time, are regarded by art historians as a significant departure from those of his peers.



_by_Henry_Edridge.jpg)
Thomas Girtin was a British watercolor painter.
Girtin, along with his artist friend J. M. W. Turner, was the founder of the national school of watercolor. Until the late 18th century, watercolor was mainly used for topographical works such as maps, but thanks to these two artists it became increasingly popular. Girtin developed his bold, spacious, romantic style, which had an indelible influence on English painting.
Girtin created many panoramic watercolor landscapes and views of London and Paris in the Romantic style. His giant panorama of London, Eidometropolis, was exhibited in 1802, shortly before his premature death.



Enos Hitchcock was an American clergyman, author, educator, and education advocate.
He graduated from Harvard College and soon began preaching. When hostilities between the colonies and Great Britain broke out in 1775, Hitchcock joined the army, serving as a chaplain in the Continental Army from 1779-1780. After the war ended, Rev. Hitchcock preached in various localities until he settled in Providence, NC, in 1783 as pastor of the First Congregational Church, becoming an active member of its benevolent society.
In 1788 Hitchcock received his doctorate from Brown University and maintained close ties with it thereafter. With the president of that university, James Manning (1738-1791), and other prominent citizens of Providence, he was active in educational matters, and by the time of his death had succeeded in establishing a public school system in Providence. In addition to these activities, Rev. Hitchcock was a member of the Pennsylvania Society for Promoting the Abolition of Slavery.
Enos Hitchcock also wrote several epistolary works in which, among other things, he objected to the use of suicide as a plot point. His bullied rural heroes and heroines are ultimately rewarded for their virtue and courage.


William Howe or How was a British botanist and physician.
He studied at St. John's College, Oxford, earning a bachelor's degree and then a master's degree in medicine. He served briefly in the King's army as a cavalry commander, and later returned to the medical profession and practiced in London.
In his Phytologia Britannica, natales exhibens Indigenarum stirpium sponte Emergentium ("Phytology Britannica"), published in London in 1650, William Howe combined Thomas Johnson's catalogs into a single alphabetical list, supplemented with additional plants from other sources. This was the first edition of the book to compile for the first time all the known plants of Britain with descriptions of their occurrence.


William Howe or How was a British botanist and physician.
He studied at St. John's College, Oxford, earning a bachelor's degree and then a master's degree in medicine. He served briefly in the King's army as a cavalry commander, and later returned to the medical profession and practiced in London.
In his Phytologia Britannica, natales exhibens Indigenarum stirpium sponte Emergentium ("Phytology Britannica"), published in London in 1650, William Howe combined Thomas Johnson's catalogs into a single alphabetical list, supplemented with additional plants from other sources. This was the first edition of the book to compile for the first time all the known plants of Britain with descriptions of their occurrence.



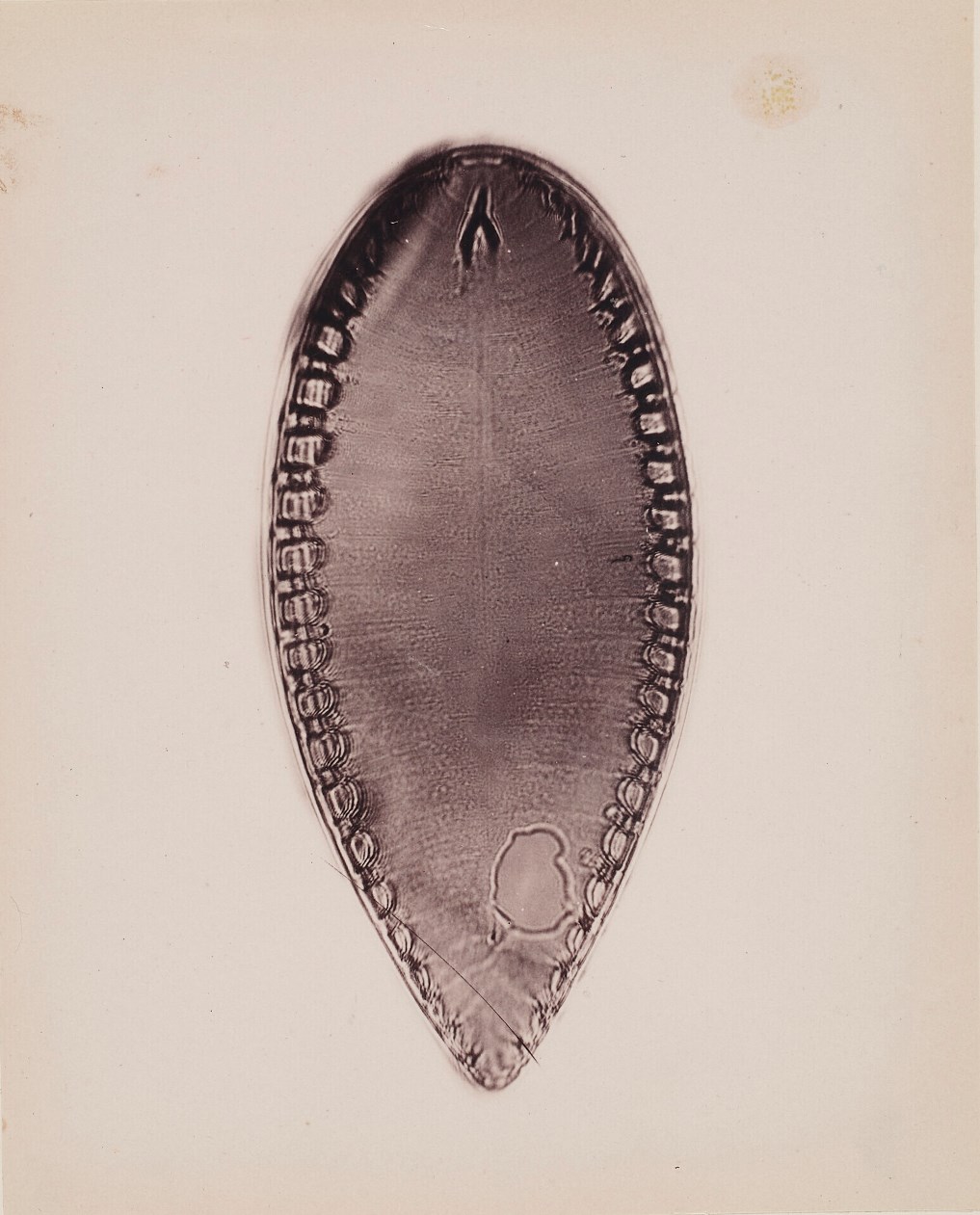
John Thomas Redmayne was a British surgeon, physician and amateur naturalist.
Redmayne trained as a physician and surgeon in Glasgow, then received his diploma at Guy's Hospital in London and was licensed by the Royal College of Physicians in Edinburgh.
In addition to being a physician, J. Redmayne was an amateur naturalist, he became interested in microscopy and specialized in diatom algae. He is considered one of the most successful microphotographers of the time, and his founding of the Bolton Microscopical Society allowed him to concentrate on the study of diatoms. His microscopic diatom plates were highly respected, particularly for the relative purity of the species. He also mounted histological preparations. Redmayne gave copies of his book to the Quekett Microscopical Club (which he joined in 1876) and the Royal Microscopical Society.