1846 - 1857
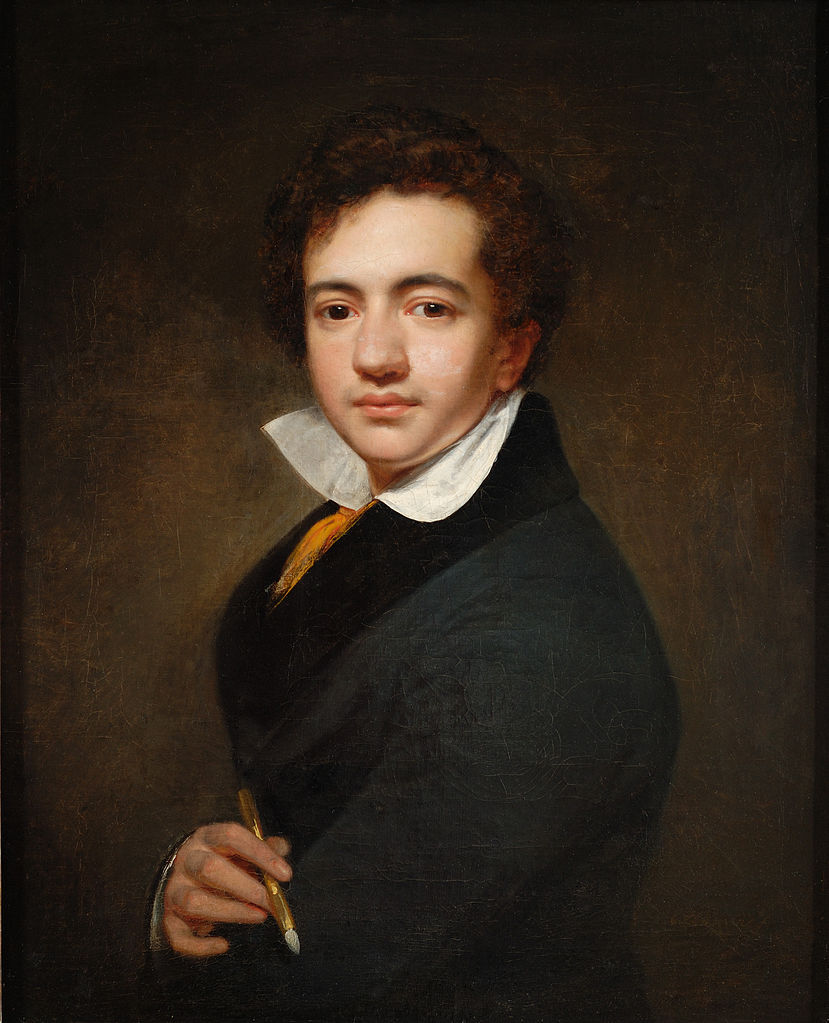
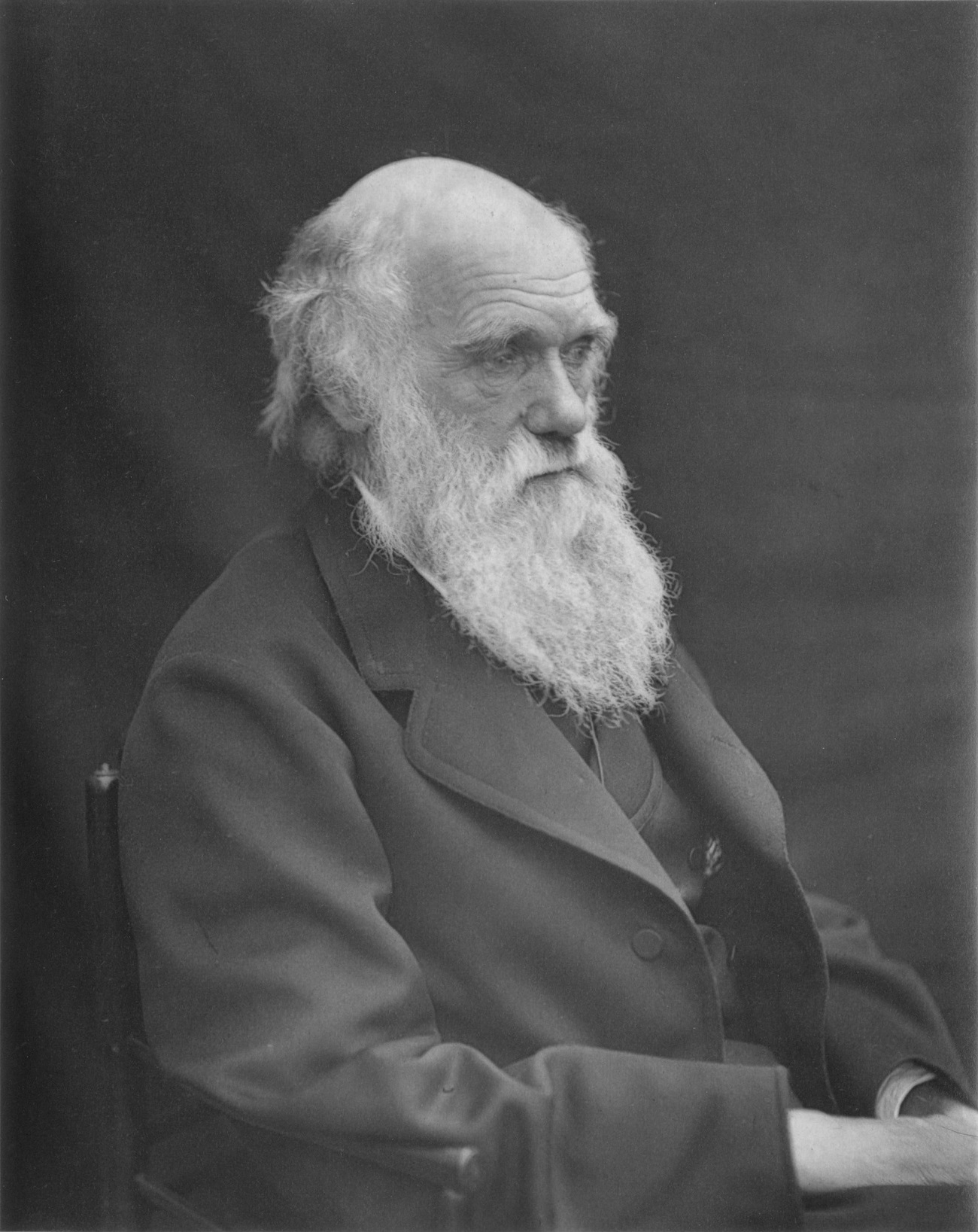




Charles Robert Darwin was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for contributing to the understanding of evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a common ancestor is now generally accepted and considered a fundamental concept in science. In a joint publication with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding. Darwin has been described as one of the most influential figures in human history, and he was honoured by burial in Westminster Abbey.
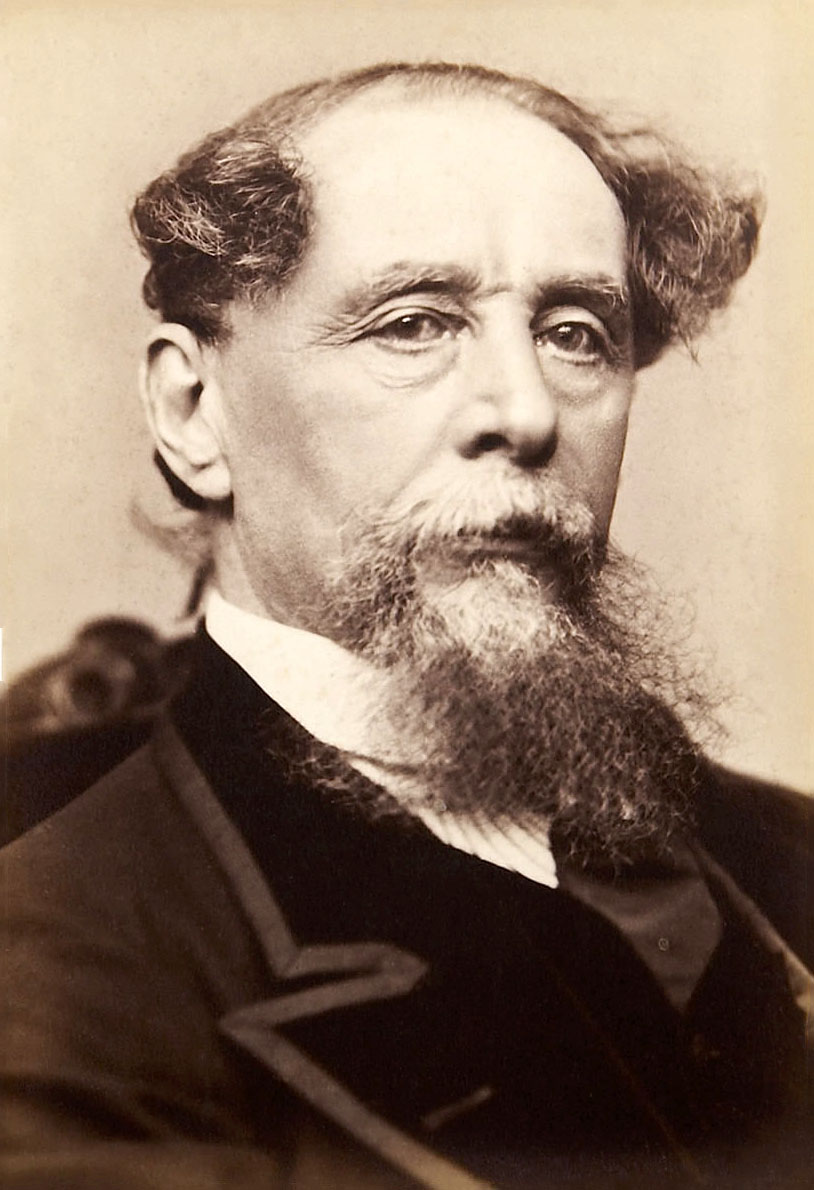


Charles Dickens, full name Charles John Huffam Dickens, is the most famous British writer of the Victorian era, a classic of world literature.
From childhood the future writer learned all the hardships of life in poverty: his father in prison for debts, hard work in a factory. Then service stenographer in court and reporter developed in him a strong attachment to journalism and contempt for both the law and parliament.
Dickens had many talents: in addition to literary work, he was an actor, published periodicals, arranged numerous literary readings, where he reveled in the admiration and love of the public. Fecund and versatile, Charles Dickens wrote many brilliant and often comic works. His novels cover a wide range of social, moral, emotional and other aspects. As a subtle psychologist, he is also very interested in the most ordinary people, but also the eccentric, the flawed, and even the insane.
Dickens was immensely popular around the world during his lifetime. His intellect, worldview, and deep reflections on society and its faults enriched his novels and made him one of the great figures of nineteenth-century literature, an influential spokesman for the conscience of his time.
Dickens' best-known and most popular novels are The Pickwick Club Posthumous Notes, Oliver Twist, Nicholas Nickleby, David Copperfield, Cold House, A Tale of Two Cities, Our Mutual Friend, Great Expectations, and The Mystery of Edwin Drood.
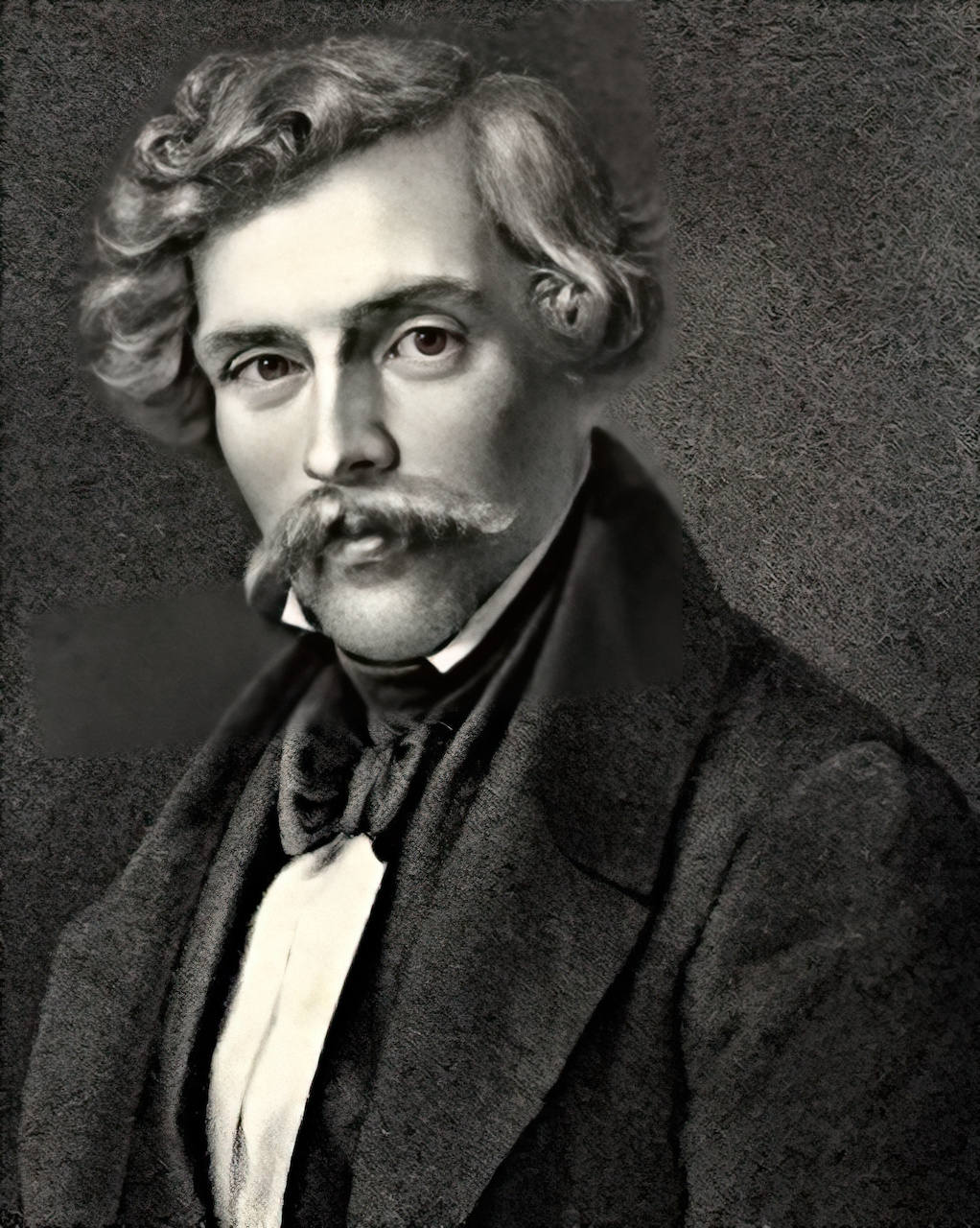



Edwin Henry Landseer was an English painter and sculptor, well known for his paintings of animals – particularly horses, dogs, and stags. However, his best-known works are the lion sculptures at the base of Nelson's Column in Trafalgar Square.
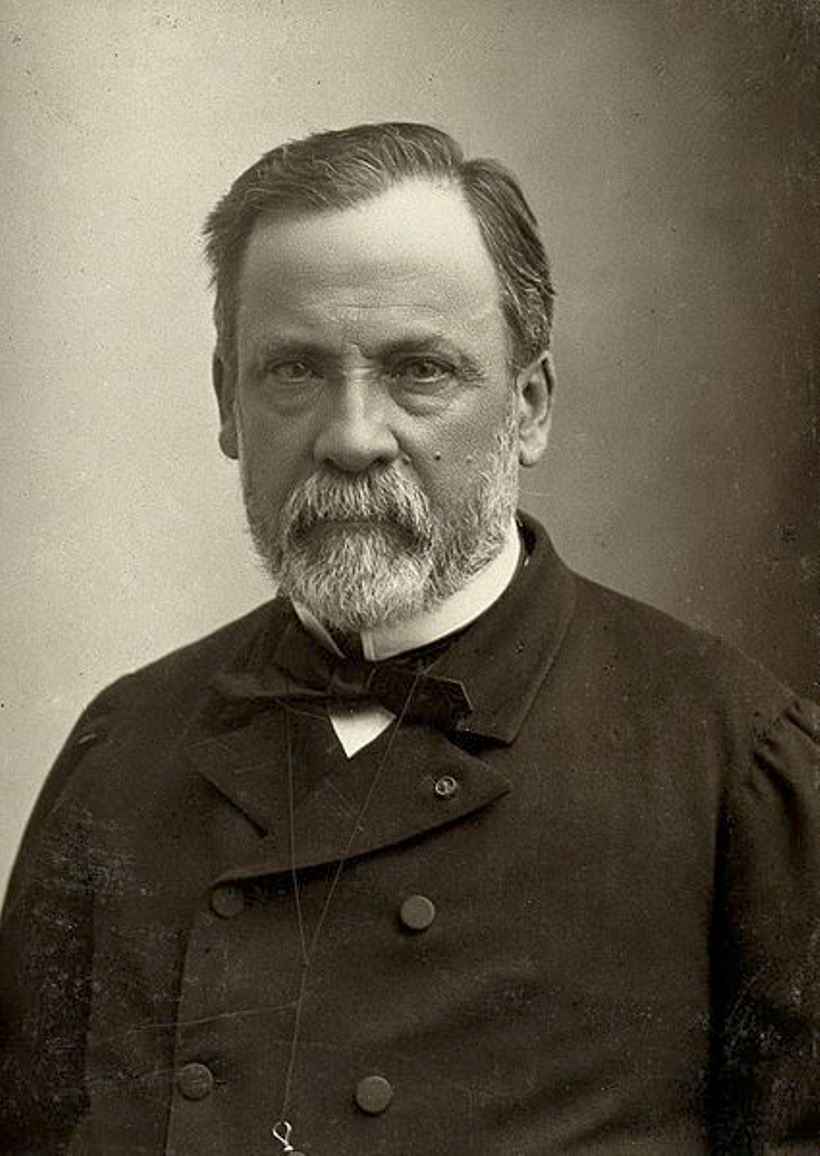


Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and the founder of microbiology and vaccination.
Pasteur received a bachelor of arts and sciences from the Royal College of Besançon and a doctorate from the École Normale in Paris, then spent several years as a researcher and teacher at the Lycée de Dijon. In 1848 he became professor of chemistry at the University of Strasbourg, and in the following year began to study the nature of wine fermentation, which began his revolutionary journey of most important scientific discoveries.
He invented a way to kill bacteria by boiling and then cooling the liquid, a process known today as pasteurization. Pasteur discovered the first vaccine in 1879 when he was exposed to a disease called chicken cholera. By accidentally exposing chickens to a weakened form of the culture, he demonstrated that they became resistant to the actual virus. Pasteur subsequently expanded his theory of germs and developed causes and vaccines against anthrax, cholera, tuberculosis, and smallpox, and the success of Pasteur's rabies vaccine in 1885 brought him worldwide fame.
Louis Pasteur's contribution to science, technology and medicine cannot be overemphasized. He pioneered the study of molecular asymmetry; discovered that microorganisms cause fermentation and disease; invented the process of pasteurization; saved the brewing, wine and silk industries in France; developed vaccines against the dreaded diseases anthrax and rabies, which saved millions of lives.
In 1873, Pasteur was elected an associate member of the Academy of Medicine, in 1882 - a member of the French Academy, and in 1888 in Paris was opened the Pasteur Institute. He was also awarded France's highest honor, the Legion of Honor.


















.webp)




























































