antiquarian books
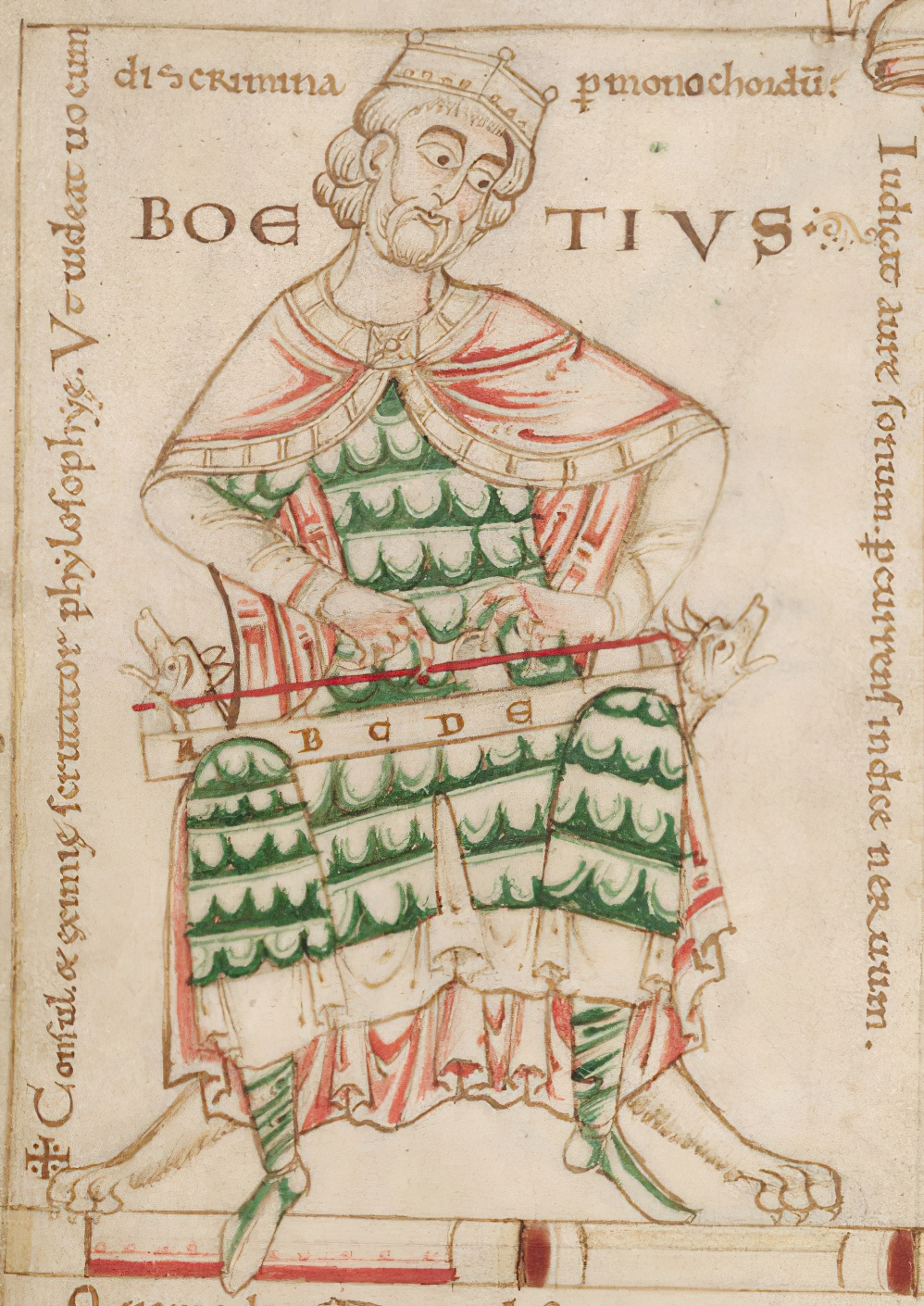


Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius, commonly known as Boethius (Latin: Boetius), was an Italian senator, consul, magister officiorum, historian, and philosopher of the Early Middle Ages. He was a central figure in the translation of the Greek classics into Latin, a precursor to the Scholastic movement, and, along with Cassiodorus, one of the two leading Christian scholars of the 6th century.






Ludwig van Beethoven was a German composer, pianist, and conductor, one of the most famous and celebrated composers in world history.
Beethoven showed an aptitude for music at a very early age; from the age of four his father began to teach him. Beethoven's early works - piano sonatas and symphonies - were composed under the strong influence of the music of the great classical composers Joseph Haydn and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. As Beethoven matured, however, he began to experiment with new forms and harmonic sequences, and his music became more complex and emotionally charged.
Unfortunately, at the height of his talent, Beethoven began to gradually lose his hearing, to the point of complete deafness by the end of his life. Despite this, he continued to compose and conduct, using special devices to feel the vibrations of the music.
Beethoven's work is considered pivotal in classical music and is a bridge between the classical and Romantic eras. His works vividly express a wide range of emotions, from triumph and joy to sadness and despair. Beethoven was also one of the first composers to include soloists and chorus in his symphonies. Beethoven's best-known works include nine symphonies, 32 piano sonatas, 16 string quartets and the heroic opera Fidelio. These and many other works have cemented Beethoven's place in music history as one of the greatest composers of all time. His music continues to be played and studied by musicians and music lovers around the world.
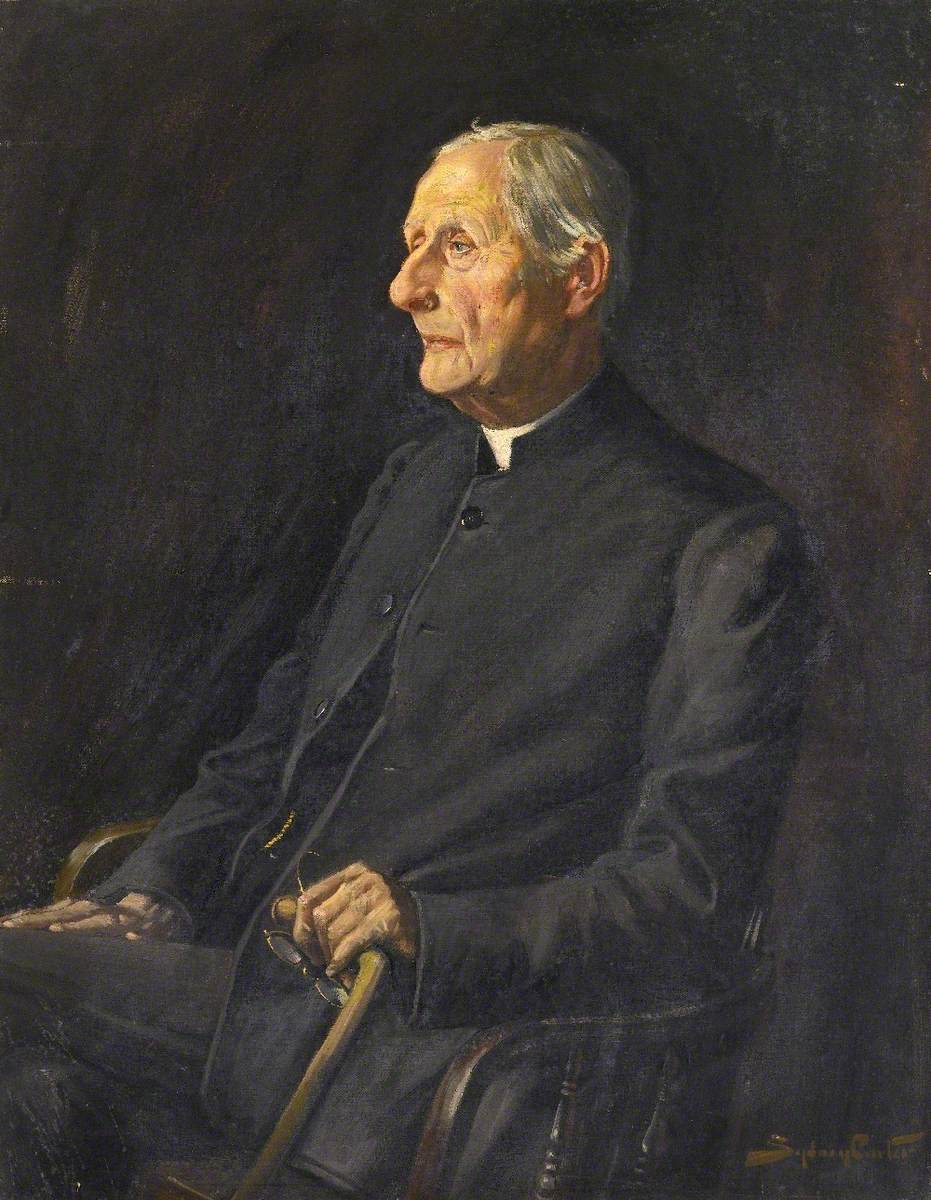


Sabine Baring-Gould was a Victorian British clergyman, poet, writer and folklorist.
He traveled extensively in Europe, studied at Clare College, Cambridge, was ordained in the Church of England in 1864, and was appointed vicar at Horbury. Baring-Gould was a polyglot and knew six languages. Despite his ministry, he had a serious interest in supernatural phenomena and in 1865 published a book called The Book of Werewolves.
In addition to this, Baring-Gould was interested in a wide range of subjects. His work is diverse and covered theology, history, poetry, hymns, fiction, biography, travel, social commentary, and folklore. Baring-Gould collected the folk songs of old English singers, personally visiting them and recording the words and music. In 1889 he published a collection of Songs of the West in four parts, of which he was proud, and also wrote several patriotic hymns.
Baring-Gould was a very prolific writer: during his life he wrote many novels, published short stories in periodicals, the popular "Curious Myths of the Middle Ages," and others, his bibliography numbering some 1,250 works.
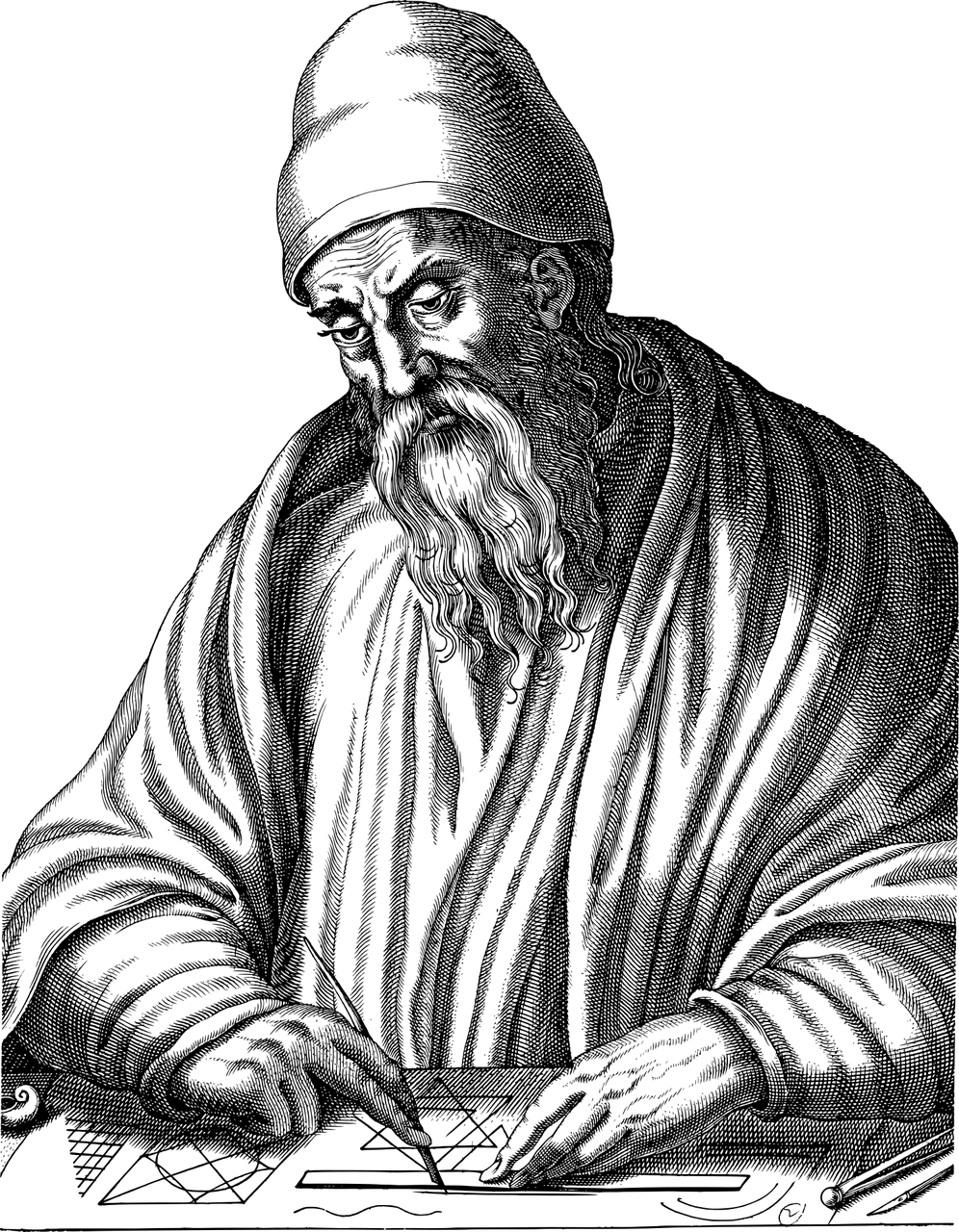



Euclid (Greek: Εὐκλείδης) was an ancient Greek mathematician active as a geometer and logician. Considered the "father of geometry", he is chiefly known for the Elements treatise, which established the foundations of geometry that largely dominated the field until the early 19th century. His system, now referred to as Euclidean geometry, involved new innovations in combination with a synthesis of theories from earlier Greek mathematicians, including Eudoxus of Cnidus, Hippocrates of Chios, Thales and Theaetetus. With Archimedes and Apollonius of Perga, Euclid is generally considered among the greatest mathematicians of antiquity, and one of the most influential in the history of mathematics.


Hartmann Schedel was a German humanist, medical scientist, historian and chronicler.
Schedel was the first to compile a world chronicle, the so-called Visual History of the Earth from the Creation of the World to the 1490s, known as Schedelsche Weltchronik (Schedel's World Chronicle). It was published in 1493 in Nuremberg. About 600 woodcuts for this book were created by the artists and engravers Michael Wolgemuth (1434-1519) and Albrecht Dürer (1471-1528). The illustrations depict biblical scenes, family trees, portraits of famous personalities, and fairy tale or legendary creatures. However, the main ones here were maps of the world, Germany and Central Europe.
Hartmann Schedel was one of the first cartographers to use machine printing. He was also a renowned collector of books, artworks and engravings by old masters.
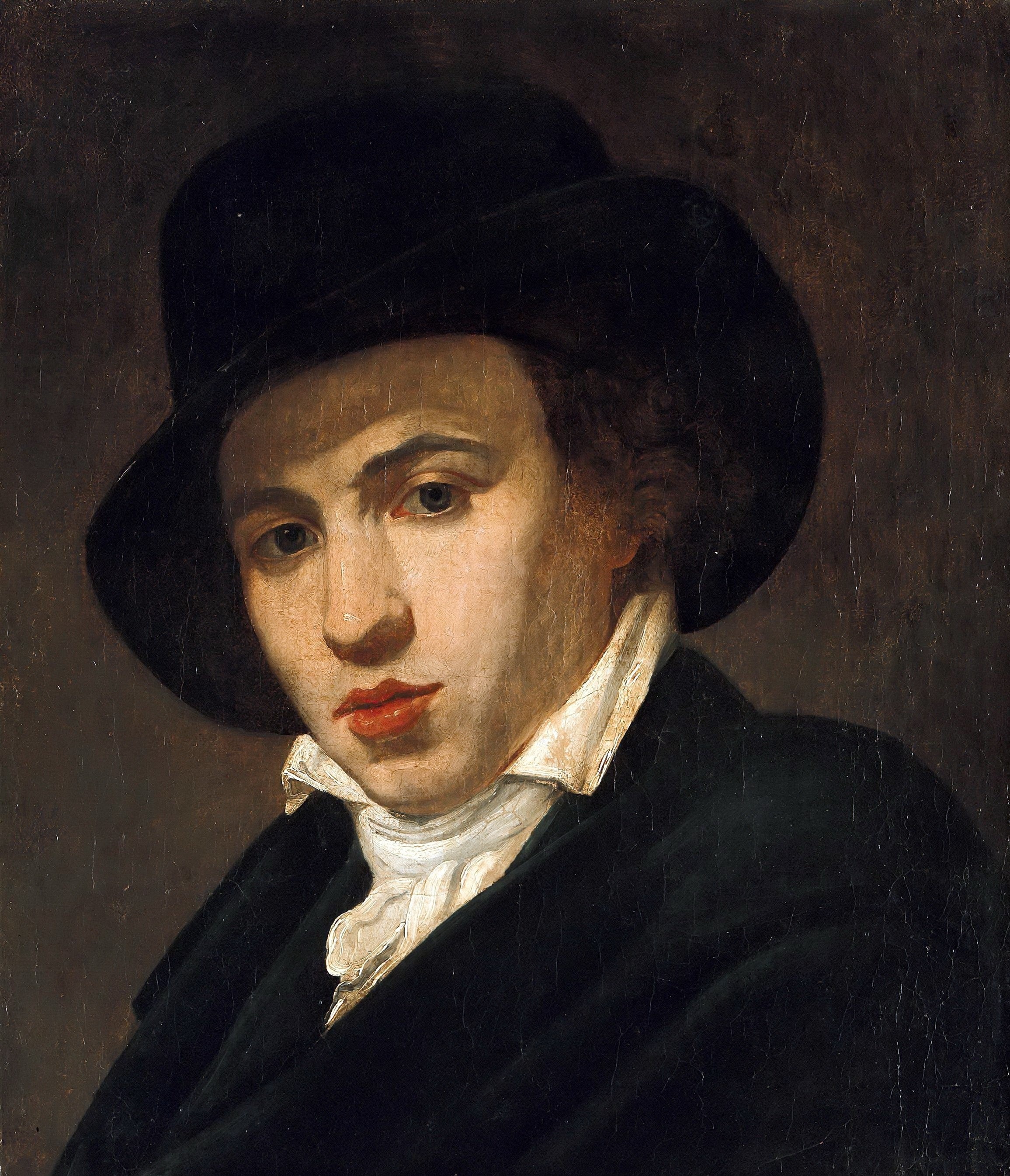


Wilhelm von Kobell was a German painter of the first half of the 19th century. He is known as a landscape painter, animalist and battle painter.
Von Kobell initially produced landscapes and animal paintings, but later focused mainly on battle painting. He visited Vienna and Paris between 1809 and 1810 to study this genre. His battle paintings, based on extensive research, are characterized by striking realism. They are important for the study of military history.