archéologie
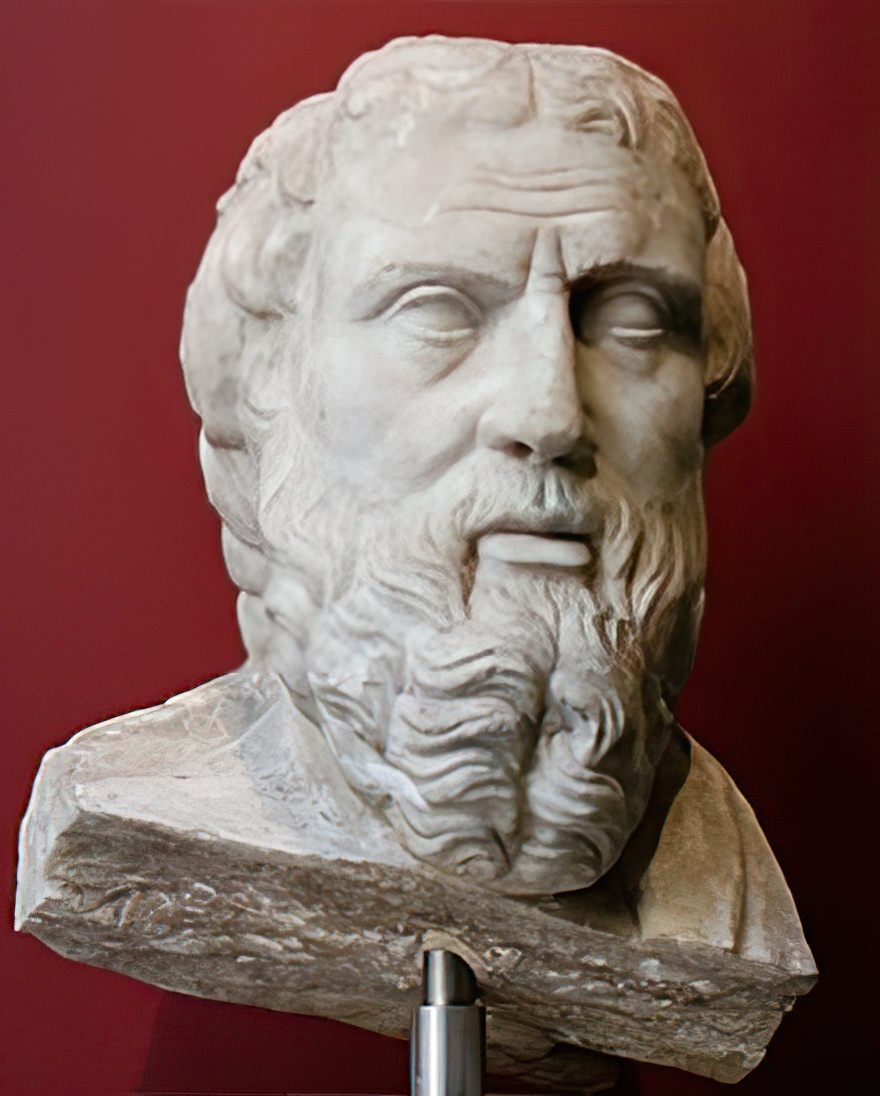

Plutarch, full Roman name Lucius Mestrius Plutarch, was an ancient Greek writer, historian and philosopher of the Roman era.
Plutarch came from a wealthy family, received a good home education, then studied in Athens with the Platonic philosopher Ammonius. In his youth he traveled a lot, twice visited Rome, where he gave public lectures, visited Alexandria, the cities of Balkan Greece. But most of his life Plutarch spent in his native Cheronea, where he was engaged in public and educational activities. At the age of about 50, he became a priest of Apollo at Delphi, as well as an honorary Athenian and Roman citizen.
Some of Plutarch's writings are devoted to various philosophical, didactic, and historical topics. These include "Moral Essays" or "Moralia", "Platonic Questions", "On Monarchy, Democracy and Oligarchy", "Instructions on State Affairs" and others. Plutarch wrote a lot of biographical works, among them "On the Fortune and Valor of Alexander the Great". The greatest popularity enjoyed "Comparative biographies", in which Plutarch recreated the images of prominent political figures of Greece and Rome. In total, 46 paired and 4 single biographies have survived.
A lot of Plutarch's publications are devoted to family and human values in general, which he considers in great detail. Plutarch's humane writings were popular during the Roman Empire, retained their importance in the Byzantine period, and with the beginning of the Renaissance became an integral part of humanistic European culture.


Plutarch, full Roman name Lucius Mestrius Plutarch, was an ancient Greek writer, historian and philosopher of the Roman era.
Plutarch came from a wealthy family, received a good home education, then studied in Athens with the Platonic philosopher Ammonius. In his youth he traveled a lot, twice visited Rome, where he gave public lectures, visited Alexandria, the cities of Balkan Greece. But most of his life Plutarch spent in his native Cheronea, where he was engaged in public and educational activities. At the age of about 50, he became a priest of Apollo at Delphi, as well as an honorary Athenian and Roman citizen.
Some of Plutarch's writings are devoted to various philosophical, didactic, and historical topics. These include "Moral Essays" or "Moralia", "Platonic Questions", "On Monarchy, Democracy and Oligarchy", "Instructions on State Affairs" and others. Plutarch wrote a lot of biographical works, among them "On the Fortune and Valor of Alexander the Great". The greatest popularity enjoyed "Comparative biographies", in which Plutarch recreated the images of prominent political figures of Greece and Rome. In total, 46 paired and 4 single biographies have survived.
A lot of Plutarch's publications are devoted to family and human values in general, which he considers in great detail. Plutarch's humane writings were popular during the Roman Empire, retained their importance in the Byzantine period, and with the beginning of the Renaissance became an integral part of humanistic European culture.