book illustration
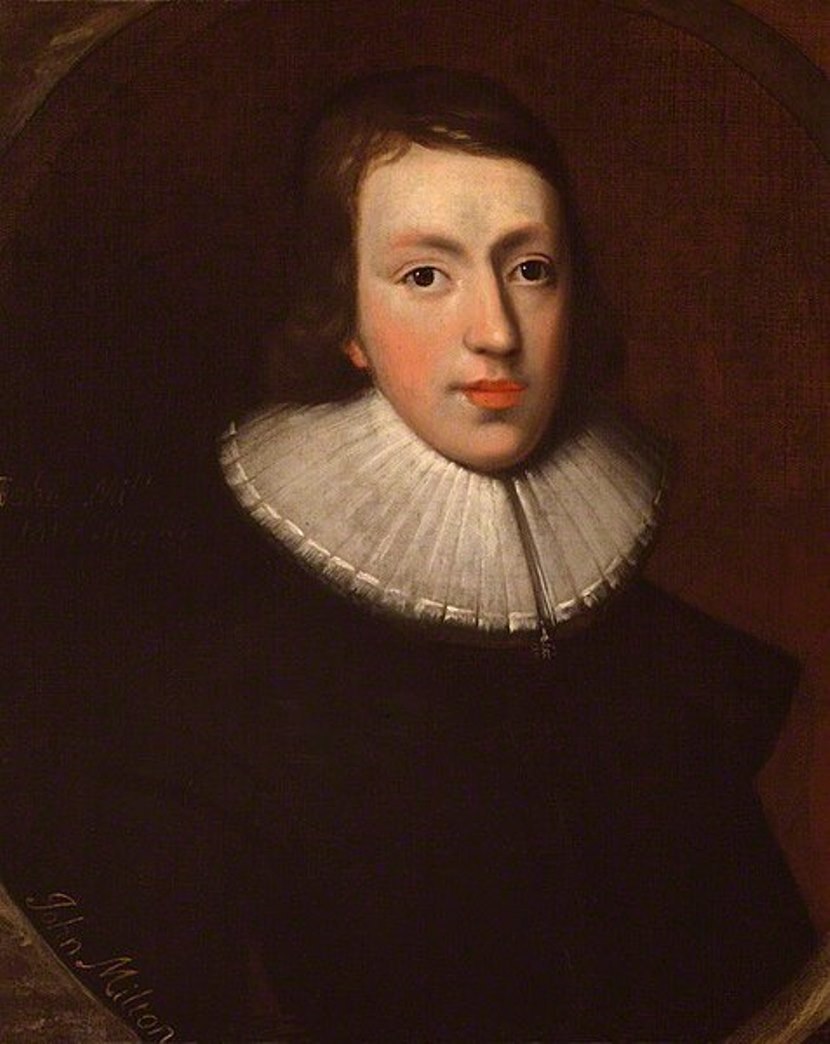


John Milton was a British poet and writer-publicist, intellectual and politician of the English Revolutionary period.
Milton first planned to become a priest, studied at Cambridge University, and then abandoned this activity. Several years he spent reading and self-education, learning many languages. In 1638 Milton traveled around the continent for about a year and a half, spending much time in Italy, primarily in Rome and Florence. He befriended young Italian literati, and his encounter with Galileo further influenced his writing.
Milton became best known for his poem Paradise Lost in Ten Books, which declares its purpose to justify the ways of God to man, but also touches on both universal and personal themes. Milton was the first author to use the word "cosmos" in our modern sense of "outer space," and his space epic takes place in a confidently Copernican universe.
In his prose works, Milton advocated the abolition of the Church of England and the execution of Charles I. From the outbreak of the English Civil Wars in 1642 and long after the restoration of Charles II as king in 1660, he spoke out against tyranny and state-sanctioned religion in all his works. As a Protestant, Milton was often in conflict with the Roman Catholic Church. As a civil servant, Milton became the voice of the English Commonwealth after 1649 and then under Oliver Cromwell, conducting international correspondence and defending the government against polemical attacks from abroad.
John Milton is considered the most important English writer after William Shakespeare. Author of political pamphlets and religious treatises, he is one of the most famous writers of the 1650s, the vibrant era of the English Revolution (Civil War).
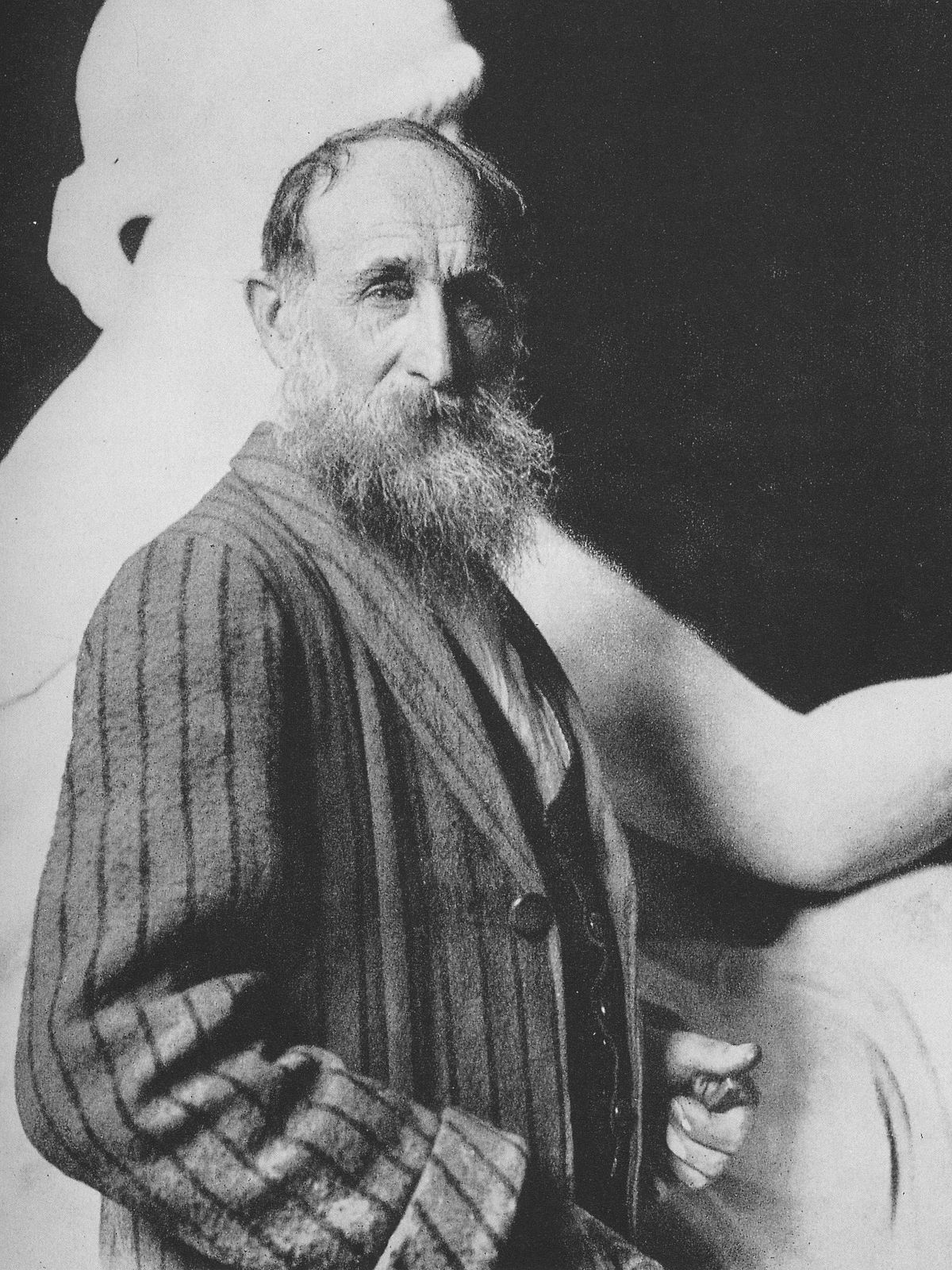


Aristide Maillol was a French artist. He was a painter, sculptor, and printmaker, and is best known for his sculptural works.
Maillol initially worked as a painter, but after seeing Auguste Rodin's sculptures in the early 1890s, he turned to sculpture himself. His early sculptures were influenced by the classical tradition, and often depicted female figures in a simplified, stylized form.
Maillol's sculptures are characterized by their smooth surfaces and simplified forms, which reflect his interest in the pure and timeless beauty of the human body. He often worked in bronze, and his sculptures were typically larger than life size.
In addition to his sculptures, Maillol also created prints, including lithographs and woodcuts. His prints were often based on his sculptural works, and reflected his interest in simplifying form and line.
Maillol continued to work and exhibit his art throughout his life, and his work was shown in galleries and museums around the world. Today, his sculptures are held in the collections of many prestigious institutions, including the Musée d'Orsay in Paris, the Museum of Modern Art in New York, and the Tate Gallery in London.
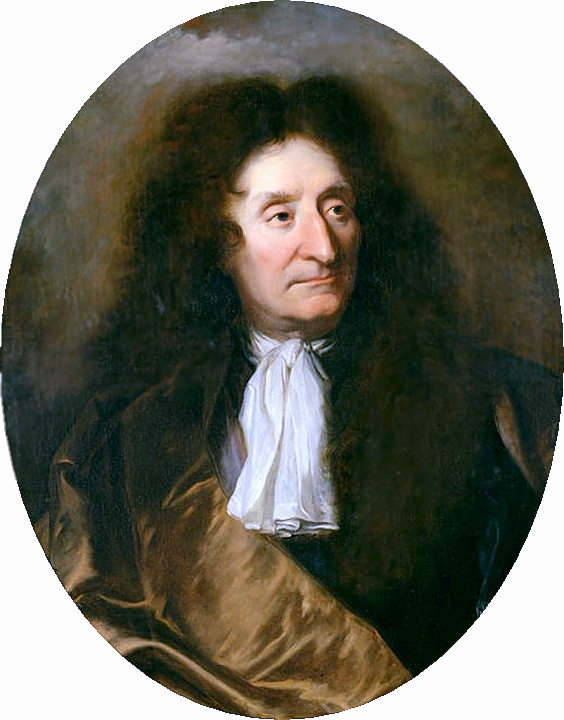
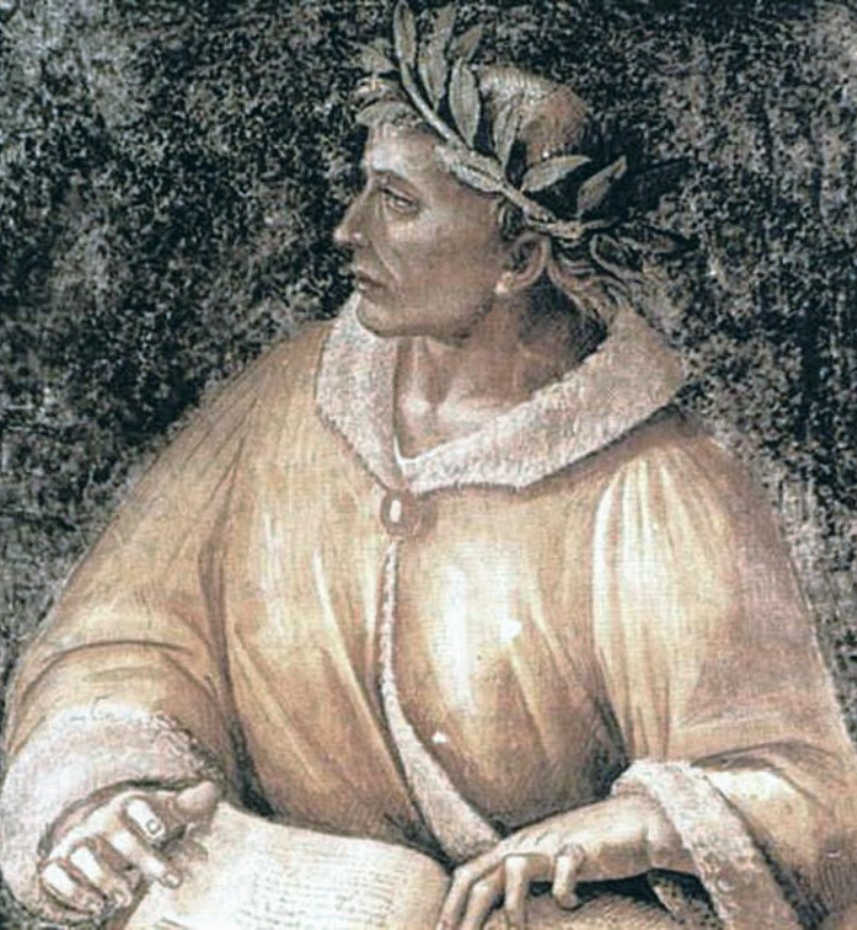






Publius Ovidius Naso, known as Ovidius (Ovid), was an ancient Roman poet who lived during the reign of Emperor Augustus.
Most of the information about the life and work of Ovid, scholars have drawn from his own works, as well as from the works of Seneca the Elder and Marcus Fabius Quintilianus. Ovid was from a fairly high class of "horsemen", studied rhetoric at the maestros of oratory of the ancient Roman Empire, and then went traveling, visiting Athens, Asia Minor and Sicily. As a young man, Ovid held minor public offices, was a member of the college of civil affairs, and served in an office that performed spiritual and secular duties at the state level.
However, Ovid was much more attracted to poetry, and he resigned and about 29-25 BC joined the circle of those chosen under the patronage of Marcus Valerius Messala Corvinus. After publishing Amores, a collection of love-erotic lyrics, around 15-16 BC, Ovid became one of Rome's most popular poets. He became famous for his works in the genre of elegy, as well as for his epic poem Metamorphoses (8 AD), which became one of the most important sources in the study of classical mythology.
For reasons unknown to us, in 8 A.D. Ovid was disgraced and exiled for the rest of his life to Tomes on the Black Sea, where he wrote his "Mournful Elegies" and a poem cycle entitled "Letters from Pontus". A contemporary of Virgil and Horace, Ovid was one of the three canonical representatives of Latin literature.










































































![Captain Thomas Brown | Illustrations of the American ornithology. Edinburgh, [1831]-1835, the dedicatee’s large-paper copy with superior colour](/assets/image/picture_3530891/4356c/d3pq3zhiust9qkvqz2se-qhtxbvjr0elnkb4s60nr-ccr4t6aso8gqamujl2v1698991970jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Captain Thomas Brown | Illustrations of the American ornithology. Edinburgh, [1831]-1835, the dedicatee’s large-paper copy with superior colour](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3530891/4356c/d3pq3zhiust9qkvqz2se-qhtxbvjr0elnkb4s60nr-ccr4t6aso8gqamujl2v1698991970jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)