fiction books
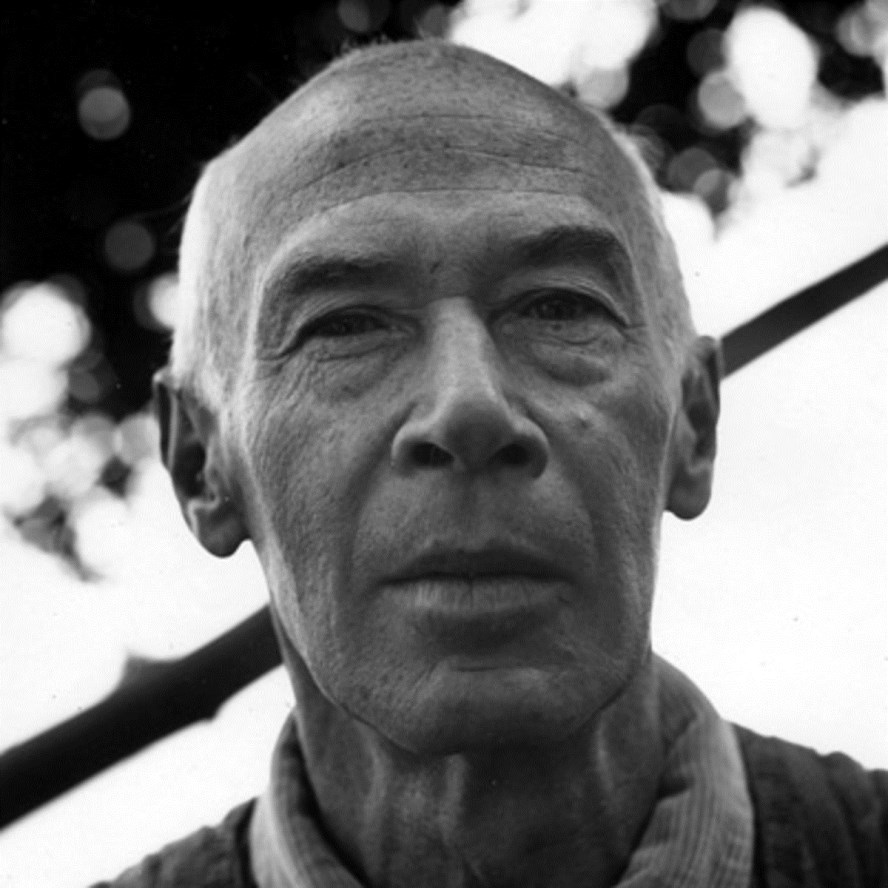



Saul Bellow, real name Solomon Bellows, is a Jewish American writer and Pulitzer Prize and Nobel Prize winner.
Sol Bellow was born in Canada to Jewish immigrant parents from St. Petersburg, Russia, and grew up in Chicago. He attended the University of Chicago and Northwestern University, majoring in anthropology and sociology. Chicago was the setting for many of his novels of the 1970s and 1980s. In 1993, he took a position in the English Department at Boston University.
Bellow wrote his first book, The Dangling Man (1944), while serving in the Merchant Marine during World War II, and he published the novel The Victim in 1947. Saul Bellow is considered one of the most important Jewish American writers who wrote after World War II. Like his predecessors, he offers a Jewish perspective on the themes of alienation and otherness in the difficult postwar era of fragmentation, translating the Yiddish American experience into English.
Bellow has received the world's highest honors for his works. In 1954, his novel The Adventures of Augie March won the National Book Award for fiction. In 1975, the Pulitzer Prize for his novel The Humboldt Gift; the International Herzog Literary Award; and the Croix de Chevalier des Arts et Lettres, France's highest literary honor for non-citizens. In 1976, Bellow was awarded the Nobel Prize for Literature.


Nathaniel Hawthorne is an American writer and author.
Hawthorne is a recognized short story writer and a master of allegorical and symbolic narrative. One of the first fiction writers in American literature, he is best known for his works The Scarlet Letter (1850) and The House of Seven Gables (1851). Hawthorne's artistic works are considered part of the American Romantic movement and, in particular, of so-called dark Romanticism, a popular mid-19th-century fascination with the irrational, the demonic, and the grotesque.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.




Johannes Gensfleisch zur Laden zum Gutenberg was a German inventor and craftsman who introduced letterpress printing to Europe with his movable-type printing press. Though not the first of its kind, earlier designs were restricted to East Asia, and Gutenberg's version was the first to spread across the world. His work led to an information revolution and the unprecedented mass-spread of literature throughout Europe. It also had a direct impact on the development of the Renaissance, Reformation and humanist movement.
His many contributions to printing include the invention of a process for mass-producing movable type; the use of oil-based ink for printing books; adjustable molds; mechanical movable type; and the use of a wooden printing press similar to the agricultural screw presses of the period. Gutenberg's method for making type is traditionally considered to have included a type metal alloy and a hand mould for casting type. The alloy was a mixture of lead, tin, and antimony that melted at a relatively low temperature for faster and more economical casting, cast well, and created a durable type. His major work, the Gutenberg Bible, was the first printed version of the Bible and has been acclaimed for its high aesthetic and technical quality.