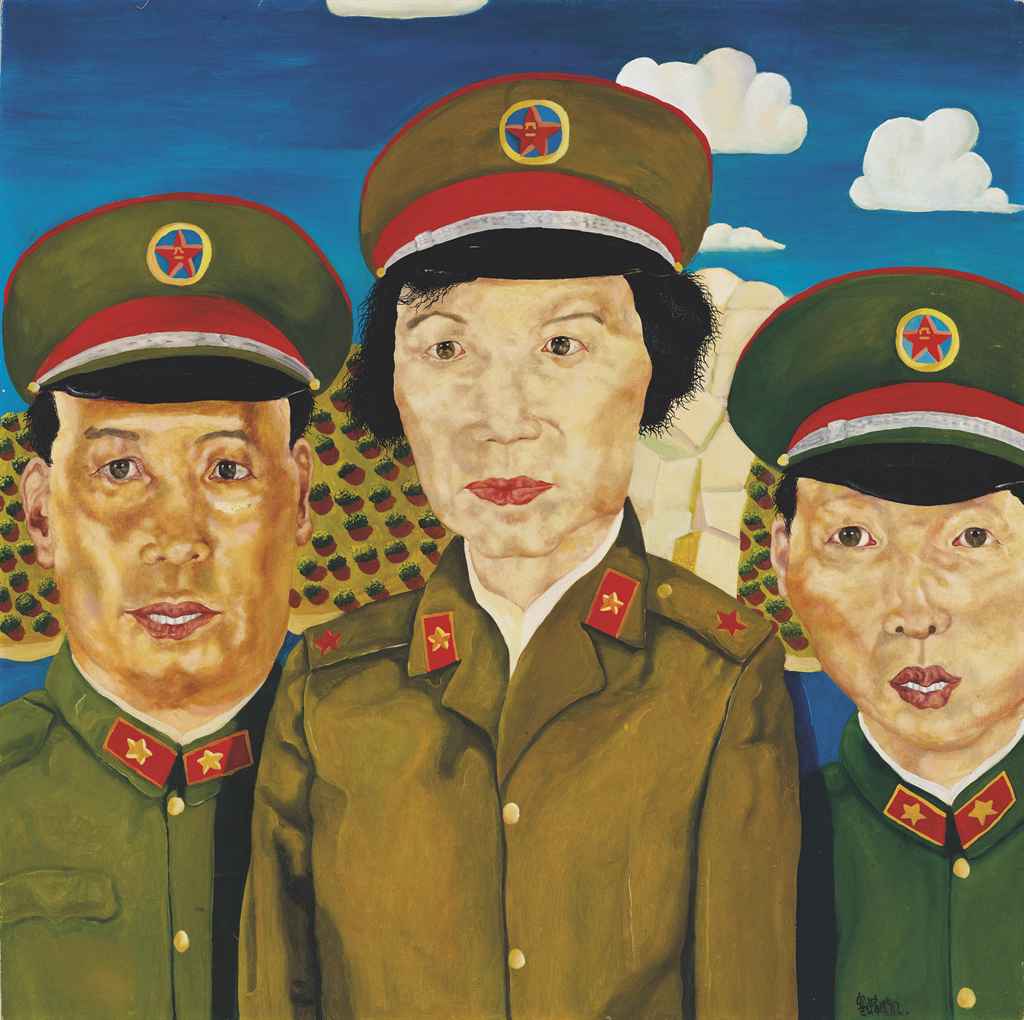
liu wei

Julius Leopold Bernhard Exter was a German painter and sculptor. His work consists mostly of landscapes and portraits.






Julius Adam d. J. was a German animal painter who became known primarily for his paintings of kittens, for which he earned the nickname Kittenadam. His father Julius Adam the Elder was a photographer and lithographer.


Julius Kaesdorf is a German abstractionist painter, poet and jurist of Hungarian origin.

Julius Seyler is a German artist and athlete, the first double European speed skating champion.
He received his art education at the Munich Academy. For several years Julius Seyler lived in the USA and created many paintings depicting the life and history of the Montana Indians, which made him famous.


Caelius Aurelianus was a Greco-Roman physician and theorist of medicine, representative of the Methodist school, and author of treatises on medicine.
He is best known for his translation from Greek into Latin of Soranus of Ephesus' lost treatise On Acute and Chronic Diseases. The bilingual and intercultural nature of the text makes it an invaluable contribution to the study of Greco-Roman medicine.
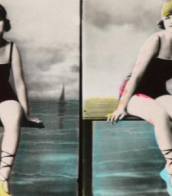

Andreas Vesalius (Dutch: Andries van Wesel) was a Flemish physician, one of the first anatomists of the Renaissance.
Vesalius came from a family of physicians and apothecaries, studied at the Catholic University of Leuven and at the medical school of the University of Paris, where he learned to dissect animals. He also had the opportunity to dissect human cadavers and devoted much time to the study of human bones. He later went to the University of Padua and, after earning his MD degree, was appointed professor of surgery, whose duties included anatomical demonstrations.
Vesalius revolutionized the study of biology and medical practice through his careful description of the anatomy of the human body. Based on observations made by himself, he wrote and illustrated the first complete textbook of anatomy. In 1543 his major work De humani corporis fabrica libri septem ("Seven Books on the Structure of the Human Body"), commonly known as Fabrica, was printed. In this epochal work, Vesalius gave far more extensive and accurate descriptions of the human body than anything that had been done by his predecessors.
In the same year, 1543, the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V appointed him staff physician of his house, and in 1559 Vesalius became physician to the Madrid court of Charles V's son, Philip II.
Vesalius' work made anatomy a scientific discipline with far-reaching implications not only for physiology but for all of biology.