lumière
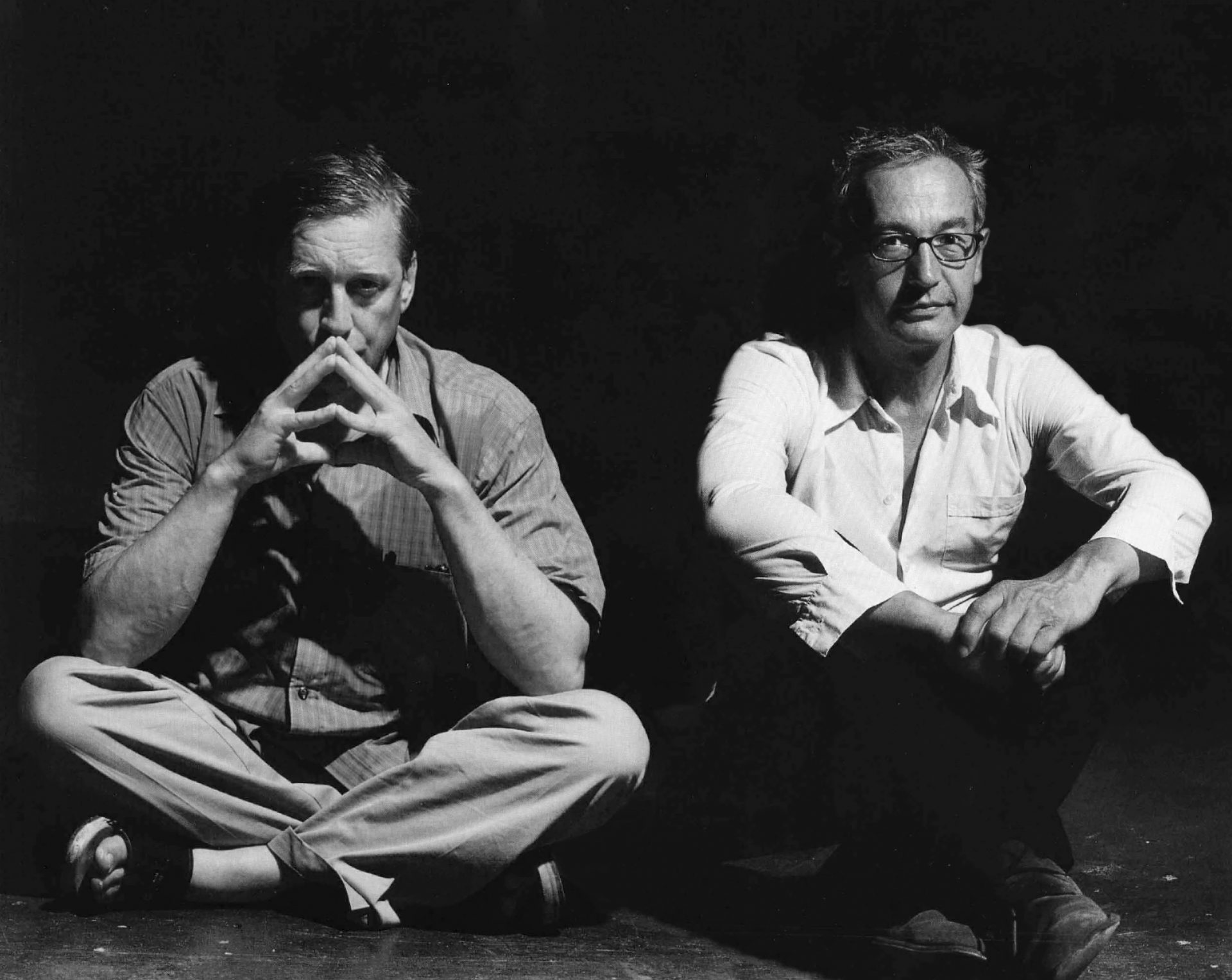

Peter Fischli and David Weiss, often shortened to Fischli/Weiss, were a Swiss artist duo that collaborated beginning in 1979. Their best-known work is the film Der Lauf der Dinge (1987), described by The Guardian as being "post apocalyptic", as it concerned chain reactions and the ways in which objects flew, crashed and exploded across the studio in which it was shot.
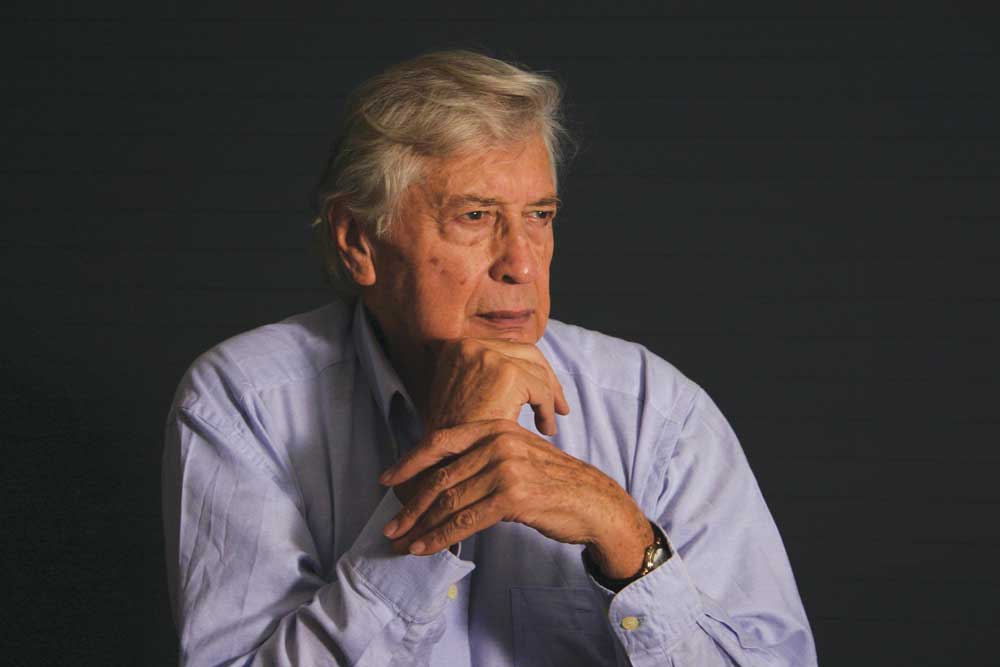


Julio Le Parc, an Argentine artist born in 1928, is celebrated for his significant contributions to modern op art and kinetic art. Educated at the School of Fine Arts in Argentina, Le Parc is a founding member of the influential Groupe de Recherche d’Art Visuel (GRAV) and has received numerous accolades for his work, cementing his status as a key figure in Argentine modern art.
Le Parc's art is renowned for its interactive nature, inviting viewers to experience his works through light, movement, and perception, rather than through narrative or representational content. His piece "Light in Movement" (1962), for example, uses painted drywall, mirrors, stainless steel, nylon thread, and spotlights to create an immersive environment of reflected and refracted light, exemplifying his focus on the sensory experience. Other notable works include "Celule Avec Luminere un Vibration" (1968), which employs light projections to create rhythmic patterns that immerse the viewer in a sensorial experience.
Le Parc's explorations extend to various series such as the "Alchemy" and "Modulation" series, where he experiments with elements like water and light to investigate movement and perception. "Alchemy 175" and "Alchemy 216," from 1991 and 1992 respectively, reflect his fascination with the transformative properties of water and light, while "Modulation 1160" (2004) is recognized for its illusion of motion, showcasing Le Parc's continuous innovation.
Julio Le Parc's works have been exhibited globally, including at prestigious venues like the Perez Art Museum Miami and the Serpentine Sackler Gallery, among others, highlighting his international acclaim and influence.
For those intrigued by the immersive and interactive qualities of Julio Le Parc's art, subscribing for updates on new product sales and auction events related to his works can offer exclusive insights and opportunities to engage with the artist's pioneering contributions to kinetic and op art.


Julio Le Parc, an Argentine artist born in 1928, is celebrated for his significant contributions to modern op art and kinetic art. Educated at the School of Fine Arts in Argentina, Le Parc is a founding member of the influential Groupe de Recherche d’Art Visuel (GRAV) and has received numerous accolades for his work, cementing his status as a key figure in Argentine modern art.
Le Parc's art is renowned for its interactive nature, inviting viewers to experience his works through light, movement, and perception, rather than through narrative or representational content. His piece "Light in Movement" (1962), for example, uses painted drywall, mirrors, stainless steel, nylon thread, and spotlights to create an immersive environment of reflected and refracted light, exemplifying his focus on the sensory experience. Other notable works include "Celule Avec Luminere un Vibration" (1968), which employs light projections to create rhythmic patterns that immerse the viewer in a sensorial experience.
Le Parc's explorations extend to various series such as the "Alchemy" and "Modulation" series, where he experiments with elements like water and light to investigate movement and perception. "Alchemy 175" and "Alchemy 216," from 1991 and 1992 respectively, reflect his fascination with the transformative properties of water and light, while "Modulation 1160" (2004) is recognized for its illusion of motion, showcasing Le Parc's continuous innovation.
Julio Le Parc's works have been exhibited globally, including at prestigious venues like the Perez Art Museum Miami and the Serpentine Sackler Gallery, among others, highlighting his international acclaim and influence.
For those intrigued by the immersive and interactive qualities of Julio Le Parc's art, subscribing for updates on new product sales and auction events related to his works can offer exclusive insights and opportunities to engage with the artist's pioneering contributions to kinetic and op art.





.jpg)
Jean Elysée Puiforcat was a French silversmith, sculptor and designer. Miller's Antiques Encyclopedia calls Puiforcat the «most important French Art Deco silversmith».
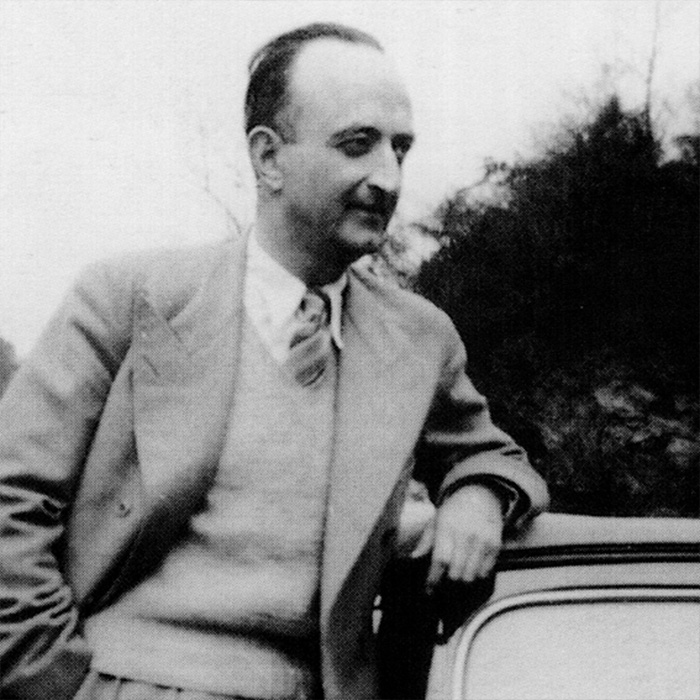
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.

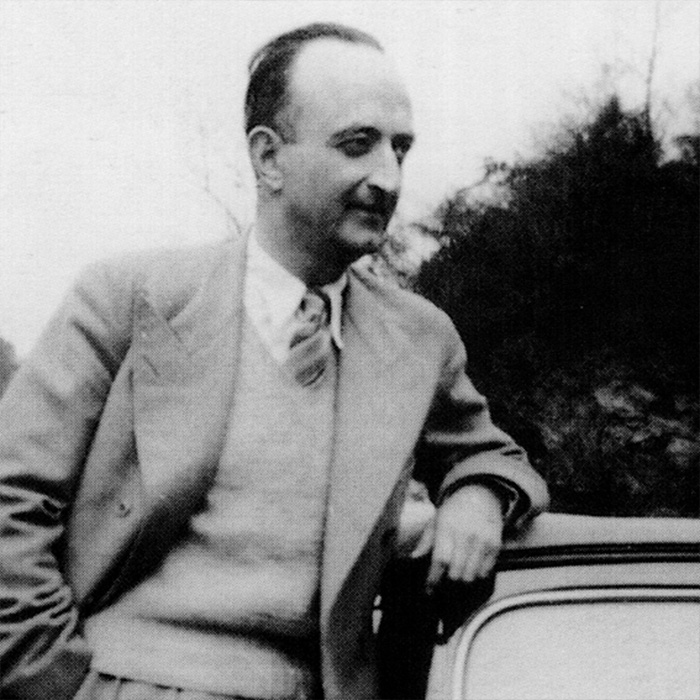
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.

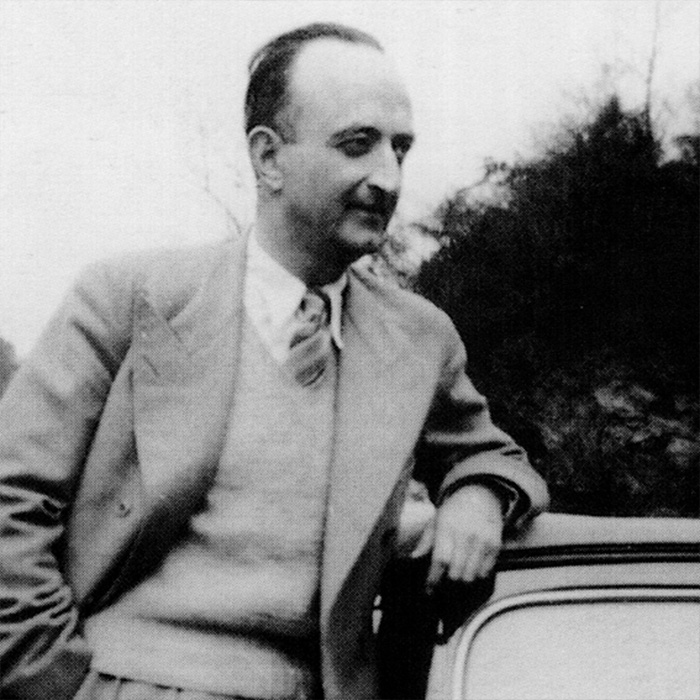
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.

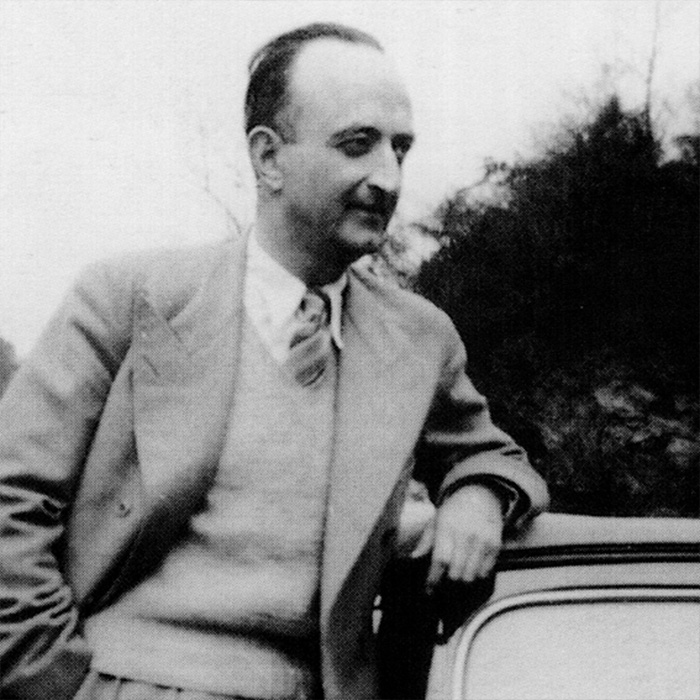
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.

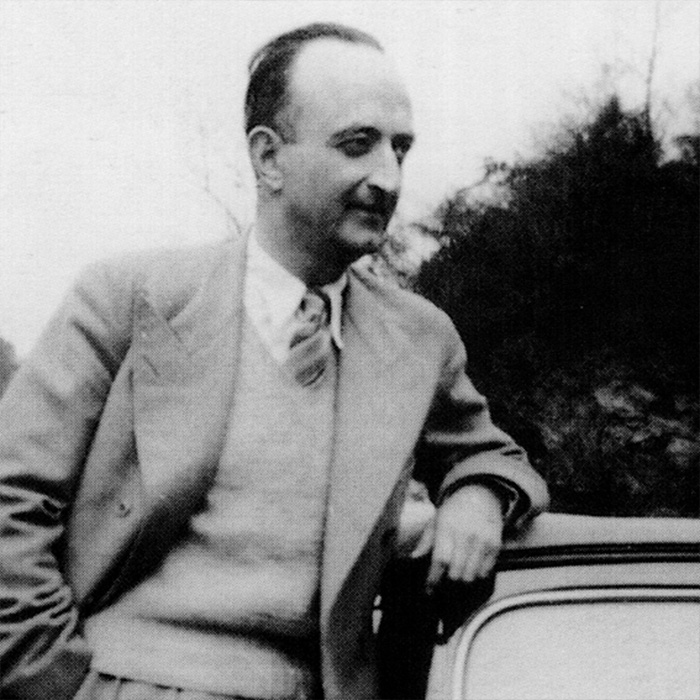
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.

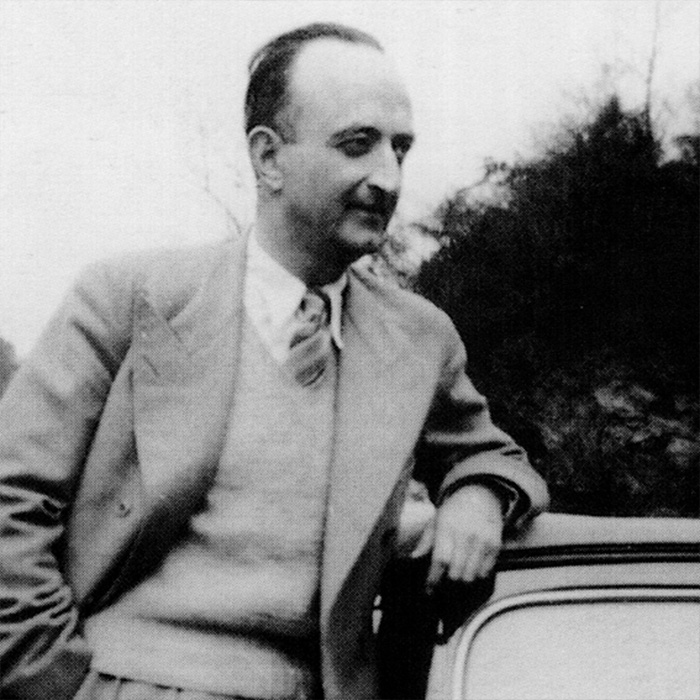
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.

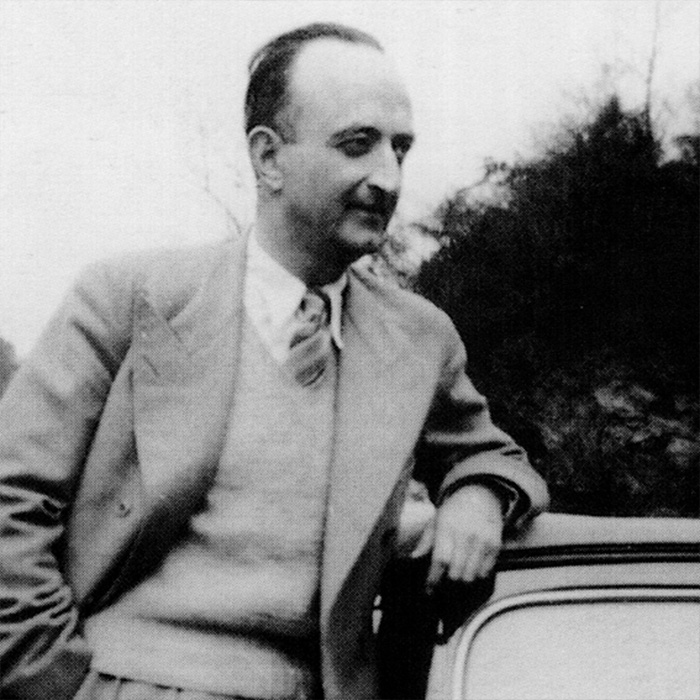
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.

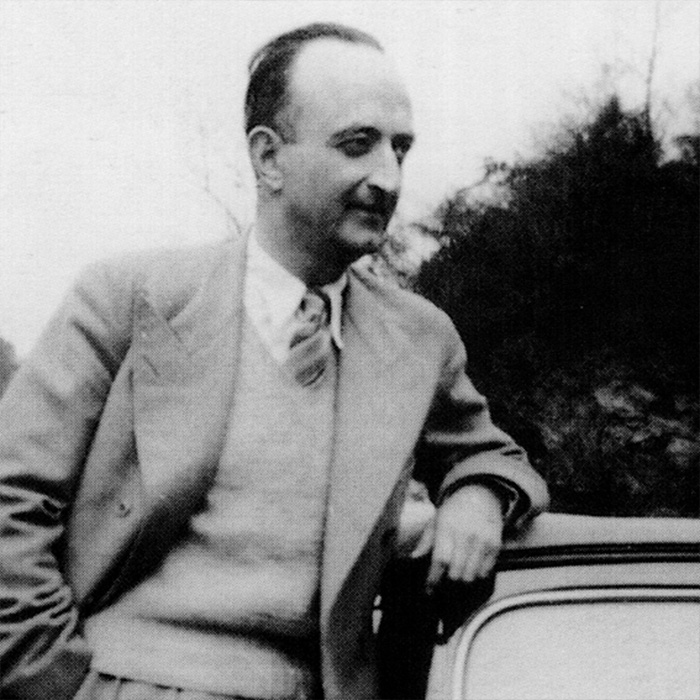
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.

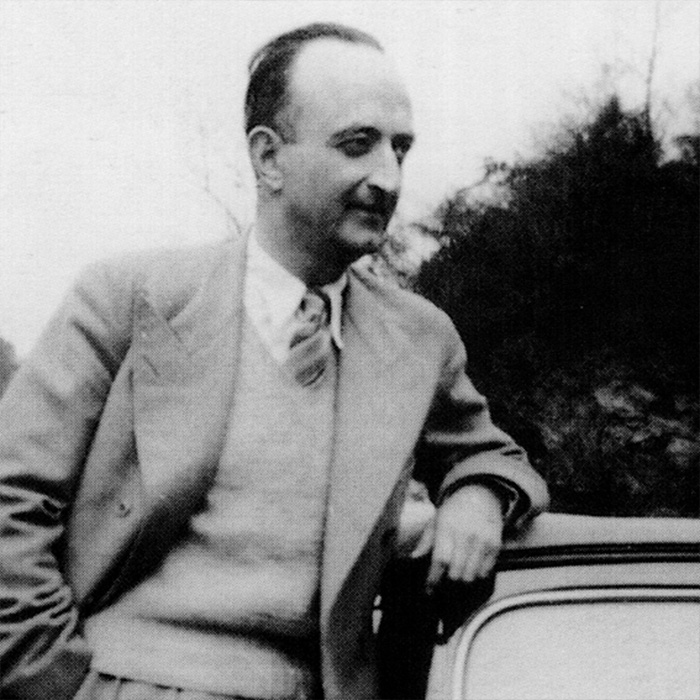
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.
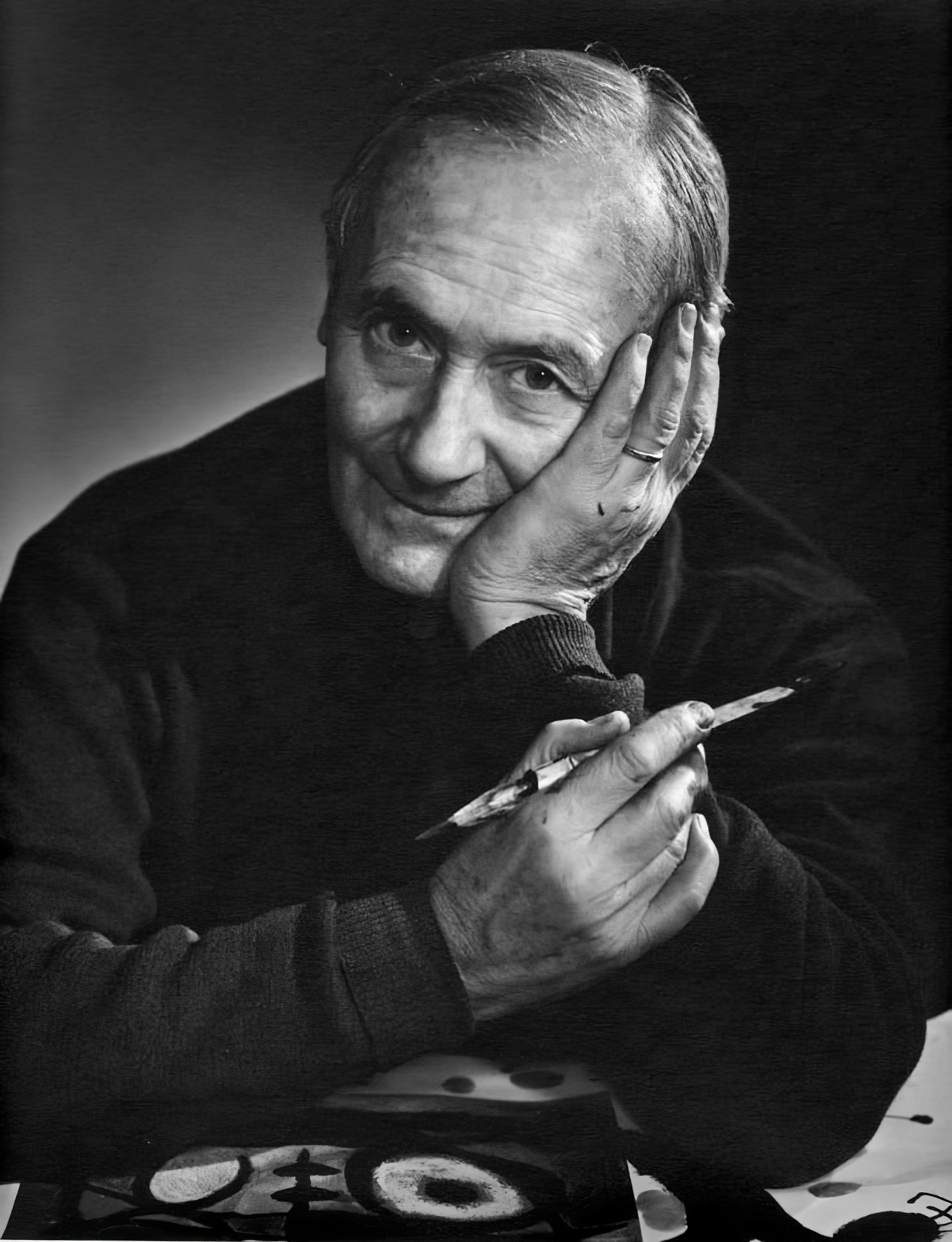


Joan Miró, a celebrated Spanish artist, was a master in painting, sculpture, and ceramics, renowned for his unique style that blurred the lines between Surrealism, Fauvism, and Expressionism. Born in Barcelona to a family of a goldsmith and a watchmaker, Miró grew up immersed in the rich cultural heritage of the Barri Gòtic neighborhood. His artistic journey began with drawing classes at the age of seven and continued at the prestigious La Llotja art academy. Despite an initial venture into the business world, Miró's passion for art prevailed, leading him to abandon his clerical career after a nervous breakdown.
Miró's work is noted for its exploration of the subconscious, often depicting a childlike perspective. This approach was both a critique of traditional painting methods and a means of expressing Catalan pride. His art, challenging to categorize, often featured symbolic elements and nationalistic qualities. One of his notable early works, "The Farm," reflects a transition to a more individual style, blending elements of his Catalan roots with broader artistic influences. This piece, later purchased by Ernest Hemingway, encapsulated the essence of Spain in its imagery.
In Paris, Miró joined the Surrealist movement in 1924, where his work began to reflect the influence of automatism, emphasizing spontaneous, automatic, or subconscious creation. He experimented with various mediums, including painting-poetry and collage, and even ventured into set and costume design for Sergei Diaghilev's Ballets Russes.
During World War II, Miró remained in Spain, and his work from this period, including the 22 Constellations series, reflected an interest in the night, music, and stars. His forms became increasingly abstracted, and he experimented with various techniques, often incorporating primary colors and evocative titles.
Miró's career spanned several decades, during which he continually evolved his style and explored new mediums. His contributions to art were recognized with numerous awards and retrospectives, including a major career retrospective at MoMA in 1941 and the Spanish Gold Medal for Fine Arts in 1980. Among his last major works was a tapestry for the World Trade Center in New York City, created in 1974.
For art collectors and enthusiasts, Joan Miró remains a figure of immense interest, not only for his distinct style and contributions to Surrealism but also for his ability to blend poetic imagery with political commentary. To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Joan Miró, sign up for our updates and immerse yourself in the world of this extraordinary artist.
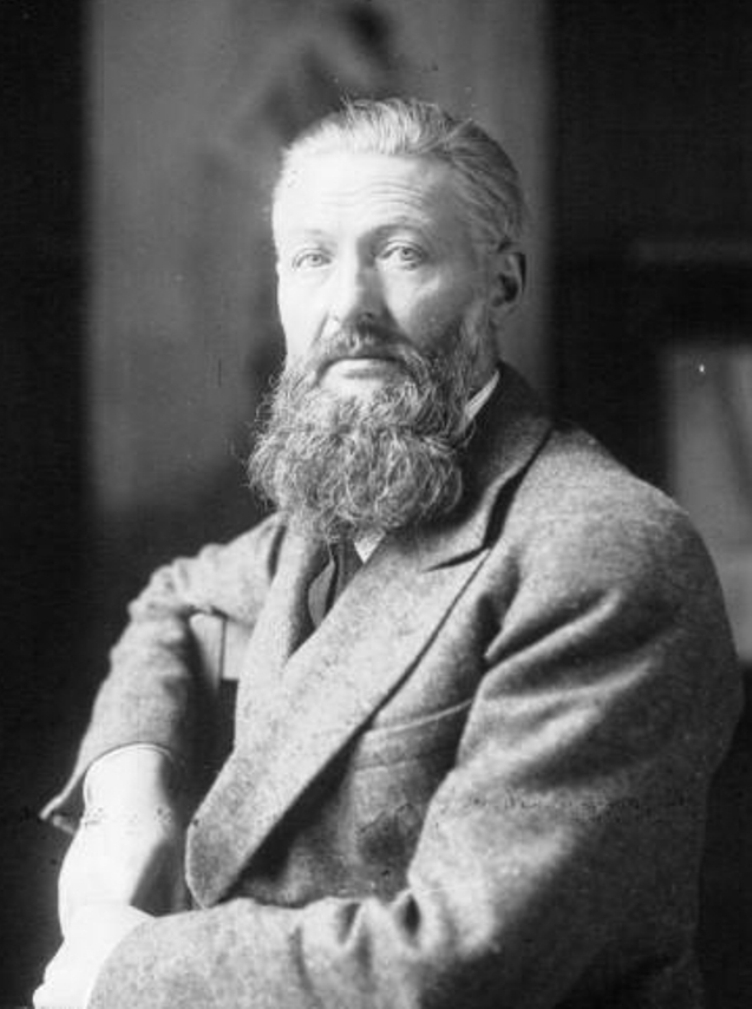




Kees van Dongen was a Dutch-French painter renowned for his vivid and expressive works that placed him at the forefront of the Fauvist movement. Born in 1877 in Delfshaven, Netherlands, van Dongen's journey into the art world began with his education at the Akademie voor Beeldende Kunsten in Rotterdam. His move to Paris in 1897 marked a pivotal moment in his career, immersing him in the bustling avant-garde scene and connecting him with influential circles, including Pablo Picasso and the Fauves. Van Dongen's art, characterized by its striking use of color and bold brushwork, captured the essence of his subjects with a unique blend of realism and abstraction.
Van Dongen's work evolved significantly over time, initially influenced by the dark tones of his Dutch heritage and the works of Rembrandt. His encounter with Fauvism around 1906 brought a dramatic shift towards brighter, more vibrant colors, marking his most iconic phase. His ability to capture the sensuousness and personality of his subjects made him a sought-after portraitist among the French bourgeoisie and celebrities of his time. Notable works include "Femme aux bas noirs" (Woman with Black Stockings), "Les lutteuses" (Lutteuses du Tabarin), and "The Dancer Anita," showcasing his fascination with the human figure, particularly sensuous depictions of women.
Beyond his remarkable contributions to Fauvism, van Dongen's ventures into illustration and his role as a society portraitist underscore his diverse talents and adaptability to the changing tastes of the art market. His works are celebrated in major collections worldwide, including the Hermitage Museum and the National Gallery of Denmark, affirming his lasting impact on the art world.
Collectors and art experts continue to appreciate van Dongen's work for its bold experimentation with color, form, and the evocative portrayal of his subjects. His legacy lives on as a testament to the vibrancy and dynamism of early 20th-century modern art.
For those keen to explore van Dongen's captivating works further and stay informed about new discoveries, exhibitions, and auction events related to his art, signing up for updates is a must. This ensures direct access to the latest sales and scholarly insights into the painter's rich oeuvre, a valuable resource for collectors and enthusiasts alike.

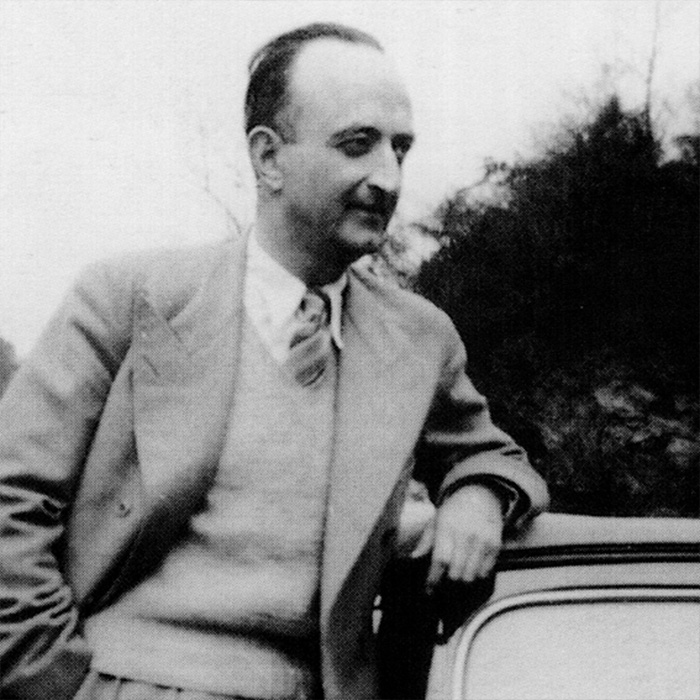
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.































































![LA NOUE, Odet de (1560-1618). Poésies Chrestiennes... Nouvellement mises en lumière par le sieur de la Violette [Joseph Du Chesne] [Genève :] pour les héritiers d’Eustache Vignon, 1594.](/assets/image/picture_1320945/0dc0b/a5989c7d2c14cd6c6b99313f4e4201521616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![LA NOUE, Odet de (1560-1618). Poésies Chrestiennes... Nouvellement mises en lumière par le sieur de la Violette [Joseph Du Chesne] [Genève :] pour les héritiers d’Eustache Vignon, 1594.](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_1320945/0dc0b/a5989c7d2c14cd6c6b99313f4e4201521616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)



