optics

Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer who discovered that the Earth and planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits.
Kepler created the three fundamental laws of planetary motion. He also did seminal work in optics and geometry, calculated the most accurate astronomical tables, and made many inventions and discoveries in physics on which further scientific discoveries by advanced scientists were based.


Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer who discovered that the Earth and planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits.
Kepler created the three fundamental laws of planetary motion. He also did seminal work in optics and geometry, calculated the most accurate astronomical tables, and made many inventions and discoveries in physics on which further scientific discoveries by advanced scientists were based.


Otto Piene was a German-American artist specializing in kinetic and technology-based art, often working collaboratively.


Marin Mersenne (also Marinus Mersennus or le Père Mersenne) was a French mathematician, physicist, philosopher and theologian, and music theorist.
Mersenne was educated at the Jesuit college of La Fleche and went on to study theology in Paris. He also became a member of the Order of the Minims and taught philosophy and theology at Nevers. He developed his ideas about the essence of the world and knowledge, insisting on the importance of experimentation and observation, and contrasted the rational natural world with human reason.
Beginning in 1635, Mersenne founded the Académie Parisienne, the forerunner of the French Academy of Sciences, where France's leading mathematicians and natural philosophers gathered. It provided a forum for the exchange of ideas among scientists and promoted the works of René Descartes and Galileo. The scientist's most famous achievement in mathematics was finding a formula for generating prime numbers, known today as Mersenne's Numbers. In 1644, Mersenne published his studies of Mersenne numbers and their relationship to prime numbers. His work in number theory and arithmetic proved pivotal to the development of mathematics in the seventeenth century.
He corresponded with many other scientists of the era, such as René Descartes, Blaise Pascal, and Pierre Fermat. However, his contributions extend much further, through his role in disseminating the work of the outstanding minds of his time. Mersenne traveled extensively throughout Europe, bringing new scientific ideas to France. He was an important mediator in the exchange of knowledge and contributed to the advancement of science in his era.


Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".




Galileo Galilei was an Italian naturalist, physicist, mechanic, astronomer, philosopher, and mathematician.
Using his own improved telescopes, Galileo Galilei observed the movements of the Moon, Earth's satellites, and the stars, making several breakthrough discoveries in astronomy. He was the first to see craters on the Moon, discovered sunspots and the rings of Saturn, and traced the phases of Venus. Galileo was a consistent and convinced supporter of the teachings of Copernicus and the heliocentric system of the world, for which he was subjected to the trial of the Inquisition.
Galileo is considered the founder of experimental and theoretical physics. He is also one of the founders of the principle of relativity in classical mechanics. Overall, the scientist had such a significant impact on the science of his time that he cannot be overemphasized.


Johann Zahn (German: Johann or Johannes Zahn) was a German scientist and philosopher, optician and astronomer, mathematician and inventor.
Zahn studied mathematics and physics at the University of Würzburg, was professor of mathematics at the University of Würzburg, and served as a canon of the Order of Regular Canon Premonstratensians. His other activities were optics as well as astronomical observations.
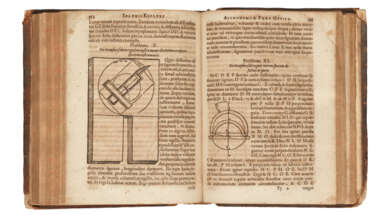
In 1686 Johann Zahn invented and designed a portable camera obscura with fixed lenses and an adjustable mirror, which is the prototype of the camera. In his treatise on optics, Oculus Artificialis Teledioptricus (1702), Zahn gives a complete picture of the state of optical science of his time. He begins with basic information about the eye and then moves on to optical instruments. The book is aimed at eighteenth-century microscope and telescope enthusiasts and includes all the necessary details of construction, from lens grinding to drawings.


Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer who discovered that the Earth and planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits.
Kepler created the three fundamental laws of planetary motion. He also did seminal work in optics and geometry, calculated the most accurate astronomical tables, and made many inventions and discoveries in physics on which further scientific discoveries by advanced scientists were based.


Benedetto Castelli, born Antonio Castelli, was an Italian mathematician. Benedetto was his name in religion on entering the Benedictine Order in 1595.