smith 1793
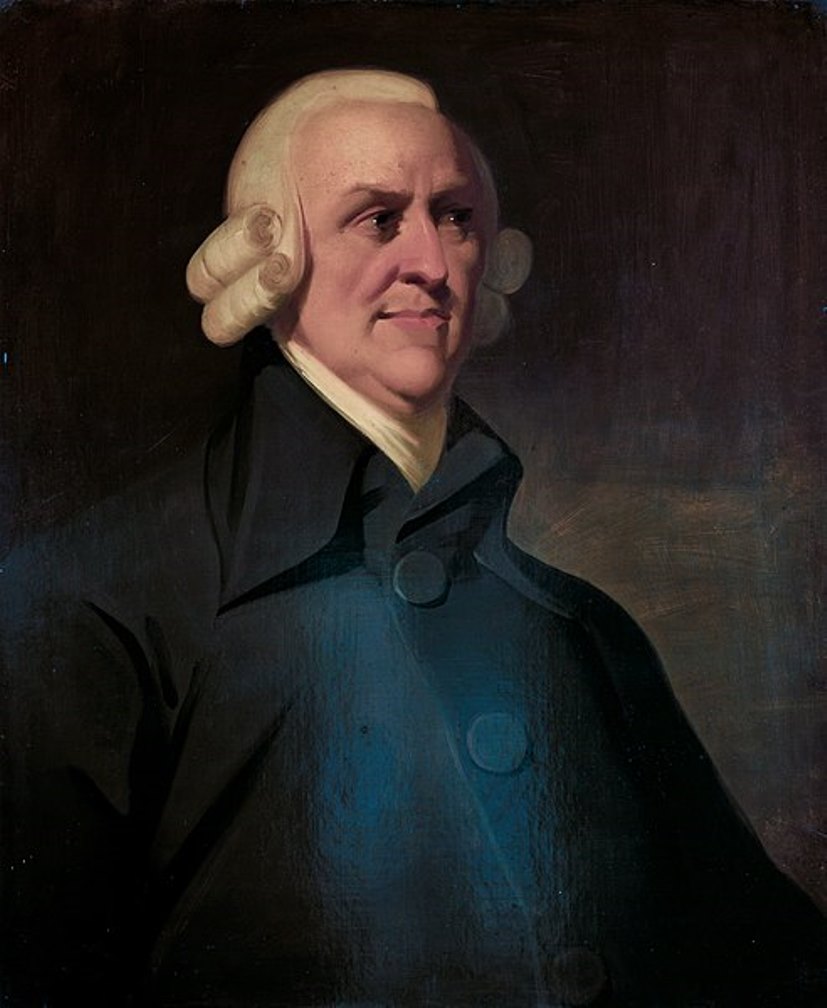






Adam Smith was a Scottish economist and philosopher, one of the founders of economic theory as a science.
After graduating from Balliol College at Oxford University, Smith in 1751 became Professor of Logic and then Professor of Moral Philosophy at the University of Glasgow. And at the same time worked on publishing some of his lectures. His book The Theory of Moral Sentiments was published in 1759. As a philosopher, he wrote on a wide range of subjects: moral philosophy, jurisprudence, rhetoric and literature, and the history of science. He was one of the leading figures of the Scottish Enlightenment. Adam Smith also studied the social forces that give rise to competition, trade, and markets. On his trip to France, he met François Kenet and the Physiocrats.
In late 1763, Smith was given the position of tutor to the young Duke of Buccleugh and resigned his professorship. He began to socialize extensively with the intellectuals of his day, aristocrats and scholars, members of the government and representatives of big commerce, and gradually moved from philosophy to economics.
Adam Smith published his most important work, An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations (abbreviated as The Wealth of Nations), in 1776. It was the first major exposition of the theory of free trade, where the author advocates individual liberty and the accumulation of wealth, while strongly advocating moral justice and duty to society. He describes a system of natural liberty and justice that seeks to raise the standard of living of the general population by equating higher wages with a healthier and more productive labor force. He proves his belief that the limits to growth are political, not economic, and outlines the principles that should guide lawmakers. Smith also lays out a history of economic theory, a historical analysis of the wealth of nations, including China, and predictions for the future.
"The Wealth of Nations" was the first and still remains the most important book on political economy. And Adam Smith himself is considered the founder of classical political economy; he introduced the term "the invisible hand of the market." Although he did not use the word "capitalism", he is called the father of modern capitalism.
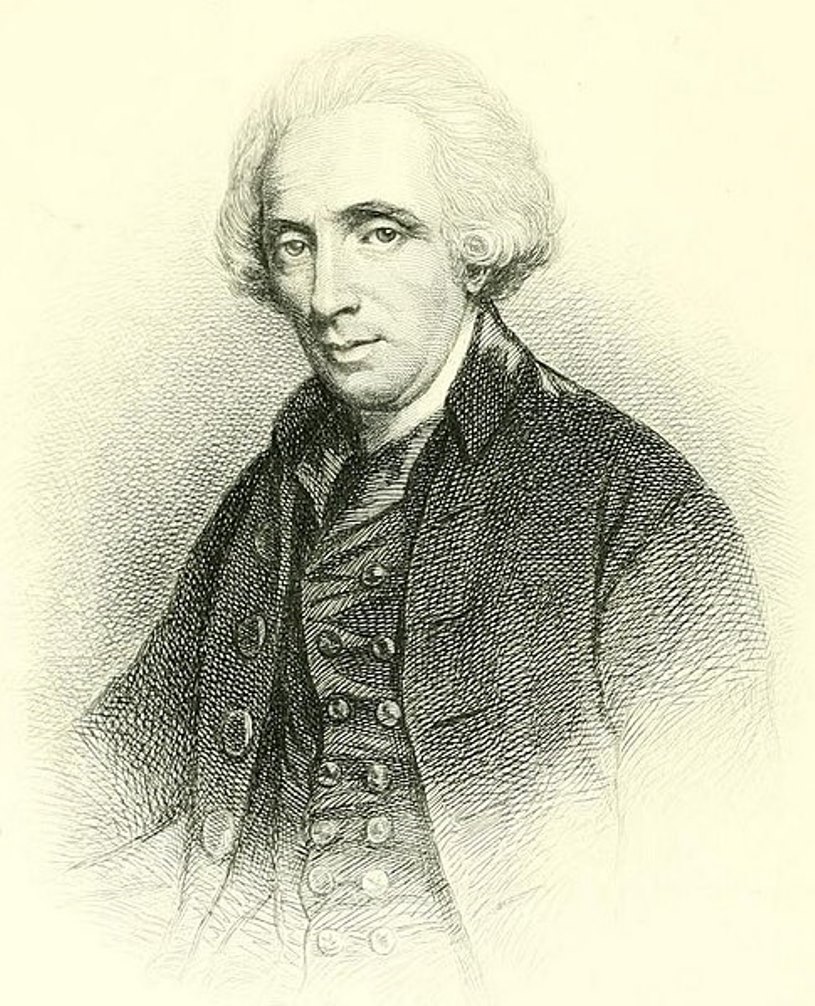







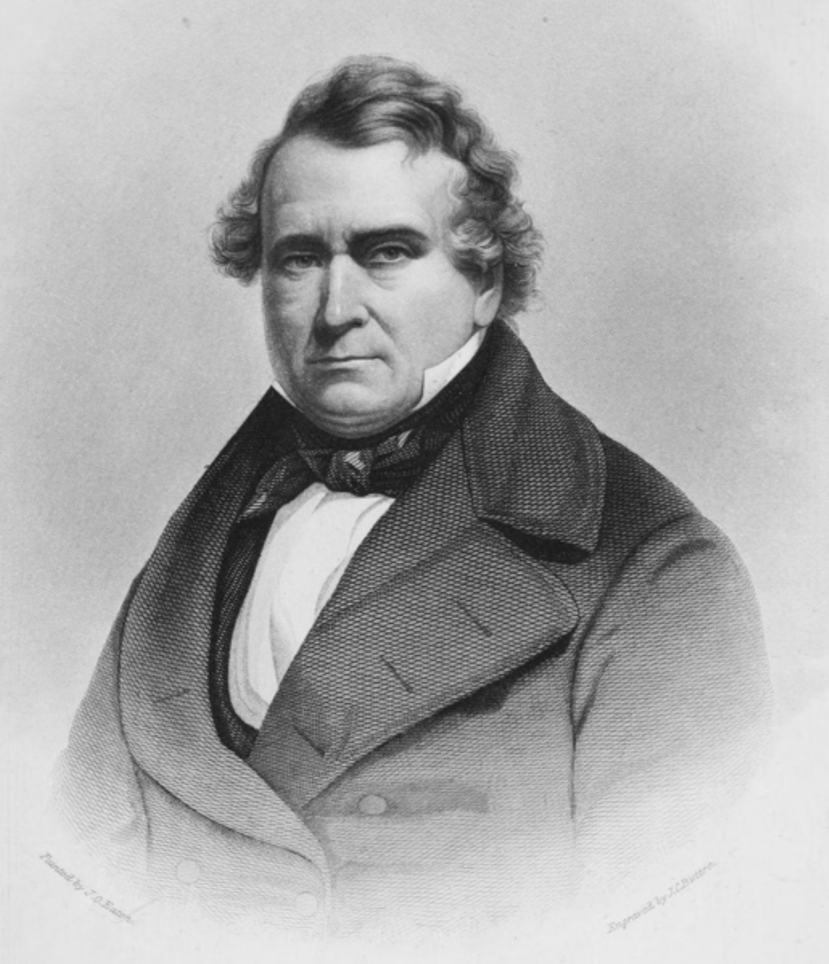
Thomas Loraine McKenney was an American statesman and author.
After the abolition of the U.S. Indian trading program in 1822, then Secretary of War John C. Calhoun established a position in the War Department called Superintendent of Indian Affairs (later to become part of the Bureau of Indian Affairs). McKenney was the first appointed to this position and held it until 1830. Over the years, he worked tirelessly to promote Indian-American relations, advocating for the interests of Indians and striving to preserve the memory of their vanishing culture. Despite his interest in Native American history, McKenney sought to have them assimilated to Euro-American culture through Christian education.
McKenney commissioned leading artists, including Charles Byrd King, to paint portraits of Indian chiefs from more than twenty tribes who visited Washington on official business over a ten-year period. These portraits formed the basis of the government's National Portrait Gallery, first housed in the War Department and later transferred to the Smithsonian Institution. This gallery was featured in part in the three-volume History of the Indian Tribes of North America (1836-1844), with biographical sketches by McKenney, co-authored with Illinois lawyer and writer James Hall.
In 1865, a fire at the Smithsonian Institution destroyed all but a few of the portraits, which are now in the White House. Thus this three-volume book represents the only reliable source on the appearance of many of the most prominent leaders of Indian tribes.

James Hall was an American lawyer, judge, treasurer, and editor.
Hall studied law, fought in the War of 1812, served as a lawyer and circuit judge, newspaper and magazine editor, Illinois state treasurer, and banker in Cincinnati, Ohio. In addition, he was also a historical and fiction writer. In 1828, Hall compiled the first western literary yearbook, Western Souvenir, and edited the Illinois Monthly Magazine. James Hall wrote a travel book, Letters from the West (1828), a novel, The Head of the Harp (1833), and several volumes of short stories.
Hall also contributed to the three-volume History of the Indian Tribes of North America (1836-1844). This book includes portraits of the chiefs of more than twenty Indian tribes, which were painted by noted artists of the day, with biographical sketches by Superintendent of Indian Affairs Thomas L. McKenney.
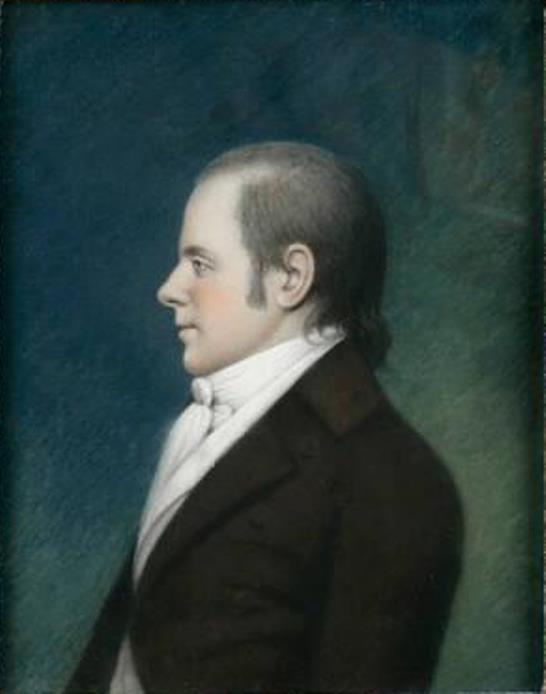


Elihu Hubbard Smith is an American author, writer, and physician.
Smith graduated from Yale College as early as age 11 with a liberal arts education, followed by a medical degree. He worked at New York Hospital and published historical articles on plague and plague fevers.
Elihu Smith was a very active writer: he was a member of the Hartford Witters, wrote the first American comic opera "Edwin and Angelina" (1796), was the editor of the first book anthology of American poetry ("American Poems, Selected and Original," 1793) and the first national American medical journal ("Medical Repository"), and corresponded extensively with many writers and writers of his time.
Smith died at age 27 of yellow fever, which he contracted while treating patients during an outbreak in New York City.
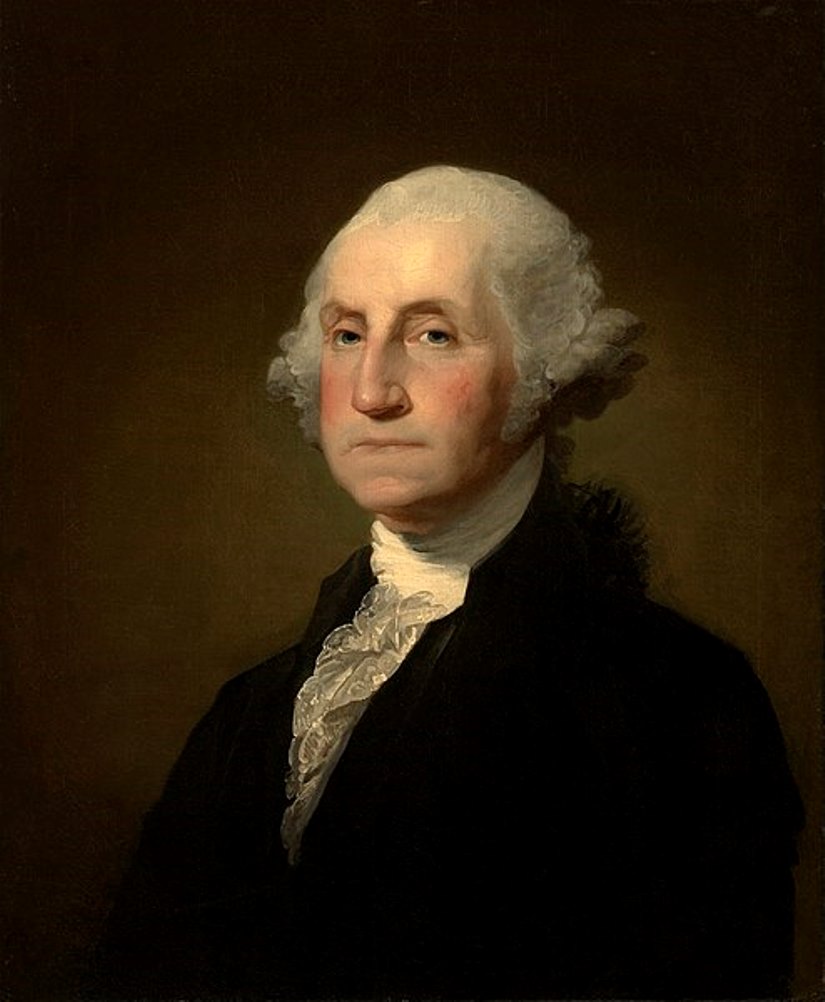


George Washington is the first popularly elected president of the United States of America and one of the founding fathers of the United States.
Born into a noble family in colonial Virginia in February 1732, George Washington served as a Virginian officer with British troops during the French-Indian War (1754-1763) from 1754-1758. This was a territorial war fought largely between the colonies of Britain and France that escalated into a worldwide conflict between the two countries. J. Washington was at the center of the conflicts in the disputed Ohio River Valley area.
In June 1775, he was elected commander-in-chief of the Continental forces in the war already for independence from Great Britain. He commanded American troops throughout the war, becoming famous for his perseverance and bravery.
In 1787, J. Washington represented the state of Virginia as a delegate to the Constitutional Convention. This convention created the Constitution of the United States. In 1789, the Electoral College unanimously elected George Washington president, and in 1792 he was re-elected for a second term. Thus George Washington was in office as President of the United States from April 30, 1789 to March 4, 1797.
As head of state, he helped to strengthen the Union, implement the principles of the Constitution and build the capital of the United States. He was engaged in the formation of the central authorities and system of government, created precedents for the institution of presidents, encouraged the development of the economy, maintained friendly relations with Congress. In foreign policy Washington avoided interference in the affairs of European states.
After leaving the post of president, George Washington lived in Mount Vernon Manor.


George Washington is the first popularly elected president of the United States of America and one of the founding fathers of the United States.
Born into a noble family in colonial Virginia in February 1732, George Washington served as a Virginian officer with British troops during the French-Indian War (1754-1763) from 1754-1758. This was a territorial war fought largely between the colonies of Britain and France that escalated into a worldwide conflict between the two countries. J. Washington was at the center of the conflicts in the disputed Ohio River Valley area.
In June 1775, he was elected commander-in-chief of the Continental forces in the war already for independence from Great Britain. He commanded American troops throughout the war, becoming famous for his perseverance and bravery.
In 1787, J. Washington represented the state of Virginia as a delegate to the Constitutional Convention. This convention created the Constitution of the United States. In 1789, the Electoral College unanimously elected George Washington president, and in 1792 he was re-elected for a second term. Thus George Washington was in office as President of the United States from April 30, 1789 to March 4, 1797.
As head of state, he helped to strengthen the Union, implement the principles of the Constitution and build the capital of the United States. He was engaged in the formation of the central authorities and system of government, created precedents for the institution of presidents, encouraged the development of the economy, maintained friendly relations with Congress. In foreign policy Washington avoided interference in the affairs of European states.
After leaving the post of president, George Washington lived in Mount Vernon Manor.


Karel Dujardin was a Dutch painter and printmaker of the Golden Age of Dutch painting.
He studied with Klaas Berchem and Paulus Potter, traveled to Italy, and lived in Lyon. In 1656 he participated in the founding of the Pictura Society in The Hague.
Dujardin painted mostly Italian landscapes, genre scenes, including scenes from rural life, portraits of elegant people and historical paintings.
Many of Dujardin's works are in the Louvre, the Hermitage (St. Petersburg), as well as in Amsterdam, The Hague, Kassel, and Berlin.


Paolo Veronese, born Paolo Caliari, was a distinguished painter of the 16th-century Venetian school. Renowned for his vibrant use of color and majestic compositions, Veronese's artworks often depicted allegorical, biblical, or historical subjects set within grandiose settings of Renaissance architecture. His mastery in color and illusionary compositions that expand beyond the canvas' confines made him a pivotal figure in the Venetian Renaissance.
His early years were marked by an apprenticeship with Antonio Badile, leading to a significant influence from Mannerist artists and a development of his unique style, characterized by radiant palettes and elegant figures. Paolo Veronese's works, including major altarpieces and large-scale feast scenes, were celebrated for their elaborate detail and classical harmony, reflecting influences from artists like Titian, Raphael, and Parmigianino.
One of Paolo Veronese's specialties was grand scenes of feasts, such as "The Wedding at Cana" and "The Feast in the House of Levi," which showcased his ability to blend narrative with ornate details, often sparking controversy and admiration alike. His significant contributions to the art world, from the full-scale decoration of the Venetian church of S. Sebastiano to the splendid ceiling and wall paintings for the library of S. Marco, left an indelible mark on the Renaissance art scene.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Paolo Veronese's works represent a blend of classical beauty, innovative use of color, and narrative depth, making his paintings a significant focus for art historical study and appreciation.
To stay informed about exhibitions and auction events featuring Paolo Veronese's works, art enthusiasts are encouraged to subscribe to updates from reputable art institutions.
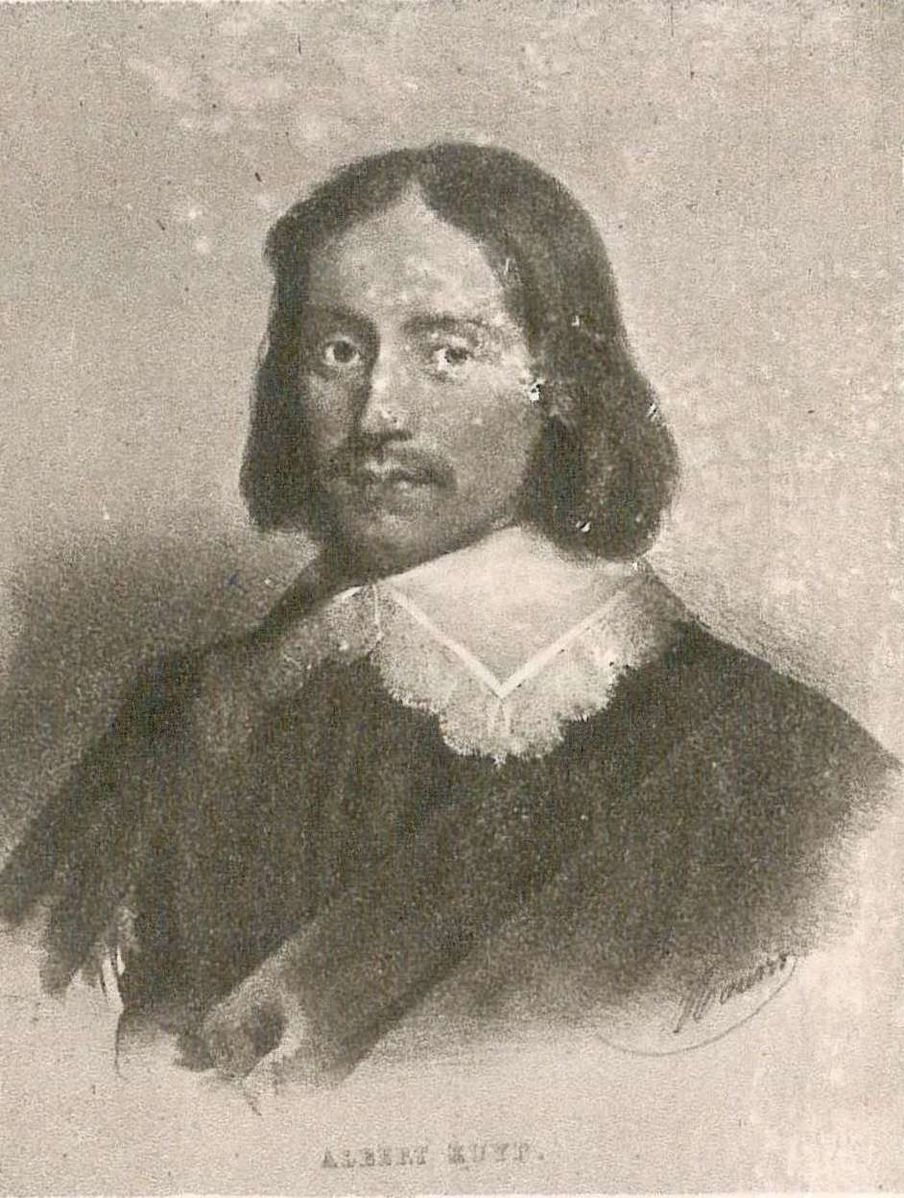


Aelbert Jacobsz. Cuyp was a Dutch Baroque painter, graphic artist and printmaker.
Aelbert is the successor of a dynasty of painters from Dordrecht. He was one of the leading Dutch landscape painters of the Dutch Golden Age. A pupil of his father, the painter Jacob Gerritsz. Cuyp (1594-1651), he is known primarily for his landscapes of the Dutch countryside in the light of early morning or late evening. But Aelbert Cuyp also painted canvases on biblical, mythological, and historical themes, still lifes, and portraits. The Italian style is evident in his works.







![[MARCHAND, Etienne (1755-1793)] and FLEURIEU, Charles Pierre Claret de (1738-1810).](/assets/image/picture_3615476/948e9/5adab94693e4ae36441ca19ea802e8991702422000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[MARCHAND, Etienne (1755-1793)] and FLEURIEU, Charles Pierre Claret de (1738-1810).](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3615476/948e9/5adab94693e4ae36441ca19ea802e8991702422000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)






























![[Icones pictae plantarum rariorum, London, 1790-93], contemporary brown half calf](/assets/image/picture_3102495/14e68/rbmeaut85mh8xwhqav2b5w7so1usfxi4ryc6dve9holgym2nzhyoecrfyvypj1694080941jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[Icones pictae plantarum rariorum, London, 1790-93], contemporary brown half calf](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3102495/14e68/rbmeaut85mh8xwhqav2b5w7so1usfxi4ryc6dve9holgym2nzhyoecrfyvypj1694080941jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)



































