song ying

Paul Gauguin, a French artist born in Paris in 1848, is renowned for his significant contributions to Post-Impressionism, Primitivism, and Synthetism. Gauguin's art is distinguished by his experimental use of color and style, which set him apart from the traditional Impressionist movement.
Gauguin's early life was marked by a period in Peru, which influenced his artistic perspective. Initially, he pursued a career in stockbroking but soon turned to art, driven by financial necessity and a growing passion. His artistic journey began under the mentorship of Impressionist artist Camille Pissarro and through exposure to the works of other avant-garde artists.
The hallmark of Gauguin's work is his exploration of non-Western cultures, particularly during his time in Tahiti and the Marquesas Islands. This period saw the creation of some of his most famous works, including "Where Do We Come From? What Are We? Where Are We Going?" His paintings from this era, characterized by vivid colors and Symbolist themes, reflect a fusion of cultural influences and his quest for a "primitive" expression of spiritual and emotional states.
Despite his innovative style, Gauguin struggled with financial difficulties and health issues throughout his life. His work received little recognition during his lifetime, but posthumously, he gained acclaim for influencing modern artists like Pablo Picasso and Henri Matisse.
Today, Gauguin's works are celebrated in galleries and museums worldwide for their unique blend of cultural influences and artistic innovation. His enduring legacy is a testament to his unique vision and the profound impact he had on the art world.
Collectors and experts in art and antiques, stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Paul Gauguin. Sign up now for exclusive updates and immerse yourself in the world of this visionary artist.


Lyonel Charles Adrian Feininger was an American-German artist renowned for his unique integration of Expressionism, Cubism, and Bauhaus principles. His body of work, which spans several critical decades in modernism's development, is celebrated for its distinctive blend of architectural and nautical motifs, articulated through planar shifts and jagged lines of Cubism, with a vibrant Orphist color palette.
Lyonel Feininger's journey as an artist began in earnest when he was 36, becoming a pivotal figure in various German expressionist groups and a founding member of the Bauhaus, where he led the printmaking workshop. His art, which also includes significant contributions to caricature and photography, explores the intricate relationship between humanity and industrialization, evident in his depictions of architectural and mechanized forms.
His work was subject to Nazi criticism, being labeled as "degenerate," which led to his return to the United States, where he continued to evolve his artistic style. Posthumously, Lyonel Feininger's art has been the focus of several retrospectives, and his pieces, like "Jesuits III," continue to fetch high figures at auctions, underscoring his lasting impact on the art world.
Notably, Lyonel Feininger's "Cathedral" woodcut, representing the Bauhaus's utopian vision, remains one of his most iconic works, symbolizing the integration of art and craftsmanship with its avant-garde yet traditional approach. His legacy is further carried by his sons, Andreas and T. Lux Feininger, who also made their marks in the arts.
For collectors and art and antiques experts, Feininger's work represents a fascinating intersection of various art movements and a testament to the enduring nature of expressive and innovative artistry. To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Lyonel Feininger, consider signing up for updates, ensuring you're informed about the latest opportunities to engage with his enduring legacy.
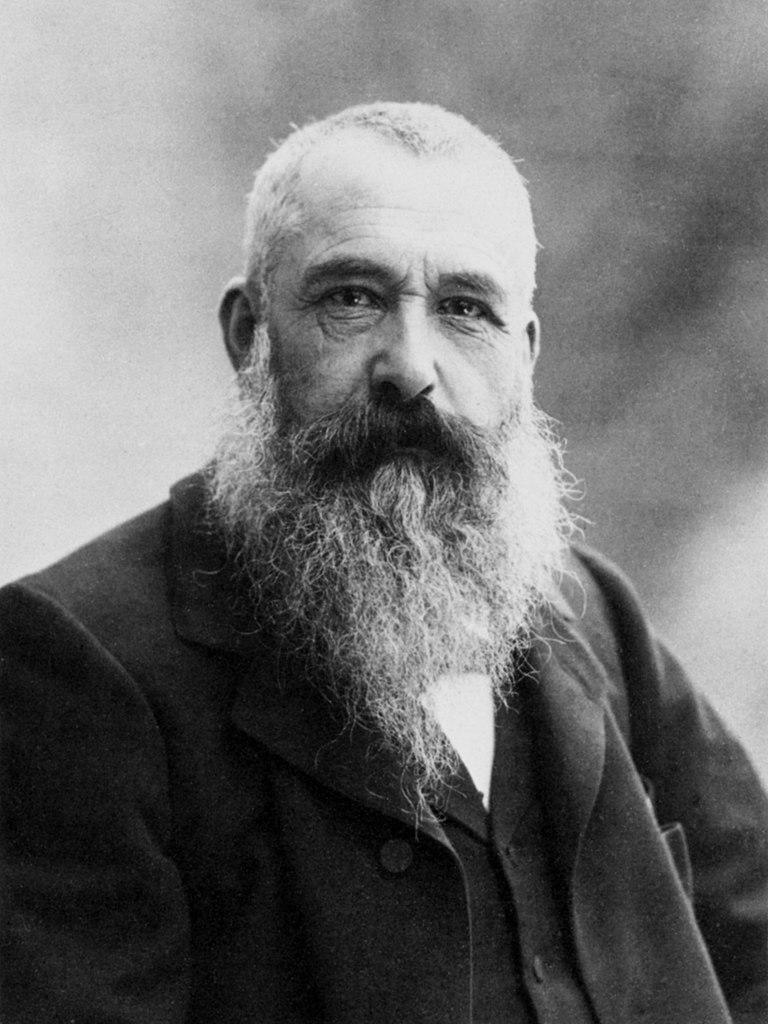


Oscar-Claude Monet, a French painter, revolutionized the art world with his Impressionist style, fundamentally altering the path of modern art. Born in Paris on November 14, 1840, Monet's journey into art was a defiance of his father's business aspirations for him, fueled instead by his mother's support. His early education in the arts began at Le Havre secondary school, where he honed his skills through charcoal caricatures and later, under the mentorship of Eugène Boudin, delved into outdoor painting, a technique that would later define his career.
Monet's works, characterized by their vibrant light and brushed color, are renowned for capturing the essence of their subjects. He often painted the same scene multiple times to depict the changing light and seasons, which is vividly displayed in his series of Haystacks, Rouen Cathedral, and the famed Water Lilies. These pieces, among others, showcase his unique ability to blend color and light, bringing scenes to life in a way that was never seen before.
His most notable works, including "Impression, Sunrise" and the "Water Lilies" series, are celebrated worldwide and remain an integral part of major museum collections, such as the Musée d'Orsay in Paris and the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York. Monet's dedication to capturing the natural world around him led him to reject traditional approaches to composition, color, and perspective. This approach not only set a new standard for art but also laid the groundwork for the Impressionist movement, influencing generations of artists to come.
As an art collector or enthusiast, the legacy of Monet offers an unparalleled glimpse into the genesis of modern art. His works are not just paintings; they are historical landmarks that mark the transition of art from traditional to modernist ideologies.
For updates on new product sales and auction events related to Monet, sign up for our newsletter. Stay informed and connected to the pulse of the Impressionist world.


Edward Lear was an English artist, illustrator, musician, author and poet, who is known mostly for his literary nonsense in poetry and prose and especially his limericks, a form he popularised.
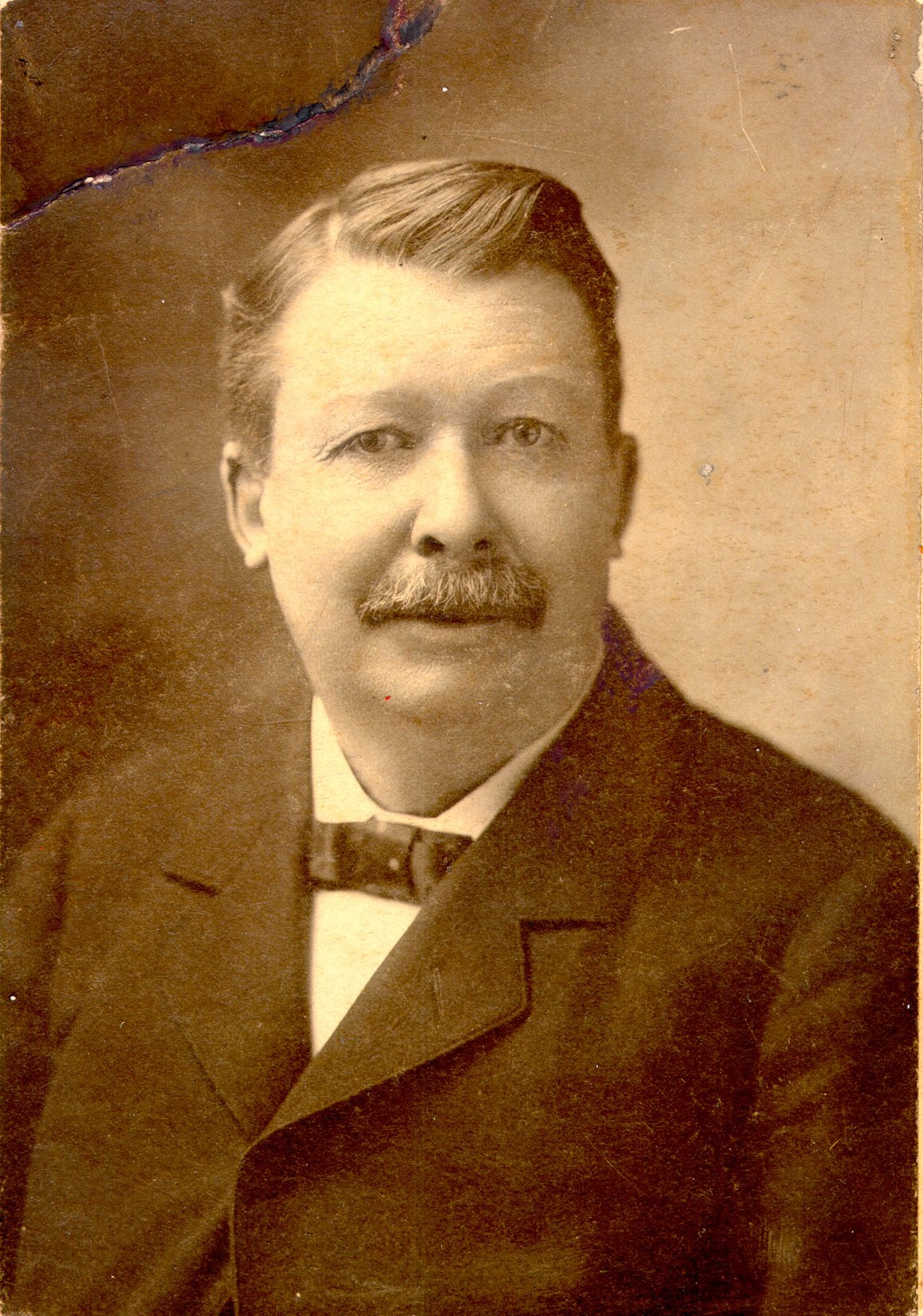


Joel Chandler Harris was an American journalist, Southern writer and folklorist, abolitionist, and author of Uncle Remus's Tales.
Joel was a very inquisitive and witty child, reading a great deal. From the age of 13 he worked as a typesetter and then as a reporter for several newspapers; in 1876 he became deputy editor at Atlanta Construction, where he worked for 24 years. As a journalist, Harris was an active abolitionist, advocating for black rights and against slavery.
At Atlanta Construction, Harris began publishing his now-famous Uncle Remus stories, using folklore he had heard from black workers on the plantation. These tales made Joel Harris famous and earned him a firm place in the classics of American literature. The general outline of the series of stories was simple: Uncle Remus, a wise and good-natured old black man, tells stories about Brother Rabbit, Brother Fox and other animals to the plantation owner's young son - through his prism of worldview.
Uncle Remus: His Songs and Sayings was first published in book form in 1880, and others followed. Harris also wrote six children's books set on a Georgia plantation, several novels and novellas.
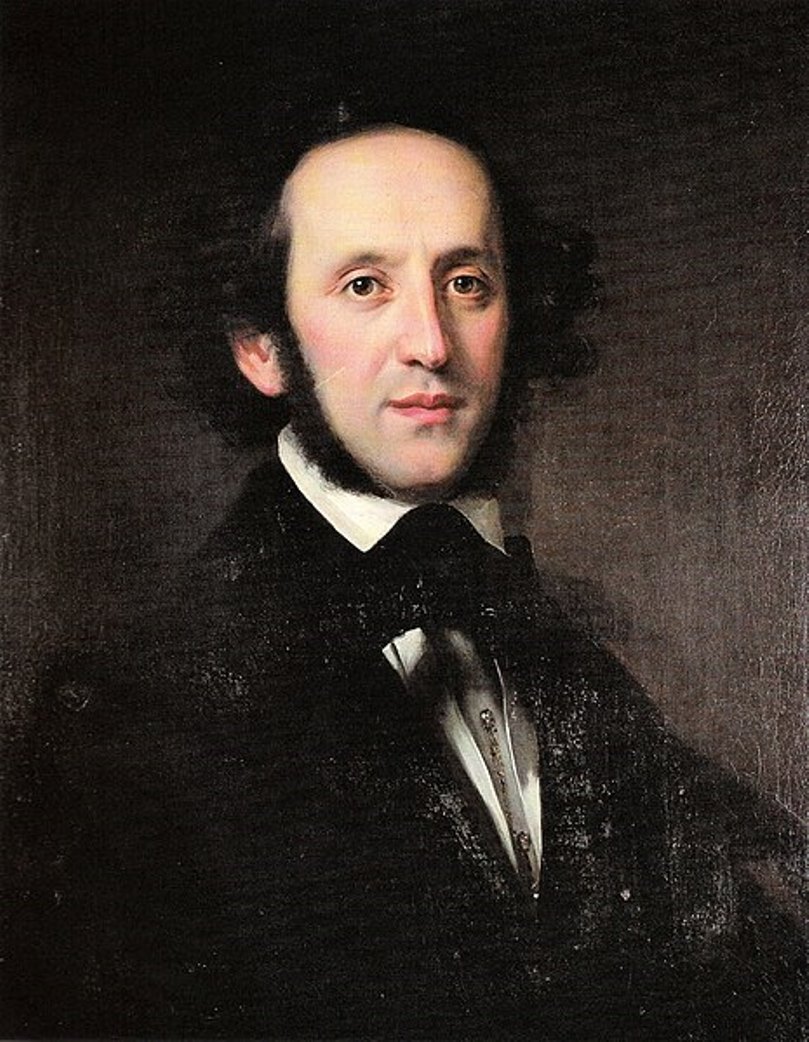


Felix Mendelssohn (full name Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy) was a German composer, pianist, conductor, teacher, and one of the greatest representatives of Romanticism in music.
Felix was born into a Jewish musical family that later converted to Christianity. He received a versatile education and already as a child wrote many musical compositions, including 5 operas, 11 symphonies for string orchestra, concertos, sonatas and fugues. Mendelssohn's first public performance took place in Berlin in 1818, when he was nine years old. In 1821 Mendelssohn was introduced to J.W. von Goethe, for whom he performed works by J.S. Bach and Mozart and to whom he dedicated his Piano Quartet No. 3 in B minor. A friendship developed between the famous wise poet and the 12-year-old musician.
A few years later, the talented musician began conducting in various orchestras in Europe, and became acquainted with Carl Weber. In England, where Mendelssohn visited very often, by the middle of the 19th century his music had become very popular, even with Queen Victoria he was the most favorite composer. He dedicated his Symphony No. 3 in A minor major (Scottish Symphony) to the Queen.
Among Mendelssohn's most famous works are A Midsummer Night's Dream (1826), the Italian Symphony (1833), a violin concerto (1844), two piano concertos (1831, 1837), the oratorio Elijah (1846) and several chamber pieces. The tradition of playing the "Wedding March" from A Midsummer Night's Dream in wedding processions dates back to its performance at the wedding of a royal princess in 1858, already after Mendelssohn's death.
In 1843, Mendelssohn founded a conservatory in Leipzig, where he taught composition with Schumann. Mendelssohn was one of the first great Romantic composers of the nineteenth century.