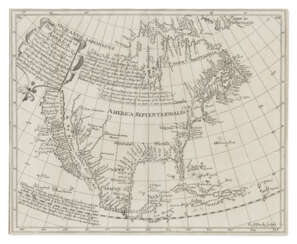
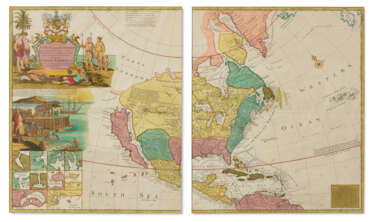
south america
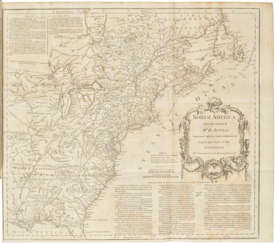
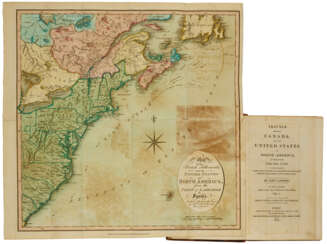
Thomas Jefferys was an 18th-century British cartographer and geographer, engraver and publisher.
As the best in the business of map-making, Jefferys held the honorary title of "King George III's geographer". He is known for his detailed and large-scale maps of the districts and counties of Great Britain as well as North America, particularly Virginia (1776). He was the leading map supplier of his day, engraving and printing maps for government and other official bodies.
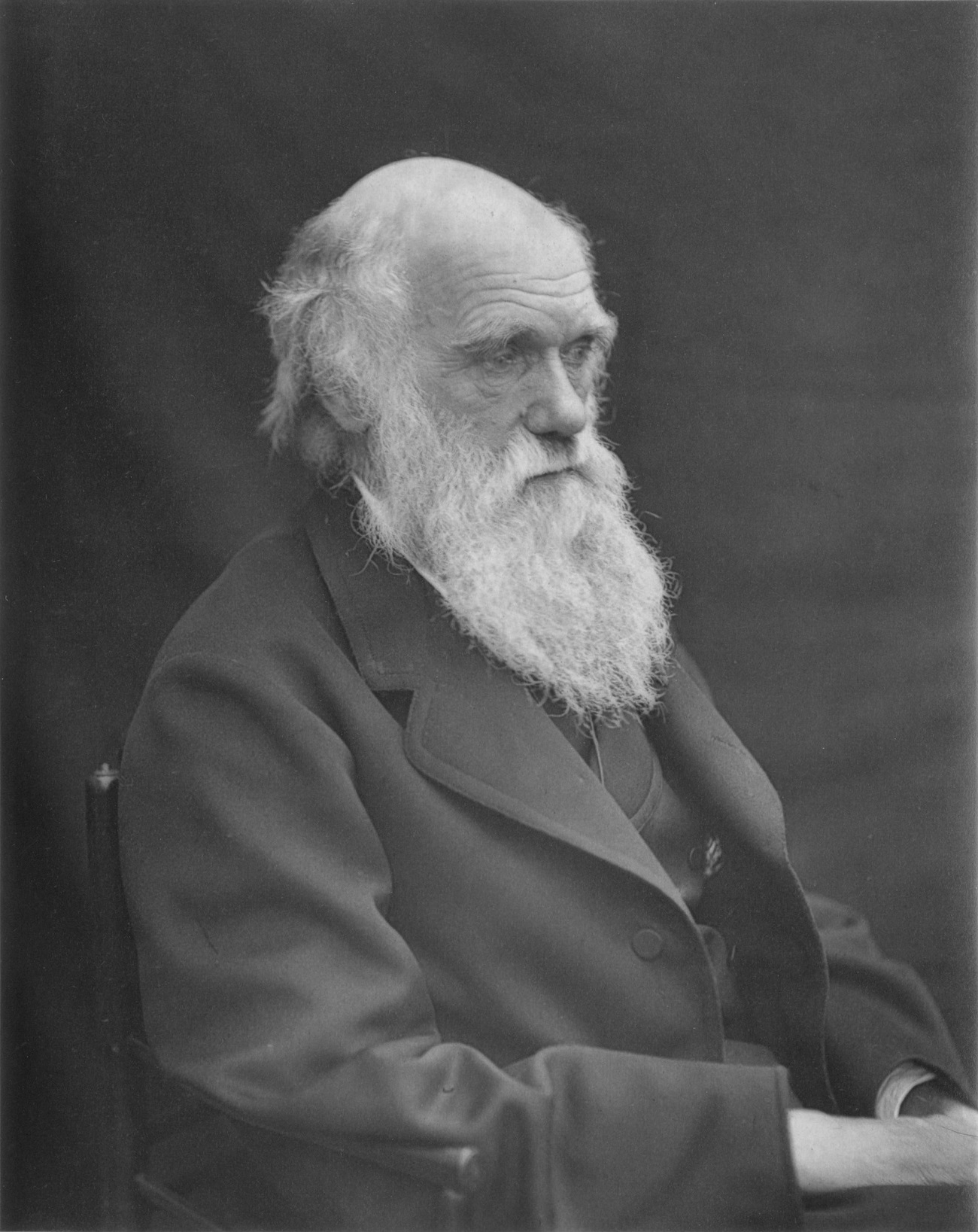


Charles Robert Darwin was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for contributing to the understanding of evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a common ancestor is now generally accepted and considered a fundamental concept in science. In a joint publication with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding. Darwin has been described as one of the most influential figures in human history, and he was honoured by burial in Westminster Abbey.


Thomas Jefferys was an 18th-century British cartographer and geographer, engraver and publisher.
As the best in the business of map-making, Jefferys held the honorary title of "King George III's geographer". He is known for his detailed and large-scale maps of the districts and counties of Great Britain as well as North America, particularly Virginia (1776). He was the leading map supplier of his day, engraving and printing maps for government and other official bodies.
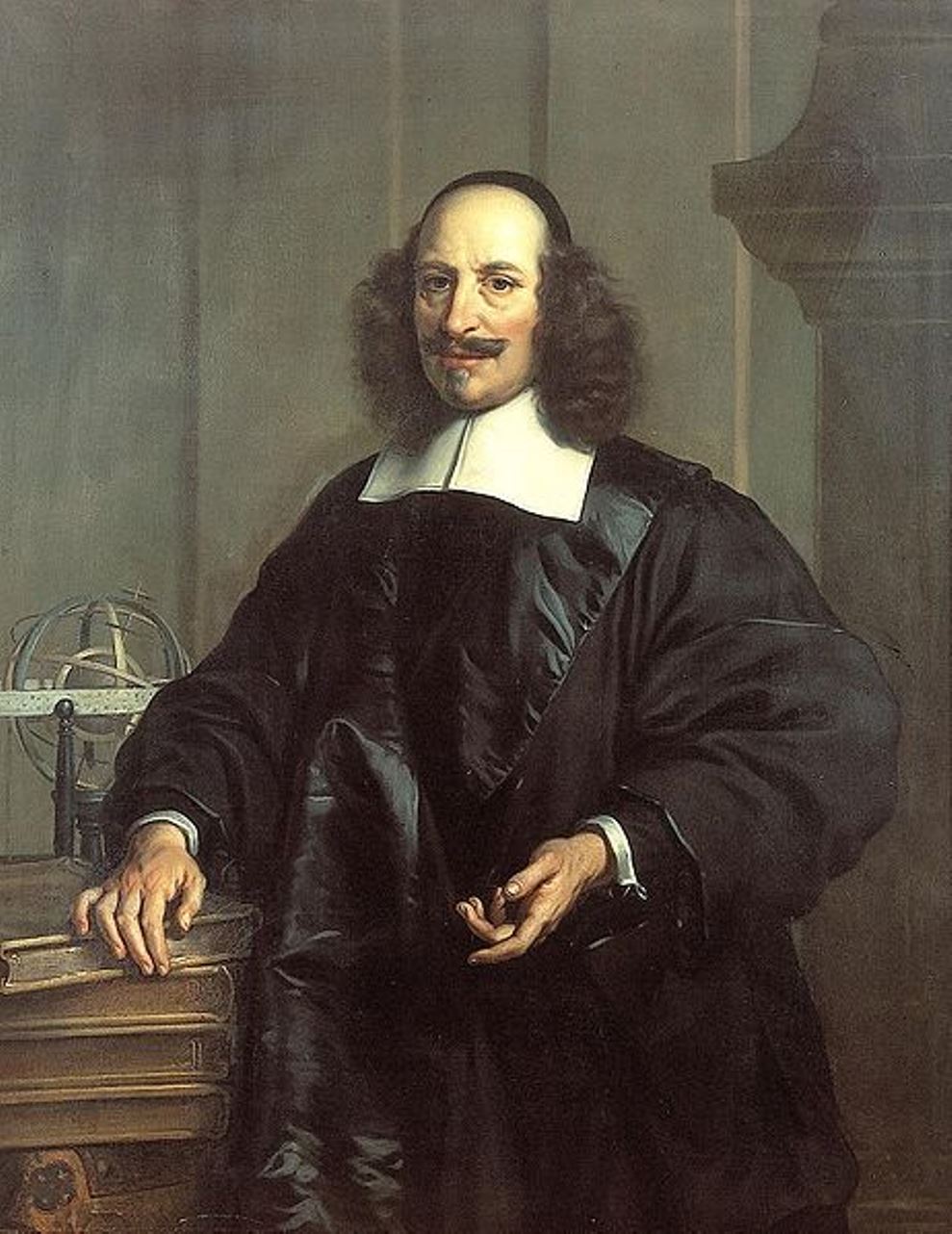


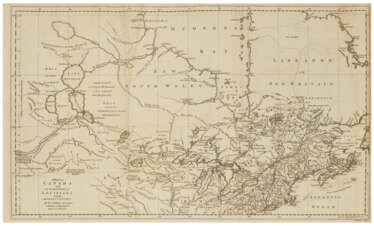
Jan (Joan) Willemsz. Blaeu was a Dutch cartographer, publisher and judge.
Jan was born into the family of the cartographer and publisher Willem Janszoon Blaeu (1571-1638). He studied in Leiden, where he earned a doctorate in law, and in Padua. He then began to assist his father, who was engaged in the manufacture of globes and maps. After his father's death, Jan, together with his brother Cornelius, continued his work, and succeeded him as cartographer for the Dutch East India Company.
In 1651 Blaeu was elected to the Amsterdam city council and later appointed as a judge. At the same time, he was engaged in his publishing business: he continued to publish volumes of Atlas novus, which contained maps of English counties and, for the first time, an atlas of Scotland, as well as one volume of maps of the Far East.
Blaeu did not have time to complete his most ambitious project, but it made him famous as the author of the famous 11-volume Dutch atlas. Based on his previous maps, Blaeu created the Great Atlas (Atlas Maior) - it contained nearly 600 maps and a total of 3,000 pages of Latin text - and was published in 1662. Blaeu's maps were groundbreaking for their time because they were created in accordance with the heliocentric theories of Nicolaus Copernicus.
In 1672, a great fire in Amsterdam destroyed Blaeu's workshop, and the cartographer died a year later, apparently never recovering from this stroke of fate.
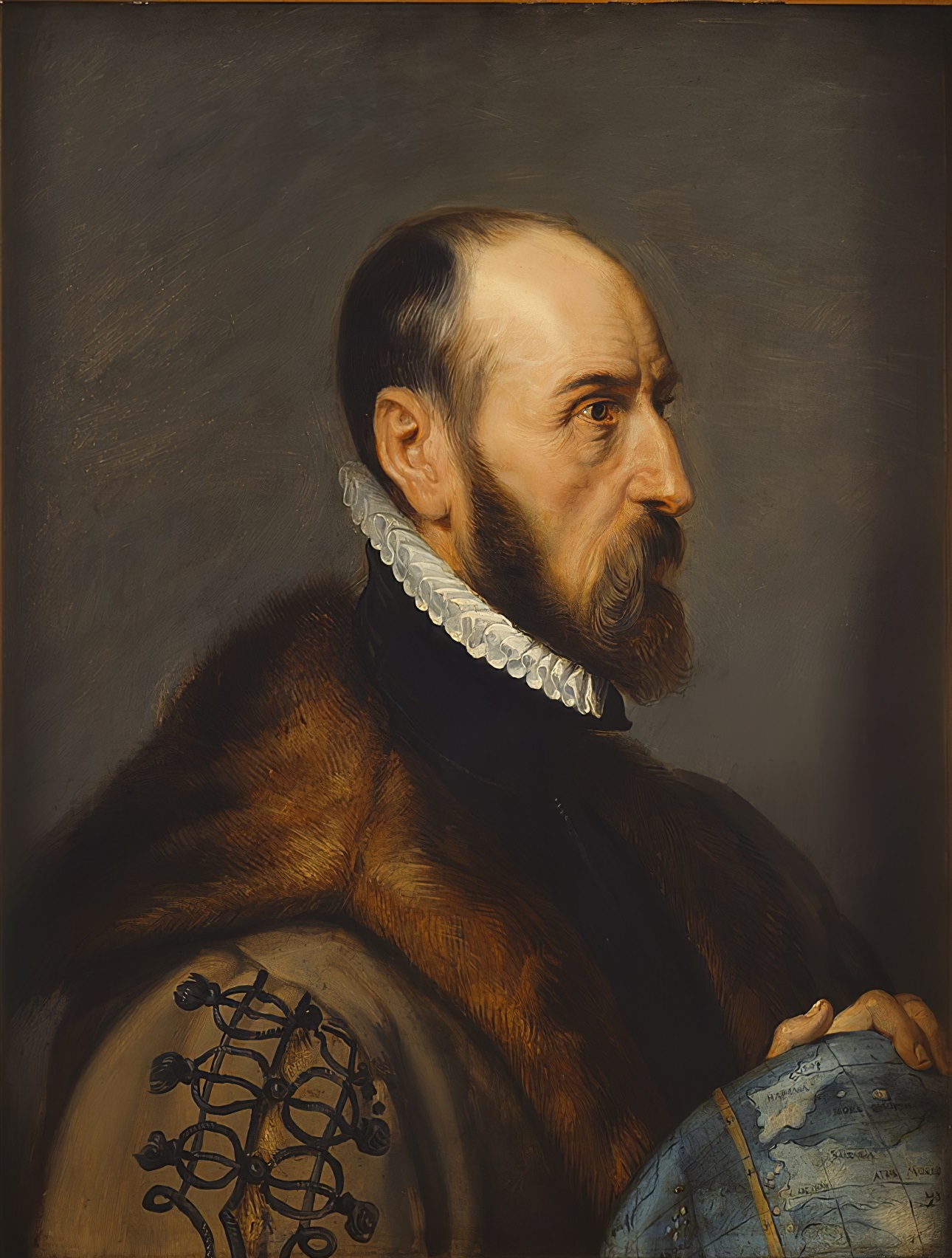


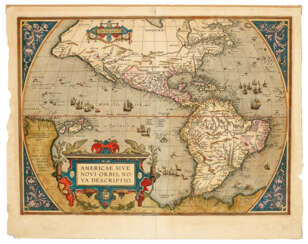
Abraham Ortelius (Ortels) was a Brabantian cartographer, geographer, and cosmographer. He is recognized as the creator of the first modern atlas, the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (Theatre of the World). Along with Gemma Frisius and Gerardus Mercator, Ortelius is generally considered one of the founders of the Netherlandish school of cartography and geography. He was a notable figure of this school in its golden age (approximately 1570s–1670s) and an important geographer of Spain during the age of discovery. The publication of his atlas in 1570 is often considered as the official beginning of the Golden Age of Netherlandish cartography. He was the first person proposing that the continents were joined before drifting to their present positions. Beginning as a map-engraver, in 1547 he entered the Antwerp Guild of Saint Luke as an illuminator of maps. In 1560 when travelling with Mercator to Trier, Lorraine, and Poitiers, he seems to have been attracted, largely by Mercator's influence, towards the career of a scientific geographer. In 1564 he published his first map, Typus Orbis Terrarum, an eight-leaved wall map of the world. On 20 May 1570, Gilles Coppens de Diest at Antwerp issued Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, the "first modern atlas" (of 53 maps).


Abraham Ortelius (Ortels) was a Brabantian cartographer, geographer, and cosmographer. He is recognized as the creator of the first modern atlas, the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (Theatre of the World). Along with Gemma Frisius and Gerardus Mercator, Ortelius is generally considered one of the founders of the Netherlandish school of cartography and geography. He was a notable figure of this school in its golden age (approximately 1570s–1670s) and an important geographer of Spain during the age of discovery. The publication of his atlas in 1570 is often considered as the official beginning of the Golden Age of Netherlandish cartography. He was the first person proposing that the continents were joined before drifting to their present positions. Beginning as a map-engraver, in 1547 he entered the Antwerp Guild of Saint Luke as an illuminator of maps. In 1560 when travelling with Mercator to Trier, Lorraine, and Poitiers, he seems to have been attracted, largely by Mercator's influence, towards the career of a scientific geographer. In 1564 he published his first map, Typus Orbis Terrarum, an eight-leaved wall map of the world. On 20 May 1570, Gilles Coppens de Diest at Antwerp issued Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, the "first modern atlas" (of 53 maps).
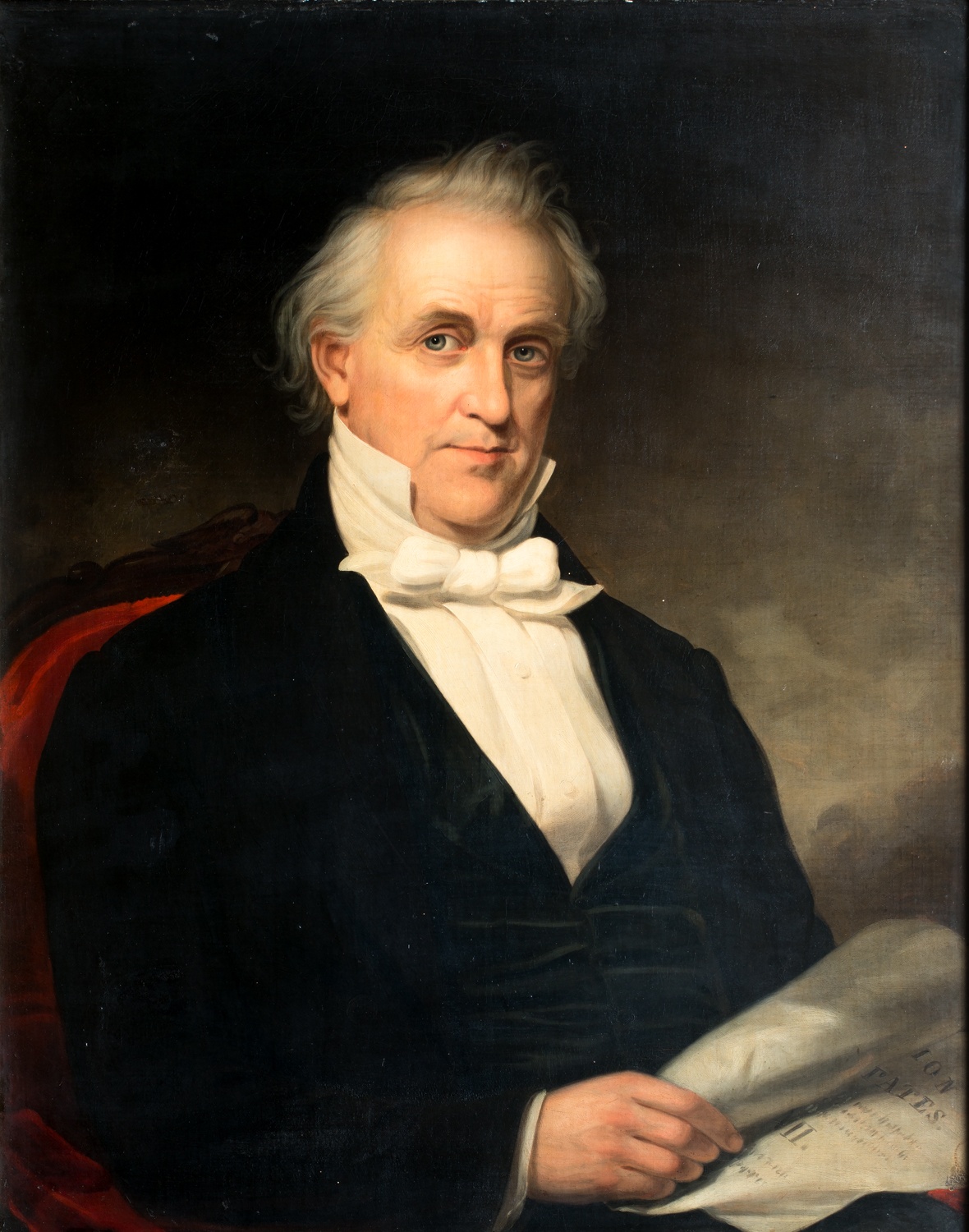



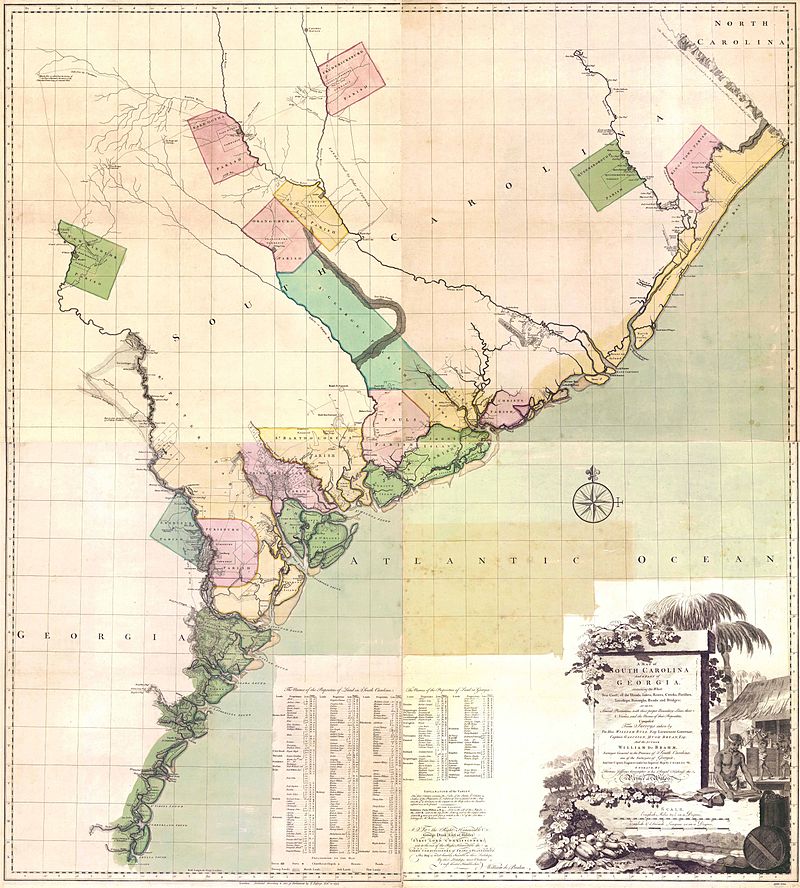
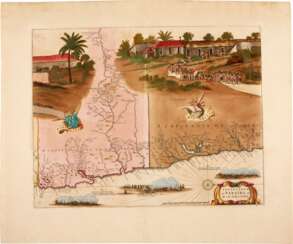
Johann Wilhelm Gerhard von Brahm, also known as John William Gerard de Brahm, was a German cartographer, military engineer, and surveyor who worked for Great Britain to develop the lands of the New World.
His father was court musician to the Elector of Trier and gave his son an excellent early education. After a successful career as a military engineer in the Bavarian army, de Brahm traveled to Georgia in 1751 at the head of a group of German emigrants. There he displayed his talents as a surveyor and engineer, worked as a cartographer, and was commissioned by South Carolina Governor James Glen to design and build a system of fortifications for Charleston.
In 1755 de Brahm was appointed inspector general of lands for South Carolina and soon for the entire New World. He settled in St. Augustine, where he spent the next six years researching and preparing maps. His major works, "Map of South Carolina" and "Map of South Carolina and Part of Georgia," provide detailed topography and even describe underwater features. And his "Report of a General Survey of the Southern District of North America" records every detail from tide times to tips on tilling the soil. De Brahm's book The Atlantic Pilot, an instruction manual for sailing in Florida, was published in London and included the first published map of the Gulf Stream.