states a - d





Albrecht Dürer, born on May 21, 1471 in Nuremberg, Germany, is widely regarded as the greatest German Renaissance painter. His contribution to painting and engraving is quite significant and has left a notable mark on the art world. Dürer's early life was spent in Nuremberg, a city that played a crucial role in his development as an artist and was also the site of his death on April 6, 1528. He was the son of the goldsmith Albrecht Dürer the Elder, from whom he initially learned the basics of drawing and metalworking.
Dürer's work is characterized by a combination of Gothic elements with the emerging Renaissance style, which is evident in his woodcuts and engravings. His oeuvre encompasses many themes, including religious works, altarpieces, portraits, and self-portraits. His outstanding prints, such as The Knight, Death and the Devil (1513), St. Jerome in his Study (1514) and Melencolia I (1514), are known for their intricate detail and artistic skill. Dürer was also one of the earliest European landscape painters, as evidenced by his watercolor paintings.
Equally significant are his theoretical writings on mathematics, perspective, and ideal proportions in art. Dürer was not only an artist but also a keen intellectual, his interests encompassing various aspects of culture and science. He served as court painter to Holy Roman Emperors Maximilian I and Charles V, completing several significant art projects for them. Dürer's keen mind and versatile interests brought him into contact with the most prominent figures of his time, including theologians and scientists of the Reformation era.
Dürer's self-portraits are particularly famous, demonstrating not only his artistic skill but also his self-awareness and personal style. These portraits attest to his growing success and confidence as an artist. Dürer's legacy is immense; he influenced not only the art of his time, but also left an indelible mark on the history of European art.
For those interested in the work and legacy of Albrecht Dürer, we recommend subscribing to our updates. Our subscription service is designed to provide information about new sales and auction events related to this remarkable artist. Join us to keep up to date on the latest art and antiques related to Albrecht Dürer.
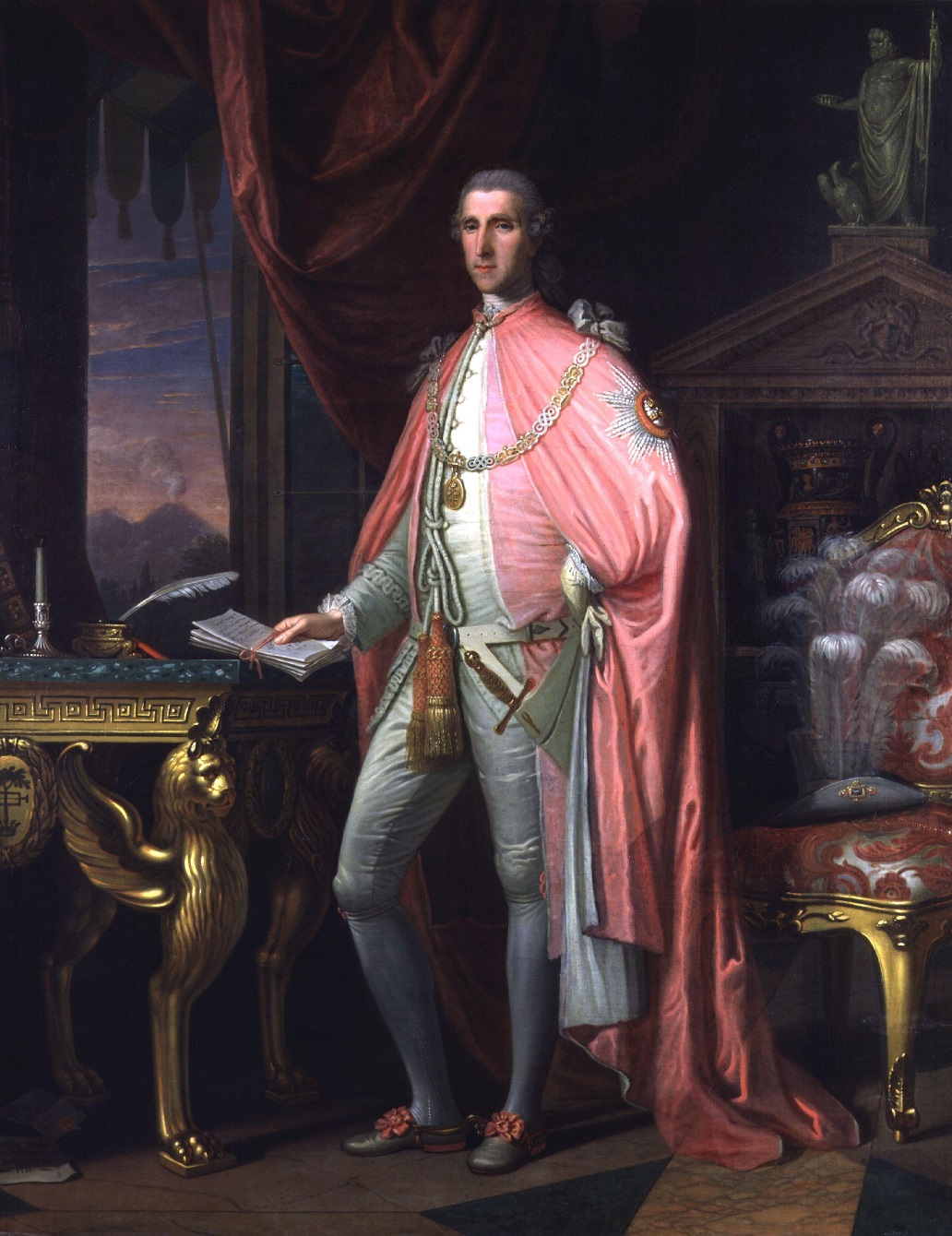


Sir William Douglas Hamilton was a British diplomat, archaeologist and volcanologist, a famous collector, and a Fellow of the Royal Society of London.
He served as British Ambassador to the Kingdom of Naples from 1764 to 1800, but most importantly, he was a passionate researcher of history, art and natural sciences and was a member of the Society of Dilettantes, established for the purpose of studying ancient art.
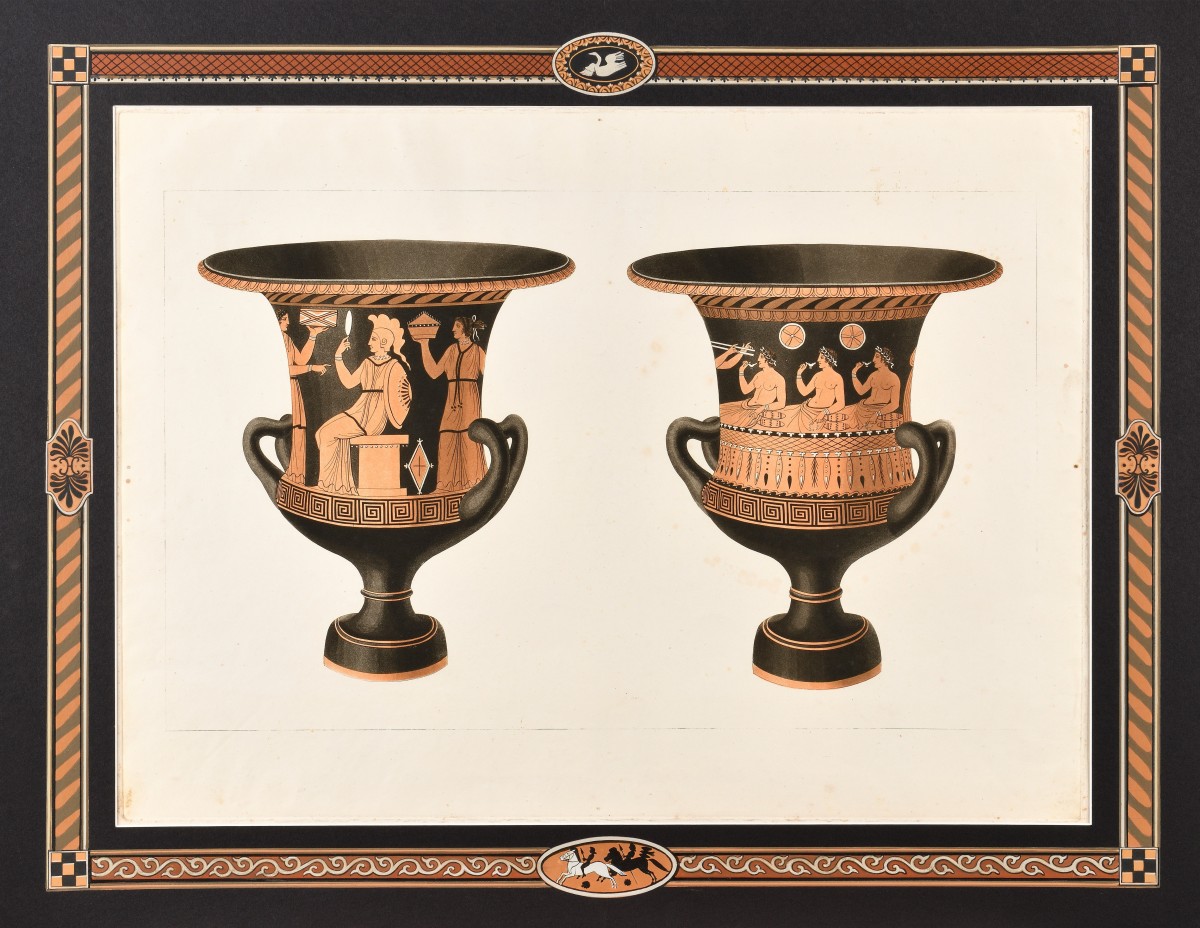
In Naples, Hamilton amassed a unique collection of antique vases and published an illustrated book about them. In parallel, Sir Hamilton studied the volcanoes Vesuvius and Etna, local volcanic and seismic activity, and the causes of earthquakes in the Neapolitan territory. As a corresponding member of the Royal Society, he sent the results of his research to London. His publications were very valuable for the time.

Pierre-François Hugues d'Hancarville, better known as Baron d'Hancarville, was an art historian, writer, and adventurer who lived most of his life in Italy.
To advance from the merchant class to high society, he studied mathematics, physics, history, literature, ancient languages, and English, Italian, and German. Traveling in Europe, he presented himself as an aristocrat under various names. Under the name Baron d'Hancarville, he was known as a connoisseur and art dealer, which is apparently why he was approached by Sir William Hamilton (1731-1803), who was ambassador to the British embassy in Naples and had amassed a large collection of ancient vases. Before selling this collection to the British Museum in 1772, Hamilton asked d'Hancarville for help in creating a complete catalog of it in descriptions and illustrations. The baron also wrote a detailed essay.
This catalog, entitled The Complete Collection of Antiquities from the Cabinet of Sir William Hamilton, is itself a neoclassical masterpiece in French and English. Antique vases have never before been depicted with such precision and aestheticism.


Albrecht Dürer, born on May 21, 1471 in Nuremberg, Germany, is widely regarded as the greatest German Renaissance painter. His contribution to painting and engraving is quite significant and has left a notable mark on the art world. Dürer's early life was spent in Nuremberg, a city that played a crucial role in his development as an artist and was also the site of his death on April 6, 1528. He was the son of the goldsmith Albrecht Dürer the Elder, from whom he initially learned the basics of drawing and metalworking.
Dürer's work is characterized by a combination of Gothic elements with the emerging Renaissance style, which is evident in his woodcuts and engravings. His oeuvre encompasses many themes, including religious works, altarpieces, portraits, and self-portraits. His outstanding prints, such as The Knight, Death and the Devil (1513), St. Jerome in his Study (1514) and Melencolia I (1514), are known for their intricate detail and artistic skill. Dürer was also one of the earliest European landscape painters, as evidenced by his watercolor paintings.
Equally significant are his theoretical writings on mathematics, perspective, and ideal proportions in art. Dürer was not only an artist but also a keen intellectual, his interests encompassing various aspects of culture and science. He served as court painter to Holy Roman Emperors Maximilian I and Charles V, completing several significant art projects for them. Dürer's keen mind and versatile interests brought him into contact with the most prominent figures of his time, including theologians and scientists of the Reformation era.
Dürer's self-portraits are particularly famous, demonstrating not only his artistic skill but also his self-awareness and personal style. These portraits attest to his growing success and confidence as an artist. Dürer's legacy is immense; he influenced not only the art of his time, but also left an indelible mark on the history of European art.
For those interested in the work and legacy of Albrecht Dürer, we recommend subscribing to our updates. Our subscription service is designed to provide information about new sales and auction events related to this remarkable artist. Join us to keep up to date on the latest art and antiques related to Albrecht Dürer.




René Boylesve, birth name René Marie Auguste Tardiveau, is a French writer and literary critic, a member of the Académie Française.
Boylesve was educated at Poitiers, Tours, and Paris, studying humanities and fine arts, natural sciences, and law. Ten years later, under his mother's maiden name, he wrote his first novel, The Physician of the Lady of Nean (1894). These were followed by other books, and then came the series known as the "Touraine novels": "Mademoiselle Cloke" (1899), "Beke" (1901), "The Child at the Balustrade" (1903), "The Educated Girl" (1909) and others. In these works, the author expertly depicts the mores of the provincial petty bourgeoisie. With a richly detailed style and characteristic irony Boylesve tells about the triumph of conventional values over artistic and spiritual aspirations.
In 1918 René Boylesve was elected a member of the French Academy.


Isaac Weld was an Irish explorer, writer, and artist.
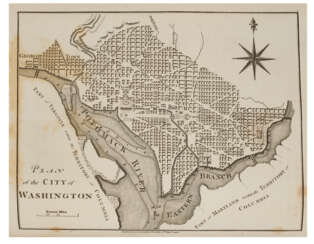
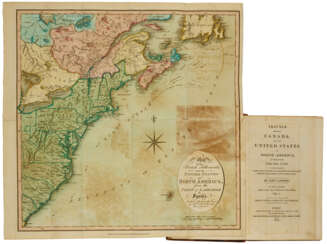
After completing his studies, Isaac Weld traveled to the new lands of America in 1795, meeting Thomas Jefferson and George Washington. The purpose of his journey was to learn of opportunities for Irish resettlement. Returning in 1797, Weld soon published his book, A Journey through the States of North America and the Provinces of Upper and Lower Canada. In general, Weld did not like the United States; he particularly noted the practice of slavery and the treatment of Native peoples by the rude new Americans. But he liked Canada and Quebec: he praised the views from the Citadel and reported that because of the low cost of land, a middle-income person could easily settle in the country for himself and his family.
This book by Weld was quite popular: it went through several editions from its first publication in 1799 to 1807. By 1820, it had also been translated into French, German, Italian, and Dutch.
In 1800 Weld was elected a member of the Royal Society of Dublin. In 1811 and 1812 he served on the library committee, and on December 4, 1828, he was elected honorary secretary. His first act in this capacity was to establish an annual exhibition of specimens of the manufactures and products of Ireland. Isaac Weld published several other books on Ireland and Great Britain, illustrated with his own drawings. Of these, his Statistical Survey of the County of Roscommon, over seven hundred pages long, published by the Royal Dublin Society in 1832, stands out.


George Washington is the first popularly elected president of the United States of America and one of the founding fathers of the United States.
Born into a noble family in colonial Virginia in February 1732, George Washington served as a Virginian officer with British troops during the French-Indian War (1754-1763) from 1754-1758. This was a territorial war fought largely between the colonies of Britain and France that escalated into a worldwide conflict between the two countries. J. Washington was at the center of the conflicts in the disputed Ohio River Valley area.
In June 1775, he was elected commander-in-chief of the Continental forces in the war already for independence from Great Britain. He commanded American troops throughout the war, becoming famous for his perseverance and bravery.
In 1787, J. Washington represented the state of Virginia as a delegate to the Constitutional Convention. This convention created the Constitution of the United States. In 1789, the Electoral College unanimously elected George Washington president, and in 1792 he was re-elected for a second term. Thus George Washington was in office as President of the United States from April 30, 1789 to March 4, 1797.
As head of state, he helped to strengthen the Union, implement the principles of the Constitution and build the capital of the United States. He was engaged in the formation of the central authorities and system of government, created precedents for the institution of presidents, encouraged the development of the economy, maintained friendly relations with Congress. In foreign policy Washington avoided interference in the affairs of European states.
After leaving the post of president, George Washington lived in Mount Vernon Manor.