union de la jeunesse
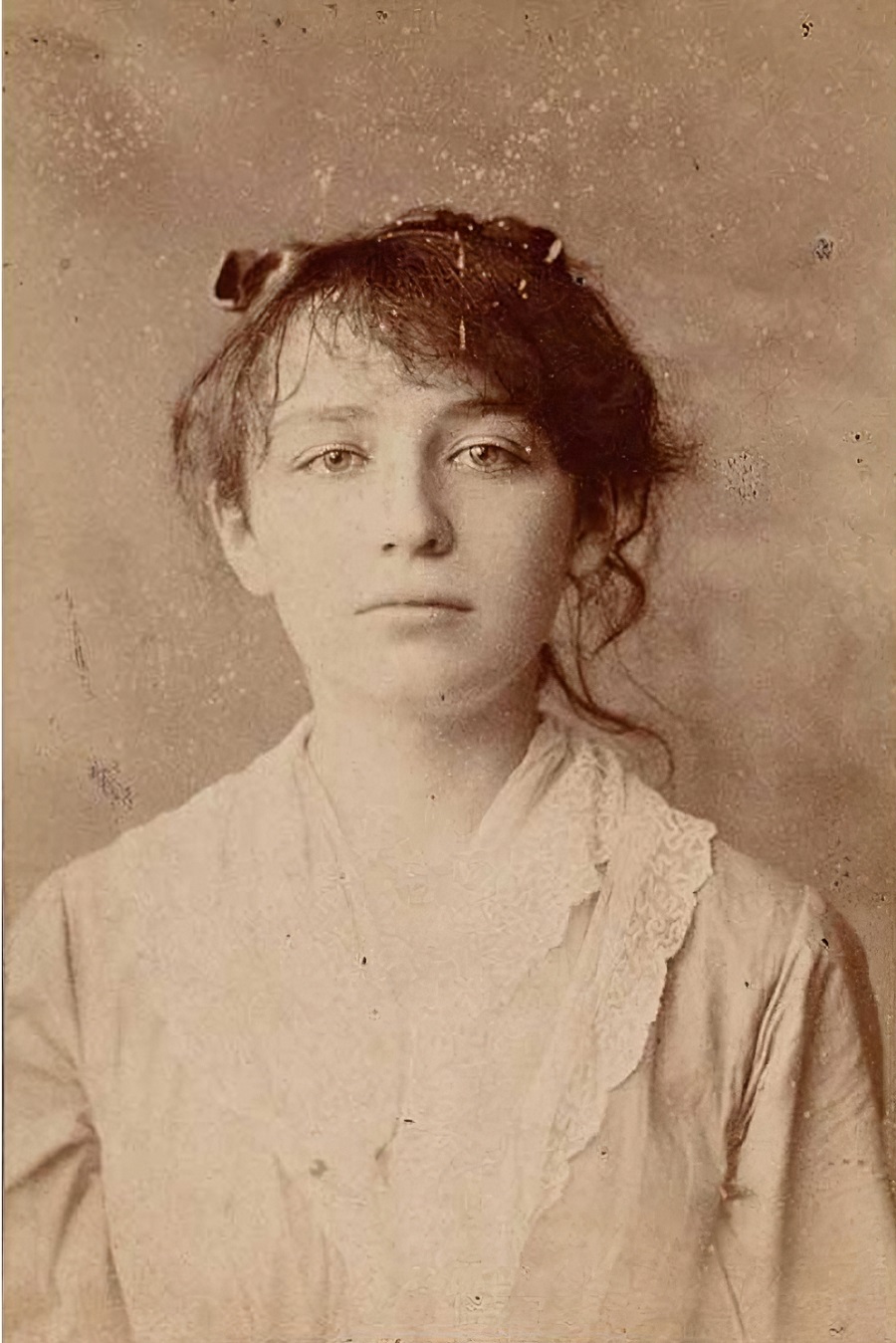


Camille Claudel was a French sculptor. She is known for her powerful and emotionally charged sculptures, which often portrayed human figures in moments of intense emotion or turmoil.
Claudel studied art in Paris under the tutelage of Auguste Rodin, and the two became lovers and collaborators for several years. Her work was heavily influenced by Rodin's style, and she often portrayed human bodies with a sense of fluidity and movement that was characteristic of his work.
Claudel's sculptures were praised for their technical skill and emotional intensity, but she struggled to gain recognition as an artist in her own right. She was frequently dismissed as simply a student of Rodin, and her personal life was marked by a series of setbacks and tragedies.
In 1913, Claudel suffered a nervous breakdown and was committed to a mental institution by her family, where she remained for the rest of her life. Her work was largely forgotten until the late 20th century, when a renewed interest in her life and career led to a reassessment of her place in the history of modern art. Today, her sculptures are celebrated for their technical virtuosity and emotional power, and her story has become an inspiration to many artists and scholars.
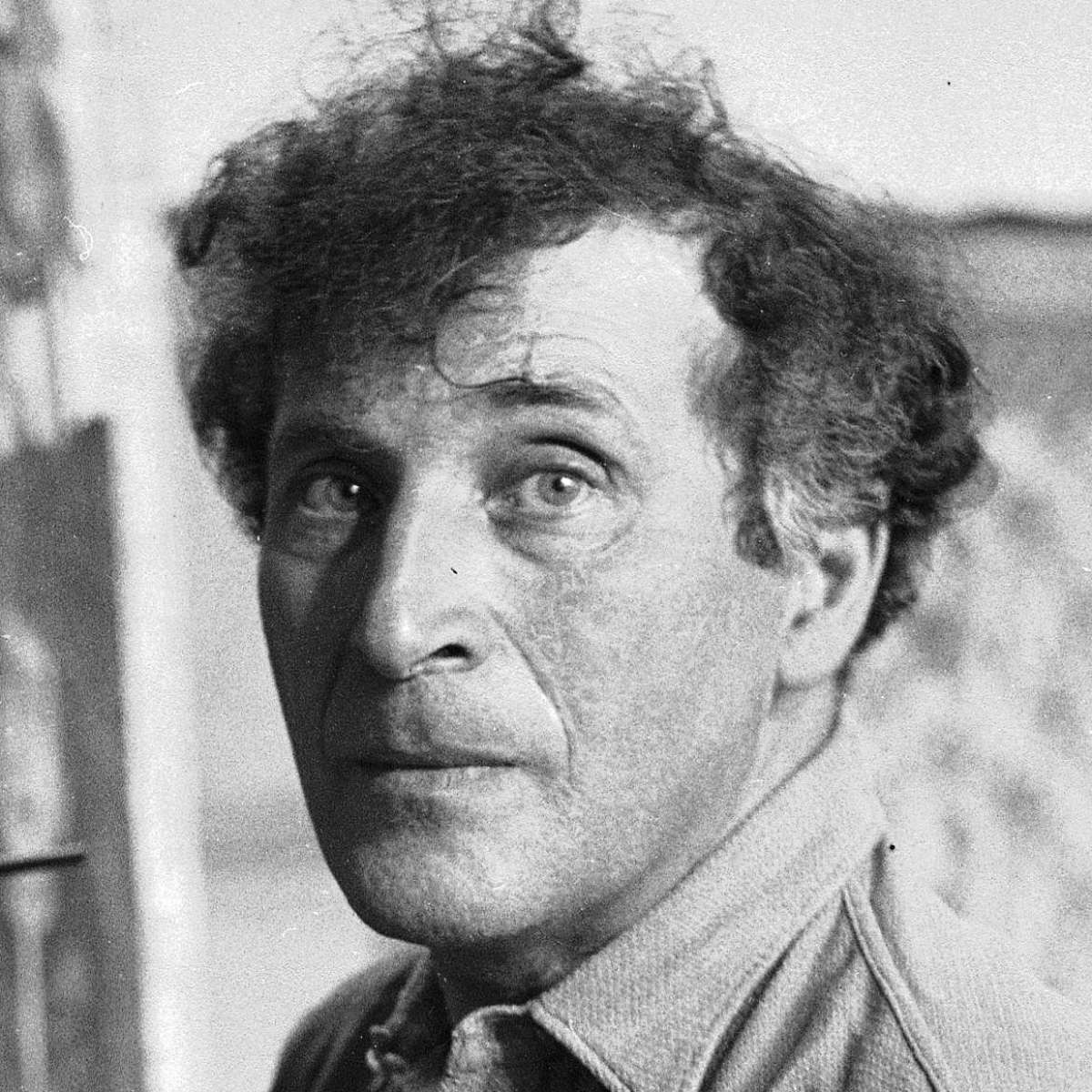


Marc Chagall (Russian: Марк Заха́рович Шага́л), born Moishe Shagal in 1887 near Vitebsk, Belarus (then part of the Russian Empire), was a Belarusian and French artist celebrated for his pivotal role in the avant-garde movement and his unique integration of Eastern European Jewish culture into modern art. His contributions spanned several artistic formats including painting, stained glass, stage sets, ceramics, tapestries, and fine art prints. Chagall's early modernist tendencies were enriched by his experiences across Saint Petersburg, Paris, and Berlin before World War I, leading to a distinctive style that melded Cubism, Symbolism, and Fauvism with his Jewish heritage.
Chagall's work is recognized for its emotional depth, often exploring themes of love, memory, and Jewish folklore through vibrant colors and dreamlike imagery. Notably, art critic Robert Hughes described him as "the quintessential Jewish artist of the twentieth century," a sentiment echoed by art historian Michael J. Lewis who regarded Chagall as a significant figure within European modernism and as the world's preeminent Jewish artist of his time.
Among Chagall's famed contributions are his stained-glass windows for the cathedrals of Reims and Metz, the UN, and the Jerusalem Windows in Israel. His monumental paintings include parts of the ceiling of the Paris Opéra and works that explore biblical themes, a hallmark of his oeuvre that underscores his enduring engagement with spiritual and religious motifs.
For art collectors and antiques experts, Chagall's works are notable not only for their artistic innovation but also for their rich cultural and historical significance. His art is housed in many prestigious museums worldwide, including the Marc Chagall National Museum in Nice, France, which focuses on his works inspired by religion and houses the series of paintings illustrating the biblical message.
For those interested in exploring Chagall's legacy and the vibrant intersection of culture, art, and history his work represents, signing up for updates on new product sales and auction events related to Marc Chagall can provide invaluable insights and opportunities. This is an invitation to engage more deeply with the world of art and culture that Chagall so uniquely encapsulated in his work.






![[DU PETIT-VAL, Raphaël (mort en 1613)] Recueil de diverses poésies, tant du feu sieur de Sponde, que des sieurs du Perron, de Bertaud, de Porcheres, & autres non encor imprimees. [avec] Second [-Troisième, Quatrième] recueil de div](/assets/image/picture_1320892/8eecc/2838af1861ad669223d69f882a3eb8901616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[DU PETIT-VAL, Raphaël (mort en 1613)] Recueil de diverses poésies, tant du feu sieur de Sponde, que des sieurs du Perron, de Bertaud, de Porcheres, & autres non encor imprimees. [avec] Second [-Troisième, Quatrième] recueil de div](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_1320892/8eecc/2838af1861ad669223d69f882a3eb8901616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)


















