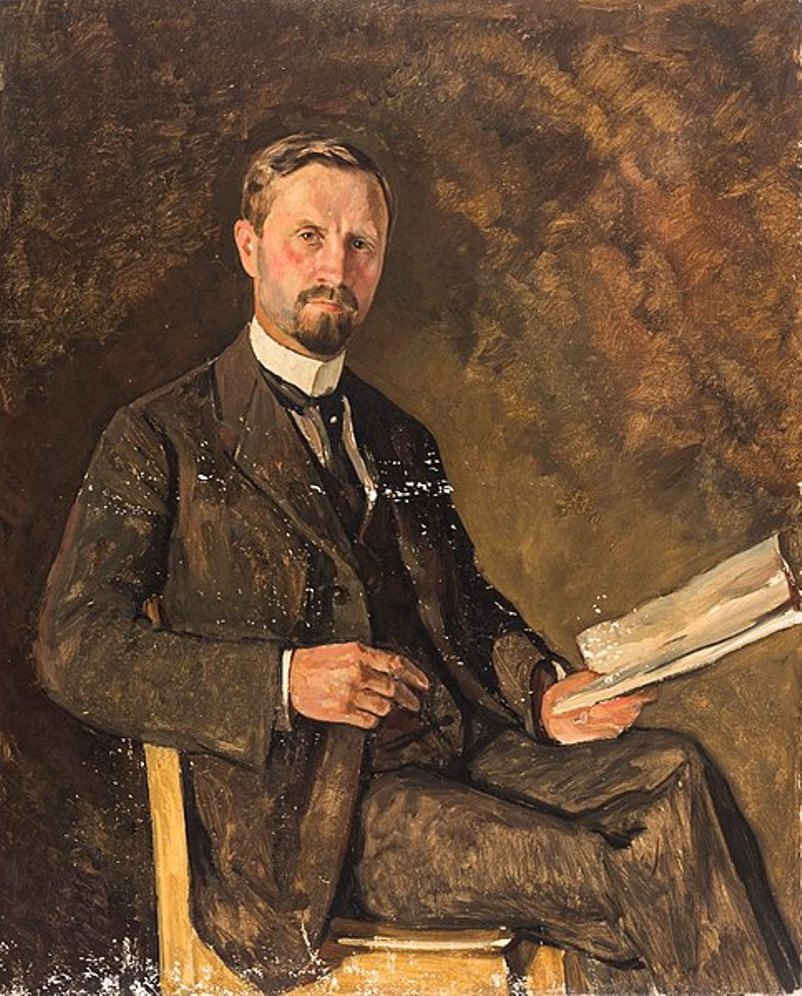
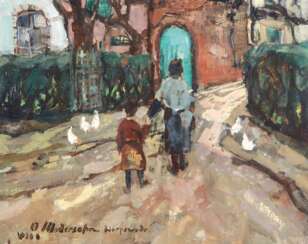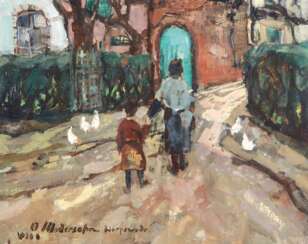wilhelm sohn
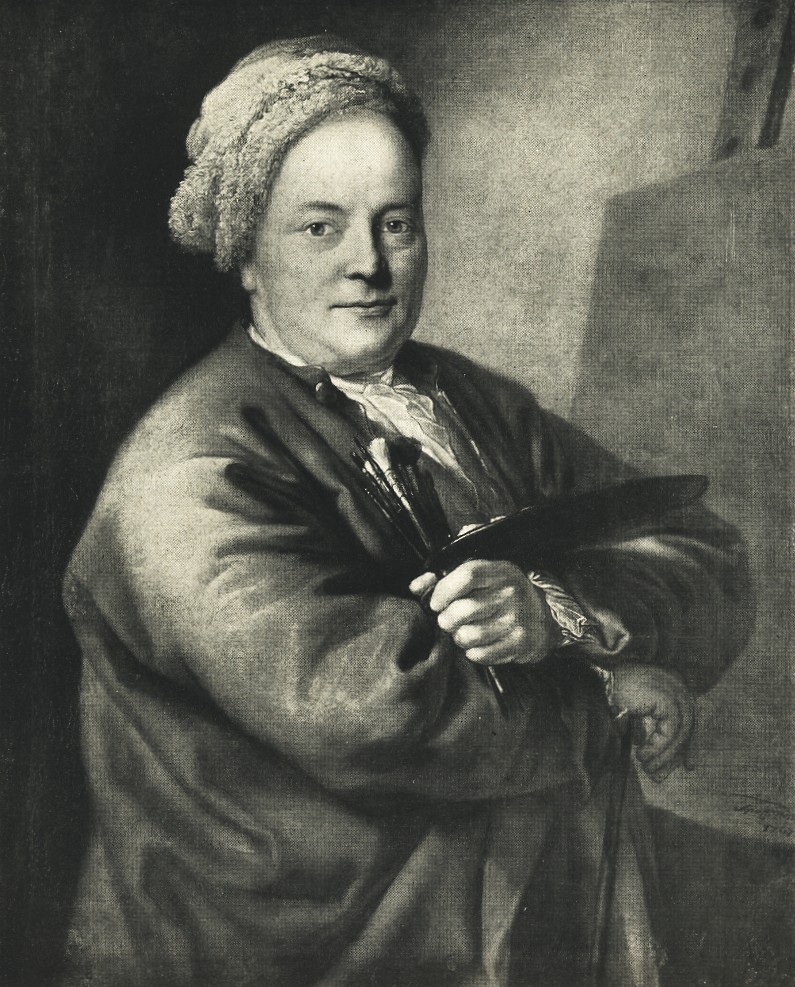



Christian Wilhelm Ernst Dietrich, also known as Christian Guillaume Ernest Dietricy, was a German painter and printmaker.
He was born in Weimar, Thuringia, into the family of the court painter Johann Georg Dietrich, and received his first training from his father. Dietrich worked in a variety of techniques and artistic movements of his time.
The talented artist took up any subjects: stories from the Old and New Testament, allegory and mythology, as well as portraits, genre scenes, portrayed ordinary people and livestock, painted coats of arms and vignettes, and more.
In 1764, Dietrich was appointed director of the painting school of the Meissen porcelain manufactory. The following year he became a professor at the Dresden Academy of Fine Arts. Works of Christian Wilhelm Dietrich can be found in many museums in Europe.
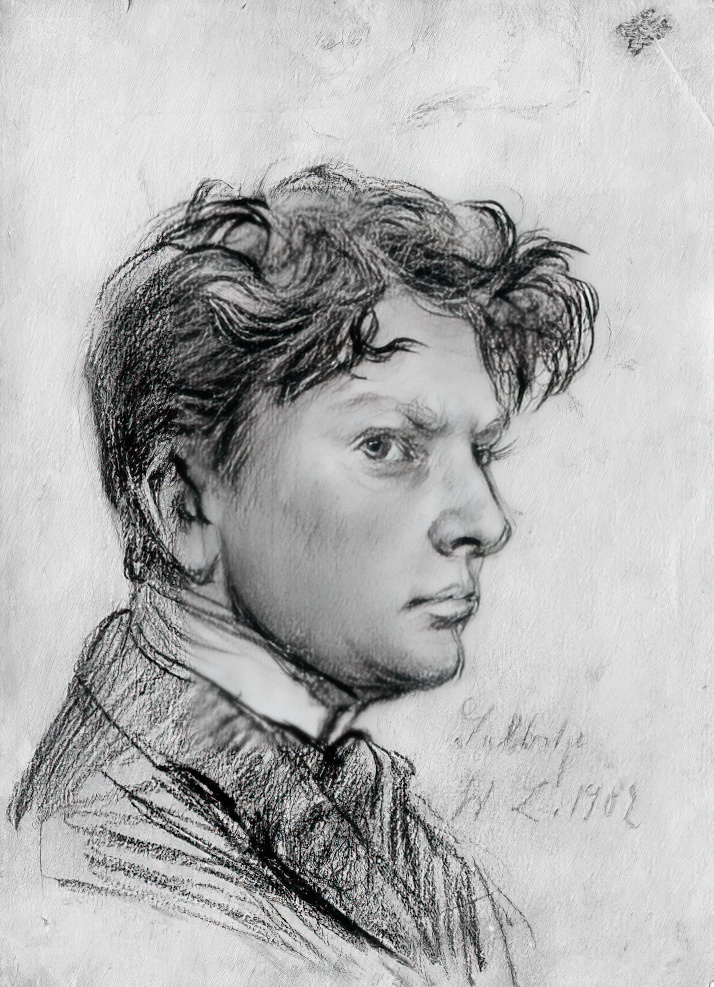


Wilhelm Lehmbruck was a German sculptor, graphic artist and medallist.
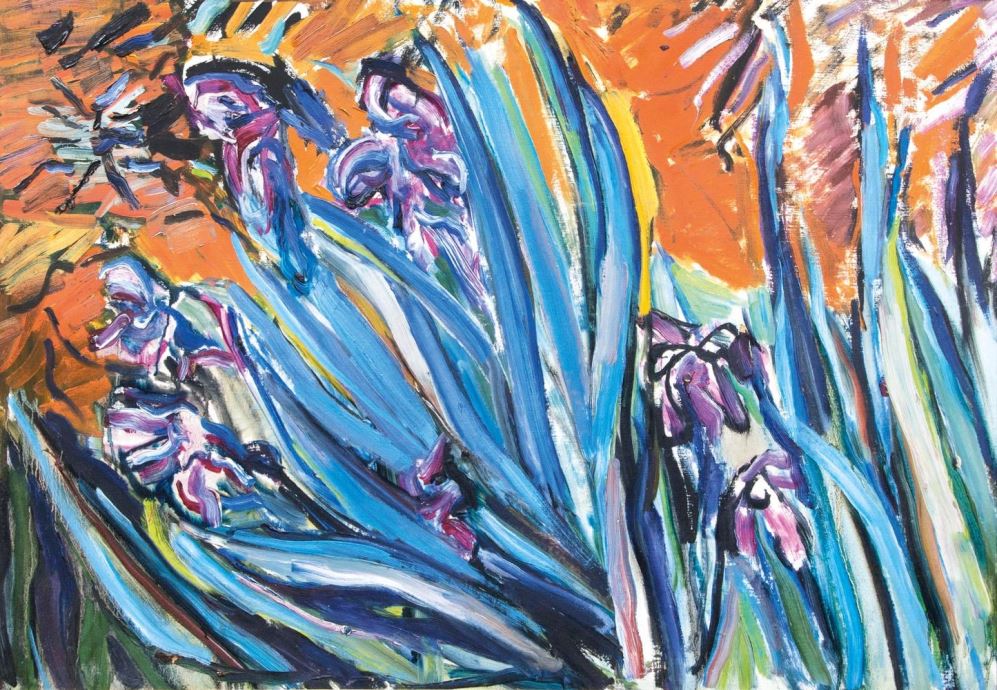


Wilhelm Ohm, full name Wilhelm Friedrich Hubert Ohm, was a German painter, draftsman, sculptor and architect.
Ohm trained in architecture and worked as a government architect and engineer, and studied sculpture and mural painting at the Prussian Academy of Fine Arts in Berlin. From 1923 to 1933 he was a member of the North German Artists' Association. In 1940 Wilhelm Ohm received a Bachelor's degree from the Technical University of Berlin on the colorful redesign of cities, through which he wanted to combine painting and architecture into a unified whole. This idea occupied him throughout his life.
Wilhelm Ohm's work of the 1920s can be stylistically categorized as New Objectivity and Surrealism. After World War II, trying to make up for lost time, he saturates his paintings with color and energy. His later works were done in a post-impressionist style. This applies to his landscapes, nature studies, floral bouquets and fruit compositions.
Wilhelm Ohm's son August Ohm, born in 1943, also became an artist.

Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Tischbein was a German painter, master of portraiture; a member of the famous Tischbein artistic dynasty, one of the closest friends of the poet Johann Wolfgang Goethe.
He studied painting with his uncle Johann Jacob Tischbein in Hamburg. In 1772-1773 he made a study trip to Holland, and from 1777 was engaged in portrait painting in Berlin. In 1779 he went to Rome on a scholarship to the Academy of Arts in Cassel. After studying the antique art monuments he gradually changed his painting style from rococo to classical. In Italy he painted mostly landscapes, still life and history.
From 1789 to 1799 Johann Heinrich Wilhelm painted in the period from 1789 to 1799. Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Tischbein was director of the Academy of Arts in Naples.
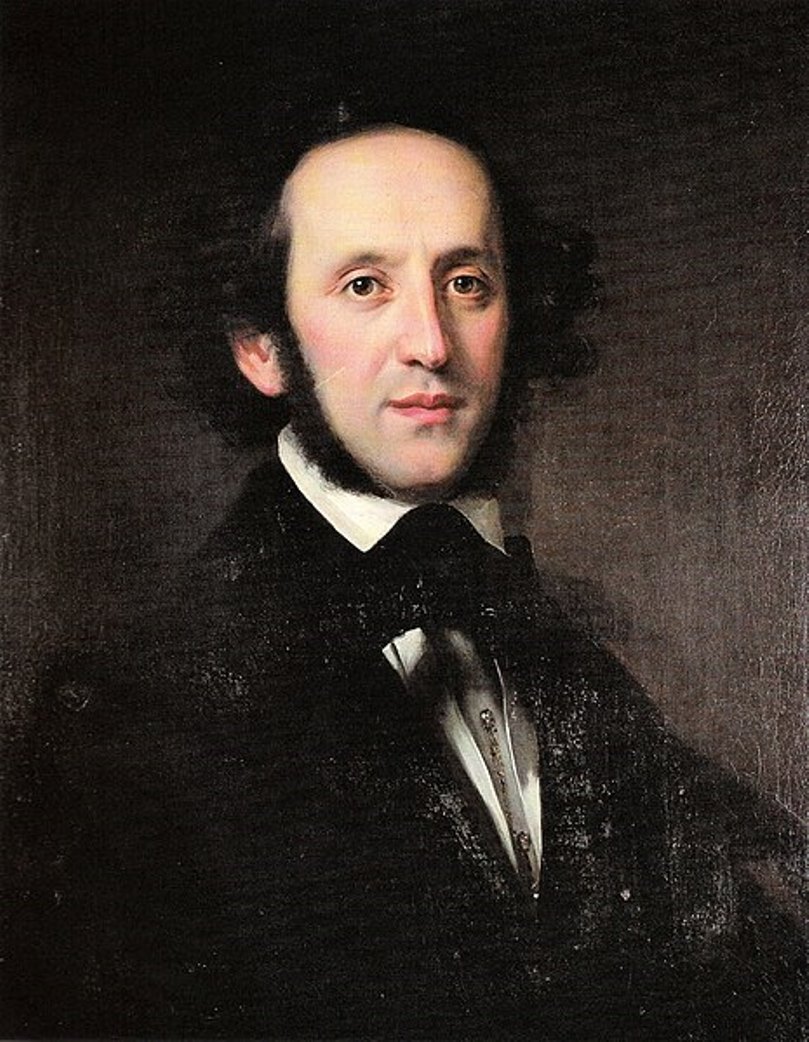


Felix Mendelssohn (full name Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy) was a German composer, pianist, conductor, teacher, and one of the greatest representatives of Romanticism in music.
Felix was born into a Jewish musical family that later converted to Christianity. He received a versatile education and already as a child wrote many musical compositions, including 5 operas, 11 symphonies for string orchestra, concertos, sonatas and fugues. Mendelssohn's first public performance took place in Berlin in 1818, when he was nine years old. In 1821 Mendelssohn was introduced to J.W. von Goethe, for whom he performed works by J.S. Bach and Mozart and to whom he dedicated his Piano Quartet No. 3 in B minor. A friendship developed between the famous wise poet and the 12-year-old musician.
A few years later, the talented musician began conducting in various orchestras in Europe, and became acquainted with Carl Weber. In England, where Mendelssohn visited very often, by the middle of the 19th century his music had become very popular, even with Queen Victoria he was the most favorite composer. He dedicated his Symphony No. 3 in A minor major (Scottish Symphony) to the Queen.
Among Mendelssohn's most famous works are A Midsummer Night's Dream (1826), the Italian Symphony (1833), a violin concerto (1844), two piano concertos (1831, 1837), the oratorio Elijah (1846) and several chamber pieces. The tradition of playing the "Wedding March" from A Midsummer Night's Dream in wedding processions dates back to its performance at the wedding of a royal princess in 1858, already after Mendelssohn's death.
In 1843, Mendelssohn founded a conservatory in Leipzig, where he taught composition with Schumann. Mendelssohn was one of the first great Romantic composers of the nineteenth century.


Felix Mendelssohn (full name Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy) was a German composer, pianist, conductor, teacher, and one of the greatest representatives of Romanticism in music.
Felix was born into a Jewish musical family that later converted to Christianity. He received a versatile education and already as a child wrote many musical compositions, including 5 operas, 11 symphonies for string orchestra, concertos, sonatas and fugues. Mendelssohn's first public performance took place in Berlin in 1818, when he was nine years old. In 1821 Mendelssohn was introduced to J.W. von Goethe, for whom he performed works by J.S. Bach and Mozart and to whom he dedicated his Piano Quartet No. 3 in B minor. A friendship developed between the famous wise poet and the 12-year-old musician.
A few years later, the talented musician began conducting in various orchestras in Europe, and became acquainted with Carl Weber. In England, where Mendelssohn visited very often, by the middle of the 19th century his music had become very popular, even with Queen Victoria he was the most favorite composer. He dedicated his Symphony No. 3 in A minor major (Scottish Symphony) to the Queen.
Among Mendelssohn's most famous works are A Midsummer Night's Dream (1826), the Italian Symphony (1833), a violin concerto (1844), two piano concertos (1831, 1837), the oratorio Elijah (1846) and several chamber pieces. The tradition of playing the "Wedding March" from A Midsummer Night's Dream in wedding processions dates back to its performance at the wedding of a royal princess in 1858, already after Mendelssohn's death.
In 1843, Mendelssohn founded a conservatory in Leipzig, where he taught composition with Schumann. Mendelssohn was one of the first great Romantic composers of the nineteenth century.


Felix Mendelssohn (full name Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy) was a German composer, pianist, conductor, teacher, and one of the greatest representatives of Romanticism in music.
Felix was born into a Jewish musical family that later converted to Christianity. He received a versatile education and already as a child wrote many musical compositions, including 5 operas, 11 symphonies for string orchestra, concertos, sonatas and fugues. Mendelssohn's first public performance took place in Berlin in 1818, when he was nine years old. In 1821 Mendelssohn was introduced to J.W. von Goethe, for whom he performed works by J.S. Bach and Mozart and to whom he dedicated his Piano Quartet No. 3 in B minor. A friendship developed between the famous wise poet and the 12-year-old musician.
A few years later, the talented musician began conducting in various orchestras in Europe, and became acquainted with Carl Weber. In England, where Mendelssohn visited very often, by the middle of the 19th century his music had become very popular, even with Queen Victoria he was the most favorite composer. He dedicated his Symphony No. 3 in A minor major (Scottish Symphony) to the Queen.
Among Mendelssohn's most famous works are A Midsummer Night's Dream (1826), the Italian Symphony (1833), a violin concerto (1844), two piano concertos (1831, 1837), the oratorio Elijah (1846) and several chamber pieces. The tradition of playing the "Wedding March" from A Midsummer Night's Dream in wedding processions dates back to its performance at the wedding of a royal princess in 1858, already after Mendelssohn's death.
In 1843, Mendelssohn founded a conservatory in Leipzig, where he taught composition with Schumann. Mendelssohn was one of the first great Romantic composers of the nineteenth century.


Felix Mendelssohn (full name Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy) was a German composer, pianist, conductor, teacher, and one of the greatest representatives of Romanticism in music.
Felix was born into a Jewish musical family that later converted to Christianity. He received a versatile education and already as a child wrote many musical compositions, including 5 operas, 11 symphonies for string orchestra, concertos, sonatas and fugues. Mendelssohn's first public performance took place in Berlin in 1818, when he was nine years old. In 1821 Mendelssohn was introduced to J.W. von Goethe, for whom he performed works by J.S. Bach and Mozart and to whom he dedicated his Piano Quartet No. 3 in B minor. A friendship developed between the famous wise poet and the 12-year-old musician.
A few years later, the talented musician began conducting in various orchestras in Europe, and became acquainted with Carl Weber. In England, where Mendelssohn visited very often, by the middle of the 19th century his music had become very popular, even with Queen Victoria he was the most favorite composer. He dedicated his Symphony No. 3 in A minor major (Scottish Symphony) to the Queen.
Among Mendelssohn's most famous works are A Midsummer Night's Dream (1826), the Italian Symphony (1833), a violin concerto (1844), two piano concertos (1831, 1837), the oratorio Elijah (1846) and several chamber pieces. The tradition of playing the "Wedding March" from A Midsummer Night's Dream in wedding processions dates back to its performance at the wedding of a royal princess in 1858, already after Mendelssohn's death.
In 1843, Mendelssohn founded a conservatory in Leipzig, where he taught composition with Schumann. Mendelssohn was one of the first great Romantic composers of the nineteenth century.


Felix Mendelssohn (full name Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy) was a German composer, pianist, conductor, teacher, and one of the greatest representatives of Romanticism in music.
Felix was born into a Jewish musical family that later converted to Christianity. He received a versatile education and already as a child wrote many musical compositions, including 5 operas, 11 symphonies for string orchestra, concertos, sonatas and fugues. Mendelssohn's first public performance took place in Berlin in 1818, when he was nine years old. In 1821 Mendelssohn was introduced to J.W. von Goethe, for whom he performed works by J.S. Bach and Mozart and to whom he dedicated his Piano Quartet No. 3 in B minor. A friendship developed between the famous wise poet and the 12-year-old musician.
A few years later, the talented musician began conducting in various orchestras in Europe, and became acquainted with Carl Weber. In England, where Mendelssohn visited very often, by the middle of the 19th century his music had become very popular, even with Queen Victoria he was the most favorite composer. He dedicated his Symphony No. 3 in A minor major (Scottish Symphony) to the Queen.
Among Mendelssohn's most famous works are A Midsummer Night's Dream (1826), the Italian Symphony (1833), a violin concerto (1844), two piano concertos (1831, 1837), the oratorio Elijah (1846) and several chamber pieces. The tradition of playing the "Wedding March" from A Midsummer Night's Dream in wedding processions dates back to its performance at the wedding of a royal princess in 1858, already after Mendelssohn's death.
In 1843, Mendelssohn founded a conservatory in Leipzig, where he taught composition with Schumann. Mendelssohn was one of the first great Romantic composers of the nineteenth century.
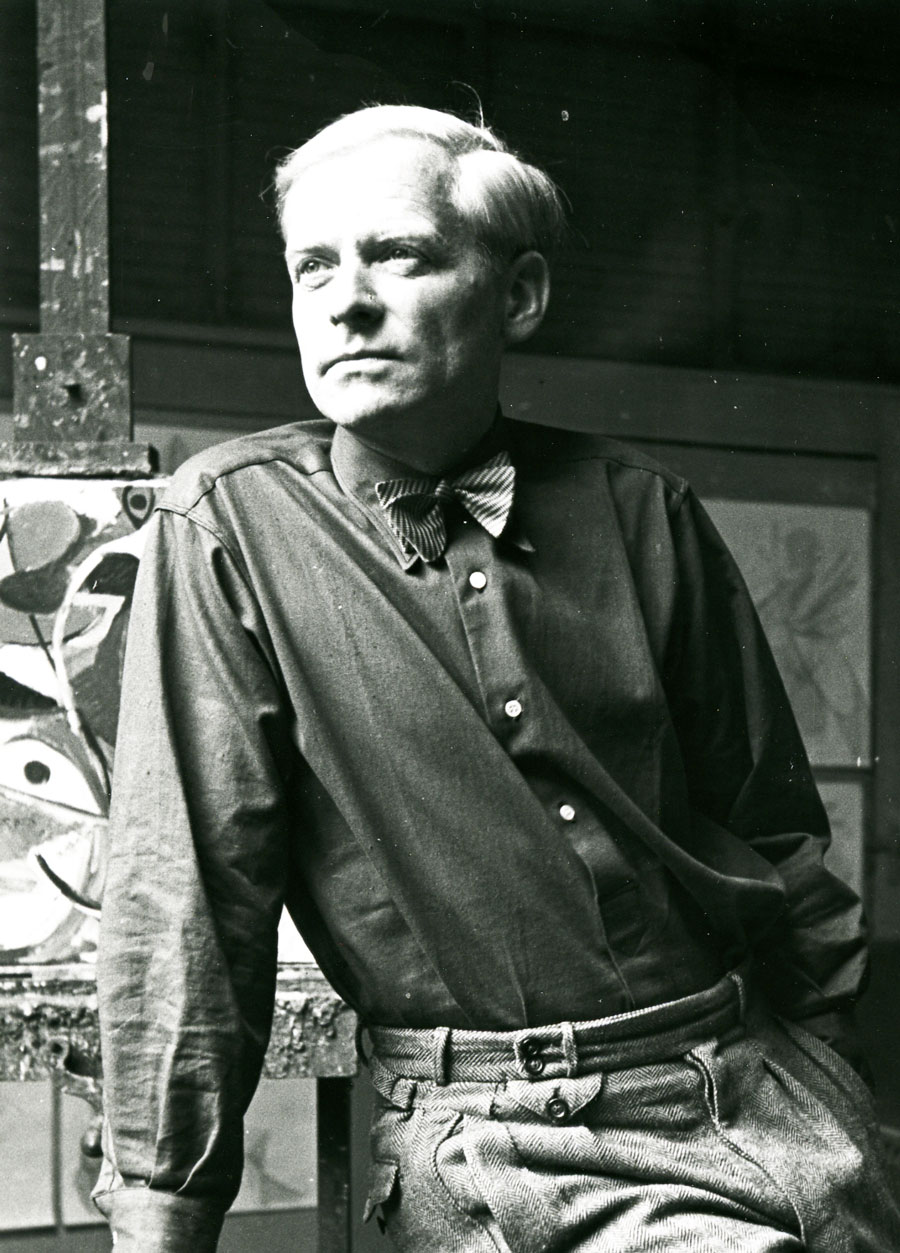


Ernst Wilhelm Nay was a German painter and graphic designer of classical modernism. He is considered one of the most important painters of German post-war art.


Felix Mendelssohn (full name Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy) was a German composer, pianist, conductor, teacher, and one of the greatest representatives of Romanticism in music.
Felix was born into a Jewish musical family that later converted to Christianity. He received a versatile education and already as a child wrote many musical compositions, including 5 operas, 11 symphonies for string orchestra, concertos, sonatas and fugues. Mendelssohn's first public performance took place in Berlin in 1818, when he was nine years old. In 1821 Mendelssohn was introduced to J.W. von Goethe, for whom he performed works by J.S. Bach and Mozart and to whom he dedicated his Piano Quartet No. 3 in B minor. A friendship developed between the famous wise poet and the 12-year-old musician.
A few years later, the talented musician began conducting in various orchestras in Europe, and became acquainted with Carl Weber. In England, where Mendelssohn visited very often, by the middle of the 19th century his music had become very popular, even with Queen Victoria he was the most favorite composer. He dedicated his Symphony No. 3 in A minor major (Scottish Symphony) to the Queen.
Among Mendelssohn's most famous works are A Midsummer Night's Dream (1826), the Italian Symphony (1833), a violin concerto (1844), two piano concertos (1831, 1837), the oratorio Elijah (1846) and several chamber pieces. The tradition of playing the "Wedding March" from A Midsummer Night's Dream in wedding processions dates back to its performance at the wedding of a royal princess in 1858, already after Mendelssohn's death.
In 1843, Mendelssohn founded a conservatory in Leipzig, where he taught composition with Schumann. Mendelssohn was one of the first great Romantic composers of the nineteenth century.


Friedrich Wilhelm Otto Modersohn was a German painter of the late 19th and first half of the 20th centuries. He is known as a landscape painter, a representative of the Barbizon School.
Otto Modersohn produced Barbizonian-style landscapes early in his career, but from about 1890 his style became more expressionist, with an emphasis on his choice of colors. The death of his second wife influenced his style: the colors became darker and the images more stark. Modersohn was one of the founders of the Worpswede artists' colony. A large collection of his works is kept in the Modersohn Museum in Fischerhude, and a street in Berlin is also named after him.
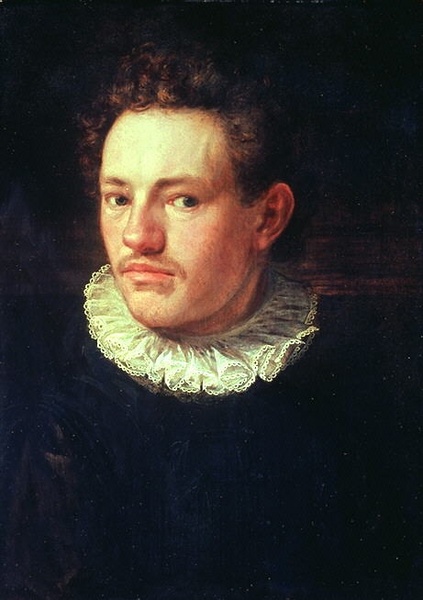





Hans von Aachen was a German painter, renowned for his role as a leading representative of Northern Mannerism. His journey into the art world took him from Rome, where he studied antique sculptures and the works of Italian masters, to Florence and then Venice, securing commissions that would define his early career. Notably, his work caught the attention of the Medici family, leading to significant commissions.
By 1592, von Aachen had become the official painter for Emperor Rudolf II in Prague. This position didn't require him to stay at court, allowing him to work from his residence. His relationship with Rudolf II was pivotal, marking a period where his art flourished under the emperor's patronage, celebrated for mythological paintings and complex allegories. The emperor's appreciation for painting and the arts transformed Prague into a significant art center, fostering a style full of elegance and sensuality known as Mannerism.
Hans von Aachen's style, influenced by Italian Mannerism and northern realism, showcased his versatility through portraits, historical, religious subjects, and allegories. His significant works include the "Allegory of Peace, Art and Abundance," depicting personifications of Peace, Science and the Liberal Arts, and Abundance, celebrated for illustrating the flourishing of these ideals under Rudolf II's reign. This piece, among others, found its home in prestigious collections like the Hermitage Museum in Saint Petersburg.
His contribution to the art world was acknowledged by the European courts, merchants, and the nobility. Even after Rudolf II's death, Hans von Aachen continued his work for Matthias, focusing on imperial portraits until his death in Prague in 1615. His legacy, momentarily overshadowed by the nationalistic perspectives of the 19th century, has been reevaluated, recognizing him as a key figure in European cultural exchange and Mannerism.
For art collectors and experts interested in Mannerism and Hans von Aachen's work, his journey from an admired artist at European courts to a celebrated figure in art history underscores the lasting impact of his work. His ability to navigate the cultural and artistic demands of his time, leaving behind a body of work that continues to be studied and appreciated, makes him a fascinating subject of study.
For updates on new product sales and auction events related to Hans von Aachen, sign up here. This subscription is your gateway to exploring the remarkable works of this distinguished Mannerist painter, ensuring you never miss an opportunity to own a piece of history.