Tables — Auction price
.jpg)
Jean Elysée Puiforcat was a French silversmith, sculptor and designer. Miller's Antiques Encyclopedia calls Puiforcat the «most important French Art Deco silversmith».
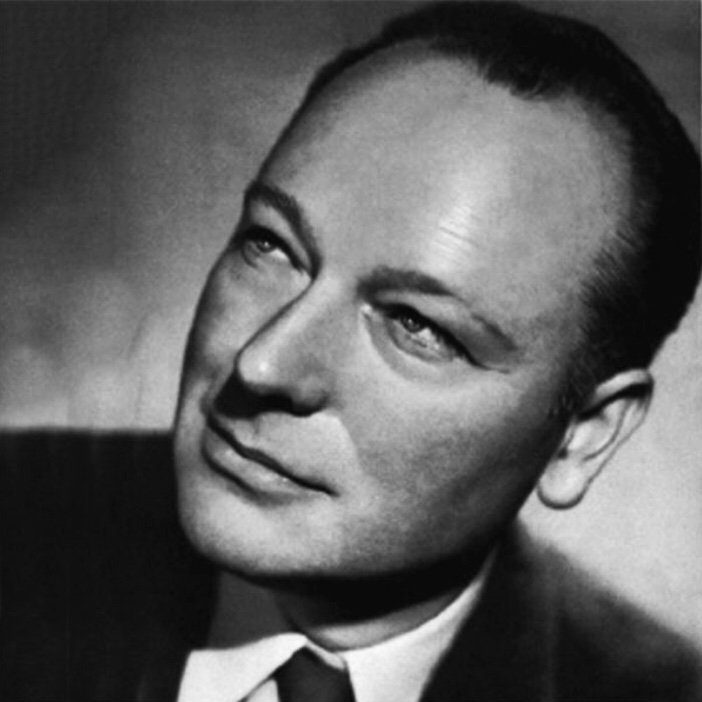

.jpg)
Jean Elysée Puiforcat was a French silversmith, sculptor and designer. Miller's Antiques Encyclopedia calls Puiforcat the «most important French Art Deco silversmith».
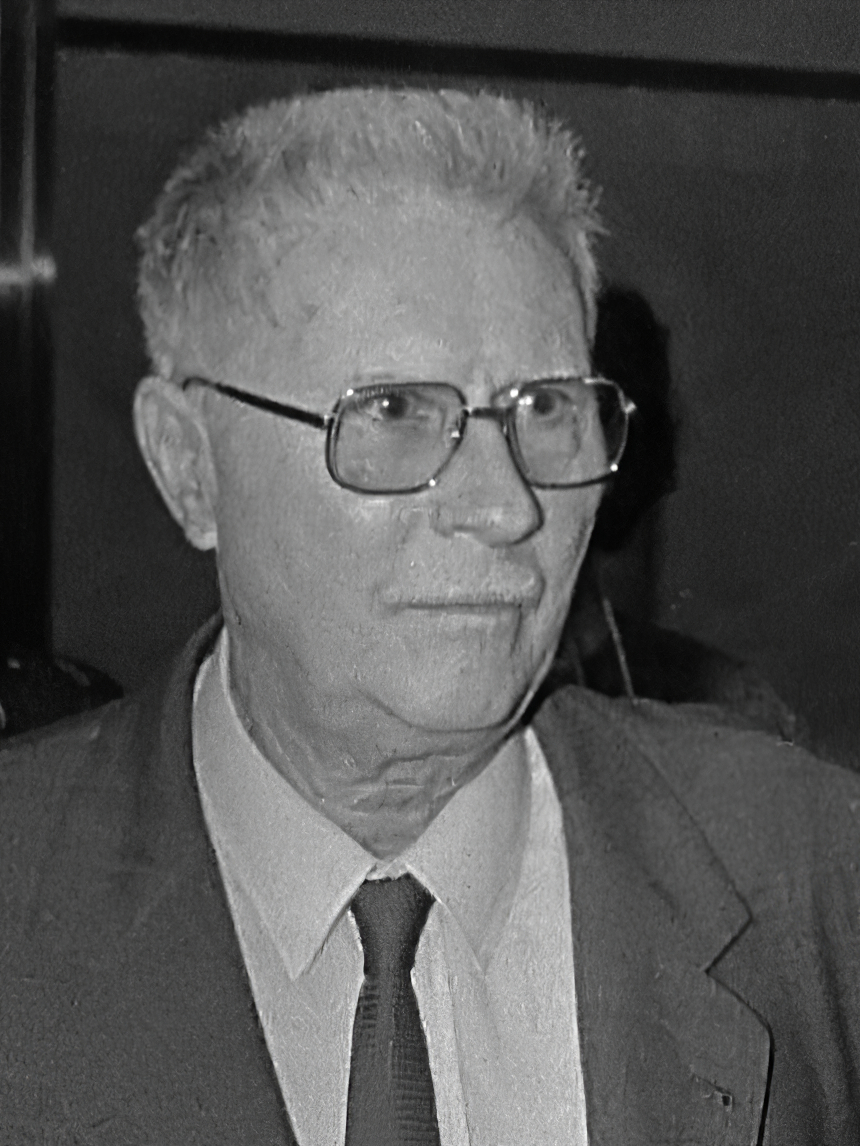

Jean Prouvé was a French metal worker, self-taught architect and designer. Le Corbusier designated Prouvé a constructeur, blending architecture and engineering. Prouvé's main achievement was transferring manufacturing technology from industry to architecture, without losing aesthetic qualities. His design skills were not limited to one discipline. During his career Jean Prouvé was involved in architectural design, industrial design, structural design and furniture design.
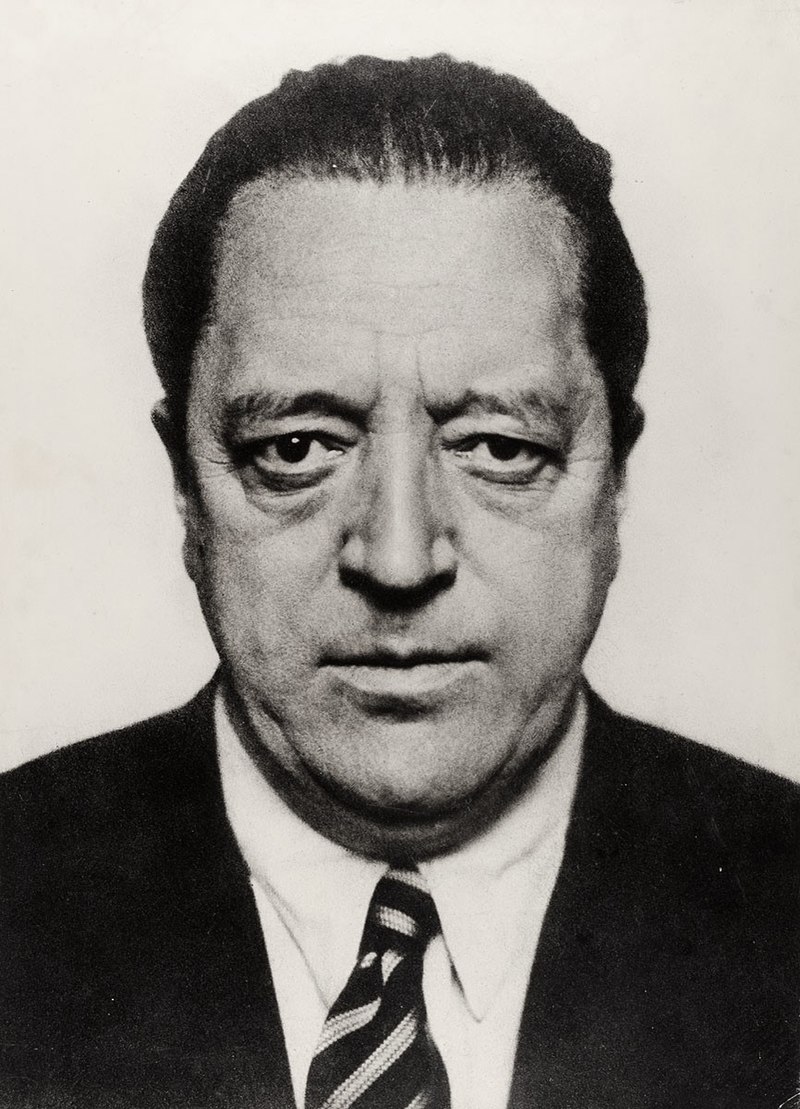


Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, born Maria Ludwig Michael Mies was a German-American architect and furniture designer. He was commonly referred to as Mies, his surname. Along with Alvar Aalto, Le Corbusier, Walter Gropius and Frank Lloyd Wright, he is regarded as one of the pioneers of modernist architecture.
In the 1930s, Mies was the last director of the Bauhaus, a ground-breaking school of modernist art, design and architecture. After Nazism's rise to power, with its strong opposition to modernism (leading to the closing of the Bauhaus itself), Mies emigrated to the United States. He accepted the position to head the architecture school at what is today the Illinois Institute of Technology in Chicago.
.jpg)
Jean Elysée Puiforcat was a French silversmith, sculptor and designer. Miller's Antiques Encyclopedia calls Puiforcat the «most important French Art Deco silversmith».

.jpg)
Jean Elysée Puiforcat was a French silversmith, sculptor and designer. Miller's Antiques Encyclopedia calls Puiforcat the «most important French Art Deco silversmith».

.jpg)
Jean Elysée Puiforcat was a French silversmith, sculptor and designer. Miller's Antiques Encyclopedia calls Puiforcat the «most important French Art Deco silversmith».
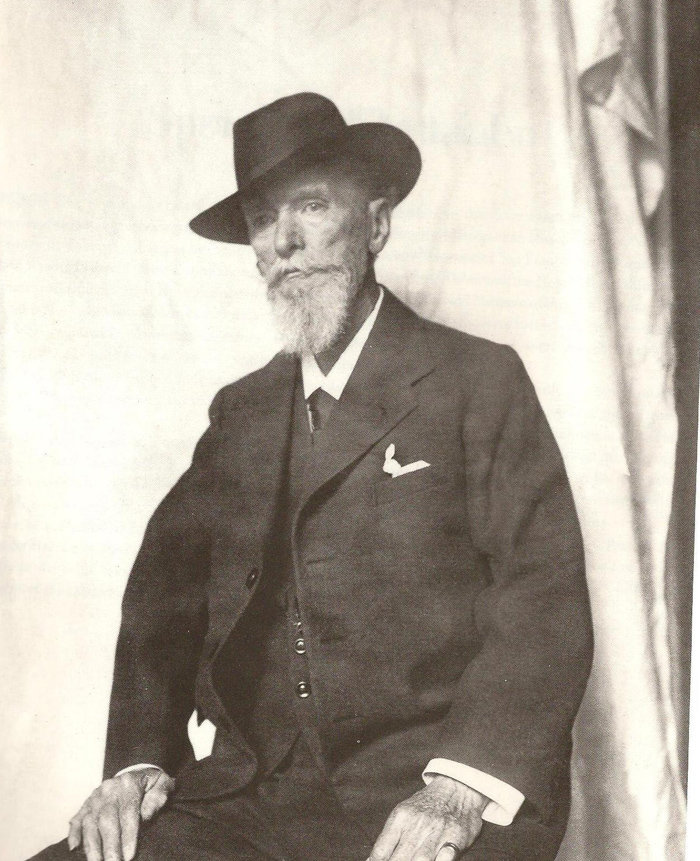


Carl Fabergé (Russian: Карл Гу́ставович Фаберже́) was a 19th- and 20th-century Russian jeweler, entrepreneur, and artist of German descent. He ran a family jewelry company for almost 50 years, which became world-famous for its products - Easter eggs made of precious metals, stones, and enamel.
Carl Fabergé met the Russian Emperor Alexander III at the All-Russian Exhibition in Moscow in 1882, which was a landmark event in the jeweler's career. The emperor ordered an Easter egg from the master for his wife, which the empress loved. From this moment on Fabergé, who became the jeweller to the Court, became responsible for the annual production of Easter eggs for the imperial court. Members of the imperial family also ordered jewelry from Fabergé for their many European relatives. This turned the Fabergé family company into one of the leaders of the world jewelry market.
Fabergé produced not only high-end jewelry products, but also items for the average buyer. In 2005, at Sotheby's in New York, several stone figurines were sold for $850,000 to $1,800,000.


Carl Fabergé (Russian: Карл Гу́ставович Фаберже́) was a 19th- and 20th-century Russian jeweler, entrepreneur, and artist of German descent. He ran a family jewelry company for almost 50 years, which became world-famous for its products - Easter eggs made of precious metals, stones, and enamel.
Carl Fabergé met the Russian Emperor Alexander III at the All-Russian Exhibition in Moscow in 1882, which was a landmark event in the jeweler's career. The emperor ordered an Easter egg from the master for his wife, which the empress loved. From this moment on Fabergé, who became the jeweller to the Court, became responsible for the annual production of Easter eggs for the imperial court. Members of the imperial family also ordered jewelry from Fabergé for their many European relatives. This turned the Fabergé family company into one of the leaders of the world jewelry market.
Fabergé produced not only high-end jewelry products, but also items for the average buyer. In 2005, at Sotheby's in New York, several stone figurines were sold for $850,000 to $1,800,000.

_4.jpg)
John Goddard (1724–1785) was a distinguished American cabinetmaker whose work significantly influenced 18th-century furniture design, particularly in Newport, Rhode Island. Born on January 20, 1724, in Dartmouth, Massachusetts, Goddard apprenticed under Job Townsend, a prominent Newport cabinetmaker. This apprenticeship not only honed his craftsmanship but also led to his marriage to Townsend's daughter, Hannah, further solidifying his ties to the esteemed Townsend-Goddard furniture-making dynasty.
Establishing his own workshop in Newport, Goddard became renowned for his exceptional skill and innovative designs. He is credited with originating the block-front knee-hole desks and secretary desks, which became highly sought after by affluent clients. His creations are characterized by distinctive features such as the block-front facade, intricately carved shells, and robust ball-and-claw feet. These elements not only exemplify the aesthetic preferences of the period but also showcase Goddard's meticulous attention to detail and mastery of proportion.
One of Goddard's most notable patrons was Nicholas Brown, a prominent Providence merchant. In the early 1760s, Brown commissioned a set of elaborately carved mahogany side chairs from Goddard. These chairs, distinguished by their pierced crest shells, double-scrolled splats, and elegantly shaped stretchers, are considered masterpieces of Newport craftsmanship. The collaboration between Goddard and Brown underscores the cabinetmaker's reputation as "the neatest workman in America," a testament to his superior craftsmanship and design sensibilities.
Goddard's influence extended beyond his lifetime, as his workshop became a training ground for future artisans, including his sons. Following the British occupation of Newport, three of his sons relocated to Nova Scotia, where they continued the family's cabinetmaking tradition, thereby disseminating the Newport style to new regions. The Goddard family's contributions to furniture making have left an indelible mark on American decorative arts, with their pieces remaining highly prized by collectors and museums alike.
Today, John Goddard's works are preserved in esteemed institutions such as The Metropolitan Museum of Art, which houses a side chair attributed to him. This chair exemplifies the characteristic Newport knee carving and the spherical ball feet associated with Goddard's style, serving as a tangible representation of his enduring legacy in American furniture design.










































